💡 class, object 그리고 그 둘의 차이점 / 객체지향언어에 대해 공부해보자!
⭐️ intro
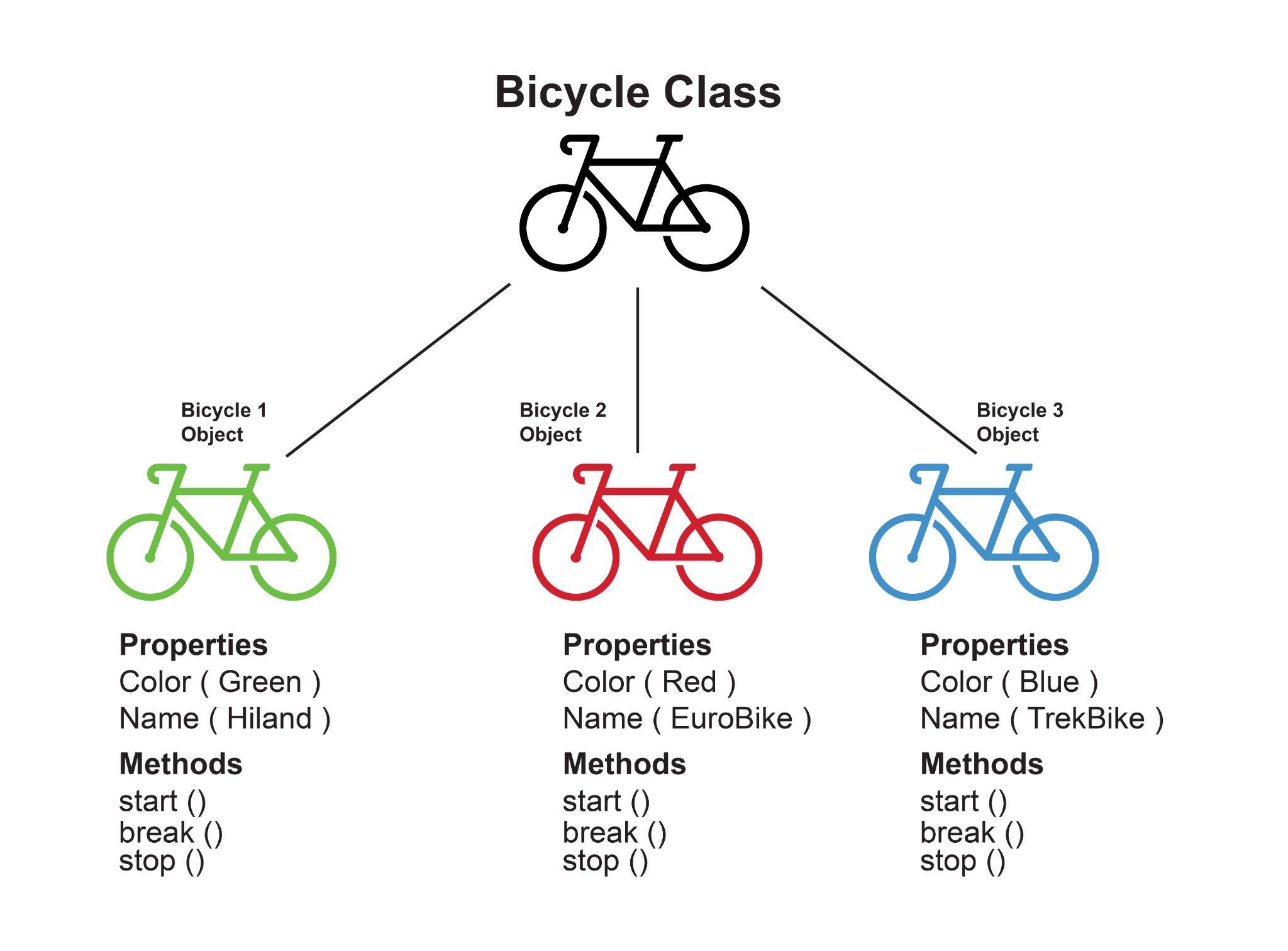
- Class : 조금 더 연관 있는 데이터를 한데 묶어 놓는 컨테이너같은 아이

- class는 fields와 methods의 집합

- 간혹 class에는 method는 들어있지 않고, fields만 들어있는 경우도 있음 ->
데이터 클래스라고 부름 - 이렇게 관련이 있는 변수나 함수들을 묶어 놓은 것을 클래스라고 하고,
클래스 안에서도 내부적으로 보여지는 변수와 밖에서 보일 수 있는 변수들을 나누어서 캡슐화(encapsulation)라고도 함 - 클래스를 이용해서 상속과 다양성이 일어날 수 있는데
이런 모든 것들이 가능한 것이 바로 객체지향 언어 - 프로그래밍을 할 때도 사물과 물체들을 클래스와 오브젝트로 정해서 프로그래밍 하는 것이 조금 더 자연스럽기 때문에 개발자들이 편하고 유연하게 프로그래밍을 할 수 있게 도와주는 것
🙄 강의가 끝난 후
내가 사물과 물체들을 어떻게 클래스로 만들 수있을지 생각해보는 시간을 가져보자!
