Invoking Programs
- Invoking external commands from inside a program
- External command is chosen by the Set-UID program
- Users are not supposed to provide the command (or it is not secure)
- Attack
- Users are often asked to provide input data to the commnad
- If the command is not invoked properly, user's input data may be turned into command name This is dangerous
Invoking Programs: Unsafe Approach
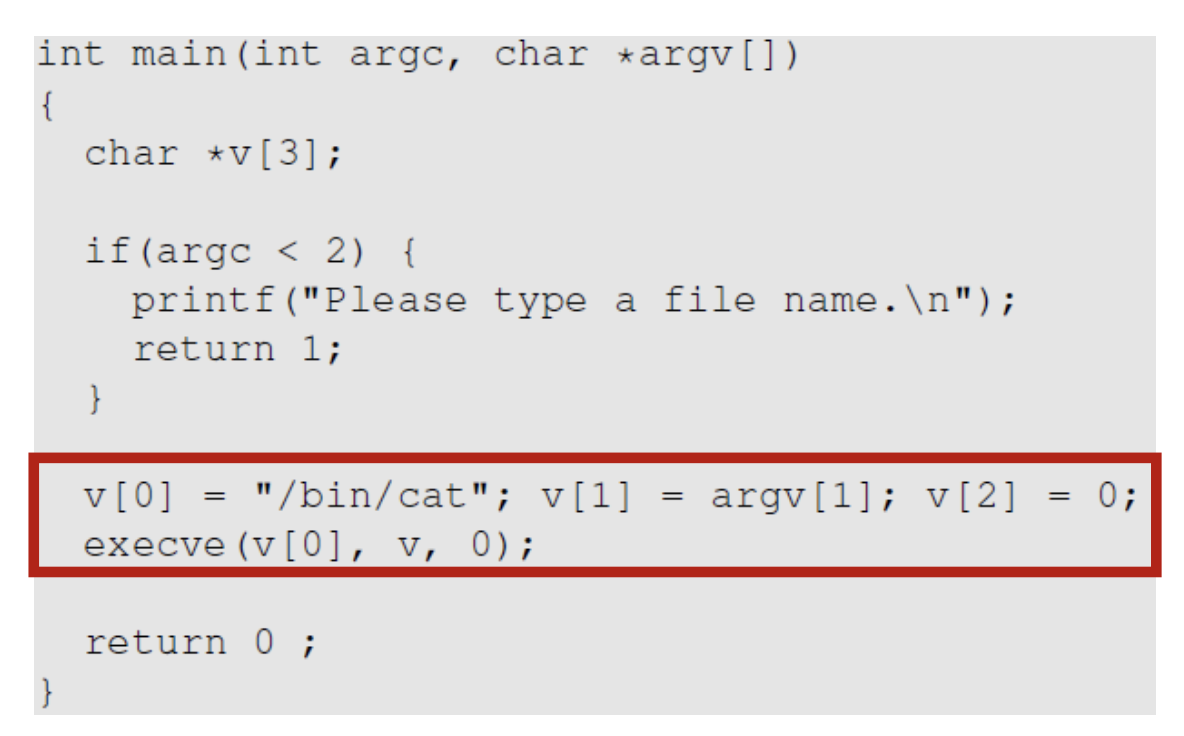
- The easiest way to invoke an external command is the
system()function - This program is supposed to run the
/bin/catprogram - It is a root-owned Set-UID program, so the program can view all files, but it can't write to any file
이 방식은 사용자의 입력값이 명령어 그대로 전달되기 때문에, 공격자가 악의적인 명령을 추가해 root 권한을 탈취할 수 있는 보안 취약점이 존재한다.

입력값을 그대로 system()으로 넘기는 구조: system("/bin/cat 사용자가 입력한 파일명")
주소 공간 크기
- char = 1 byte, char * = 4 or 8 byte
- char *: 특정 위치에서 오직 1 byte만 읽어온다.
