
Image Sampling
Image Sub-Sampling
일부 픽셀들을 제거하며 이미지의 사이즈를 줄이는 기법

그러나 이 방법을 사용하면 이미지의 정보 손실이 많이 일어남

이렇게 사이즈를 복구 시켰더니 원본 이미지의 정보가 많이 손상된 것을 알 수 있음
Good sampling
- sample often or
- sample wisely
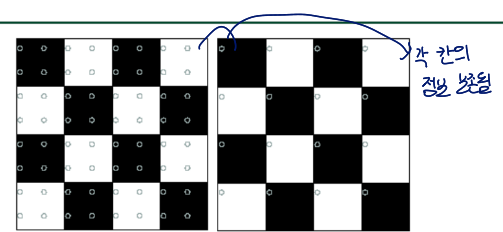
각 점들이 sampling point인데, 보면 검은 칸과 흰 칸에 고르게 퍼져 있음 → 정보 손실小
Bad sampling
- Aliasing
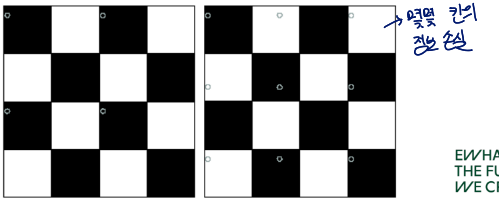
왼쪽은 모든 흰 칸들과 몇몇 검은 칸들에 대한 정보가 모두 담기지 않음
오른쪽도 몇몇 칸에 대한 정보가 손실됨
Aliasing
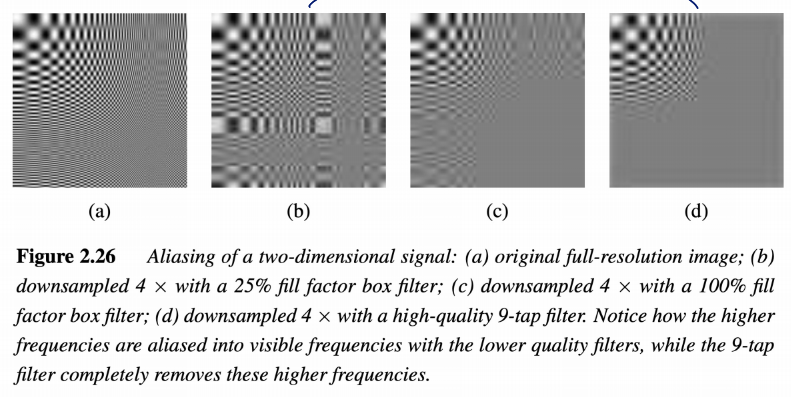
위의 그림에서 lower frequency regions은 정보유지가 잘 됐지만 high frequency는 보존되지 못한 것을 확인할 수 있음
Alias
a false or assumed identity
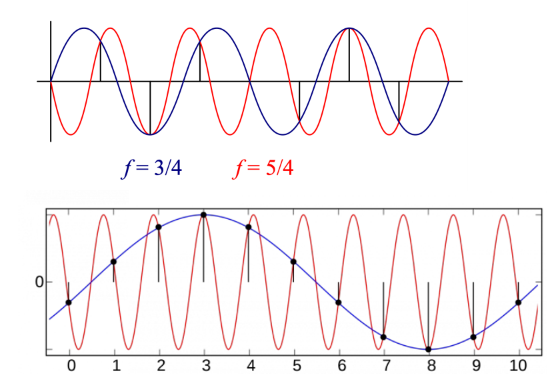
- red : original
- blue line : reconstructed
- back dots : sampled points
dots를 통해 reconstruction을 하는 과정에서, high frequency를 low frequency로 잘못 추정하는 일이 발생함 sample의 양 小
→ 원본과 일치X
Wagon-wheel effect
굴러가는 바퀴를 주기적으로 사진을 찍는다고 할 때
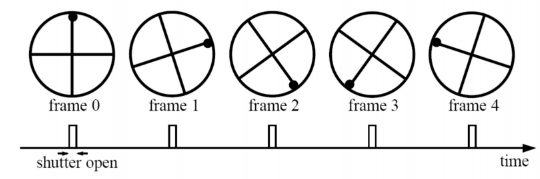
이렇게 바퀴에 점이 있는 경우, 돌아가는 방향을 인식하기 쉬움
그러나 저 예시의 상황에서 바퀴에 점이 없는 경우에는 돌아가는 방향을 잘못 인식하게 됨
