Priority queue
- A queue that stores items with priority
- The data with the higher priority is output first, not the FIFO order
들어오는 순서가 priority가 될 수도 있고, 다른 것에 기반하여 priority를 매길 수 있음
→ 들어오는 순서가 중요하지 않고, priority가 중요
이렇게 보면 queue는 들어오는 순서가 priority인 것
priority queue: most common data structure
stack과 FIFO queue를 priority queue로 implement할 수 있음
| Data structure | Elements to be removed |
|---|---|
| Stack | Most recent data |
| Queue | First incoming data |
| Priority queue | Highest priority data |
Applications
- Simulation system (priority: the event time)
- Network traffic control
- Scheduling Jobs in the Operating System
ADT of Priority Queue
-
Object
A collection of elements with a priority of n element types
-
Operation
- Create() ::= creates a priority queue
- Init(q) ::= Initializes the priority queue q
- is_empty(q) ::= checks if the priority queue q is empty
- is_full(q) ::= checks if the priority queue q is full
- insert(q, x) ::= add an element x to the priority queue q
- delete(q) ::= removes the highest priority element from the priority queue and returns this element
- find(q) ::= returns the highest priority element without deleting it
Priority Queue Types
priority queue은 두 카테고리로 나뉨
1. Minimum priority queue
minimum을 takeout
2. Maximum priority queue
maximum을 takeout
Priority Queue Implementation
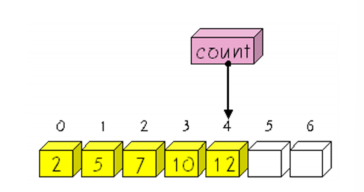
1. priority queue with arrays
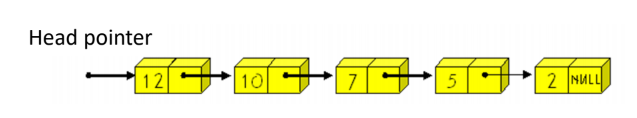
2. priority queue with linked list
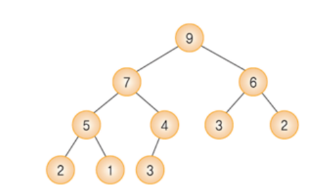
3. priority queue with heap
Time complexity of each data structures
Data structure Insertion operation Deletion operation Unordered array O(1) O(n) Unordered linked list O(1) O(n) Ordered array O(n) O(1) Ordered linked list O(n) O(1) Heap O(logn) O(logn) → priority queue에서는 heap을 사용할 것임
Heap
Complete binary tree satisfying the following conditions
Max heap
key(parent node) >= key(child node)
Min heap
key(parent node) <= key(child node)
max heap과 min heap은 binary search tree와는 약간 다름
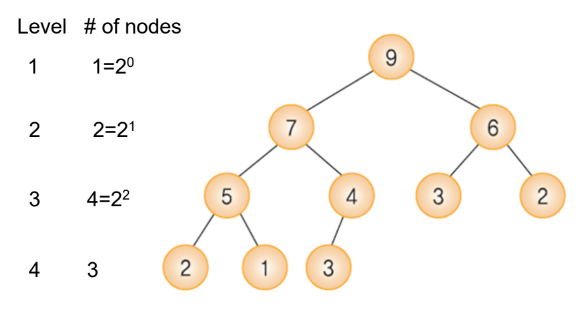
Heap Height
O(log₂n)
- Note) the heap is a complete binary tree
- Except for the last level, there are 2^(i-1) nodes at each level i
Heap Implementation
Heap is implemented using arrays
- since it is a complete binary tree, each node can be numbered
- think of this number as the index of the array
Index of parent and child
- parent node of node i: i/2
- left child node of node i: 2i
- right child node of node i: 2i+1
인덱스는 0이 아닌 1에서 시작함
Insertion in Max Heap
Procedure
- the new node is inserted next to the last node in the heap
- the nodes in the path from the inserted node to the root are compared and exchanged to satisfy the heap property
Insertion in min heap 또한 유사한 procedure
if the key k is less than or equal to the parent node, the comparison terminates
Time complexity: O(_log₂_n)
worst case에 heap의 높이만큼 비교하기 때문!