쇼핑몰을 만들 때, 수강 신청 프로그램을 만들 때 어떻게 클래스로 잘 정리할 수 있을지 한번 생각해보자!
🔴 Class & Object
🟤 Class
- class는 붕어빵을 만들 수 있는 틀이라고 생각하자!
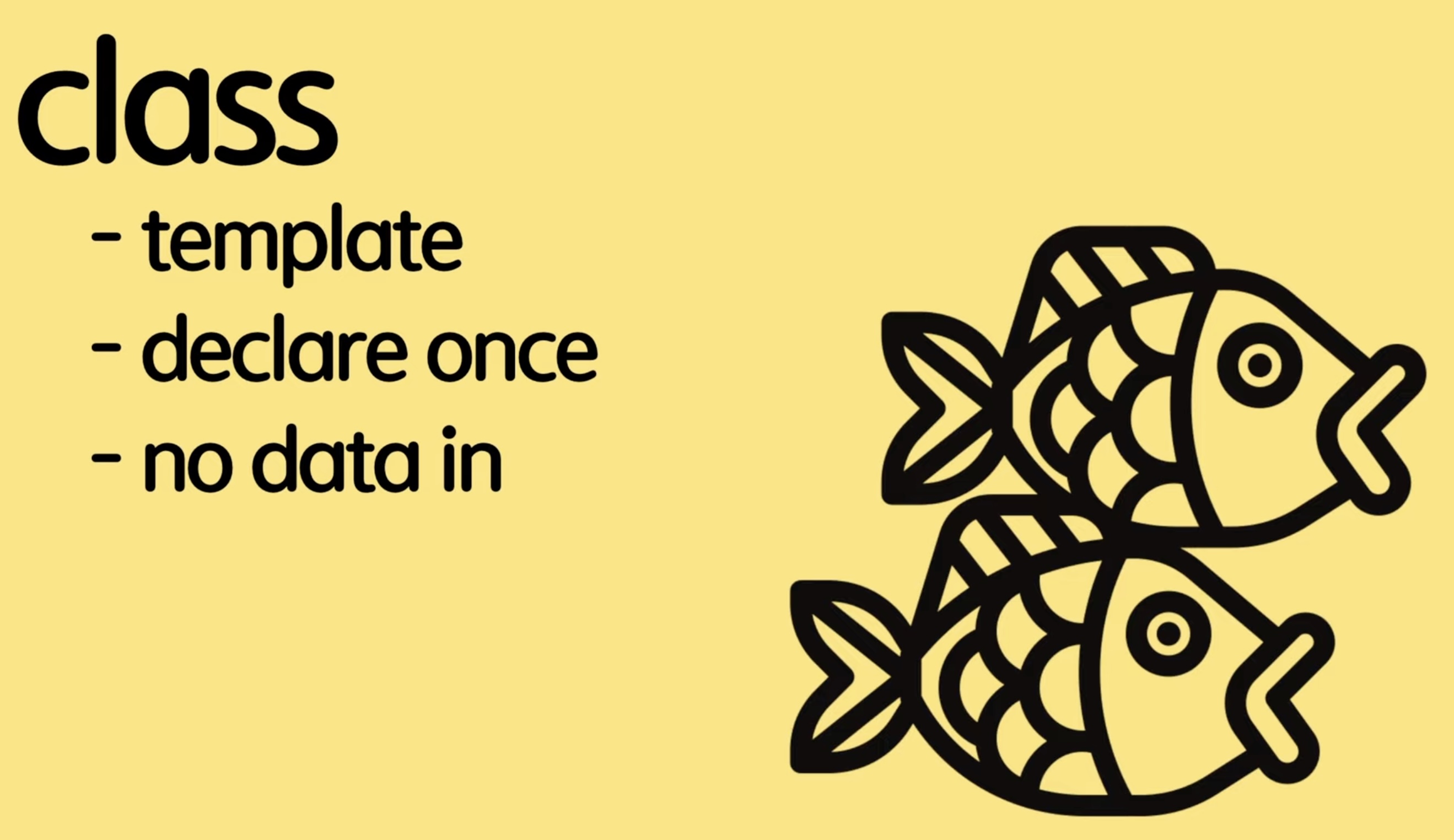
- 청사진이라고도 불리고, template이라고도 불린다.
