1. 퀵 정렬
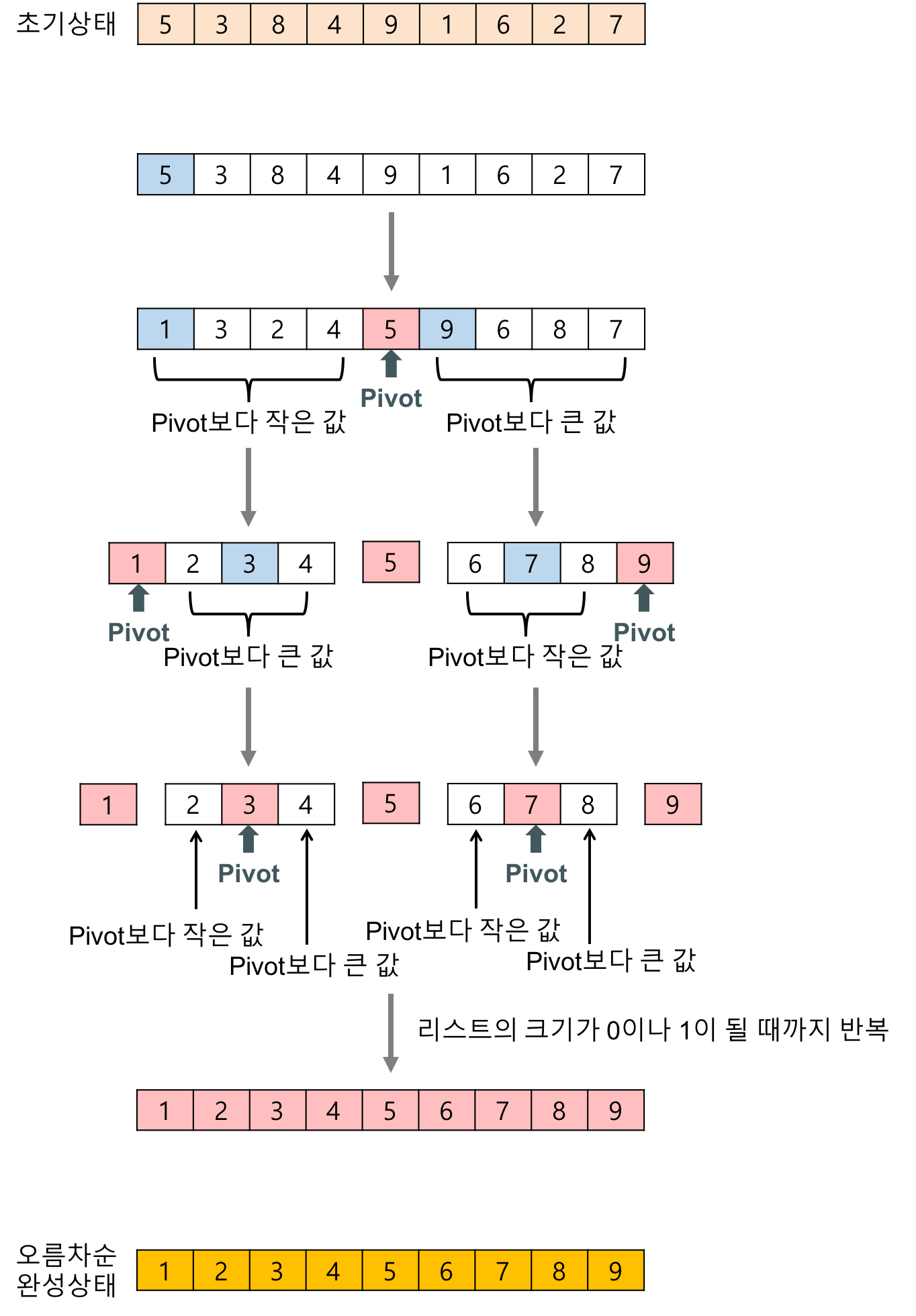
퀵 정렬은 가장 빠른 정렬 알고리즘으로 알려져 있으며 널리 사용된다.
