Neighborhood Operations
근처의 픽셀까지 고려하여 이미지를 변환하는 방법
- Convolution
- Cross-Correlation
- Gaussian Smoothing
- Median Filter
Convolution
Integral of the product of the two functions after one is reversed and shifted
h(x)=−∞∫∞f(τ)g(x−τ)dτh=f∗g
convolution 과정을 보자면
-
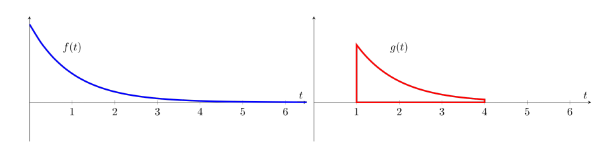
dummy variable τ에 따라 각 함수 표현
-
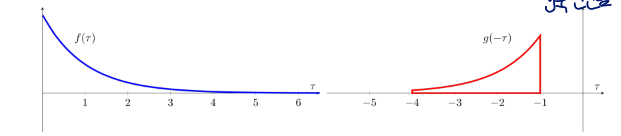
reflect one of the functions g→g(x−τ)
g를 y축에 대해서 반전시킴
-
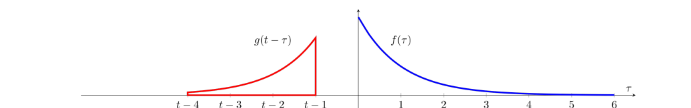
t에 따라 그래프를 x축 방향으로 이동(slide시킴)
-
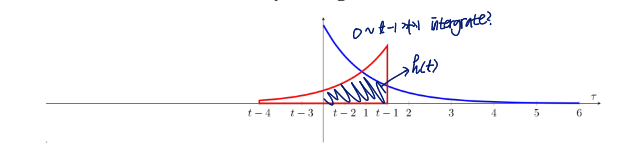
두 함수가 겹치는 공간의 넓이가 바로 integral의 값
Properties of Convolution
formal definition of convolution에서만 해당하는 properties임
딥러닝과 같은 곳에서는 적용이 안 되는 경우도 있음
finite하기 때문..?
- Commutativity: f∗g=g∗f
f: image, g: filter
이건 딥러닝에서는 불가능하고, image processing에서만 가능한 property임
- Associativity: f∗(g∗h)=(f∗g)∗h
order is not important하다는 뜻
- Distributivity: f∗(g+h)=(f∗g)+(f∗h)
- Linearity: f1→□→g1f2→□→g2
αf1+βf2→□→αg1+βg2
여기서 g는 convolution의 결과
- Shift invairance: f(x−a)→□→g(x−a)는 f(x)→□→g(x)를 x축 방향으로 a만큼 이동한 것
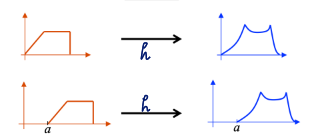
What h will give us g=f?
Dirac Delta Fucntion (Unit Impulse)
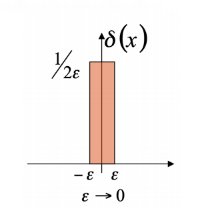