- 32-bit: 4 byte
- 64-bit: 8 byte
system() 동작 과정
- shell 실행
- argument로 command 넣고 실행
Can you use this program to run other command, with the root privilege?
- 누구나 root 권한으로 실행할 수 있어 위험하다.
Problem
Some part of the data becomes code(command name)
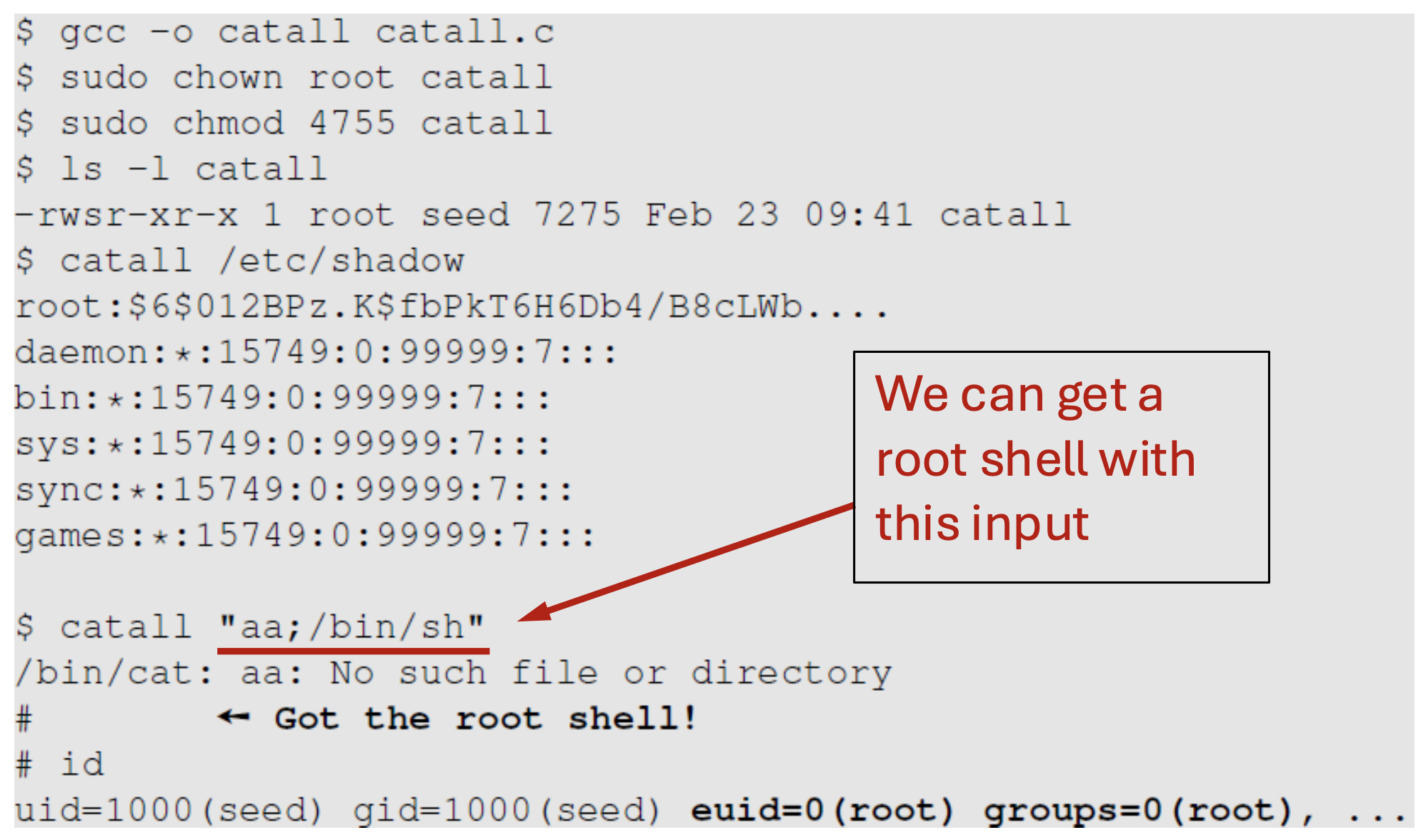
- catall 프로그램이 내부적으로 system() 함수를 직접 호출하기 때문에 쉘 명령어가 그대로 실행되는 문제가 발생한다.
