확인 문제
1. Tree가 무엇인지 알고 있나요? Tree의 종류에는 어떤 것들이 있나요?
내 답:
트리(Tree)는 컴퓨터 과학에서 널리 사용되는 자료구조 중 하나로, 계층적 관계를 표현하는 데 사용됩니다. 트리는 노드(Node)들로 구성되며, 하나의 루트 노드(Root Node)에서 시작해 여러 개의 자식 노드(Child Node)를 가질 수 있습니다. 각 노드는 0개 이상의 자식 노드를 가질 수 있으며, 자식 노드가 없는 노드를 리프 노드(Leaf Node)라고 합니다. 트리 구조에서는 두 노드 사이를 연결하는 경로(Path)가 유일하며, 사이클(Cycle)이 존재하지 않습니다.
이진 트리(Binary Tree)
각 노드가 최대 두 개의 자식 노드를 가질 수 있는 트리입니다. 이진 트리는 다음과 같이 여러 하위 유형으로 나뉩니다:
• 완전 이진 트리(Complete Binary Tree): 모든 레벨이 노드로 꽉 차 있으며, 마지막 레벨을 제외하고는 왼쪽부터 오른쪽으로 노드가 채워져 있습니다.
• 포화 이진 트리(Full Binary Tree): 모든 노드가 0개 또는 2개의 자식 노드를 가지고 있습니다.
• 균형 이진 트리(Balanced Binary Tree): 모든 리프 노드까지의 거리가 대략적으로 동일하게 유지되는 트리입니다.
이진 탐색 트리(Binary Search Tree, BST)
이진 탐색 트리는 이진 트리의 한 종류로, 각 노드에는 유일한 키가 있으며, 모든 노드는 다음과 같은 이진 탐색 속성을 만족합니다: 모든 왼쪽 자식 노드의 키는 해당 노드의 키보다 작고, 모든 오른쪽 자식 노드의 키는 해당 노드의 키보다 큽니다.
모범 답:
2. 다음의 트리를 DFS로 방문할 때와 BFS로 방문할 때의 순서가 어떻게 될까요?
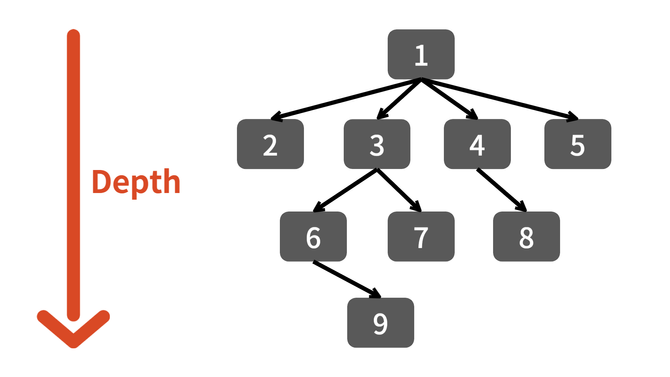
내 답:
DFS : 1 - 2 - 3 - 6 - 9 - 7 - 4 - 8 - 5
BFS : 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7 - 8 - 9
모범 답:
3. 아래와 같은 형식의 미니맵이 있습니다.
나의 현재 위치로부터 보스방까지 어떻게 가야 가장 빠르게 갈 수 있는지 체크하려고 합니다.
DFS와 BFS 중 어느 방법이 더 적절할까요?
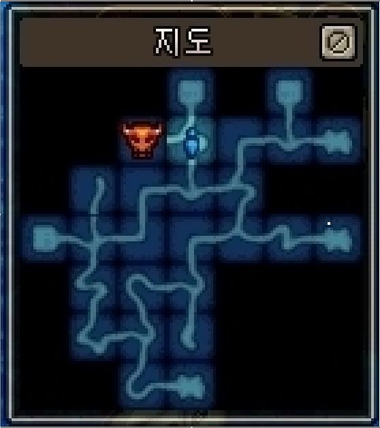
내 답:
BFS를 통해 찾는 것이 몇 번째 트리에서 보스 방에 도달할 수 있을지 체크가 빠를 것이라 생각됩니다.
모범 답:
설명 문제
- Tree의 순회(Traversal) 방법에 대해 설명해주세요.
내 답:
트리 순회는 트리의 모든 노드를 체계적으로 방문하는 과정입니다. 주로 다음 세 가지 기본적인 방법이 사용됩니다:
• 전위 순회(Pre-order Traversal): 루트 노드를 먼저 방문하고, 그 다음 왼쪽 서브트리, 마지막으로 오른쪽 서브트리를 순회합니다.
