💡 유용한 배열 APIs, 배열 함수를 예제로 공부해보자

⭐️ Array APIs
- 배열 API들을 응용해서 Quiz를 함께 풀어보자!
🔴 join
Q1. make a string out of an array
{
const fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'];
const result1 = fruits.join('/');
const result2 = fruits.join();
}
- 구분자를 넣어서 string으로 만들어주는 api
- 구분자를 정해주면 해당 구분자로 구분해서 출력, 아무것도 안적으면 ,가 구분자가 된다
🟠 split
Q2. make an array out of a string
{
const fruits = '🍎, 🥝, 🍌, 🍒';
const result = fruits.split(',');
console.log(result);
}
- 스트링의 API -> split
fruit는 string 이다.- 구분자(필수)와 limit(선택)을 전달받는다.
{
const fruits = '🍎, 🥝, 🍌, 🍒';
const result = fruits.split(',', 2); // limit:2
console.log(result);
}
🟡 reverse
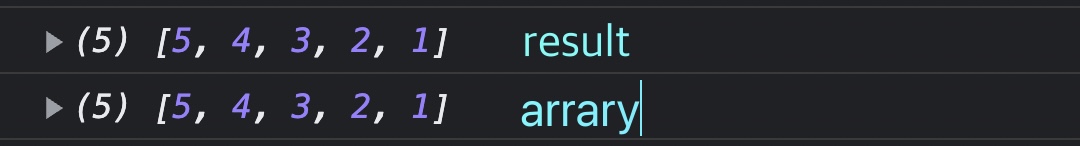
Q3. make this array look like this: [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
{
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const result = array.reverse();
console.log(result);
console.log(array);
// 함수를 호출한 arrary 배열 자체도 reverse 된다.
}reverse는 배열 자체를 변화시키고, 리턴값 또한 변화된 배열 자체를 return 한다.
🟢 slice
Q4. make new array without the first two elements
- 처음 2개를 없앤 새로운 배열을 만들어야한다.
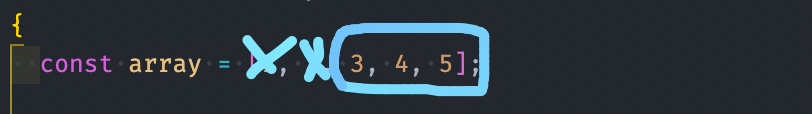
splice사용 했을 때,[3, 4, 5]가 나오는 배열을 원했지만 짤려나간 부분이 리턴되었다.
{
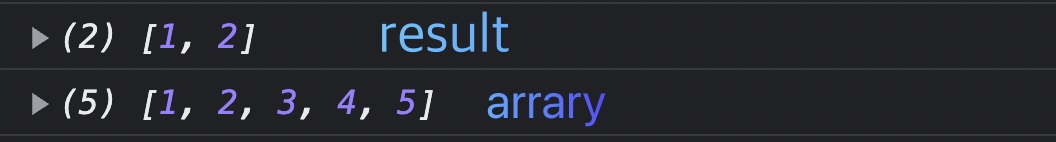
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const result = array.splice(0, 2);
console.log(result);
console.log(array);
}
- 그래서 slice를 써야한다.
{
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const result = array.slice(2, 5);
console.log(result);
console.log(array);
}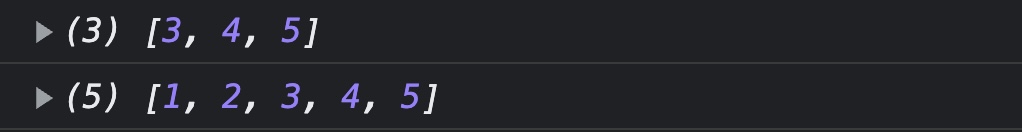
slice는 (시작인덱스, 끝인덱스) 이렇게 작성하는데 끝 인덱스를 제외하고! 이다. 만약 끝 인덱스에 4를 적었음 인덱스 4번은 제외하고[3, 4]만 출력된다.

