- 기하학적 변환의 목적 : point, polygon, sampled parametric curve 등을 각 목적에 맞게 변환
- 좌표 프레임을 바꾸기 위해(world, window, viewport, device)
- 개개의 부품들이 연결point에 의해 묶여져서 하나의 객체를 변환하기 위해
- 새 모양을 만들기 위해 변형 사용
- animation에 효과적이므로
💻 What Is Geometrical Transformations?
Three Basic classes of transformation
- Rigid Body
- 크기와 각도 유지(모양이 변하지 않음)
- 가장 엄격한 조건의 변환
- ex) translation(위치이동), rotation(회전)
- Conformal
- 각도만 유지
- ex) translation(위치이동), rotation(회전), uniform scaling(확대/축소 같은 비율로 변환)
- Affine
- 평행만 유지, 선만 평행하게 남음
- ex) translation, rotation, Scaling, shear(찌그러짐, 비틀림), reflection(거울 반사)
Translation
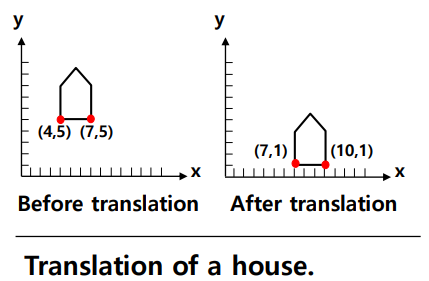
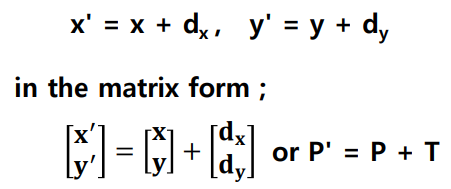
- 점에서 만큼 이동
Scaling
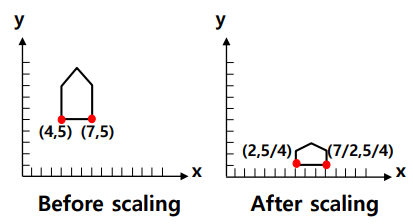
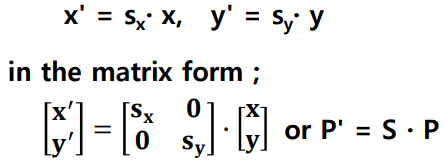
- , 가 같으면 Uniform Scaling(크기는 바뀌어도 모양은 안바뀜)
- , 가 다르면 Different Scaling(크기, 모양 둘다 바뀜)
Rotation
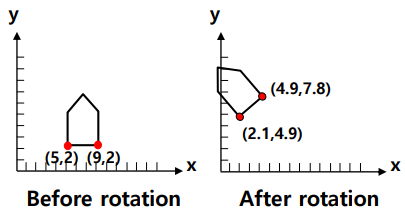
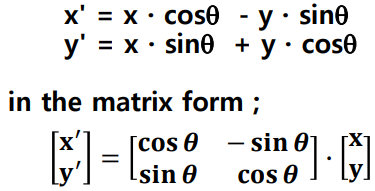
- 이면 회전 방향은 반시계 방향
- 반대로 이면 회전 방향은 시계 방향
rotation 방정식

Matrix Representation in Cartesian Coordinates
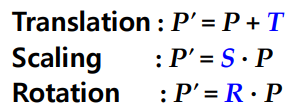
- Cartesian Coordinates에서 translation만 add 연산이고 scaling과 rotation은 mul이다.