- class 자체에는 데이터가 들어있지 않고, 틀만 즉, template만 정해 놓는 것이다.
- 이런 클래스에는 요런 요런 데이터가 들어올 수 있어~~ 라고만 정의를 해놓고, 한번만 선언한다.
🟤 Object
- 이 클래스를 이용해서 실제로 데이터를 넣어서 만드는 것이 바로 오브젝트

- 클래스를 이용해서 새로운 인스턴스를 생성하면 오브젝트가 되는 것
- 클래스를 이용해 오브젝트를 굉장히 많이 생성할 수 있다.
- 클래스는 정의만 한 것이라서 실제로 메모리에 올라가지는 않지만 이렇게 실제로 데이터를 넣으면 이제 오브젝트는 메모리에도 올라가게 된다.
- 붕어빵이라는 class를 이용해서 팥 데이터를 넣으면 팥붕어빵이되고, 슈크림 데이터를 넣으면 슈크림붕어빵이 되고, 이렇게 만들어진 붕어빵 자체는 object이고, 붕어빵을 만들기 위해 우리가 정의한 붕어빵의 틀은 class가 되는 것이다.
🟠 객체 지향 언어

- 캡슐화, 상속, 다양성, 추상화
🟡 Class

- class : templete
- object : 실제로 데이터를 넣어서 만드는 것
- ES6부터 추가되어짐
클래스가 도입되기 전에는 클래스를 정의하지 않고 바로 오브젝트를 생성할 수 있었음 (오브젝트를 만들 때 function을 이용해서 템플릿을 만드는 방법이 존재했음) - class가 완전히 새롭게 완벽하게 추가된 것이 아니라 기존에 존재하던 프로토타입을 베이스로 한 것을 기반으로 우리가 간편하게 쓸 수 있도록 문법만 class가 추가된 것 ->
syntactical sugar(가짜의 편리함) 라고 부름
🟢 Class declarations
class Person {
// constructor
constructor(name, age) {
// field
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// methods
speak() {
console.log(`${this.name}: hello!`);
}
}
class라는 키워드를 이용해서 클래스를 생성constructor생성자를 이용해서 나중에 object를 생성할 때 필요한 데이터를 전달한다.- 전달 받은 데이터를 클래스에 존재하는 2가지
fields인 name과 age에 우리가 전달받은 데이터를 바로 할당해준다. - class에는 이름과 나이라는
fields가 있고,speak()라는 말하는 메소드도 존재한다.
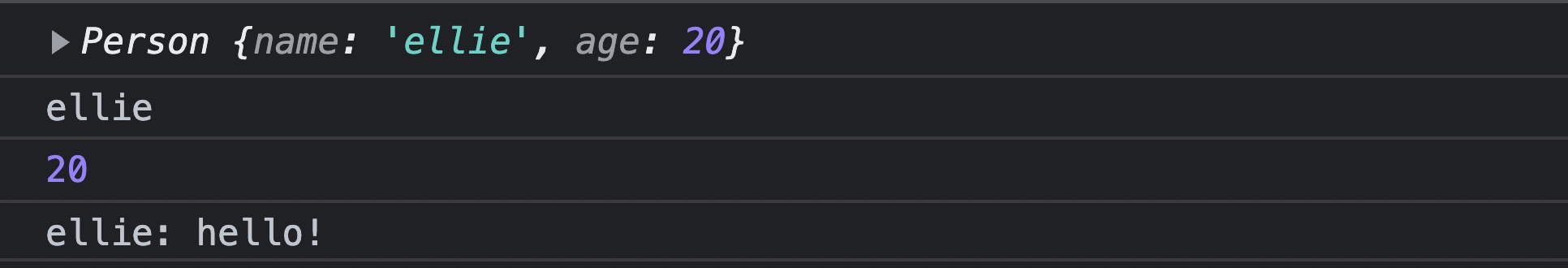
// 오브젝트 생성하기
const ellie = new Person('ellie', 20);
console.log(ellie);
console.log(ellie.name);
console.log(ellie.age);
ellie.speak();- 새로운 오브젝트를 만들 때는
new라는 키워드를 쓴다.