- 단순한 file name이 아니라, command로 동작하면 문제된다.
"" 없이 하면 어떻게 되는가?
- normal user shell이 열린다.
A Note
- In Ubuntu 16.04, /bin/sh points to /bin/dash, which has a countermeasure
- It drops privilege when it is executed inside a set-uid process
- Therefore, we will only get a normal shell in the attack on the previous slide
- Do the following to remove the countermeasure

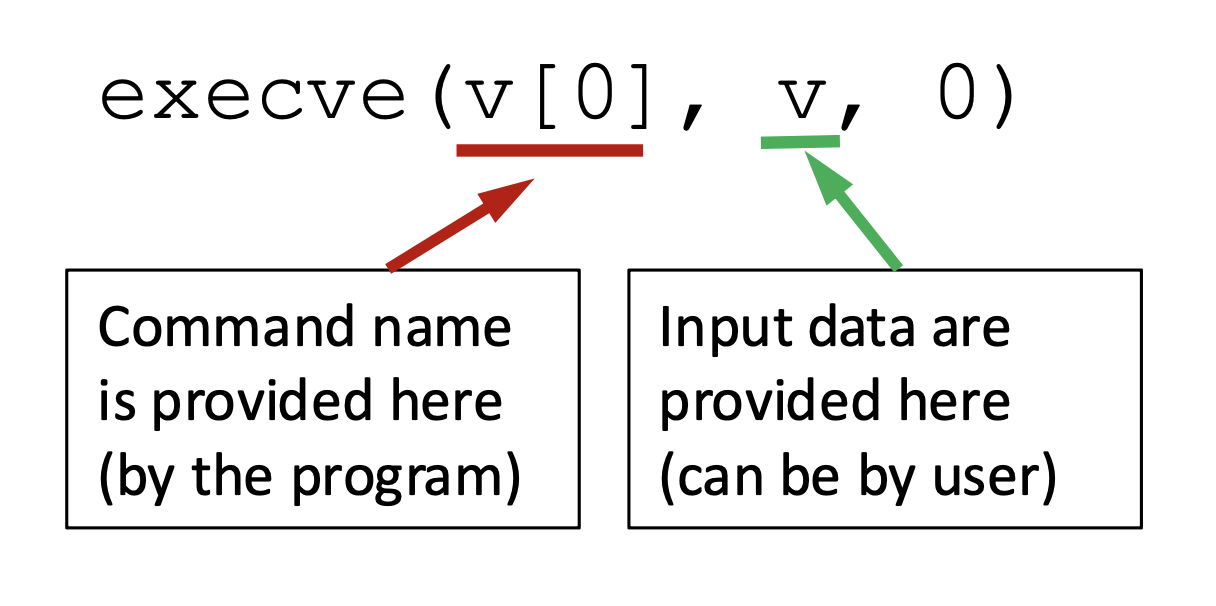
Invoking Programs Safely: using execve()
Why is it safe?