Pseudo code
insert_max_heap(A, key)
heap_size = heap_size + 1;
i = heap_size;
A[i] = key; //우선 current heap의 last index에 key 놓기
while(i!=1 && A[i]>A[PARENT(i)]) do
swap A[i] and A[PARENT];
i = PARENT(i);heap의 특성에 따라 다른 child와는 비교하지 않아도 됨
children are always smaller or equal to parent node
→ new node가 parent보다 크면 당연하게 other child보다 큼
C code
void insert_max_heap(HeapType *h, element item){
int i;
i = ++(h->heap_size);
//heap은 인덱스가 1부터 시작하기 때문에 heap size를 키운 뒤 i가 heap size 값을 가지도록 함
while((i!=1) && (item.key > h->heap[i/2].key)){
h->heap[i] = h->heap[i/2];
i/=2;
//new node보다 부모 노드가 작은 경우 new node의 위치에 부모 노드가 가도록 함
//효율성을 위해 일일이 new node까지 이동시키는 일은 하지 않음(no exchange operation)
}
h->heap[i] = item; //맨 마지막에 new node 위치 지정
}Deletion in Map Heap
deleting the node with the largest key value
Procedure
- Delete the root node
- Move the last node to the root node
- The nodes in the path from the root to the leaf nodes are compared and exchanged to satisfy the heap property
If the key k is larger than or equal to the child nodes, the comparison terminates
* complete binary tree의 조건만족을 위해 last location(not the smallest one)의 노드를 root에 놓는 것 *
Time complexity: O(_log₂_n)
worst case에 heap의 높이만큼 비교하기 때문!
Pseudo code
delete_max_heap(A)
item = A[1];
A[1] = A[heap_size];
heap_size -= 1;
i = 2;
while(i<=heap_size) do
//두 자식 중 크기가 더 큰 것 확인
if (i < heap_size && A[i+1] > A[i+1])
then largest = i+1;
else largest = i;
if(A[PARENT(largest)] > A[largest])
then break;
swap A[PARENT(largest)] and A[largest];
i = CHILD(largest);
return item;C code
element delete_max_heap(HeapType *h){
int parent, child;
element item, temp;
item = h->heap[1];
temp = h->heap[(h->heap_size)--];
parent = 1;
child = 2;
while(child <= h->heap_size){
if((child < h->heap_size) && (h->heap[child].key)<(h->heap[child+1].key))
child++;
if(temp.key >= h->heap[child].key) break;
h->heap[parent] = h->heap[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
h->heapp-[parent] = temp;
return item;
}Building Max Heap
Time complexity: O(n)
Build-Max-Heap()
- when an array is given, put all elements into the heap first
- then, we can build a heap in a bottom-up manner by moving the element to meet the heap property
- for the array of length n, all elements in [n/2]+1 ... n already meet the heap property!
- Thus
- walk backwards through the array from [n/2] to 1, moving the element on each node until it meets the heap property
- the order of processing guarantees that the children of node i are heaps when i is processed
Analyzing Build-Max-Heap()
- Moving element in the heap takes O(_log₂_n) time
- There are O(n) moving operations (specifically, [n/2])
- Thus, the time complexity may be seen as O(n_log₂_n)
- A tigher bound is O(n)

time complexity 도출 과정
Heap Application: Heap Sort
Heap sort
the sorting algorithm using the heap
Procedure
1. Insert n elements to be sorted in the max heap
2. Delete a root from the max heap and save it in and array n times
Time complexity: O(n_log₂_n)
Step 1: O(n_log₂_n) + Step 2: O(n_log₂_n)
Step 1에서 build-max-heap()을 사용해도 heap sort의 time complexity는 계속 O(n_log₂_n)
Heap sort is useful, when you need a few of the largest values, not sorting the entire data
Ex) 1000개의 elements 중 10개의 data만 가져오고 싶을 때
Step 1에서 build-max-heap()을 사용하면 효율적으로 할 수 있음
C code
void heap_sort(element a[], int n){
int i;
HeapType h;
init(&h);
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
insert_max_heap(&h, a[i]);
}
for(i=(n-1); i>=0; i--){
//ascending order로 data를 저장할 것이기 때문에 n-1부터 1 순서로 저장
a[i] = delete_max_heap(&h);
}
}Heap Application: Discrete Event Simulation
Computer Simulation
designs a model of physical system, runs the model using computers, and then analyzes the execution results
Type of computer simulation
- Continuous time simulation
- Discrete time simulation:
is performed by generating an event as time passes
queue 강의에 나왔던 backing simulation이 바로 이 시뮬레이션!
while(clock < duration){
clock++;
.....