🔵 Getter and Setters
🟤 User 클래스 생성
class User {
constructor(firstName, lastName, age) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.age = age;
}
}🟤 user1 오브젝트 생성
- user1를 생성하는 중에 사용자가 나이를 실수로
-1이라고 설정함
// 실수로 나이를 -1로 지정함
const user1 = new User('Steve', 'Job', -1);
console.log(user1);- 당연히 출력값을 확인해 보면 나이에
-1이라고 설정되어 있음

- 객체 지향적인 개념으로 봤을 때 말이 안되는 상황
- 사람의 나이는 절대로
-1이 될 수 없음 - 클래스를 사용하는 사용자, 혹은 내가 작성한 클래스를 누군가가 잘못 사용해도 우리가 조금 더 방어적인 자세로 만들 수 있도록 해주는 것이 바로
Getter and Setters이다.
class User {
constructor(firstName, lastName, age) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.age = age;
}
get age() {
return this.age;
}
set age(value) {
this.age = value;
}
}
- 유져의 나이가 절대로 -1이 될 수 없기 때문에
get이라는 키워드를 이용해 값을 리턴하고,set이라는 키워드를 이용해서 값을 설정할 수가 있다.- 대신
set은 값을 설정하기 때문에value를 받아와야만 한다. - 사용자가
get age()를 호출하게 되면 우리는this.age를 리턴해야하고,
새로운 value를 받으면 우리가this.age를 새로운 value로 설정하게 된다.
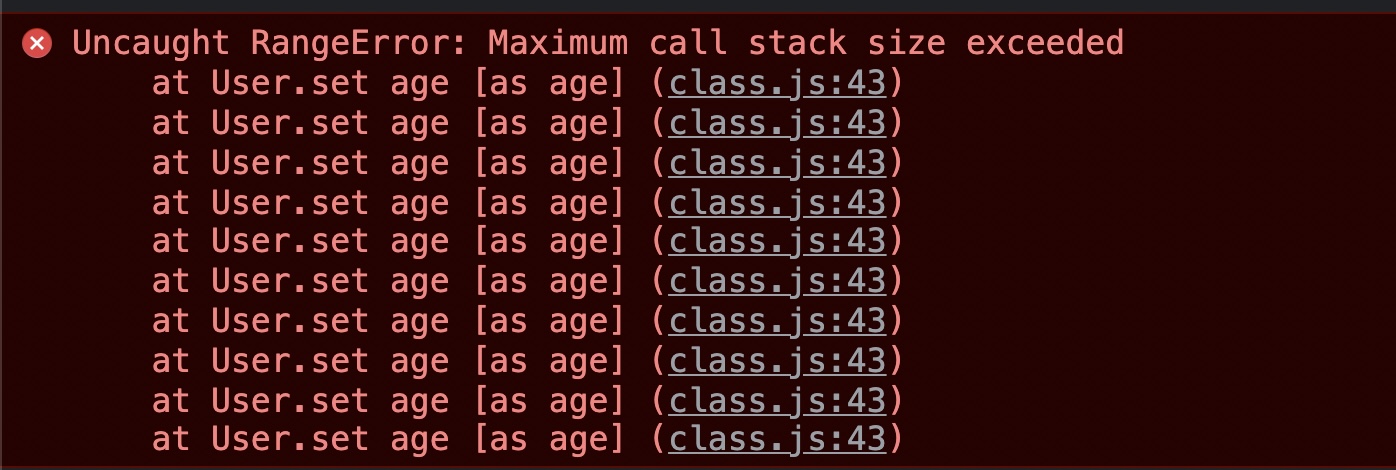
call stack이 초과되었다는 에러 메세지가 뜬다.