1 ) 배열을 두 그룹으로 나누기
구현해보기
const partition = (arr: number[]): void => {
const n = arr.length;
let pivotLeft = 0;
let pivotRight = n - 1;
const PIVOT_IDX = Math.floor(n / 2);
const pivot = arr[PIVOT_IDX];
while (pivotLeft <= pivotRight) {
while (arr[pivotLeft] < pivot) pivotLeft++;
while (arr[pivotRight] > pivot) pivotRight--;
if (pivotLeft <= pivotRight) {
[arr[pivotLeft], arr[pivotRight]] = [
arr[pivotRight],
arr[pivotLeft],
];
pivotLeft++;
pivotRight--;
}
}
console.log("기준 이하 그룹 :", arr.slice(0, pivotLeft));
console.log("기준 이상 그룹 :", arr.slice(pivotRight + 1, n));
};
partition([1, 8, 7, 4, 5, 2, 6, 3, 9]);
// 기준 이하 그룹 : [ 1, 3, 2, 4, 5 ]
// 기준 이상 그룹 : [ 5, 7, 6, 8, 9 ]2 ) 재귀로 구현하는 퀵 정렬
구현해보기
const partition = (arr: number[], left: number, right: number): void => {
let pivotLeft = left;
let pivotRight = right;
const PIVOT_IDX = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
const pivot = arr[PIVOT_IDX];
while (pivotLeft <= pivotRight) {
while (arr[pivotLeft] < pivot) pivotLeft++;
while (arr[pivotRight] > pivot) pivotRight--;
if (pivotLeft <= pivotRight) {
[arr[pivotLeft], arr[pivotRight]] = [
arr[pivotRight],
arr[pivotLeft],
];
pivotLeft++;
pivotRight--;
}
}
if (left < pivotRight) partition(arr, left, pivotRight);
if (pivotLeft < right) partition(arr, pivotLeft, right);
};
const quickSort = (arr: number[]): void => {
partition(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
console.log(arr);
};
quickSort([1, 8, 7, 4, 5, 2, 6, 3, 9]);
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]3 ) 비재귀적인 퀵 정렬
구현해보기
const partition = (arr: number[], left: number, right: number): void => {
const range = [];
range.push([left, right]);
console.log(range);
while (range.length !== 0) {
const [left, right] = range.pop();
let [pivotLeft, pivotRight] = [left, right];
const PIVOT_IDX = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
const pivot = arr[PIVOT_IDX];
while (pivotLeft <= pivotRight) {
while (arr[pivotLeft] < pivot) pivotLeft++;
while (arr[pivotRight] > pivot) pivotRight--;
if (pivotLeft <= pivotRight) {
[arr[pivotLeft], arr[pivotRight]] = [
arr[pivotRight],
arr[pivotLeft],
];
pivotLeft++;
pivotRight--;
}
}
if (left < pivotRight) range.push([left, pivotRight]);
if (pivotLeft < right) range.push([pivotLeft, right]);
}
};
const quickSort = (arr: number[]): void => {
partition(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
console.log(arr);
};
quickSort([1, 8, 7, 4, 5, 2, 6, 3, 9]);
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]2. 병합 정렬
병합 정렬은 배열을 앞부분과 뒷부분의 두 그룹으로 나누어 각각 정렬한 후 병합하는 작업을 반복하는 알고리즘이다.
