개요
Series
- Pandas의 자료 형태중 하나로 1차원 배열과 같은 자료구조
- 인덱스와 값이 자동으로 생성되는 데이터 단위
- 리스트와 딕셔너리와 달리 키가 있으면 세로로 출력됨
- 만약 Series를 만들 때 인덱스를 따로 지정 안했다면 기본적으로 0부터 시작하는 정수값이 인덱싱 됨
Series 생성해보기
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
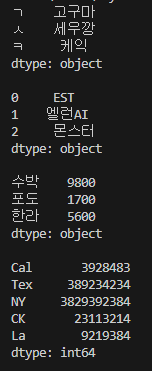
sr1 = pd.Series(['고구마', '세우깡', '케익'] , index = ['ㄱ', 'ㅅ', 'ㅋ'])
print(sr1)
print()
sr2 = pd.Series(['EST', '엘런AI', '몬스터'])
print(sr2)
print()
sr3 = pd.Series(['9800', '1700', '5600'] , index = ['수박', '포도', '한라'])
print(sr3)
print()
city = {'Cal': 3928483, 'Tex': 389234234, 'NY': 3829392384, 'CK': 23113214, 'La' : 9219384}
pop = pd.Series(city)
print(pop)
print()
생성된 Series를 이용하여 데이터 출력해보기
- index의 값과 values의 값을 따로 출력해보기
- Tex~ CK까지의 데이터만 출력해보기
- NY 데이터만 추력해보기
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
city = {'Cal': 3928483, 'Tex': 389234234, 'NY': 3829392384, 'CK': 23113214, 'La' : 9219384}
pop = pd.Series(city)
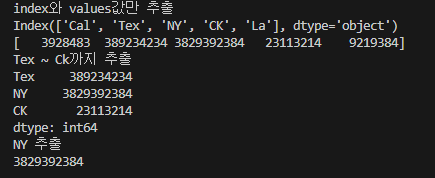
print('index와 values값만 추출')
print(pop.index)
print(pop.values)
print('Tex ~ Ck까지 추출')
print(pop.loc['Tex': 'CK'])
print('NY 추출 ')
print(city['NY'])
print()
DataFrame
- Pandas의 자료 형태중 하나로 2차원 형태의 자료구조
- Series의 조합
- 행과 열로 구성되어 있음
- 데이터를 테이블의 형태로 처리하는 자료구조
DataFrame 생성해보기
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
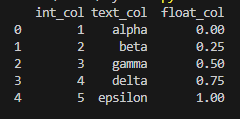
int_values = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
text_values = ['alpha', 'beta', 'gamma', 'delta', 'epsilon']
float_values = [0.0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0]
df = pd.DataFrame({
'int_col': int_values,
'text_col': text_values,
'float_col': float_values})
print(df)
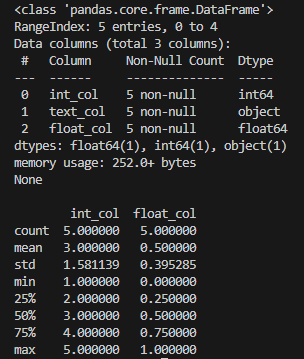
- DataFrame의 정보 및 table형태로 출력해보기
print(df.info())
print()
print(df.describe())
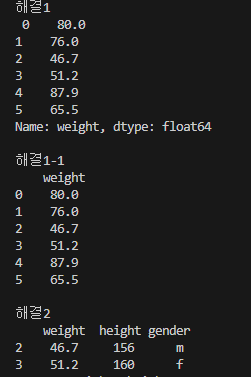
DataFrame에서 특정 행, 열의 데이터 값 출력해보기
- weight 열 데이터 추출
- index가 2, 3인 데이터 추출
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = [
[80.0, 170, 'm'],
[76.0, 180, 'f'],
[46.7, 156, 'm'],
[51.2, 160, 'f'],
[78.9, 190, 'm'],
[65.5, 164, 'm']
]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['weight', 'height', 'gender'])
print('해결1 \n',df['weight'])
print()
print('해결1-1 \n',df[['weight']])
print()
print('해결2 \n',df[2:4])
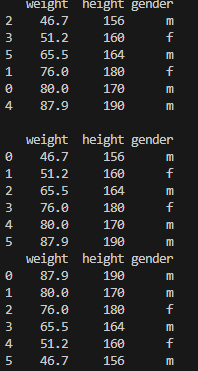
DataFrame 정렬
print(df.sort_values(by = 'weight'))
print()
print(df.sort_values(by = 'weight', ignore_index = True))
print(df.sort_values(by='weight', ascending = False ))
print(df.sort_values(by='weight', ascending = False, ignore_index= True ))
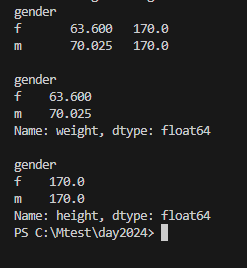
groupby
- 데이터를 그룹화 함
- 그룹화된 데이터에 대한 연산을 수행하는데 유용한 기능
avg_all= df.groupby('gender').mean()
avg_w = df.groupby('gender')['weight'].mean()
avg_h = df.groupby('gender')['height'].mean()
print(avg_all)
print()
print(avg_w)
print()
print(avg_h)
DataFrame에 새로운 데이터 추가하기
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = [
[40, 70, 80],
[55, 55, 95],
[66, 66, 100],
[77, 20, 77],
[34, 40, 90]
]
idx = ['고길동', '김희동', '김연아', '손흥민', '박찬호']
cul = ['kor', 'mat', 'eng']
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns= cul, index= idx)
tot = df['kor'] + df['eng'] +df['mat']
df.insert(loc = 3, column = 'tot', value = tot )
avg = round(tot / 3, 2)
df.insert(loc = 4, column = 'avg', value = avg )
pass_score = ['O' if score >= 60 else 'X' for score in df['avg']]
df.insert(loc=5, column='pass', value=pass_score)
print(df)
Pandas 실습
- spam_data.cvs파일 열기
- list comprehension 이용하여 spam 1 ham 0
- spam 1 ham 0 결과값을 이용하여 안심, 고려 나누기
- 한글 문자만 추출
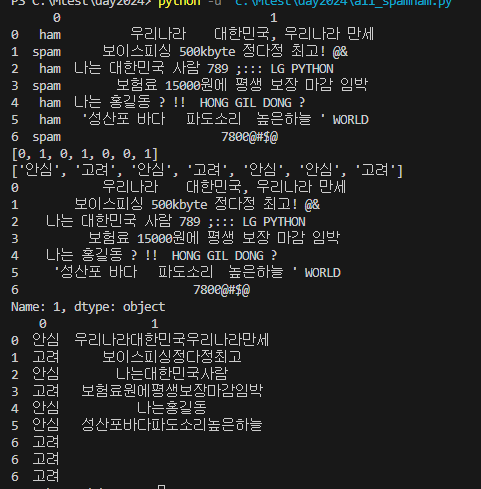
import pandas as pd
import re
nfile = './data/spam_data.csv'
spam_data = pd.read_csv(nfile, encoding= 'cp949', header= None)
print(spam_data)
spam = [1 if i == 'spam' else 0 for i in spam_data[0]]
print(spam)
re_spam = ['안심' if i == 0 else '고려' for i in spam]
print(re_spam)
text = spam_data[1]
print(text)
msg = spam_data[1].apply(lambda x: re.sub(r'[^가-힣]', '', str(x)))
df = pd.DataFrame({0:re_spam, 1:msg})
print(df)