- 변환의 효율성과 변환 행렬의 일관성을 위해 Homogeneous Coordinate(동차 좌표계)를 사용한다.
💻 Homogeneous Coordinates
-
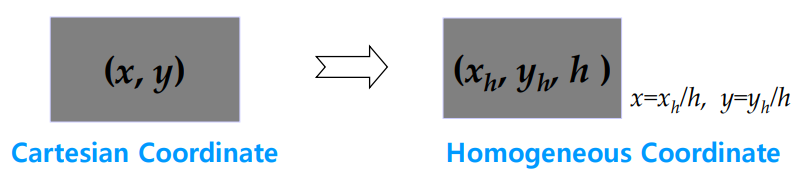
Cartesian Coordinate에서 h라는 값 하나를 더 추가했다
-
2차원 좌표계지만 항이 3개
-
h는 0을 제외한 모든 수 가능하다
- 가장 유용한 수는 1, ()
Translation Equation
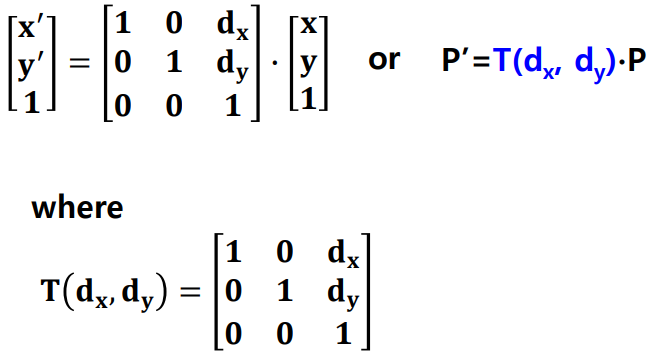
- 같은 값을 얻을 수 있으면서 행렬의 곱셈으로 표현 가능
Composte Translation : additive
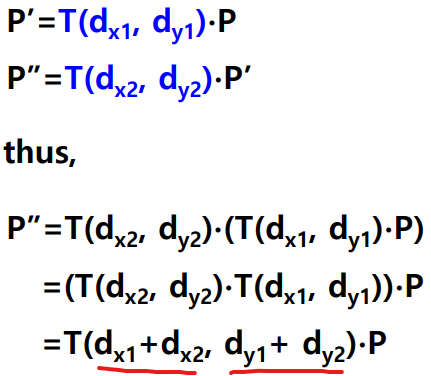
- Composte Translation = Translation이 2번 이상 일어나게 되는 경우\
- 복합 Translation은 덧셈의 형태
Scaling Equation
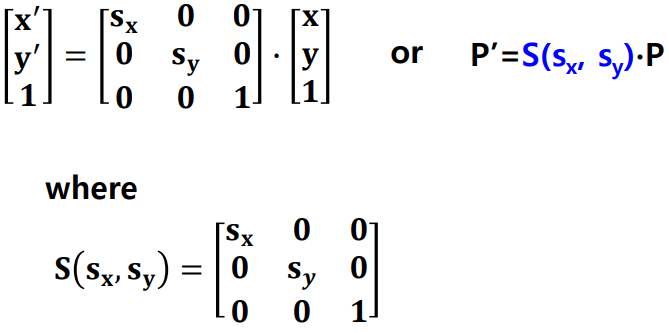
Composite Scaling : multiplicative

- 복합 Scaling은 곱셈의 형태
Rotation Equation
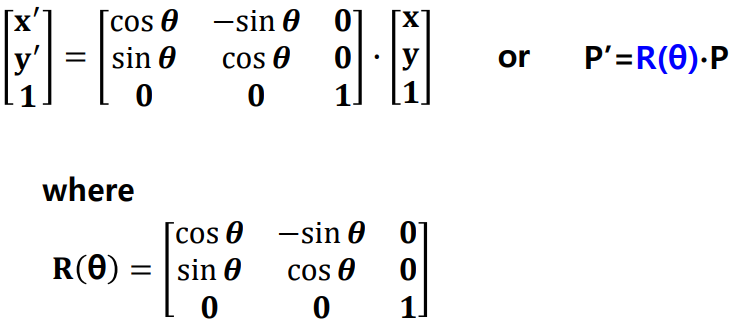
Composite Rotation : additive
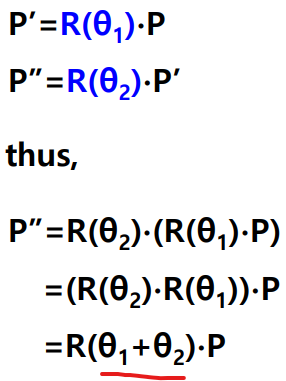
- 복합 Rotation은 덧셈 형태
Affine Transformation
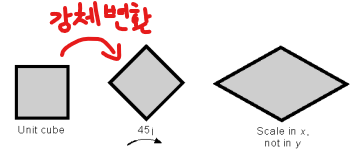
- Affine transformation은 선의 평행성을 보존하는 특성이 있지만, 길이와 각도는 보존하지 않는다
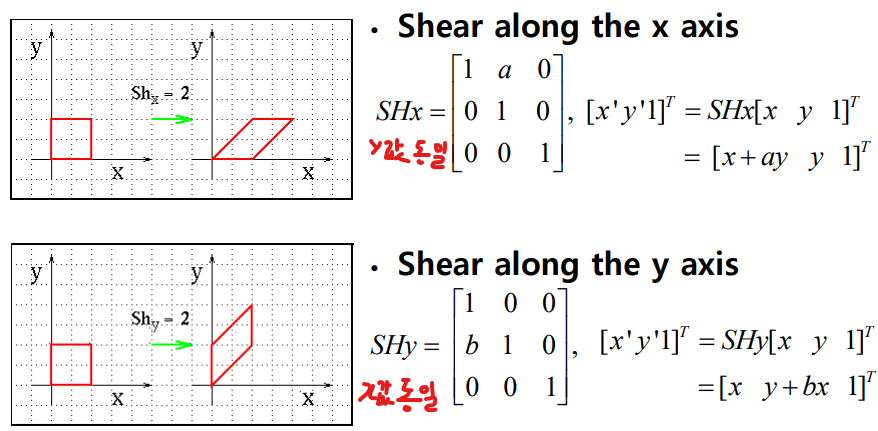
Shear Transformation
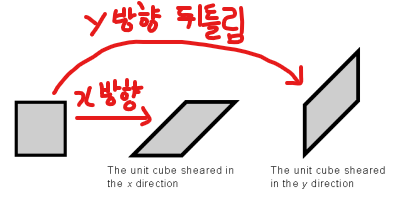
-
선분의 평행선은 그대로 유지
-
Affine transformation 범주에 속해 있음 : 선의 평행만 유지
-
x방향, y방향 비틀림
Shear Equation in Homogeneous Coordinate