[15주차], [17주차]
TIL
Path Planning
-
차선이 있을 때 경로계획
-
차선이 없을 때 경로계획
Dijkstra Algorithm
- dijkstra함수 구현 python 코드 첨부
A* Algorithm
- A*
- weighted A*
- hybrid A*
RRT
15, 17주차 skill set
1) 차선이 있는 경우의 patg planning을 할 수 있다.
2) 차선이 없는 경우 lead 차량의 pose를 기반으로 path를 생성할 수 있다.
3) Dijkstra Algorithm을 구현할 수 있다.
4) (Weighted) A Algorithm을 구현할 수 있다.
5) Hybrid A Algorithm을 구현할 수 있다.
6)
학습내용
15 주차 path planning 이론 강의를 기반으로 17주차에서 모든 이론을 코드로 구현하는 실습을 진행한다.
[0] Control Review
-
4, 5주차에 학습한 내용을 간단하게 되짚어보자.
https://velog.io/@dominico97/series/Control-
Noisy한 데이터를 처리하는 filtering 방법
(이동평균, Kalman 등...) -
Feedback PID 제어
(시스템의 model을 몰라도, Data의 변화 양상만을 제어할 수 있는 강력한 제어기) -
차량동역학, Vehicle Dynamics
(Longitudinal / Lateral) -
차선, Driving Lanes
(4차 Polynomial, 클로소이드 곡선 등) -
차량제어, Vehicle Control
(Longitudinal / Lateral)
-
-
키워드만 봐도 어떤 내용을 배웠는지 remind 된다!!
-
control 시리즈에서 제어 하는 방법을 배웠다면,
지금부턴 제어를 위한 path를 계획하는 방법을 학습한다.
[1] Path Planning
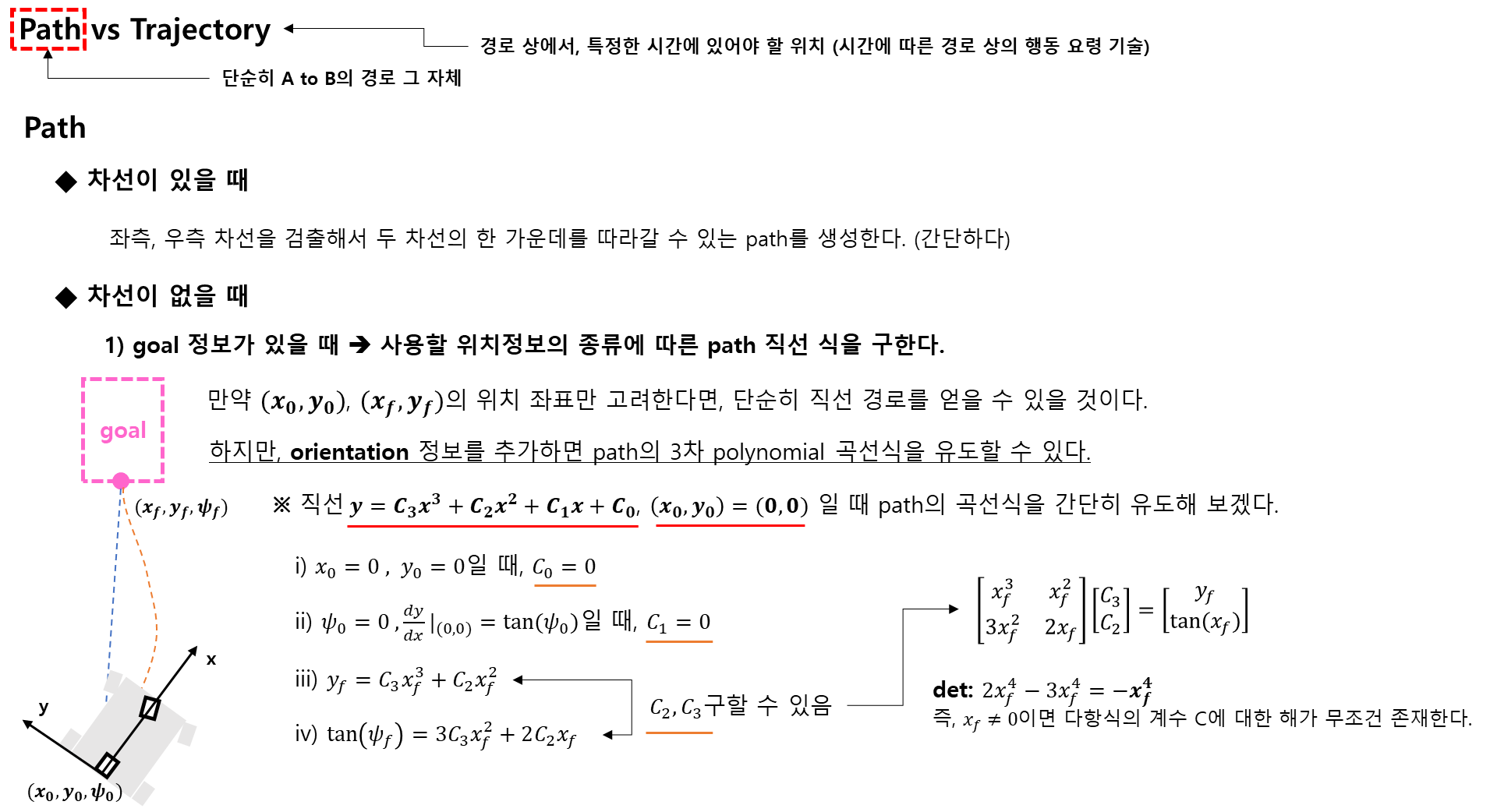
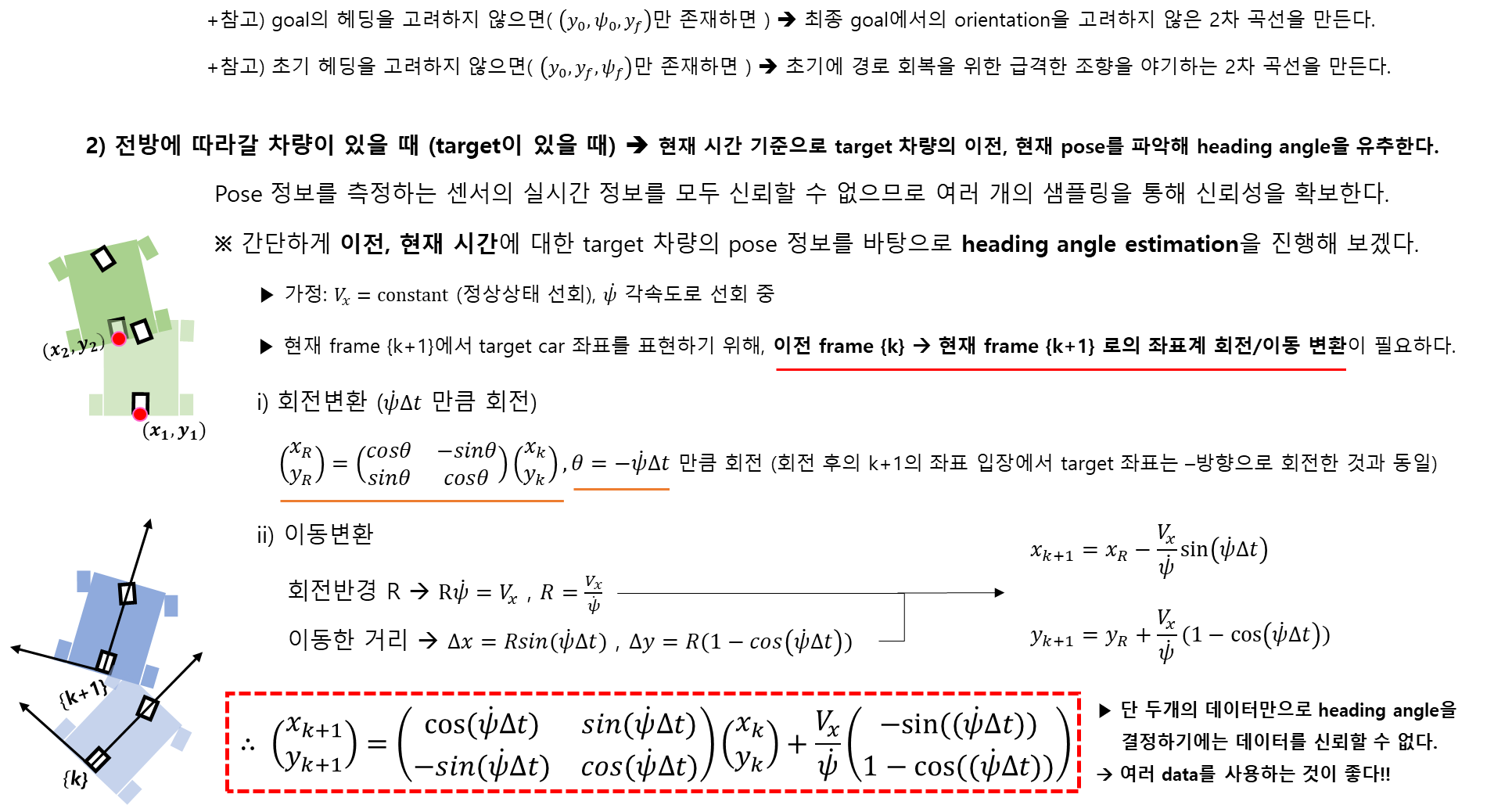
[2] Dijkstra Algorithm
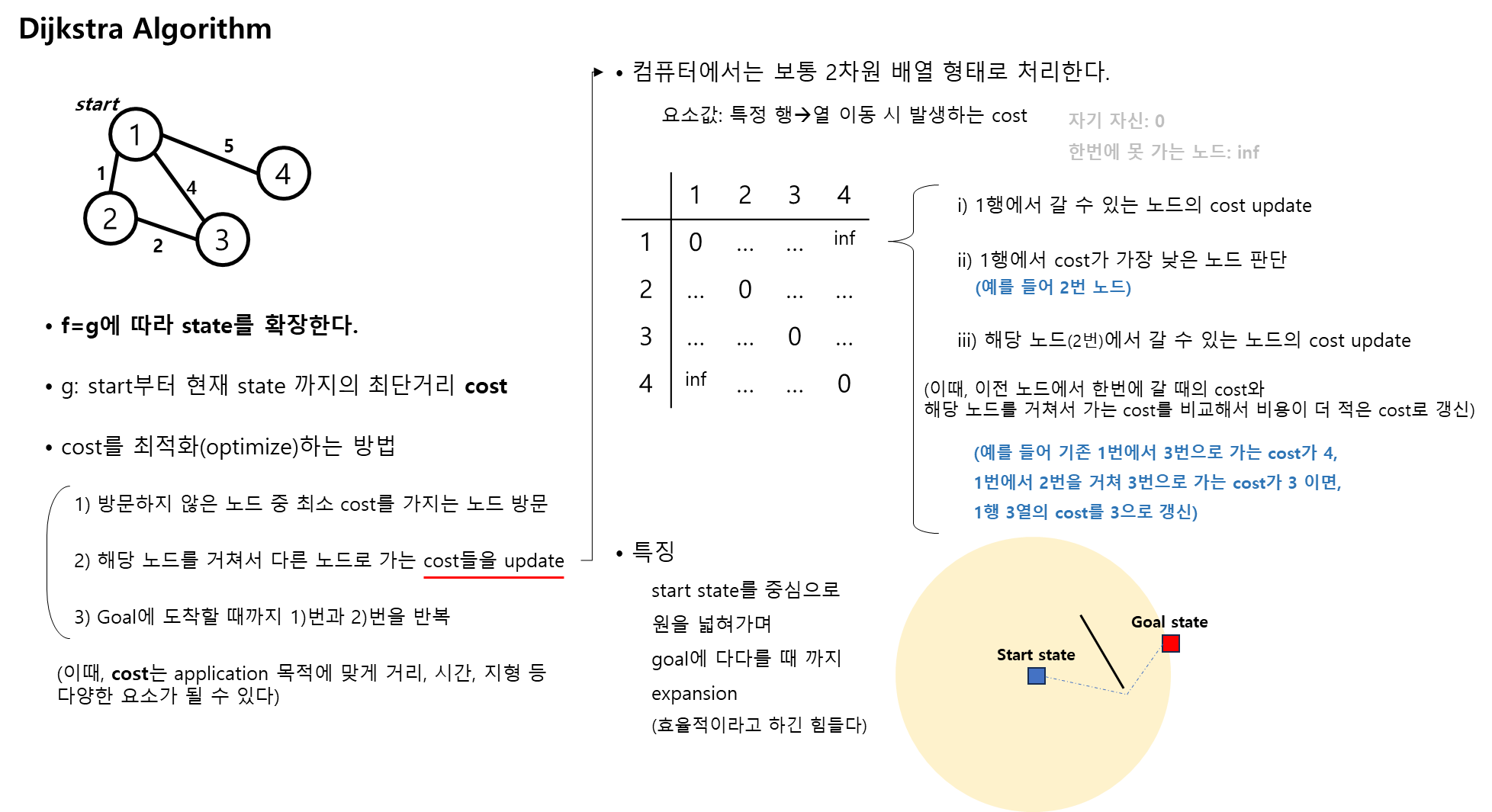