}- Discrete event simulation:
is performed by the occurrence of an event
while(t < test_time){
t += random(max_arr_interval+1);
//generate an event below
}1,2는 base on the time, 3은 base on the event
Discrete event simulation
- all time progress is made by the occurrence of an event
- events are stored using priority queues, and they are processed based on the event time
Ice cream shop simulation
Example of discrete event simulation
Guests visit the ice cream shop. If there is no seat available, then, they will just leave. Our goal is to predict how many chairs can be placed to maximize profits.
Definition of event
typedef struct{
int id; //guest group ID
int type; //event type(arrived or leaving..)
int key; //time when the event occurred(ex. arrival time)
int number; //number of guests for the event
}element; //element == event- event types
- ARRIVAL: the guests arrives the ice cream shop
- ORDER: the guest orders the ice cream
- LEAVE: the guest leaves the ice cream shop
도착 → 주문 → 떠남
- ARRIVAL event
- If # of guests for this event <= # of remaining chairs,
then receive the guests and # of remaining chairs is reduced by # of guests - otherwise, guests will leave without ordering
- If # of guests for this event <= # of remaining chairs,
- ORDER event
- this event recieves the order according to # of guests, and then they will leave after a while
- LEAVE event
- this event increases # of remaining chairs by # of guests leaving
Random variables
-
ARRIVAL event
- arrival time of guests
- the number of guests of a single event
-
ORDER event
- time to order after arrival
- the number of scoops that each guest orders
-
LEAVE event
- time to stay in the shop before leaving
주문하고 다 먹을 때까지의 시간
- time to stay in the shop before leaving
Note that min heap is used in this simulation, since the event that occurs first must be processed
C code
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "string.h"
#include "time.h"
#define ARRIVAL 1
#define ORDER 2
#define LEAVE 3
#define MAX_ELEMENT 1000
typedef struct element {
int id; //guest group ID
int type; //event type(arrived or leaving..)
int key; //time when the event occurred(ex. arrival time)
int number; //number of guests for the event
}element;
typedef struct HeapType{
element heap[MAX_ELEMENT];
int heap_size;
}HeapType;
int free_seats = 10;
int test_time = 10;
double profit_per_icecream = 0.35;
double profit = 0.0;
int groups = 0; //total number of guest groups
//Random variables of ARRIVAL event
int max_arr_interval = 6; //손님은 0~6분 사이에 도착함
int max_num_of_guests = 4 //손님은 1~4명 가능
//Random variables of ORDER event
int max_time_to_order = 4 // 주문에 걸리는 시간은 1~4분
int max_num_icecream = 3 //손님은 3스쿱까지 주문 가능
//Random variables of LEAVE event
int max_time_to_stay = 10; //먹고 떠날 때까지 걸리는 시간 1~10분
//Basic functions of heap
void init(HeapType *h){
h->heap_size = 0;
}
int is_empty(HeapType *h){