• 중위 순회(In-order Traversal): 왼쪽 서브트리를 먼저 순회하고, 루트 노드를 방문한 다음, 오른쪽 서브트리를 순회합니다. 이진 탐색 트리에서 중위 순회를 사용하면 노드들을 오름차순으로 방문할 수 있습니다.
• 후위 순회(Post-order Traversal): 왼쪽 서브트리, 오른쪽 서브트리를 순회한 후에 루트 노드를 방문합니다.
모범 답:
- DFS와 BFS에 대해 설명해주세요.
내 답:
• 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS, Depth-First Search): DFS는 트리나 그래프에서 한 방향으로 가능한 깊게 노드를 탐색한 후, 더 이상 탐색할 노드가 없으면 마지막으로 방문한 노드에서 다른 방향으로 탐색을 계속하는 방식입니다. DFS는 스택(Stack)이나 재귀(Recursion)를 사용하여 구현할 수 있습니다.
• 너비 우선 탐색(BFS, Breadth-First Search): BFS는 루트 노드에서 시작하여 인접한 노드를 먼저 탐색하는 방식입니다. 즉, 시작 노드로부터 가까운 노드를 먼저 방문하고, 멀어질수록 나중에 방문합니다. BFS는 주로 큐(Queue)를 사용하여 구현됩니다.
모범 답:
2-1. DFS와 BFS를 본인의 프로젝트에 활용한 경험이 있다면 설명해주세요.
내 답:
모범 답:
- 행동 트리 (Behaviour Tree) 에 대해 설명해주세요.
내 답:
행동 트리는 인공 지능(AI) 프로그래밍에서 주로 사용되는 계층적 상태 머신의 일종으로, 복잡한 태스크 선택, 상태 관리, 의사 결정 과정을 모델링하는 데 사용됩니다. 특히 게임 개발에서 NPC(Non-Player Character)의 행동을 제어하는 데 널리 사용됩니다.
행동 트리는 루트 노드에서 시작하여 트리 구조를 따라 노드를 순회하며, 각 노드는 특정한 조건을 검사하거나 행동을 실행합니다. 노드 유형에는 다음과 같은 것들이 있습니다:
• 조건 노드(Condition Nodes): 특정 조건이 참인지 거짓인지를 평가합니다.
• 행동 노드(Action Nodes): 실제 작업을 수행합니다(예: 이동, 공격).
• 제어 노드(Control Nodes): 자식 노드들을 어떤 순서로 실행할지 결정합니다. 대표적인 제어 노드로는 시퀀스 노드(Sequence Nodes), 선택 노드(Selector Nodes), 병렬 노드(Parallel Nodes) 등이 있습니다.
행동 트리는 유연성과 확장성이 뛰어나며, 복잡한 AI 행동을 직관적으로 설계하고 관리할 수 있게 해줍니다.
모범 답:
실습 문제
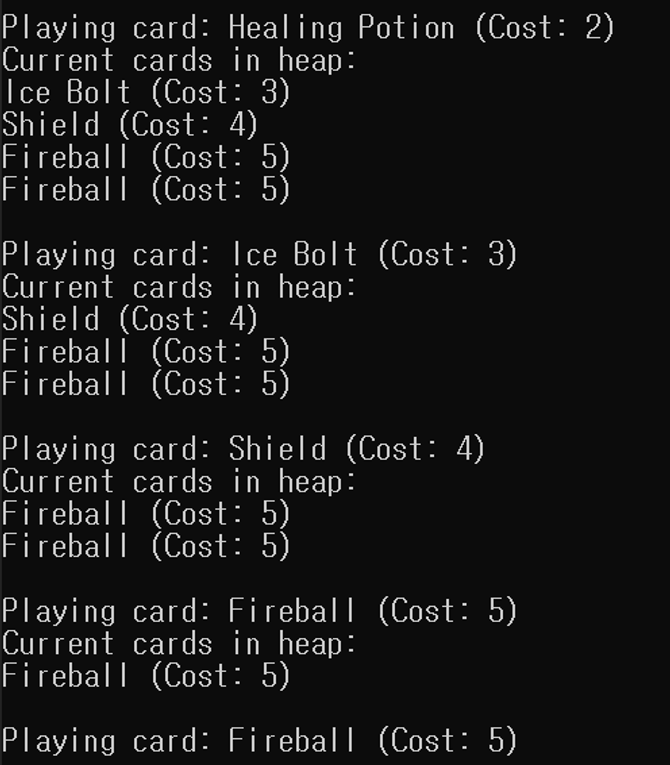
💡 [최소 힙을 사용해 카드 정렬하기]
카드 게임의 AI를 만들고 싶습니다.