- Code and data are clearly separated
- there is no way for the user data to become code
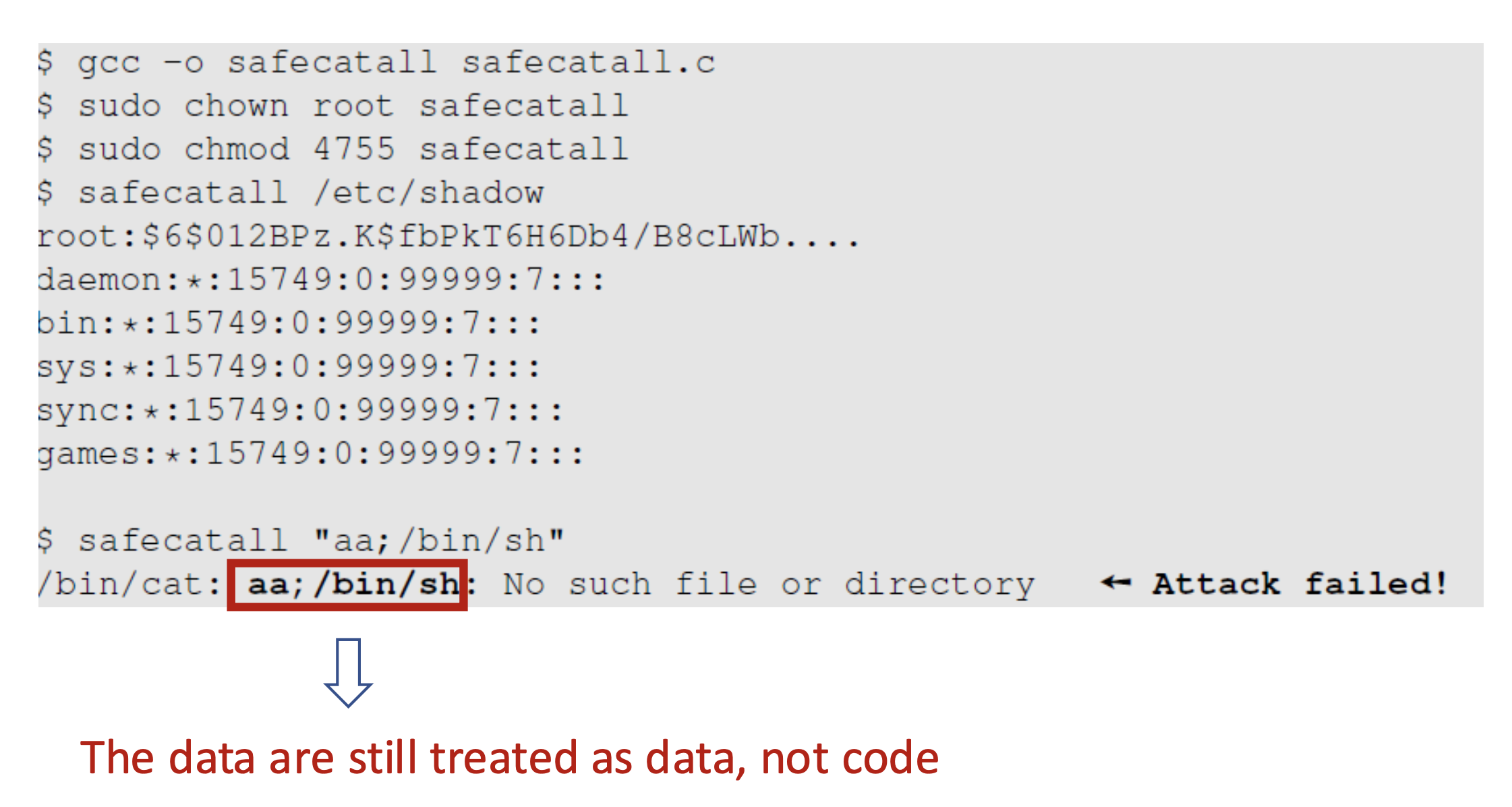
큰 따옴표에 쓴 전체 문자열을 파일명으로 보고, 해당 파일이 존재하지 않으니 fail 출력하고 끝나게 됨
Attacks via System Inputs
System Inputs
- Race Condition
- Symbolic link to privileged file from an unprivileged file
- Influence programs
- Writing inside world writable folder
/tmp: 모든 유저 접근 가능
- 일반 유저가 symbolic link를 이용하여 root 권한의 shell을 띄우거나, shadow file을 가리키게 할 수 있음
sticky bit
- drwxrwxrwt
- 누구나 파일을 만들고 쓸 수 있지만, 다른 사용자가 파일을 지우거나 덮어쓸 수 없음
Capability Leaking
- In some cases, Privileged programs downgrade themselves during execution
하향 조정할 때, 이전에 얻은 특권 능력을 제대로 정리하지 않으면 발생한다.