1 ) 두 배열을 병합하기
구현해보기
const mergeSortedList = (arrA: number[], arrB: number[], mergedArr: number[]): void => {
let IdxA = 0,
IdxB = 0,
IdxM = 0;
let lenA = arrA.length,
lenB = arrB.length;
while (IdxA < lenA && IdxB < lenB) {
if (arrA[IdxA] <= arrB[IdxB]) {
mergedArr[IdxM] = arrA[IdxA];
IdxA++;
} else {
mergedArr[IdxM] = arrB[IdxB];
IdxB++;
}
IdxM++;
}
while (IdxA < lenA) {
mergedArr[IdxM] = arrA[IdxA];
IdxA++;
IdxM++;
}
while (IdxB < lenB) {
mergedArr[IdxM] = arrB[IdxB];
IdxB++;
IdxM++;
}
console.log(mergedArr);
};
const arrA = [2, 4, 6, 8, 11, 13];
const arrB = [1, 2, 3, 4, 9, 16, 21];
const mergedArr = new Array(arrA.length + arrB.length);
mergeSortedList(arrA, arrB, mergedArr);
// [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 6, 8, 9, 11, 13, 16, 21]2 ) 병합 정렬 만들기
구현해보기
const mergeSortedList = (arr: number[], left: number, right: number, tempArr: number[]): void => {
if (left < right) {