if(h->heap_size == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void insert_min_heap(HeapType *h, element item){
int i;
i = ++(h->heap_size);
while((i!=1) && (item.key < h->heap[i/2].key)){
h->heap[i] = h->heap[i/2];
i /= 2;
}
h->heap[i] = item;
}
element delete_min_heap(HeapType *h){
int parent, child;
element item, temp;
item = h->heap[1];
temp = h->heap[(h->heap_size)--];
parent = 1;
child = 2;
while(child <= h->heap_size){
if((child < h->heap_size) && (h->heap[child].key) > (h->heap[child+1].key))
child++;
if(temp.key <= h->heap[child].key) break;
h->heap[parent] = h->heap[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
h->heap[parent] = temp;
return item;
}
//Integer random number generation function between 0 and n-1
int random(int n){
return rand()%n;
}
//If seats are available, reduce the number of remaining chairs by the number of guests
int is_seat_available(element e){
printf("group %d of %d guests arrive\n", e.id, e.number);
if(free_seats >= e.number){
free_seats -= e.number;
return true;
}
else {
printf("group %d of %d quests leave because there is no seat\n", e.id, e.number);
return false;
}
}
//when you receive an order, increase the variable representing the net profit
void order(element e, int scoops){
printf("in group %d, %d ice creams orders\n", e.id, scoops);
profit += profit_per_icecream * ((double)scoops);
}
void leave(element e){
printf("group %d of %d guests leaves\n", e.id, e.number);
free_seats += e.number;
}
// MAIN SUB FUNCTION
void process_event(HeapType *heap, element e){
int i=0;
element new_event;
printf("\nCurrent Time = %d\n", e.key);
switch(e.type){
case ARRIVAL:
if(is_seat_available(e)){
//create an ORDER event
new_event.id = e.id;
new_event.type = ORDER;
new_event.key = e.key+1+random(max_time_to_order);
new_event.number = e.number;
insert_min_heap(heap, new_event);
}
break;
case ORDER:
//주문 받고
for(i=0; i<e.number; i++){
order(e, 1+random(max_num_icecream));
}
//LEAVE event 만들기
new_event.id = e.id;
new_event.type = LEAVE;
new_event.key = e.key+1+random(max_time_to_stay);
new_event.number = e.number;
insert_min_heap(heap, new_event);
break;
case LEAVE:
//increase the number of free seats when guests leave
leave(e);
break;
}
}
int main(){
time_t t1;
/*initialize random number generator*/
srand((unsigned) time (&t1));
element event;
HeapType heap;
int t=0;
init(&heap);
while(t<test_time){
t += random(max_arr_interval+1);
event.id = groups++;
event.type = ARRIVAL;
event.key = t;
event.number = 1+random(max_num_of_guests);
insert_min_heap(&heap, event);
}
while(!is_empty(&heap)){
event = delete_min_heap(&heap);
process_event(&heap, event);
}
printf("\nTotal net profit = %f.\n\n", profit);
}코드가 길어서 복잡해 보이는데 보면 생각보다 간단함!
Huffman Code
Huffman coding tree
- a binary tree can be used to compress the data for which the frequency of each element is known
- this kind of binary tree is called the huffman coding tree
데이터를 압축할 때 사용하는 거라고 보면 됨