splice는 배열 자체를 수정하는 api, slice는 배열에서 원하는 부분만 리턴해서 받아오고 싶을 때 쓰면됨
📌 이 밑은 class Student 참고해서 문제 풀기
class Student {
constructor(name, age, enrolled, score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.enrolled = enrolled;
this.score = score;
}
}
const students = [
new Student('A', 29, true, 45),
new Student('B', 28, false, 80),
new Student('C', 30, true, 90),
new Student('D', 40, false, 66),
new Student('E', 18, true, 88),
];🔵 find
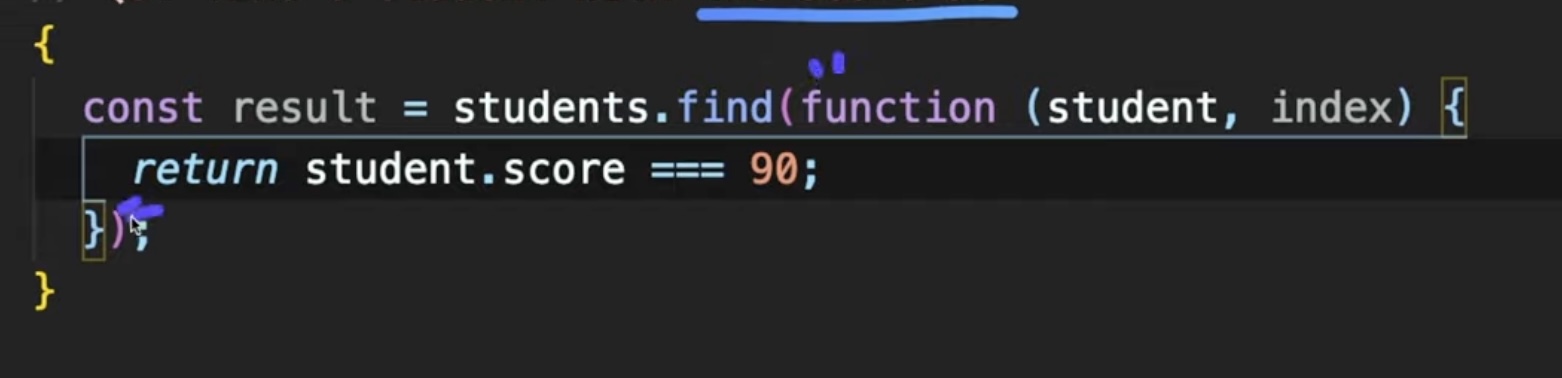
Q5. find a student with the score 90
{
const result = students.find((student) => student.score === 90);
console.log(result);
}students배열의findapi사용하면 풀 수 있음- 첫번째로 true가 리턴되면 콜백함수를 멈춘고, 배열의 요소를 리턴해준다.

🟣 filter
Q6. make an array of enrolled students
{
const result = students.filter((student) => student.enrolled);
console.log(result);
}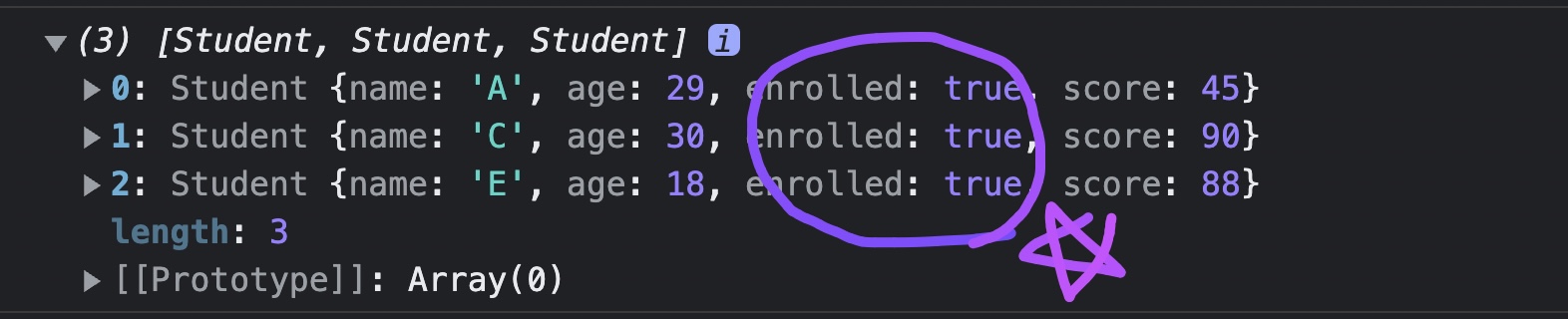
- true인 학생들만 리턴된 것을 확인해 볼 수 있다.
⚪️ map
Q7. make an array containing only the students' scores
result should be: [45, 80, 90, 66, 88]
- 배열에서 점수만 뽑아와서 점수만 들어있는 배열 만들기
{
const result = students.map((student) => student.score);
console.log(result);
}- map : 배열 안에 들어있는 요소 한가지 한가지를 다른 것으로 변환해주는 것!
-> 우리가 지정한 콜백 함수가 어떤 일을 하냐에 따라서 다른 값으로 매핑되어서 만들어진다.
- 학생들이 가지고 있는 점수만 리턴해서 점수만 들어있는 배열을 만든다.

map은 배열 안에 들어있는 모든 요소들을 우리가 전달해 주는 콜백 함수를 호출하면서 콜백 함수에서 리턴되어진 값들로 대체하는 것이다.- 배열 안에 있는 요소들을 우리가 원하는 함수를 이용해서 다른 방식의 데이터를 만들고 싶을 때는 맵을 이용하면 되는 것이다.
- 콜백 함수 인자는 최대한 이해하기 쉽게 쓴다.
⚫️ some, every
Q8. check if there is a student with the score lower than 50
- 학생 점수가 50점 보다 낮은 학생이 있는지 없는지 확인하시오
{
const result = students.some((student) => student.score < 50);
console.log(result); // true
// every를 이용한 위에와 똑같은 문장
const result2 = !students.every((student) => student.score >= 50);
console.log(result2); // true
}some: 배열의 요소 중에서 이 콜백 함수가 리턴이 true가 되는 요소가 있는지 없는지를 확인해준다.