Sifting property:
kind of filtering property
−∞∫∞f(x)δ(x)dx=−∞∫∞f(0)δ(x)dx=f(0)−∞∫∞δ(x)dx=f(0)
g(x)=−∞∫∞f(τ)δ(x−τ)dτ=f(x)
Discrete Convolution
f(x,y)→h(x,y)→g(x,y)
Image들은 사용하는 space가 dicrete하고 finite함
따라서 g(i,j)=m=1∑Mn=1∑Nh(m,n)f(i−m,j−n)
h: kernel, f: image
- kernel(= filter = mask)를 horizontal and vertical direction으로 flip
- 각 kernel의 value를 corresponding pixel value와 곱하고 합함
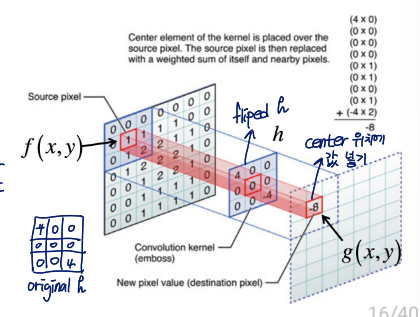
그림에 나온 것처럼 center 위치에 구한 값 넣으면 됨
Border problem
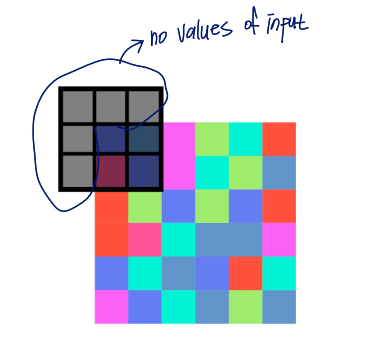
모서리 부근은 input으로 넣을 값들이 없는 문제 발생함
해결법
- input으로 넣을 값들이 없는 위치는 convolution을 실행하지 않기(ignore)
output 크기가 줄어드는 문제 발생
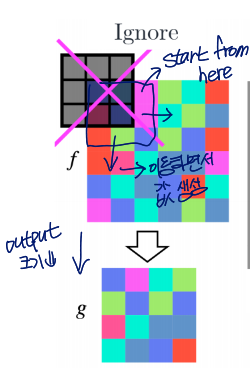
- 원본 이미지를 padding 통해 size를 넓혀서 모든 위치 convolution 가능하도록 하기
2.1 zero padding : 0으로 패딩
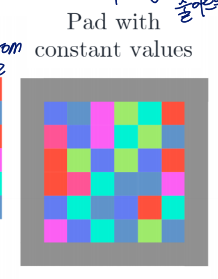
2.2 reflection
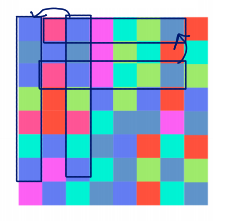
Cross-Correlation

템플릿을 알맞은 위치에 놓고자 함!
i,jargminE(i,j)=m=i+1∑i+Mn=j+1∑j+N[f(m,n)−t(m−i,n−j)]2=m∑n∑[f2(m,n)+t2(m−i,n−j)−2f(m,n)t(m−i,n−j)]2
f(m,n)t(m−i,n−j)이 constant가 아니기 때문에 focus
→ Maximize Rtf(i,j)=m∑n∑t(m−i,n−j)f(m,n) → Cross-correlation
Rtf=t⊗f일 때, Rtf의 값이 큰 게 최적의 위치라고 할 수 있는데,,,,