const center = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
mergeSortedList(arr, left, center, tempArr);
mergeSortedList(arr, center + 1, right, tempArr);
let [j, k] = [0, left];
let [p, i] = [j, k];
while (i <= center) {
tempArr[p] = arr[i];
p++;
i++;
}
while (i <= right && j < p) {
if (tempArr[j] <= arr[i]) {
arr[k] = tempArr[j];
j++;
} else {
arr[k] = arr[i];
i++;
}
k++;
}
while (j < p) {
arr[k] = tempArr[j];
k++;
j++;
}
}
};
const mergeSort = (arr: number[]): void => {
const n = arr.length;
const tempArr = new Array(n);
mergeSortedList(arr, 0, n - 1, tempArr);
console.log(arr);
};
mergeSort([5, 8, 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 9, 7]);
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]3. 힙 정렬
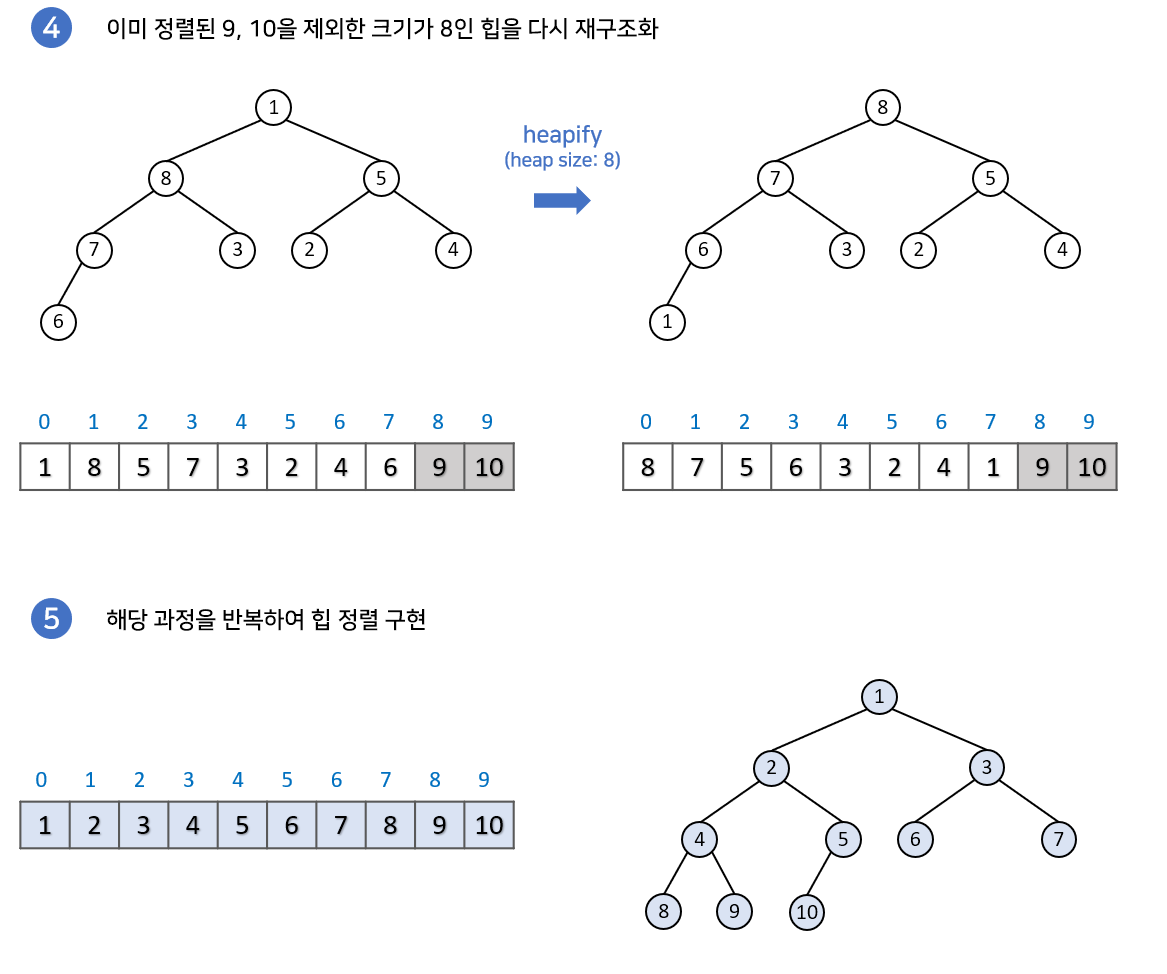
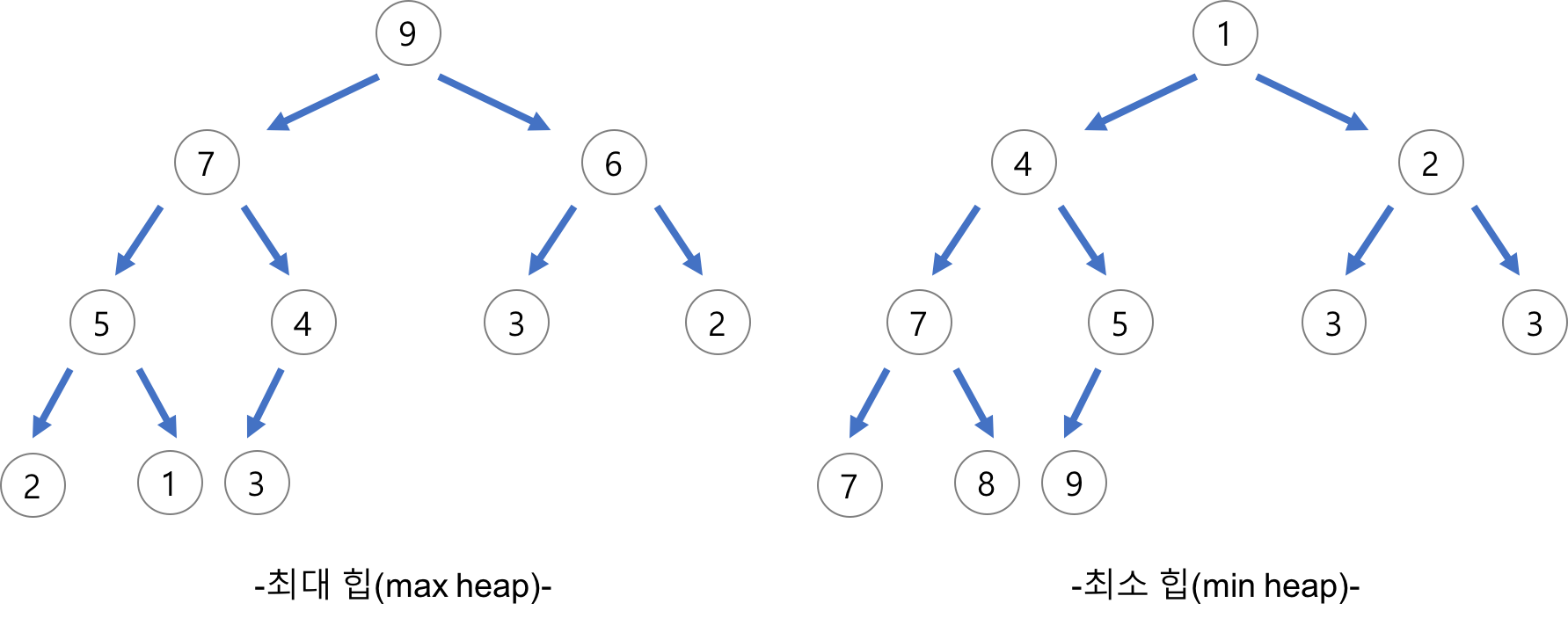
힙 정렬은 힙의 특성을 이용하여 정렬하는 알고리즘이다.
힙은 '부모의 값이 자식의 값보다 항상 크다'는 조건을 만족하는 완전 이진 트리이다.
힙 정렬은 '힙에서 최댓값은 루트에 위치한다'는 특징을 이용하여 정렬하는 알고리즘이다.