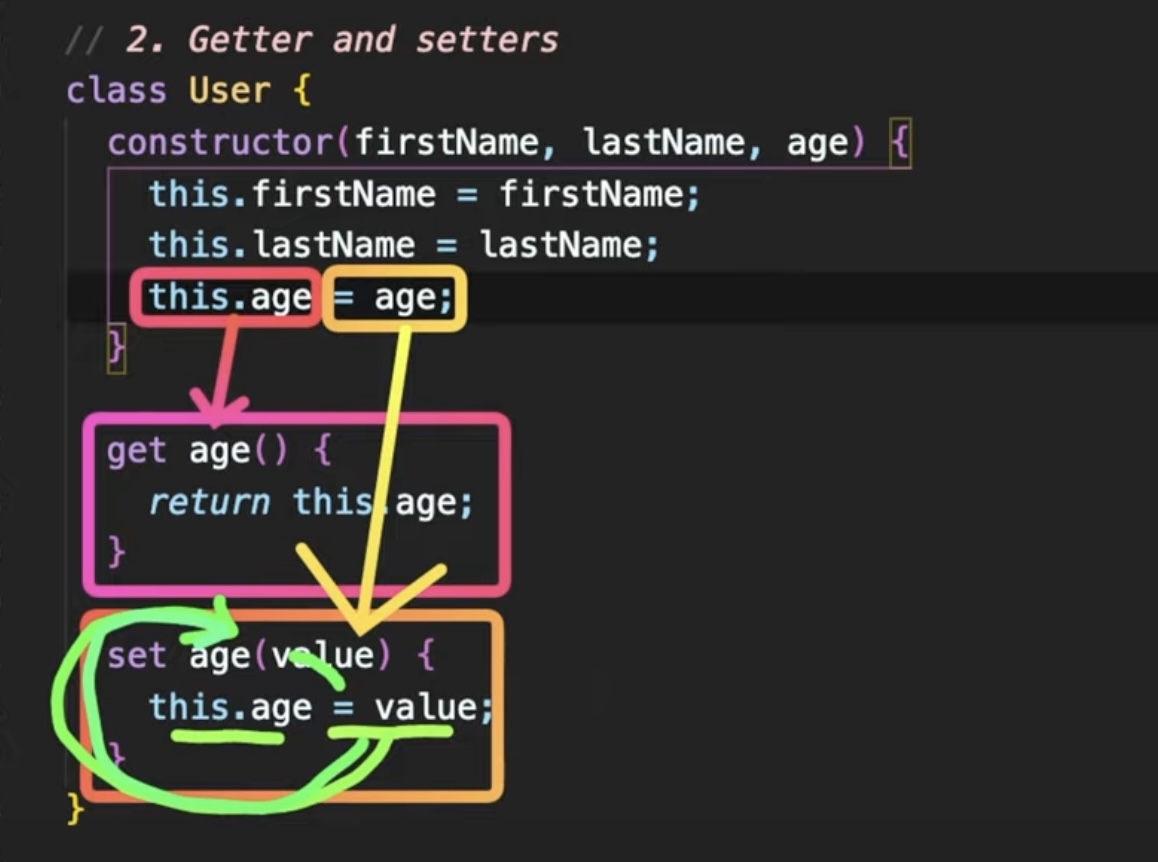
age라는 getter를 정의하는 순간this.age는 메모리에 올라가 있는 데이터를 읽어오는 것이 아니라, 바로 getter를 호출하게 된다.- setter를 정의하는 순간
= age를 호출 할 때, 즉 값을 할당 할 때, 바로 메모리의 값을 할당하는 것이 아니라set age라는 setter를 호출하게 된다. - setter 안에서 우리가 전달된 value를
this.age에 할당 할 때 메모리의 값을 업데이트하는 것이 아니라 이 setter를 호출하게 되는 것 -> 즉= value는 계속해서 setter를 호출하는 무한정 반복이 생기는 것 - 해결하기 위해서는?