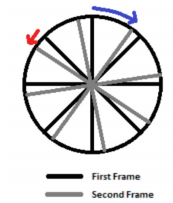
이전 본인의 위치와의 차보다 옆의 것과의 차가 더 작아서 회전 방향을 착각하게 됨
좀,,, 말이 이해가 안 되게 써졌는데,... 그냥 파란색 화살표가 맞는 방향인데 빨간 화살표의 길이가 더 작아서 빨간 화살표 방향으로 회전한다고 착각하게 된다고 이해하면 됨
Stroboscopic effect
visual phenomenon caused by aliasing that occurs when continuous rotational or other cyclic motion is represented by a series of short or instantaneous samples
간단하게 이해하자면 sampling 속도가 낮아 원본보다 속도가 낮아 보이게 되는 현상
Sampling Theorem
- continuous signal
original signal
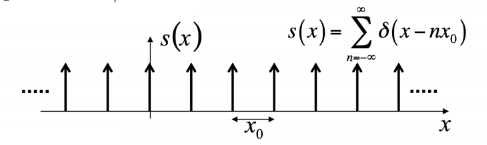
- Shah function (Impulse train)
unit impulse function
- Sampled function
그냥 sampling point들 값 구하는 함수라고 보면 됨
Sampled function
sampling frequency:
→일정 간격으로 F(u)가 여러 개 반복되는 모양 형성됨
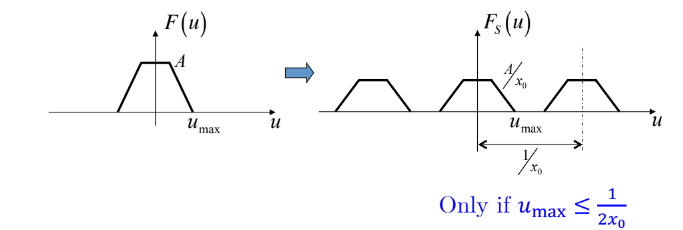
저 모양 하나의 폭은 이기 때문에 각 모양들이 겹치지 않으려면 을 만족해야 함
if
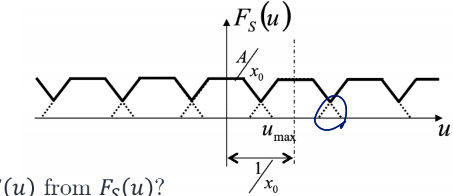
overlap 발생 → Aliasing 원본 이미지로 복구 불가
Nyquist Frequency
에서 로 복구하기 위해서는 Sampling frequency must be greater than
일 때에만
Sub-Sampling with Gaussian Pre-Filtering
