개요
- 함수의 데코레이터
- numpy 실습
함수의 데코레이터
- Python에서 기존 함수를 바꾸지 않고 기능을 확장할 수 있게 해줌
@데코레이터이름을 함수 위에 붙여서 사용- 실행 시간 측정, 로그인 체크, 로깅, 권환 확인등에 활용 가능함
실습
class MyEST:
count = 3700
#정적메소드는 self파라메타를 사용안함, 클래스 자신접근 인자 기술시 에러
@staticmethod
def isSquare(w, h):
area = w * h
return area
@classmethod
def printCount(self):
print(f'갯수는 = {self.count}')
# 데코레이션 사용시
hap = MyEST.isSquare(5, 5)
print(f'hap는 = {hap}')
MyEST.printCount()@Staticmethod는 클래스 변수에 접근 하지 않는 독립적인 함수
데코레이터를 이용하여 시간 측정해보기
import time
def check_time(function):
def measure(*mlist, **mtuple):
start_time = time.time()
result = function(*mlist, **mtuple)
end_time = time.time()
print(f"시간측정: {function.__name__}함수에서 {round( end_time - start_time ,5)}")
return result
return measure
@check_time
def myTotal(n):
total = 0
for k in range(1, n+1):
total = total + k
return total
myTotal(1000000)
print()Numpy 실습
Numpy where
- np.where()을 이용하여 특정 조건을 만족하는 원소의 index를 찾을 수 있음
- 특정 조건 만족시 값을 대체하는 것도 가능
실습
import numpy as np
eng = np.array( [ 7, 5, 3 ,9, 1, 2, 4, 6 ] )
print(eng)
print()
# numpy에서의 where절 -> 타 언어의 삼항 연산과 비슷함 조건 ? 참: 거짓
print(np.where(eng > 5, 1, 0))
print()
# ret
ret = np.where(eng >= 5, 1, 0)
print(ret)
print()
data = np.arange(1,11)
print(np.where(data < 5 , data, 5*data))
- where() 중복 사용
eng = np.array( [ 7, 5, 3 ,9, 1, 2, 4, 6 ] )
grade = np.where(eng <= 4, np.where(eng <= 7, '중급', '상급'),'초급')
print(grade)np.save
- Numpy 라이브러리에서 배열 데이터를 파일로 저장 및 불러오기가 가능함
- 확장자를 따로 지정 안하면 .npy 확장자로 저장됨
실습
import numpy as np
import time
score = np.array(
[ [1,2,3] ,
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9],
[10,11,12]
] )
print(score)
np.save('./data/myarray', score)
print('./data/myarray.npy 저장성공')
print()
time.sleep(1)
print(np.load('./data/myarray.npy'))
print('./data/myarray.npy 열기성공')linspace
- 시작값과 끝값 사이를 균등한 간격으로 나눈 숫자 배령을 생성하는 함수
- 간격의 크기를 결정할 수 있음 (arange()는 지정한 간격 만큼 값을 생성함)
- np.linspace(start, stop, num)의 구조로 num의 기본값은 50
실습
import numpy as np
import time
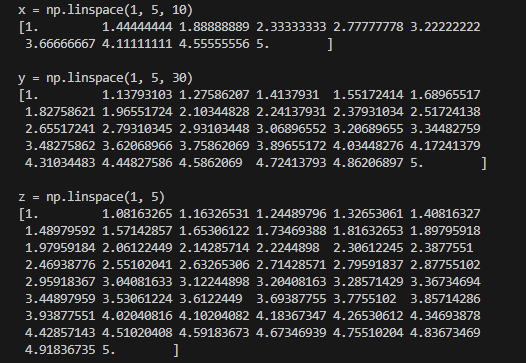
print('x = np.linspace(1, 5, 10)')
x = np.linspace(1, 5, 10)
print(x)
print()
print('y = np.linspace(1, 5, 30)')
y = np.linspace(1, 5, 30)
print(y)
print()
time.sleep(1)
print('z = np.linspace(1, 5)')
z = np.linspace(1, 5)
print(z)
print()실행결과
Unique(), trim()
- Unique()
- Numpy에서 배열의 중복을 제거할 때 사용함
- trim()
- Numpy에서 배열의 앞, 뒷부분에 해당하는 0을 제거하는데 사용함
- 'f'면 앞, 'b'면 뒷부분, 'fb'or 'bf'는 앞뒤 전부 0을 제거함
실습
import numpy as np
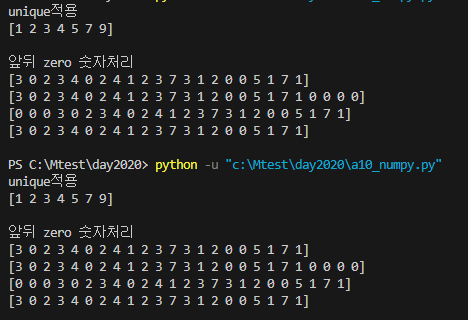
print('unique적용')
a = np.array( [9,5,4,3,1,2,3,4,3,2,4,1,2,3,7,3,1,2,1,2,5,1,7,1,2,2,1,3] )
ret = np.unique(a) #[1 2 3 4 5 7 9]
print(ret)
print()
print('앞뒤 zero 숫자처리')
b = np.array( [0,0,0,3,0,2,3,4,0,2,4,1,2,3,7,3,1,2,0,0,5,1,7,1,0,0,0,0] )
print(np.trim_zeros(b))
print(np.trim_zeros(b, trim = 'f'))
print(np.trim_zeros(b,trim= 'b'))
print(np.trim_zeros(b,trim= 'bf'))
print()transpose()
- 행과 열을 바꾸는데 사용
vstack은 수직(행 기준)으로 배열 연결- 열(컬럼) 수가 같아야 함
hstack은 수평(열 기준)으로 배열 연결- 행(로우)수가 같아야함
실습
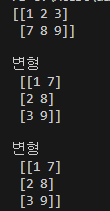
c = np.array(([1,2,3], [7,8,9]))
print(c)
print()
print('변형\n', np.transpose(c))
print()
# c.T로도 변형 가능함
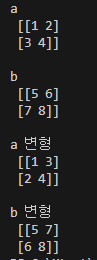
print('변형\n', c.T)a = np.array( [ [1,2], [3,4] ] )
b = np.array( [ [5,6], [7,8] ] )
print('a\n', a)
print()
print('b\n', b)
print()
print('a 변형\n',np.transpose(a))
print()
print('b 변형\n',b.T)dot()
- 행렬곱 함수
- 기본적으로 2개의 input만 받음
- A*B를 계산하다고 했을때 A의 열의 갯수와 B의 행의 갯수가 같아야함
[a_00, a_01] [b_00, b_01] [a_10, a_11] X [b_10, b_11] 계산 과정 [a_00 * b_00 + a_01*b_10][a_00 * b_01 + a_01*b_11] [a_10 * b_00 + a_11*b_10][a_10 * b_01 + a_11*b_11]
실습
import numpy as np
kor = np.array([[3,2], [5,4]]) # 2*2행렬
ret = np.dot(kor,kor)
print(ret)