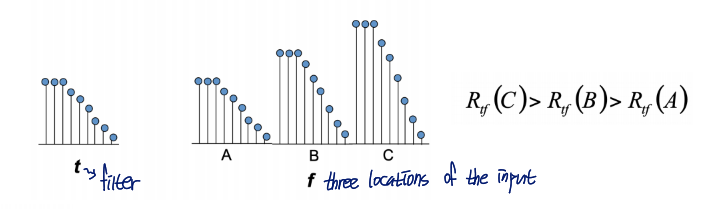
이렇게 무작정 location의 값들이 크다고 결과값이 크게 나오는 참사가 발생할 수 있음
A가 변수로 들어갔을 때 R값이 제일 크게 나와야 하는데 위에서는 그렇지 않게 나옴
→ Ntf(i,j)=[m∑n∑t2(m−i,n−i)]1/2[m∑n∑f2(m,n)]1/2m∑n∑t(m−i,n−j)f(m,n)
magnitude로 나눠서 위와 같은 일이 벌어지지 않도록 함
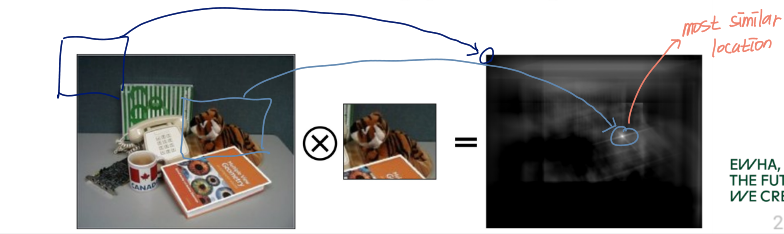
Convolution and Cross-Correlation
- convolution과 cross-correlation은 convolution은 kernel을 flip한다는 점을 빼면 동일함
현재는 correlation도 convolution이라고 부른다고 함(signal 관련 처리 때는 둘을 구분함)
- 많은 경우, the distiction between the two is not strictly made
-CNN(Convolutional Neural Networkds) apply multiple cascaded convolution kernels with applications in machine vision and artificial intelligence
- 그리고 이들은 대부분 사실상 convolution이 아닌 cross-correlation 방식을 사용함
Convolution is a Generic Function
Separable linear filter: K=vhT
2D filter를 1D filter 2개로 쪼갬
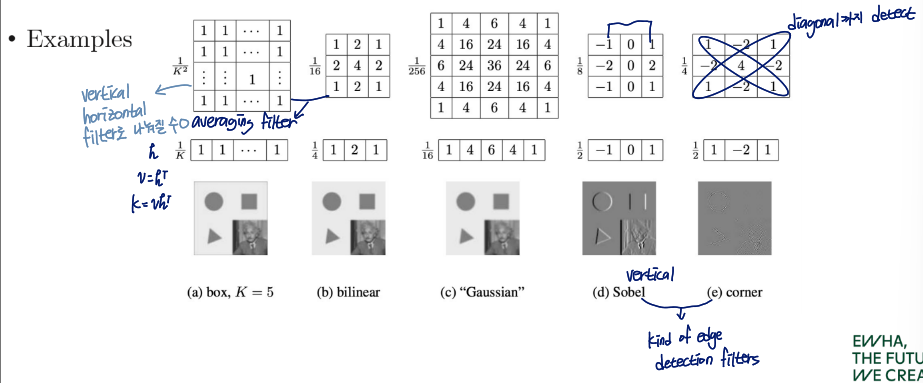
These operations can be significantly sped up by first performing a one-dimensional horizontal convolution followed by a one-dimensional vertical convolution
1차원 벡터 두 개로 쪼갬으로써 계산 속도를 높일 수 있음
O(k2)→O(2k)
Gaussian Smoothing
Gaussian kernel: h(i,j)=2πσ21e−21(σ2i2+j2)
→g(i,j)=2πσ21m=1∑n=1∑e−21(σ2m2+n2)f(i−m,j−n)