- 아래 코드를 찬찬히 읽어보면 dijkstra 함수 작동 방법을 이해할 수 있다.
#python
def dijkstra(start, goal, map_obstacle):
start_node = Node(None, start)
goal_node = Node(None, goal)
open_list = []
closed_list = []
open_list.append(start_node)
while open_list is not None:
# Find node with lowest cost
cur_node = open_list[0]
cur_index = 0
'''
enumerate() function
a built-in function that sequentially returns indexes and values of a list
>> for index, value in enumerate(iterable):
>> 1st iter => index=0, value=interable[0]
>> 2nd iter => index=1, value=interable[1]
>> 3rd iter => index=2, value=interable[2]
'''
# Check the all nodes in the open_list
# Update the node with smallest "f" to "cur_node"
for index, node in enumerate(open_list):
if node.f < cur_node.f:
cur_node = node
cur_index = index
# If goal, return optimal path
if cur_node.position == goal_node.position:
opt_path = []
node = cur_node
# From goal_node to start_node, the positions of parent nodes are stored in reverse order in opt_path list
while node is not None:
opt_path.append(node.position)
node = node.parent
# return in reverse order
return opt_path[::-1]
# If not goal, move from open_list to closed_list
open_list.pop(cur_index)
closed_list.append(cur_node)
# Generate child candidate
action_set = get_action()
for action in action_set:
child_candidate_position = (cur_node.position[0] + action[0], cur_node.position[1] + action[1])
# If collision expected, do nothing
if collision_check(map_obstacle, child_candidate_position):
continue
# If not collision, create child node
child = Node(cur_node, child_candidate_position)