Example: su
- This is a privileged Set-UID program
- Allows one user to switch to another user
- Program starts with EUID as root and RUID as user1
- After password verification, both EUID and RUID become user2’s (via privilege downgrading)
- user1 user2
- Such programs may lead to capability leaking
- Programs may not clean up privileged capabilities before downgrading
Attacks via Capability Leaking: An Example
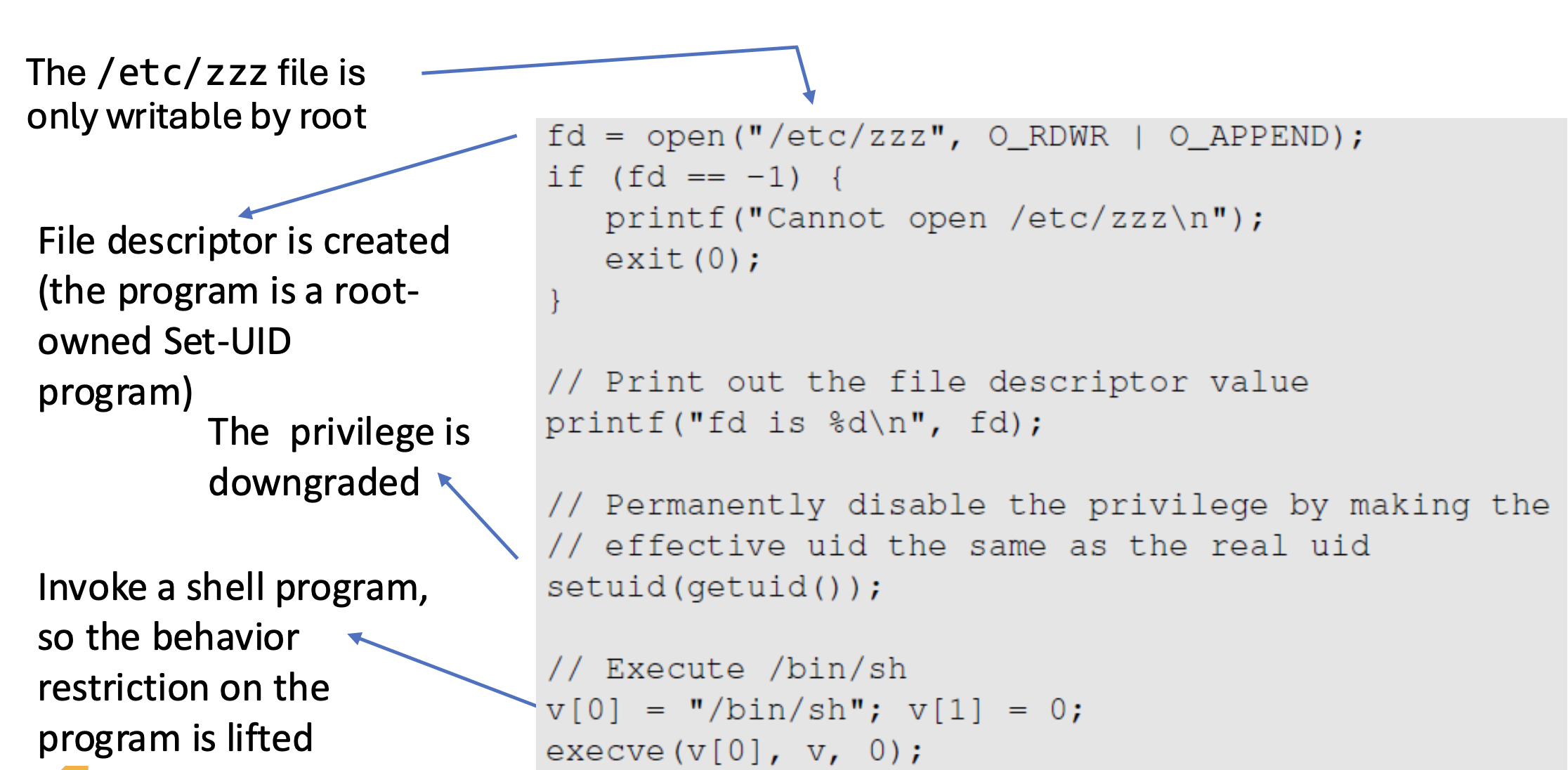 setuid(getuid())로 EUID와 RUID를 downgraded한 뒤,
setuid(getuid())로 EUID와 RUID를 downgraded한 뒤,
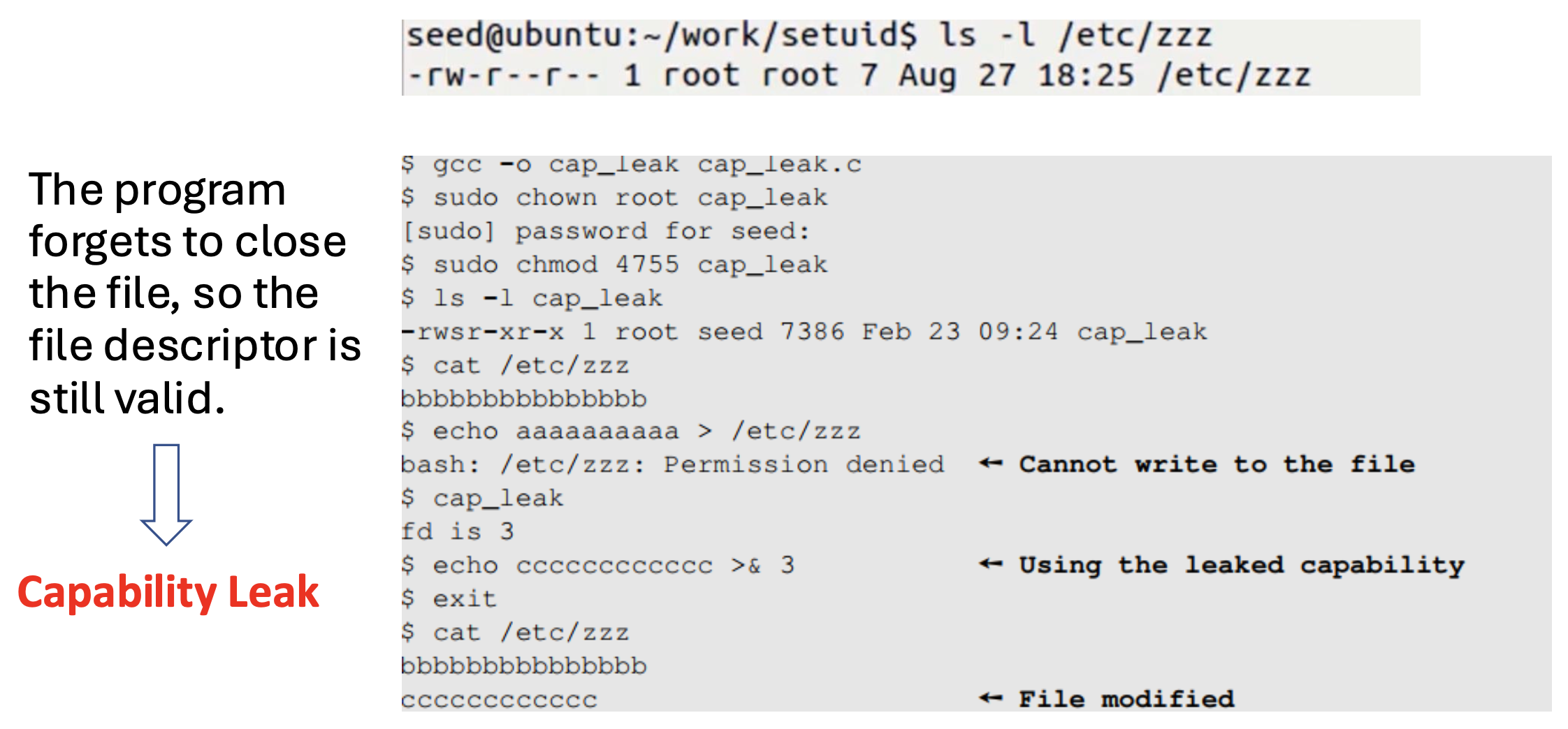
Set-UID root 프로그램이 실행되어 root 권한으로 fd가 생성된다. 프로그램 내부에서 권한을 downgrade하더라도, fd는 여전히 열려있기 때문에 shell에서 fd를 통해 파일 조작이 가능하다.