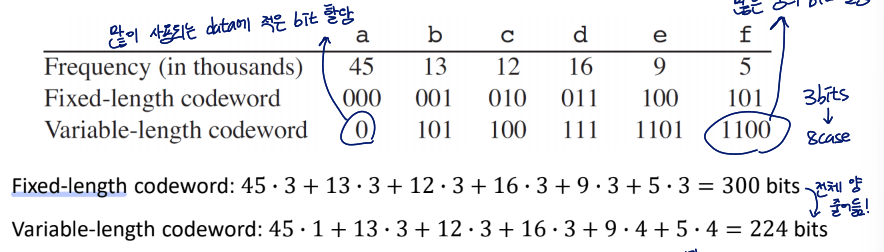
Huffman code
is for data compression(e.g., JPEG)
- designing a binary code
- each character is represented by a unique binary string(codeword)
- the length of codeword varies according to frequency
자주 나오는 문자의 길이가 가장 짧을 때, 가장 압축이 잘 될 수 있기 때문
Prefix codes
- No codeword is also a prefix of some other codewords
- It achieves an optimal data compression among any character code
prefix가 겹치면 해석이 불가능해지므로 겹치지 않도록 해야 함
Ex) a: 0, b: 01일 때, a와 b 해석 불가능
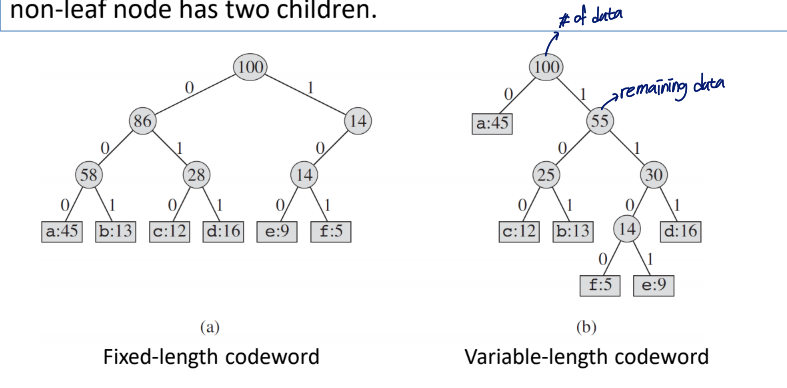
Optimal codeword is represented by a full binary tree, in which every non-leaf node has two children
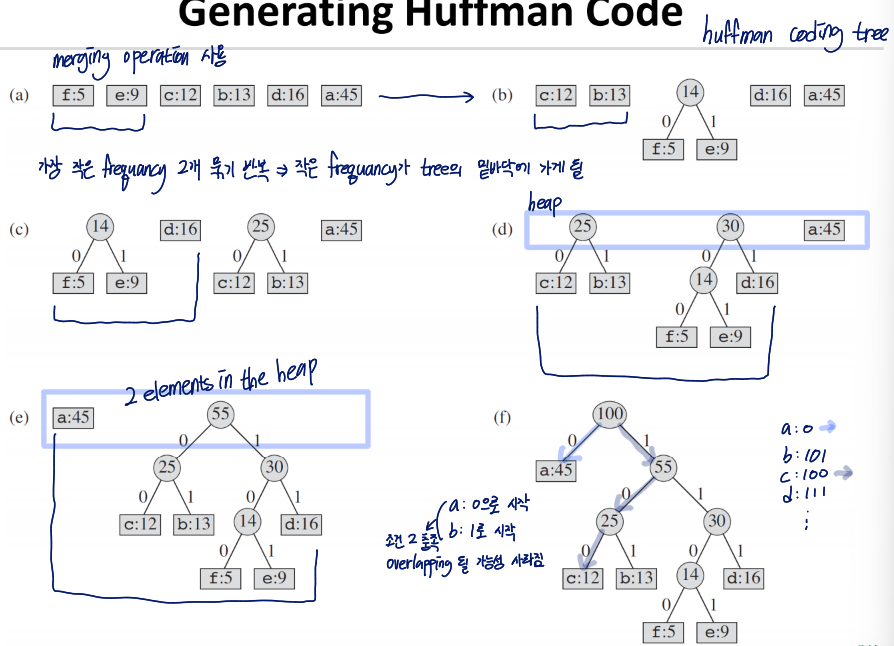
Generating Huffman Code
C code
#define MAX_ELEMENT 1000
typedef struct TreeNode{
int weight;
struct TreeNode *left_child;
struct TreeNode *right_child;
}TreeNode;
typedef struct {
TreeNode *ptree;
int key;
}element;
typedef struct{
element heap[MAX_ELEMENT];
int heap_size;
}HeapType;
//initialization
void init(HeapType *h){
h->heap_size = 0;
}
int is_empty(HeapType *h){
if(h->heap_size==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void insert_min_heap(HeapType *h, element item){
int i;
i = ++(h->heap_size);
while((i!=1) && (item.key < h->heap[i/2].key)){
h->heap[i] = h->heap[i/2];
i /= 2;
}
h->heap[i] = item;
}
element delete_min_heap(HeapType *h){
int parent, child;
element item, temp;
item = h->heap[1];
temp = h->heap[(h->heap_size)--];
parent = 1;
child = 2;
while(child <= h->heap_size){
if((child < h->heap_size) && (h->heap[child].key) > (h->heap[child+1].key))
child++;
if(temp.key <= h->heap[child].key) break;
h->heap[parent] = h->heap[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
h->heap[parent] = temp;
return item;
}
//Node generation in binary tree
TreeNode *make_tree(TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right){
TreeNode *node = (TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
if(node == NULL){
fprintf(stderr, "memory allocation error\n");
exit(1);
}
node->left_child = left;
node->right_child = right;
return node;
}
//binary tree removal
void destroy_tree(TreeNode *root){
if(root==NULL) return;
destroy_tree(root->left_child);
destroy_tree(root->right_child);
free(root);
}
//Huffman code generation
void huffman_tree(int freq[], int n){
int i;
TreeNode *node, *x;
HeapType heap;
element e, e1, e2;
init(&heap);
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
node = make_tree(NULL, NULL);
e.key = node->weight = freq[i];
e.ptree = node;
insert_min_heap(&heap, e);
}
for(i=1; i<n; i++){
//delete two nodes with minimum values
e1 = delete_min_heap(&heap);
e2 = delete_min_heap(&heap);
//merge two nodes
x = make_tree(e1.ptree, e2.ptree);
e.key = x->weight = e1.key+e2.key;
e.ptree = x;
insert_min_heap(&heap, e);
}
e = delete_min_heap(&heap); //final huffman binary tree
destroy_tree(e.ptree);
}
void main(){
int freq[] = {15, 12, 8, 6, 4};
huffman_tree(freq, 5);
}