getter와 setter에 쓰여지는 변수의 이름을 조금 다르게 만들어주면 된다. (_언더바 많이 사용)
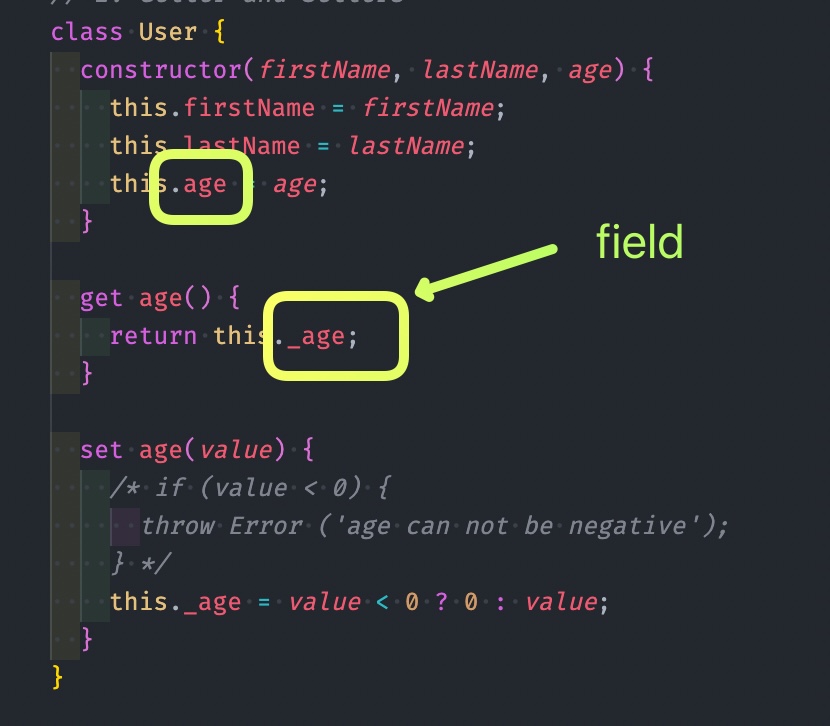
class User {
constructor(firstName, lastName, age) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.age = age;
}
get age() {
return this._age;
}
set age(value) {
this._age = value;
}
}- User class 안에는 총 3개의 필드가 존재 (firstName, lastName, _age)
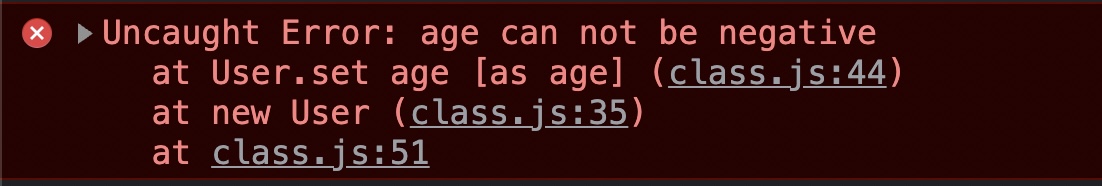
- setter를 통해 경고를 보낼 수 있다.
- 방법1 - 경고메세지 출력
set age(value) {
if (value < 0) {
throw Error ('age can not be negative');
}
this._age = value;
}
- 방법2 - 음수면 0이 나오게 해준다.
set age(value) {
this._age = value < 0 ? 0 : value;
}
- field는
_age이지만 우리가.age라고 호출할 수 있는 것,.age에 값을 할당할 수 있는 것은 바로 내부적으로 getter와 setter를 이용하기 때문이다.
🟣 Fields (public, private)
- 엄청 최근에 추가되어진 것! (쓰려면 BABEL을 사용해야 할 수 도)
class Experiment {
publicField = 2;
#privateField = 0;
}
const experiment = new Experiment();
console.log(experiment.publicField); // 2
console.log(experiment.privateField); // undefined- 생성자(constructor)를 쓰지않고 필드를 정의할 수 있음
- 그냥 정의하면 외부에서 접근이 가능
#해쉬 기호를 붙이게 되면Private Field-> 클래스 내부에서만 값이 보여지고, 접근되고, 값이 변경이 가능하지만 외부에서는 이 값을 읽을 수도 변경할 수도 없음
⚪️ Static properties and methods
- 엄청 최근에 추가되어진 것! (쓰려면 BABEL을 사용해야 할 수 도)
class Article {
static publisher = 'Dream Coding';
constructor(articleNumber) {
this.articleNumber = articleNumber;
}
static printPublisher() {
console.log(Article.publisher);
}
}- 오브젝트에 상관없이
데이터의 상관없이
가지고 있는 고유한 값과 이런 데이터의 상관없이 동일하게 반복적으로 사용되어지는 method가 존재할 수 있다. - 이런 method들을
static이라는 키워드를 사용하면 오브젝트에 상관없이 클래스 자체에 연결되어 있다.
const article1 = new Article(1);
const article2 = new Article(2);
console.log(article1.publisher); // undefined
console.log(Article.publisher); // Dream Coding
Article.printPublisher(); // Dream Codingarticle1과article2라는 object를 만들게 되면
static키워드 사용하지 않았더라면console.log(article1.publisher);출력 가능했을 것 -> 그러나static때문에undefined출력static은 object 마다 할당되어지는 것이 아니라 클래스 자체 즉Article이라는 클래스 자체에 붙어있기 때문이다.static함수를 호출 할 때도 클래스 이름을 이용해서 호출한다.
🟤 어디에 쓸까?
- 오브젝트 상관없이, 들어오는 데이터에 상관없이 공통적으로 class에서 쓸 수 있는 거라면
static과static method를 이용해서 작성하는 것이 메모리의 사용을 조금 더 줄여줄 수 있다.