cap_leak 프로그램을 실행하여 execve()로 /bin/sh을 띄우고, 이전에 root 권한으로 열린 fd를 이용해여 echo 명령을 실행했기 때문에 /etc/zzz 파일을 수정하는 데 성공한다.
fd가 계속 열려있는 쉘은 현재 Root는 아니지만, root 권한을 가지고 있을 당시에 열어놓은 파일을 종료하지 않았기 때문에, 파일에 대한 접근 권한이 열려있는 것이다.
How to fix the program?
sub shell을 띄우기 전에 close해야 한다.
User Identity
getuid()- returns the real user ID of the calling process
geteuid()- returns the effective user ID of the calling process
uid_t getuid(void);
uid_t geteuid(void); seteuid()- sets effective user ID
setuid()- sets the effective user ID of the calling process
- If the calling process is privileged (more precisely: if the process has the CAP_SETUID capability in its user namespace), the real UID and saved set-user-ID(tmp) are also set
int setuid(uid_t uid);Capability Leaking in OS X - Case Study
- Added features to dynamic linker
dyld- DYLD_PRINT_TO_FILE environment variable
- The dynamic linker can open any file, so for root-owned Set-UID programs, it runs with root privileges. The dynamic linker dyld, does not close the file. There is a capability leaking.
- Scenario 1 (safe): Set-UID finished its job and the process dies. Everything is cleaned up and it is safe.
- Scenario 2 (unsafe): Similar to the
“su”program, the privileged program downgrade its privilege, and lift the restriction.

DYLD_PRINT_TO_FILE을 /etc/sudoers로 지정, su로 쉘 진입, fd(&3)를 통해 root 권한으로 /etc/sudoers 파일에 쓰기가 가능하다.
Invoking External Commands in Other Languages
- Risk of invoking external commands is not limited to C programs
- We should avoid problems similar to those caused by the system() functions
- Examples
- Perl: open() function can run commands, but it does so through a shell
- PHP: system() function

- Attack
- http://localhost/list.php?dir=.;date
- Command executed on server: "/bin/ls .;date"
Priciple of Isolation
Priciple: Don't mix code and data
Attacks due to violation of this priciple:
- system() code execution
system("/bin/ls " . $userInput); // 사용자 입력이 코드로 실행됨 - Cross Site Scripting
<div>안녕하세요 <?= $userName ?></div> - SQL injection
SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = '$userInput'; - Buffer Overflow attacks
char buffer[100]; strcpy(buffer, userInput); // 사용자 데이터가 메모리 구조를 덮어씀
Priciple of Least Privilege
- A privileged program should be given the power which is required to perform it’s tasks.
- Disable the privileges (temporarily or permanently) when a privileged program doesn’t need those.
- In Linux, seteuid() and setuid() can be used to disable/discard privileges.
- Different OSes have different ways to do that.
Zero Trust
- 최소한의 설정, 모든 사용자를 기본적으로 신뢰하지 않고, 항상 검증하는 보안 모델
White list
- 허용할 대상만 명시해서 나머지는 모두 차단하는 방식
- 관리가 까다롭지만 훨씬 safe한 방식
Black list
- 금지할 대상만 명시하고, 나머지는 기본적으로 허용하는 방식
- 관리가 편리하지만, 우회 위험이 있음