# If already in closed list, do nothing
if child in closed_list:
continue
# If not in closed list, update open list
child.g = action[2]
child.f = cur_node.f + child.g
if child in open_list:
if child.f < open_list[open_list.index(child)].f:
open_list[open_list.index(child)] = child
else:
open_list.append(child)
[3] A* Algorithm
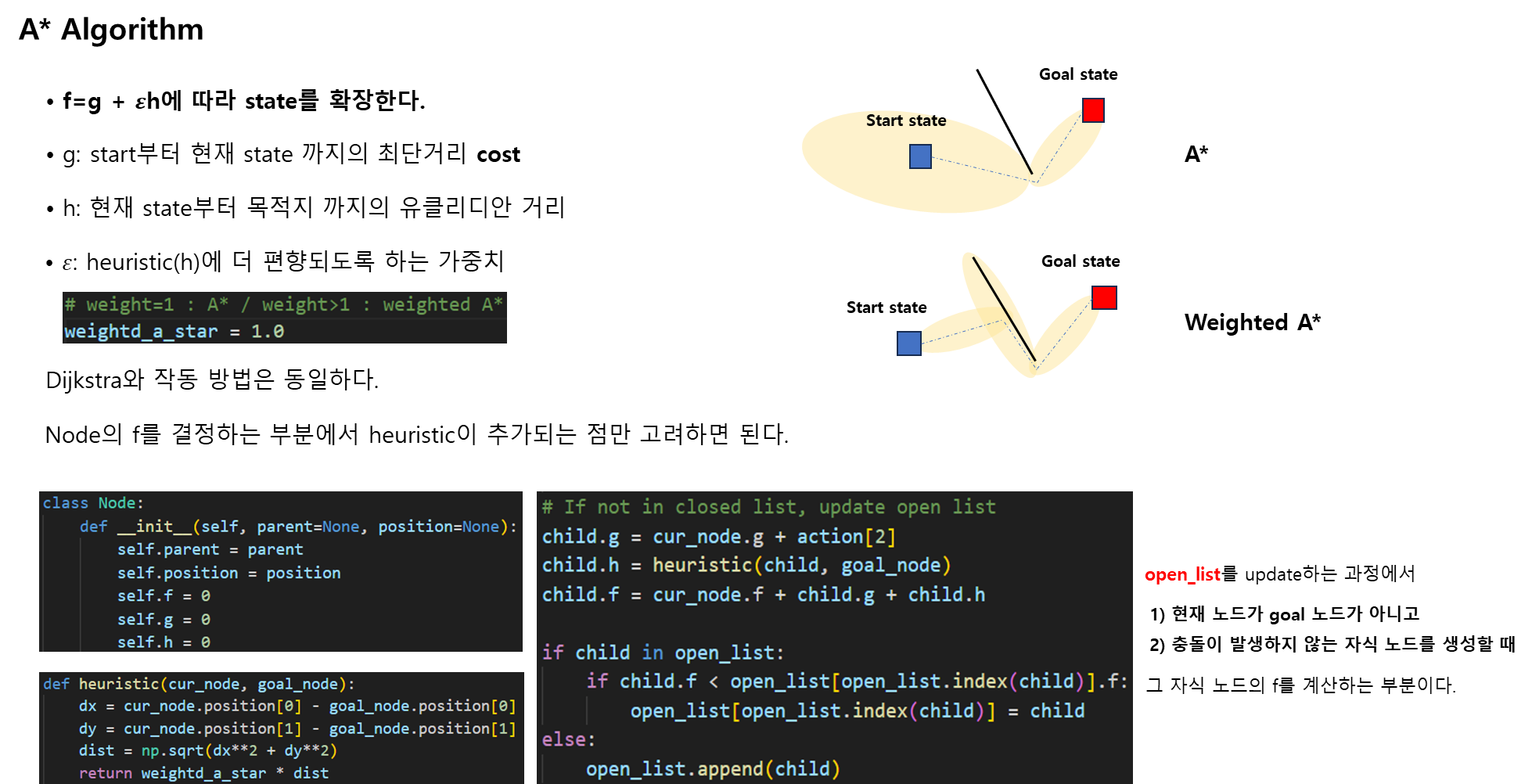
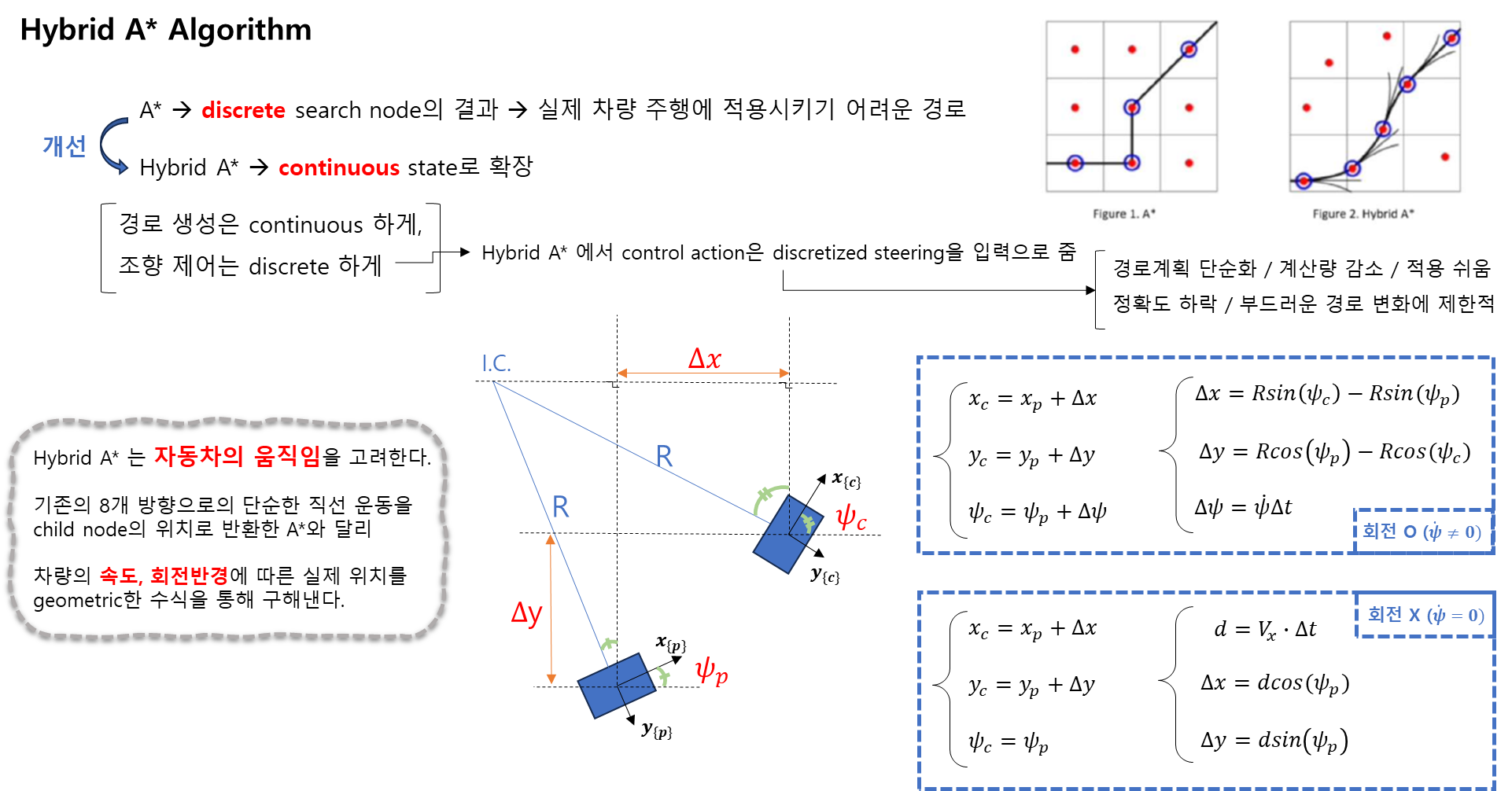
[4] RRT
<출처>
(1) Programmers K-Digital-Training: 자율주행 데브코스 Planning & Control, Path Planning
(2)