⚫️ 상속 & 다양성
- 네모, 세모, 동그라미 등을 정의한다.
-> 높이, 너비, 색상 등의 속성으로 나타낼 수 있다./색칠할 수 있다, 넓이를 구할 수 있다 등의 메소드들도 있을 수 있다
-> 반복되어지는 것들이 보여짐 (동그라미에도 높이, 너비 ... 네모에도 높이, 너비 .... 등)
-> 반복되어지는 것들을 각각 따로 만들어서 동일한 것을 반복하는 것보단
-> 도형이라는 공통점으로 한번에 정의한 다음에
-> shape에 공통적으로 쓰이는 속성 값을 계속 재사용하면 더 간편함
-> 재사용이 편하고 이 때문에 유지보수도 쉽다(문제가 생기면 공통적인 shape 한곳만 수정해주면 되기 때문에)
🟤 Inheritance
Shape이라는 class가 존재
class Shape {
constructor(width, height, color) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
this.color = color;
}
draw() {
console.log(`drawing ${this.color} color of`);
}
getArea() {
return width * this.height;
}
}- 만약
Rectangle이라는 클래스를 만들고 싶다면 동일한 부분을 계속 작성하기 보다는
extends라는 클래스를 이용해서Shape을 바로 연장한다.
class Rectangle extends Shape {}
class Triangle extends Shape {}- 이렇게만 작성해도
Shape에서 정의한 fields와 methods가 자동적으로 포함이된다.
const rectangle = new Rectangle(20, 20, 'blue');
console.log(rectangle);
rectangle.draw();
const triangle = new Triangle(20, 20, 'yellow');
console.log(triangle);
triangle.draw();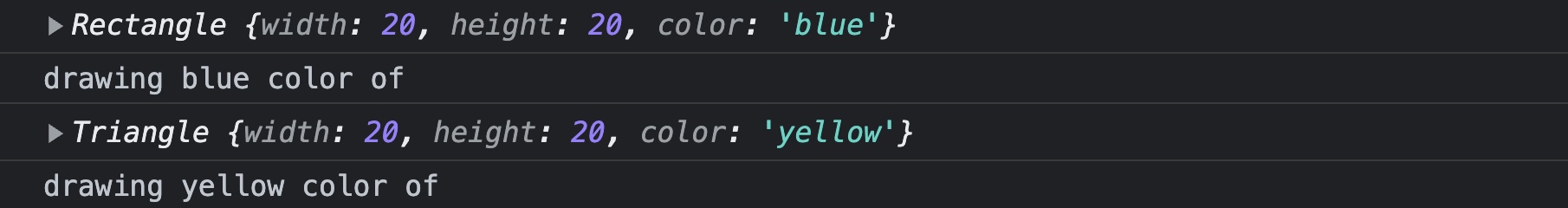
🟤 다양성
console.log(rectangle.getArea()); // 400
console.log(triangle.getArea()); // 400- 삼각형은 1/2를 해줘야한다!
- 어떻게 해결할까?
- 우리가 필요한 함수만 재정의해서 사용할 수 있다. ->
overriding오버라이딩이라고 한다.
class Triangle extends Shape {
getArea() {
return this.width * this.height / 2;
}
}
console.log(triangle.getArea()); // 200- 필요한 함수들만 오버라이딩해서 작성 가능하다.
class Triangle extends Shape {
draw() {
console.log('🔺');
}
getArea() {
return this.width * this.height / 2;
}
}- 삼각형의
draw메소드를 오버라이딩 해서 다른 문구가 출력되게 할 수도 있다.
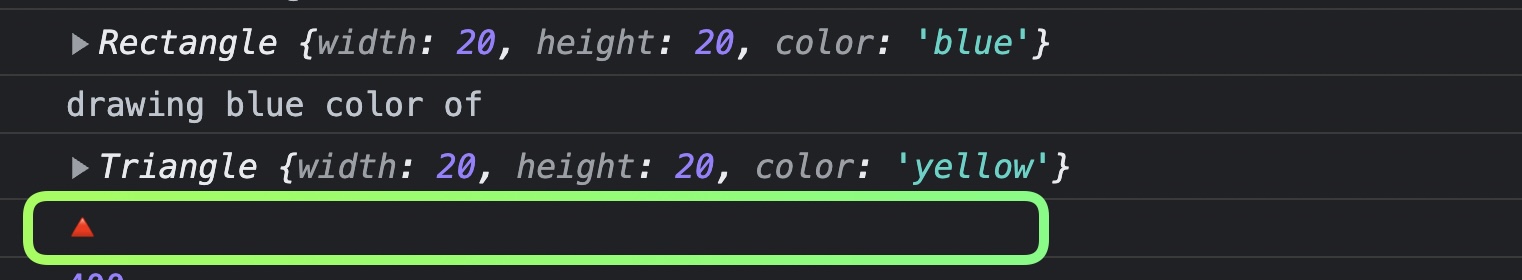
draw메소드를 오버라이딩 하니까,Shape에 정의 된draw함수가 호출되지 않음
-> 해결하기 위해서super부모의draw라는 함수를 호출하면된다.