1 ) 배열을 힙으로 변환하기
구현해보기
const downHeap = (arr: number[], left: number, right: number): void => {
const temp = arr[left];
let parent = left;
while (parent < Math.floor((right + 1) / 2)) {
let leftChild = parent * 2 + 1;
let rightChild = leftChild + 1;
let child =
rightChild <= right && arr[rightChild] > arr[leftChild]
? rightChild
: leftChild;
if (temp >= arr[child]) break;
arr[parent] = arr[child];
parent = child;
}
arr[parent] = temp;
};
const heapSort = (arr: number[]): void => {
const n = arr.length;
const ROOT_OF_LEEF = Math.floor((n - 1) / 2);
for (let i = ROOT_OF_LEEF; i > -1; i--) {
downHeap(arr, i, n - 1);
}
console.log(arr);
};
heapSort([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]);
// [7, 5, 6, 4, 2, 1, 3]2 ) 힙 정렬 만들기
구현해보기
const downHeap = (arr: number[], left: number, right: number): void => {
const temp = arr[left];
let parent = left;
while (parent < Math.floor((right + 1) / 2)) {
let leftChild = parent * 2 + 1;
let rightChild = leftChild + 1;
let child =
rightChild <= right && arr[rightChild] > arr[leftChild]
? rightChild
: leftChild;
if (temp >= arr[child]) break;
arr[parent] = arr[child];
parent = child;
}
arr[parent] = temp;
};
const heapSort = (arr: number[]): void => {
const n = arr.length;
const ROOT_OF_LEEF = Math.floor((n - 1) / 2);
for (let i = ROOT_OF_LEEF; i > -1; i--) {
downHeap(arr, i, n - 1);
}
for (let i = n - 1; i > 0; i--) {
[arr[0], arr[i]] = [arr[i], arr[0]];
downHeap(arr, 0, i - 1);
}
console.log(arr);
};
heapSort([6, 4, 3, 7, 1, 9, 8]);
// [1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9]4. 도수 정렬
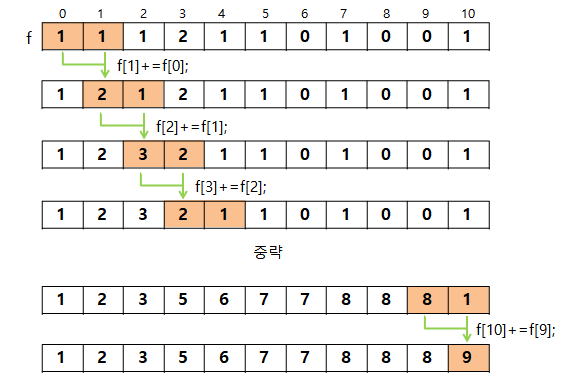
도수 정렬은 원소의 대소 관계를 판단하지 않고 빠르게 정렬하는 알고리즘으로, 분포수 세기 정렬이라고도 한다.
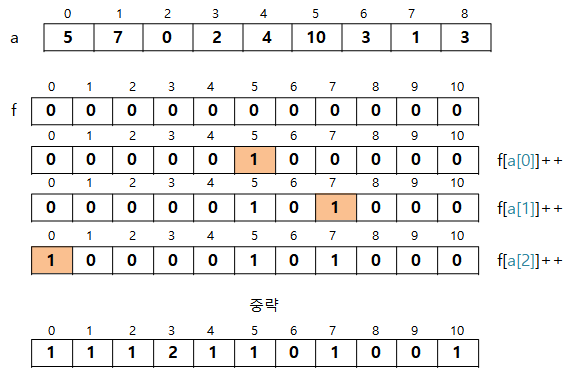
구현해보기
const fSort = (arr: number[], max: number): void => {
const n = arr.length;
const countingArr = new Array(max + 1).fill(0);
const tempArr = new Array(n).fill(0);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const target = arr[i];
countingArr[target]++;
}
for (let i = 1; i < max + 1; i++) countingArr[i] += countingArr[i - 1];
for (let i = n - 1; i > -1; i--) {
const target = arr[i];
const tempIdx = --countingArr[target];
tempArr[tempIdx] = target;
}
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) arr[i] = tempArr[i];
};
const countingSort = (arr: number[]): void => {
fSort(arr, Math.max(...arr));
console.log(arr);
};
countingSort([22, 5, 11, 32, 99, 68, 70]);
// [5, 11, 22, 32, 68, 70, 99]