배열의 요소 중 1명이라도 50점 보다 낮은 점수가 있으면 true를 리턴한다.every: 배열에 들어있는 모든 요소들이 이 콜백함수의 조건을 충족해야지만 true가 리턴이 된다.- 배열 중에 어떤 것 1개라도 만족되는 것이 있는지 없는지 검사할 때는
some을 사용하고, 모든 배열의 조건이 만족해야하면every를 사용하자
🟤 reduce
Q9. compute students' average score
- 학생들의 평균점수 구하기
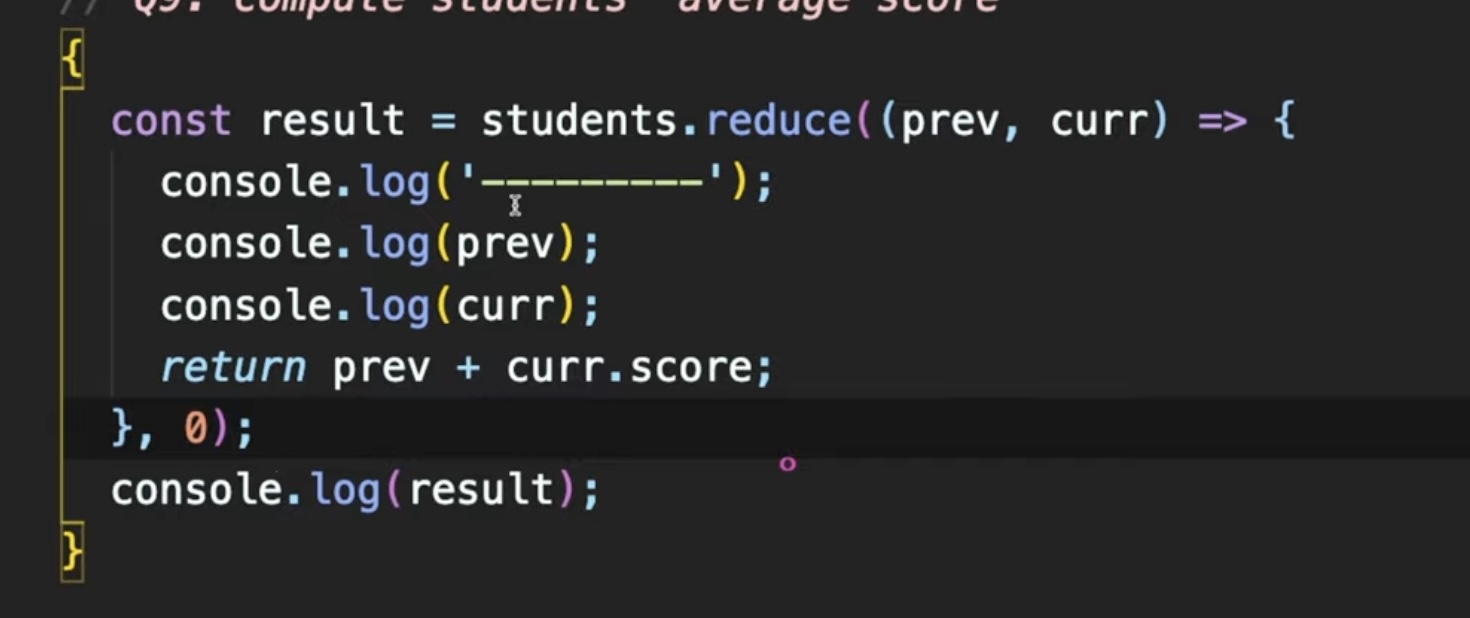
{
const result = students.reduce((prev, curr) => prev + curr.score, 0);
// 평균값은 학생수로 나눠줘야함
console.log(result / students.length); // 73.8
}reduce: 배열에 있는 모든 요소들의 값을 무언가 누적하는, 함께모아둘 때 사용하는 것 -> 우리가 원하는 시작 점부터 모든 배열을 돌면서 어떤 값을 누적할 때 쓰는 것- 0 -> initial value
reduceRight: 순서가 거꾸로 도는 것prev는 이전의 콜백함수에서 리턴된 값이 전달 되어서 오고,curr은 배열의 아이템을 순차적으로 전달 받는다.
🟤 함수형 프로그래밍
Q10. make a string containing all the scores
result should be: '45, 80, 90, 66, 88'
{
const result = students
// 학생들의 배열을 점수로 변환
.map((student) => student.score)
// 50점 이상만
.filter((score) => score >= 50)
// join으로 string으로
.join();
console.log(result);
}
➕ Bonus : sort
Q11. sorted in ascending order
result should be: '45, 66, 80, 88, 90'
{
const result = students
.map((student) => student.score)
// a - b는 - value라서 내림차순으로 정렬된다.
// b - a는 + 라서 오름차순으로 정렬된다.
.sort((a, b) => b - a)
.join();
console.log(result);
}