이미지에 필터를 적용한 후, subsample 진행
high frequency를 걸러내고 sampling
filter size should double for each size reduction


위의 Sub-sampling 때보다는 정보 유지가 잘 된 것을 볼 수 있음
Anti-aliasing
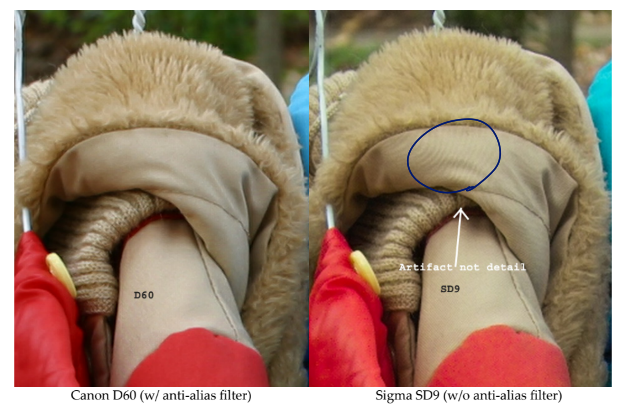
Image Pyramids
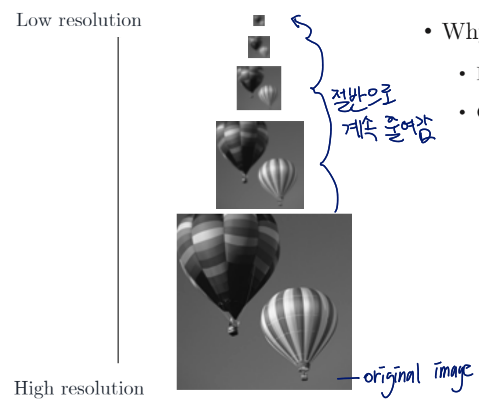
Multi-Resolution Image Pyramids
- 사람의 visual encoding에서 영감을 받은 방법
- resolution을 계속해서 절반씩 줄여감
- 계산적으로 효율적
Space required for pyramids
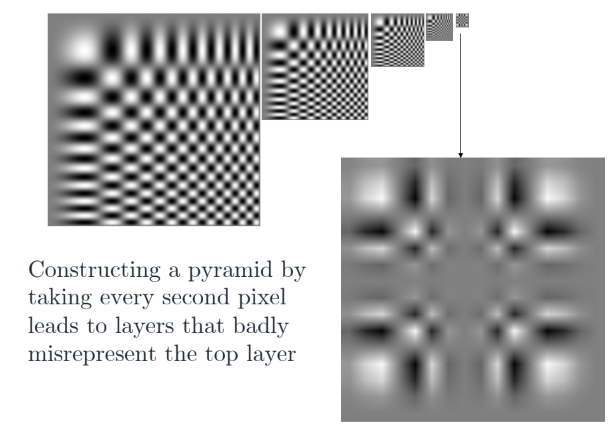
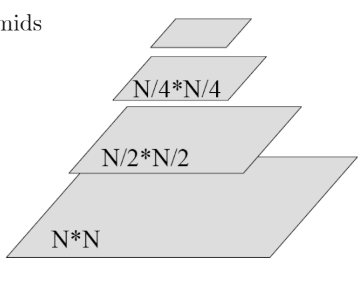

무작정 짝수번째 행,열의 픽셀들을 선택하여 줄이는 방법을 사용하면 aliasing이 발생하게 됨
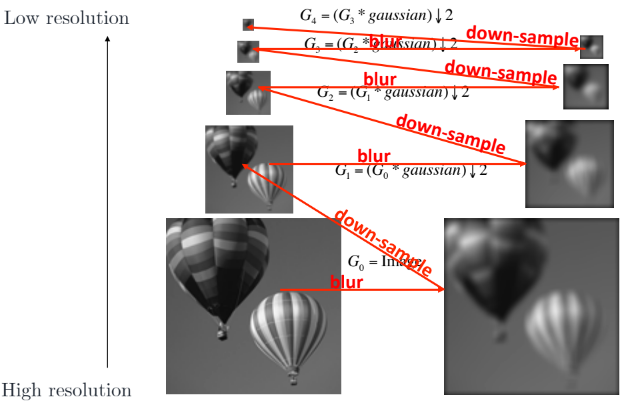
Gaussian Pyramid
gaussian pyramid로 aliasing을 없애보고자 함
Smooth with Gaussian and downsample
- high frequencies는 샘플링에 문제를 가져옴
- 샘플링 전에 high frequencies를 제거(suppress)
- Gaussians are low-pass filters
- Gaussian * Gaussian = another Gaussian
Kernel의 width는 각 레벨마다 두 배
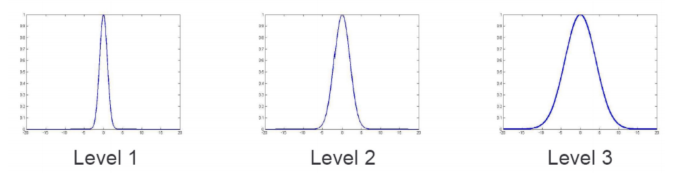
이렇게
- filter
- subsample
과정을 min resolution에 reach할 때까지 반복
Gaussian Pyramid Frequency Composition