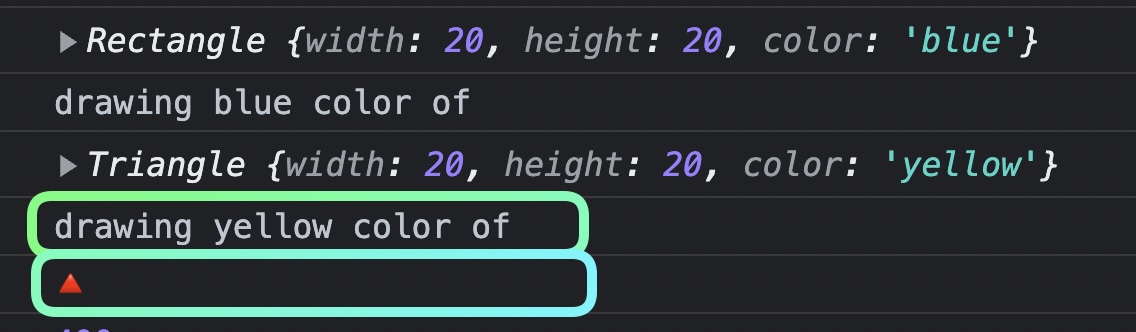
class Triangle extends Shape {
draw() {
super.draw();
console.log('🔺');
}
getArea() {
return this.width * this.height / 2;
}
}
⚫️ instanceOf
instanceOfoperator : class checking- true 와 false를 리턴한다.
- 이 오브젝트는 클래스를 이용해서 만들어진 새로운 인스턴스이다.
console.log(rectangle instanceof Rectangle); // T
console.log(triangle instanceof Rectangle); // F
console.log(triangle instanceof Triangle); // T
console.log(triangle instanceof Shape); // T
console.log(triangle instanceof Object); // T- 왼쪽에 있는 오브젝트가 오른쪽에 있는 클래스의 인스턴스 인지? 아닌지? -> 이 오브젝트가 이 클래스를 이용해서 만들어진 아이인지 아닌지를 확인하는 것이다.
triangle는Object의 인스턴스 인가? true- 우리가 자바스크립트에서 만드는 모든 오브젝트 클래스들은 자바스크립트에 있는
Object를 상속한 것
🟤 자바스크립트 Object
- 이미 지정된 것들이 있음
- 어떤 오브젝트든지 간에 공통적으로 존재하는 method를 사용할 수 있음
console.log(triangle.toString()); // [object Object]Triangle에서 오브젝트 안에 공통적으로 있는 함수를 오버라이딩도 할 수 있음
class Triangle extends Shape {
draw() {
super.draw();
console.log('🔺');
}
getArea() {
return this.width * this.height / 2;
}
toString() {
return `Triangle: color: ${this.color}`
}
}- 의미 없는 내용을 의미있게 바꿔서 출력할 수 있다.
[object Object]->Triangle: color: ${this.color}

✏️ 자바스크립트 mdn reference
: 자바 스크립트의 내부에 포함되어 있는 object들에는 어떤 것들이 있는지 카테고리로 묶여져 있다!
- Value properties
- Error Objects
- Indexed Collections : 다양한 array를 볼 수 있다.
- Keyed collections : key와 value를 관리할 수 있는 키 컬렉션 파트
- 백엔드에서 데이터를 비동기적으로 받아올 수 있는
promise-> Control abstraction - JSON도 자바스크립트 내부에 포함되어져 있는 오브젝트이다.
➕ 추가적으로 공부하기
1.syntactical sugar찾아보기
2. 프로토타입 베이스에 링크된 글 읽고, 추가 궁금한 것 찾아보기!
3. 오버라이딩 찾아보기
4. 자바스크립트 mdn reference 페이지 공부하기
5. 이 사이트 참고해서 읽어보기