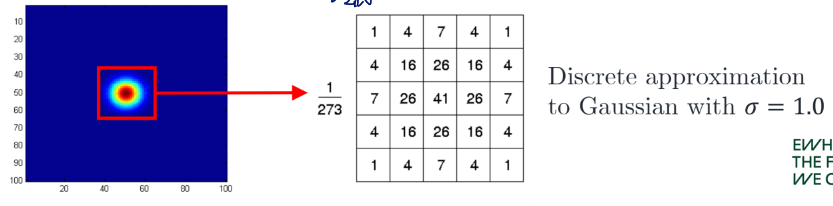
2D Gaussian is separable
g(i,j)=2πσ21m=1∑n=1∑e−21(σ2i2+j2)f(i−m,j−n)=2πσ21m=1∑e−21σ2m2n=1∑e−21σ2n2f(i−m,j−n) → Use two 1D Gaussian filters

Repeated averaging ≒ Gaussian smoothing
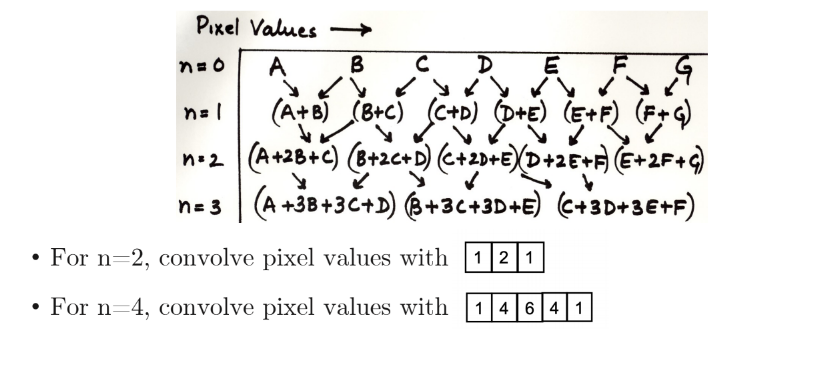
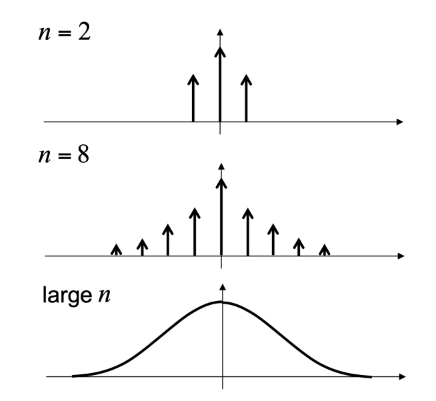
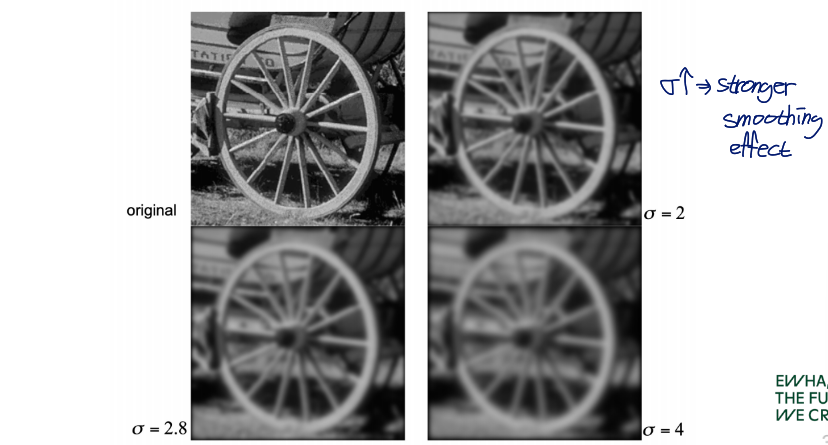
가우시안 필터는 σ의 값이 커질수록 smoothing effect가 강해짐

그리고 가우시안 스무딩은 사람이 초점을 잘 못 맞춰서 볼 때랑 유사한 결과를 만들어냄

이런 그림에 가우시안 필터를 취하면
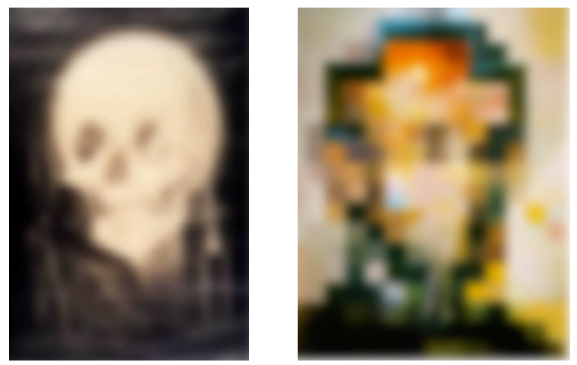
이렇게 사람이 그림을 흐릿하게 볼 때와 같은 효과를 줌
은 평균값을 통한 Smoothing의 경우
- edge가 blur해짐
- outliers에 민감함
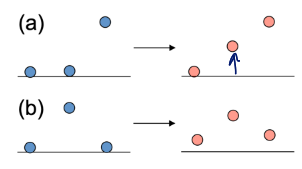
(a): blurs edges, (b): sensitive to outliers
가우시안 스무딩은 average smoothing보다 더 자연스러운 결과를 내보임
- 픽셀 주변의 k2 values 정렬
- 중앙값 선택
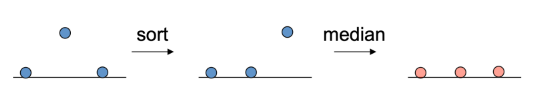
- Non-linear하기 때문에 convolution으로 구현 불가능함
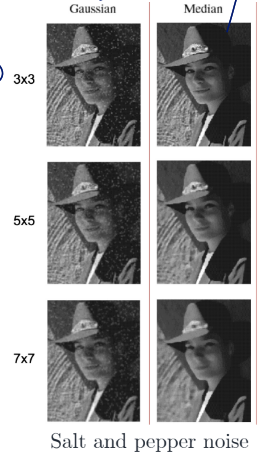
gaussian noise와 salt-and-pepper noise
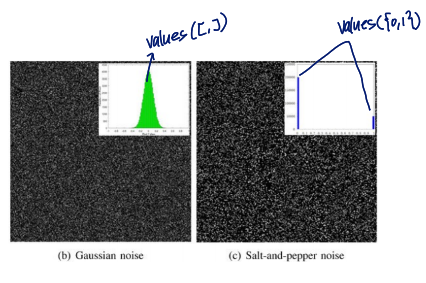
Salt and pepper noise
salt and pepper noise는 outlier가 심함
→ outlier에 robust한 median filter의 성능이 더 좋음
Gaussian noise
Gaussian filter의 성능이 더 좋음

⇒ 이미지의 특징에 따라 smoothing의 기법이 적절한 방법을 골라서 적용해야 함


