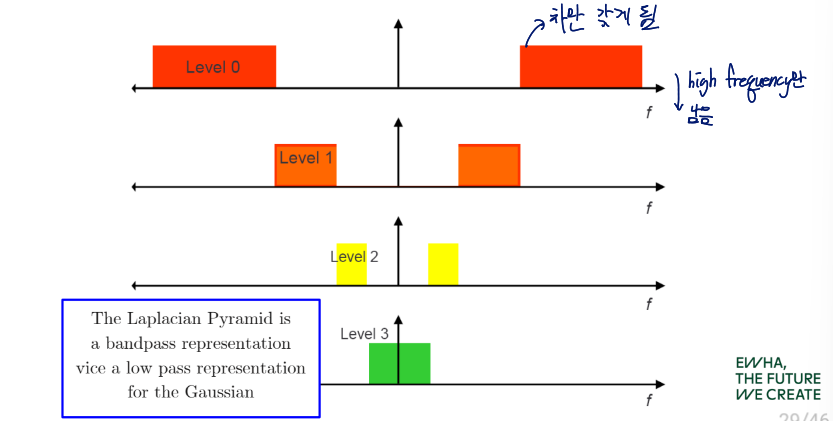
Level 별로 Gaussian filtering을 통해 제거되는 high frequency를 보면
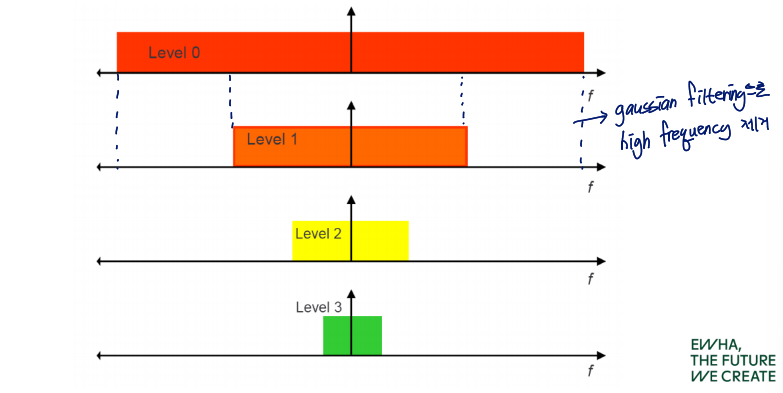
이렇게 됨
Laplacian Pyramid
Laplacian of an image (i.e., the second derivative)
- : intensity of image (x,y)
- edge detection에 유용
i.e., rapid intensity change - interest point detection에 유용
i.e., SIFT
이미지 픽셀에서의 change에 대한 정보를 담고 있음
문제
- noise에 민감
- Laplacian of Gaussian을 통해 해결
가우시안 스무딩 먼저 적용 후 라플라시안 구하는 방법
- Laplacian of Gaussian을 통해 해결
- 계산적으로 버거움(burdensome)
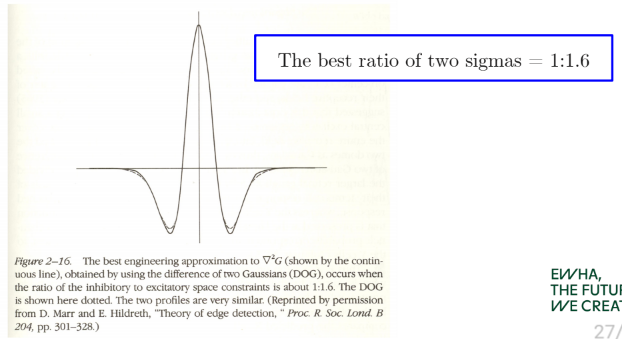
Difference of Gaussians (DoG)
두 Gaussians 간의 차를 통해 Laplacian of Gaussian을 추정할 수 있음
Laplacian Pyramid
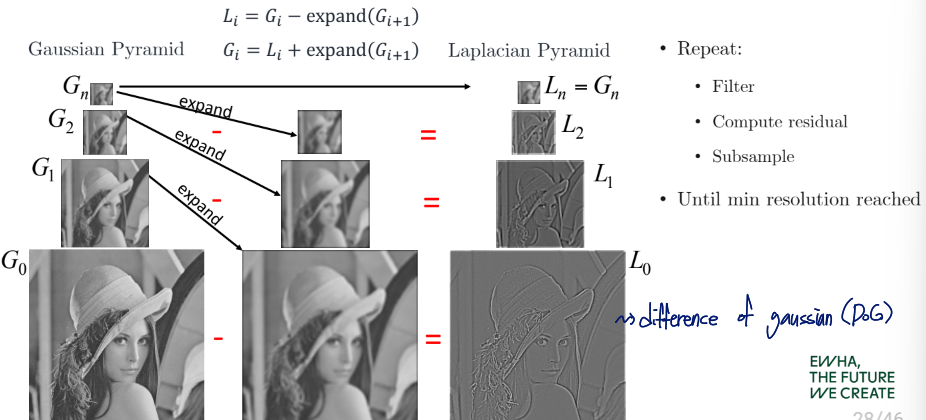
윗 단계의 이미지를 확대 시킨 후 이미지에서 그 이미지를 빼면 DoG를 구할 수 있음
Laplacian Pyramid Frequency Composition
Other Types of Pyramids
Steerable pyramid
At each level keep multiple versions, one for each direction
Wavelets
Huge area in image processing

Applications of Image Pyramids
What Are Image Pyramids Used For?