가장 초급 AI를 먼저 만드려고 하는데, 이 초급 AI는 매 턴 가장 작은 비용의 카드를 사용하게 설정하려고 합니다.
이 경우 매 턴마다 가장 적은 비용의 카드를 손에서 탐색해야하는 걸까요?
고민하고 있던 도중 최소 힙(Min Heap)에 대해 알게 되어 이를 이용하여
가장 작은 비용의 카드가 항상 앞에 있게 하려고 합니다.
이미 구현된 최소 힙을 이용하여 카드의 기능을 완성해봅시다.
MinHeap 기능
public void Insert(T item): 새로운 요소를 힙에 삽입하고 힙의 속성을 유지합니다.public T ExtractMin(): 최소 요소를 제거하고 반환합니다. 제거 후 힙의 속성을 유지합니다. 힙이 비어 있으면 예외를 던집니다.public T Peek(): 힙의 최소 요소를 반환합니다. 힙이 비어 있으면 예외를 던집니다.private void HeapifyUp(int index): 주어진 인덱스에서 위로 올라가며 힙의 속성을 유지합니다.private void HeapifyDown(int index): 주어진 인덱스에서 아래로 내려가며 힙의 속성을 유지합니다.
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 카드 풀 생성
List<Card> cardPool = new List<Card>
{
new Card("Fireball", 5),
new Card("Ice Bolt", 3),
new Card("Healing Potion", 2),
new Card("Shield", 4)
};
// 랜덤 객체 생성
Random rand = new Random(1);
// MinHeap 생성
MinHeap<Card> cardHeap = new MinHeap<Card>();
// 카드 풀에서 랜덤하게 5장의 카드를 뽑아 힙에 삽입
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
int randomIndex = rand.Next(cardPool.Count);
cardHeap.Insert(cardPool[randomIndex]);
}
// TODO: cardHeap이 빌 때까지 가장 적은 비용의 카드만 내기
while (cardHeap.Count > 0)
{
Card card = cardHeap.ExtractMin();
PlayCard(card);
}
}
static void PlayCard(Card card)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Playing card: {card}");
}
}
public class Card : IComparable<Card>
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Cost { get; set; }
public Card(string name, int cost)
{
Name = name;
Cost = cost;
}
public int CompareTo(Card other)
{
if (other == null) return 1;
return Cost.CompareTo(other.Cost);
}
public override string ToString()
{
return $"{Name} (Cost: {Cost})";
}
}
public class MinHeap<T> where T : IComparable<T>
{
private List<T> heap;
public MinHeap()
{
heap = new List<T>();
}
public int Count => heap.Count;
public void Insert(T item)
{
heap.Add(item);
HeapifyUp(heap.Count - 1);
}
public T ExtractMin()
{
if (heap.Count == 0)
throw new InvalidOperationException("Heap is empty.");
T min = heap[0];
heap[0] = heap[heap.Count - 1];
heap.RemoveAt(heap.Count - 1);
if (heap.Count > 0)
HeapifyDown(0);
return min;
}
public T Peek()
{
if (heap.Count == 0)
throw new InvalidOperationException("Heap is empty.");
return heap[0];
}
public void DisplayHeap()
{
Console.WriteLine("Current cards in heap:");
foreach (T item in heap)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
private void HeapifyUp(int index)
{
int parentIndex = (index - 1) / 2;
if (index > 0 && heap[index].CompareTo(heap[parentIndex]) < 0)
{
Swap(index, parentIndex);
HeapifyUp(parentIndex);
}
}
private void HeapifyDown(int index)
{
int smallest = index;
int leftChild = 2 * index + 1;
int rightChild = 2 * index + 2;
if (leftChild < heap.Count && heap[leftChild].CompareTo(heap[smallest]) < 0)
{
smallest = leftChild;
}
if (rightChild < heap.Count && heap[rightChild].CompareTo(heap[smallest]) < 0)
{
smallest = rightChild;
}
if (smallest != index)
{
Swap(index, smallest);
HeapifyDown(smallest);
}
}
private void Swap(int index1, int index2)
{
T temp = heap[index1];
heap[index1] = heap[index2];
heap[index2] = temp;
}
}