- image compression
- multi-scale texture mapping
- image blending
- focal stack compositing
- multi-scale detectioin
- denoising
- multi-scale registration
Fast Template Matching
- image
- template
이 상황에서 2D pattern recognition task의 복잡도는
this gets even worse for a family of templates
size나 회전 정도에 따라 복잡도는 더 높아지게 됨
해결법
lower resolution에서 matching 진행
Multi-Resolution Template Matching
Algorithm
- template과 image의 resolution을 image pyramid를 생성함으로써 줄임
- small template을 small image에 match
- identify locations of strong matches
- expand the image and template, and match the higher resolution template selectively to higher resolution image
이미지와 템플릿의 크기를 키운 다음에, 일치도가 높게 나온 부근 근처에서 다시 탐색 - iterate on higher and higher resolution images
Issue
각 레벨에서 detection threshold를 어떻게 선정할지
- 너무 낮으면 too much cost 유발
- 너무 높으면 match 못함
Example
피라미드 레벨을 3까지 만들고 진행
-
Level 3 search
- highest pyramid level
- lowest resolution
- search the entire image with the correlation template
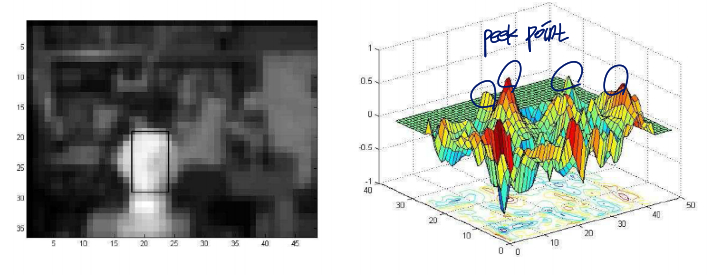
-
Level 2 search
- level 3 search에서 나온 peek point의 근처를 탐색
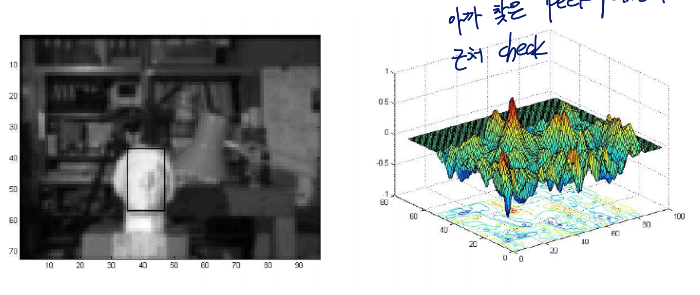
- level 3 search에서 나온 peek point의 근처를 탐색
-
Level 1 search
- level 2와 동일
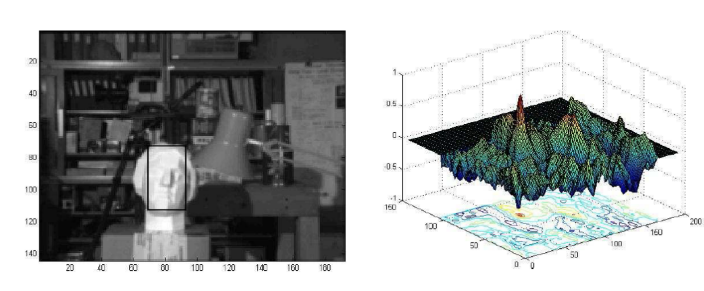
- level 2와 동일
-
Level 0 search
- 여기까지 진행한 결과, 탐색 시간 0.5초
multi-resolution template matching을 사용하지 않았을 때는 31초
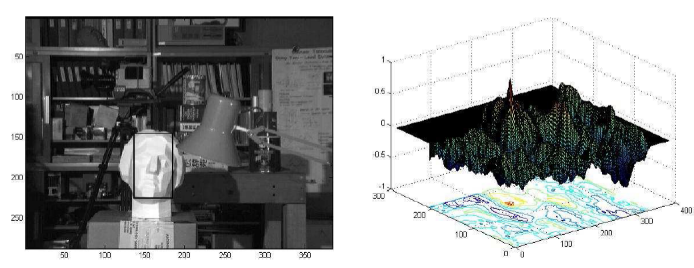
- 여기까지 진행한 결과, 탐색 시간 0.5초
Image Blending
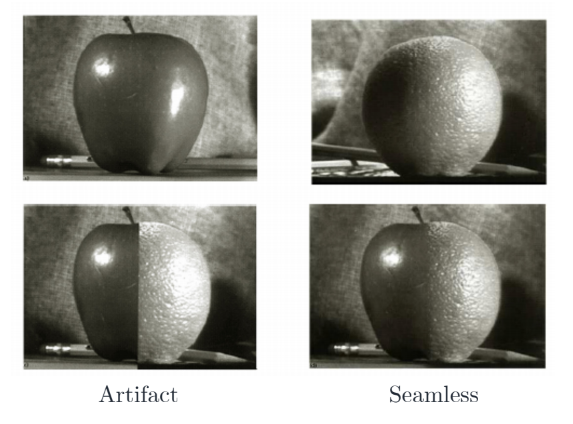
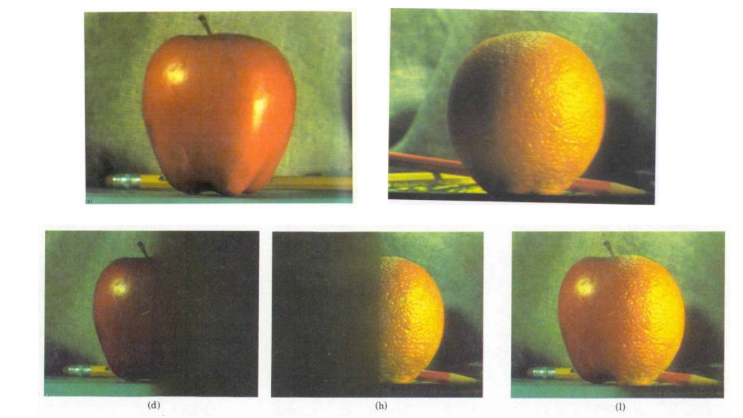
Blending Apples and Oranges
- General Approach
- 이미지 A와 B로부터 Laplacian pyramids , 생성
- selected region R로부터 Gaussian pyramid 생성
- 을 weights로 사용하여 combined pyramid 생성
물론 와 를 combine한 것
- sum all levels of the pyramid to get the final blended image
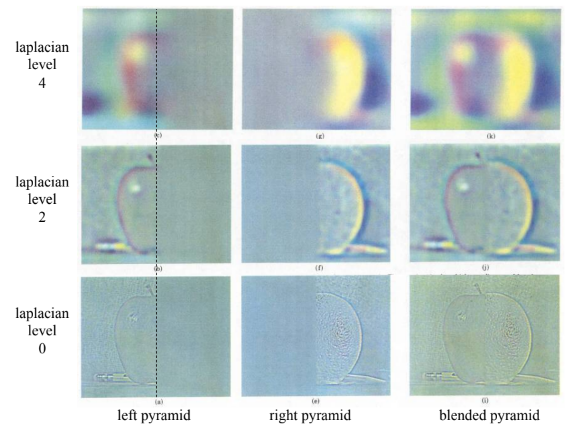
Pyramid Blending of Regions
그냥 위의 방법 사용한 다른 예시
손바닥에 눈 붙이기
