✨개요및 소개
🔥개요
리그오브레전드같은 탑다운게임에서는 플레이어가 마우스를 클릭한 곳으로 캐릭터가 이동합니다.
본 포스팅에서는 2차원배열내에서 출발점에서 도착점까지 최단경로로 이동하는 A*알고리즘을 구현하겠습니다.
이 글은 어디까지나 저의 개인적인 노트, 정리같은것이기 때문에 이론들을 깊게 설명하는것은 하지 않겠습니다.
🔥개발환경
2021-08-08기준 Windows10 Home 사용했으며, 컴파일러는 GCC를 사용했습니다.
c++버전은 17사용했습니다.
🔥참고
GeeksforGeeks
일반적으로 소스코드를 복붙하는것보다는 소스코드에대한 전반적인 이해를 하시는것을 추천드립니다.
✨A*알고리즘
🔥정의
A*알고리즘은 어떠한 2차원배열에서 출발점과 도착점이 주어졌을때, 최단경로를 탐색하는 알고리즘입니다.
🔥소스코드
" MAP1.txt "
4 8 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 1 0 3
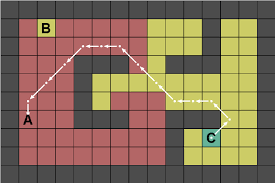
" MAP2.txt " ( 위에 썸네일의 맵과 동일합니다. )
10 15 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 3 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
C++17
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
constexpr int MAX = 101;
constexpr double INF = 1e9+7;
// 직선
const int dx1[4] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
const int dy1[4] = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
// 대각선
const int dx2[4] = { 1, -1, -1, 1 };
const int dy2[4] = { -1, 1, -1, 1 };
using Pair = std::pair<int, int>;
using pPair = std::pair<double, Pair>;
struct Cell {
int parent_x, parent_y;
double f, g, h;
};
char zmap[MAX][MAX];
int ROW = 0, COL = 0;
bool isDestination(int row, int col, Pair dst) {
if (row == dst.first && col == dst.second) return true;
return false;
}
bool isInRange(int row, int col) {
return (row >= 0 && row < ROW && col >= 0 && col < COL);
}
bool isUnBlocked(std::vector<std::vector<int>>& map, int row, int col) {
return (map[row][col] == 0);
}
double GethValue(int row, int col, Pair dst) {
return (double)std::sqrt(std::pow(row - dst.first, 2) + std::pow(col - dst.second, 2));
}
void tracePath(Cell cellDetails[MAX][MAX], Pair dst) {
std::stack<Pair> s;
int y = dst.first;
int x = dst.second;
s.push({ y, x });
// cellDetails의 x, y의 부모좌표가 모두 현재좌표와 동일할때까지 반복
while (!(cellDetails[y][x].parent_x == x && cellDetails[y][x].parent_y == y)) {
int tempy = cellDetails[y][x].parent_y;
int tempx = cellDetails[y][x].parent_x;
y = tempy;
x = tempx;
s.push({ y, x });
}
while (!s.empty()) {
zmap[s.top().first][s.top().second] = '*';
s.pop();
}
}
bool aStarSearch(std::vector<std::vector<int>>& map, Pair src, Pair dst) {
if (!isInRange(src.first, src.second) || !isInRange(dst.first, dst.second)) return false;
if (!isUnBlocked(map, src.first, src.second) || !isUnBlocked(map, dst.first, dst.second)) return false;
if (isDestination(src.first, src.second, dst)) return false;
bool closedList[MAX][MAX];
std::memset(closedList, false, sizeof(closedList));
Cell cellDetails[MAX][MAX];
// 내용초기화
// 이 구조 많이 보셨을겁니다. (최대유량알고리즘과 유사)
// 계산해야할 값부분은 INF로하고, 계산할 경로는 -1로 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < COL; ++j) {
cellDetails[i][j].f = cellDetails[i][j].g = cellDetails[i][j].h = INF;
cellDetails[i][j].parent_x = cellDetails[i][j].parent_y = -1;
}
}
// src의 좌표가 첫좌표가 된다.
int sy = src.first;
int sx = src.second;
cellDetails[sy][sx].f = cellDetails[sy][sx].g = cellDetails[sy][sx].h = 0.0;
cellDetails[sy][sx].parent_x = sx;
cellDetails[sy][sx].parent_y = sy;
std::set<pPair> openList;
openList.insert({ 0.0, { sy, sx } });
// 이 반복구조 bfs와 엄청 똑같습니다.
while (!openList.empty()) {
pPair p = *openList.begin();
openList.erase(openList.begin());
int y = p.second.first;
int x = p.second.second;
closedList[y][x] = true;
double ng, nf, nh;
// 직선
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int ny = y + dy1[i];
int nx = x + dx1[i];
if (isInRange(ny, nx)) {
if (isDestination(ny, nx, dst)) {
cellDetails[ny][nx].parent_y = y;
cellDetails[ny][nx].parent_x = x;
tracePath(cellDetails, dst);
return true;
}
// bfs와 굳이 비교하자면, closedList를 방문여부라고 생각하시면 됩니다.
else if (!closedList[ny][nx] && isUnBlocked(map, ny, nx)) {
// 이부분 y x, ny nx 헷갈리는거 조심
ng = cellDetails[y][x].g + 1.0;
nh = GethValue(ny, nx, dst);
nf = ng + nh;
// 만약 한번도 갱신이 안된f거나, 새로갱신될 f가 기존f보다 작을시 참
if (cellDetails[ny][nx].f == INF || cellDetails[ny][nx].f > nf) {
cellDetails[ny][nx].f = nf;
cellDetails[ny][nx].g = ng;
cellDetails[ny][nx].h = nh;
cellDetails[ny][nx].parent_x = x;
cellDetails[ny][nx].parent_y = y;
openList.insert({ nf, { ny, nx } });
}
}
}
}
// 대각선
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int ny = y + dy2[i];
int nx = x + dx2[i];
if (isInRange(ny, nx)) {
if (isDestination(ny, nx, dst)) {
cellDetails[ny][nx].parent_y = y;
cellDetails[ny][nx].parent_x = x;
tracePath(cellDetails, dst);
return true;
}
else if (!closedList[ny][nx] && isUnBlocked(map, ny, nx)) {
ng = cellDetails[y][x].g + 1.414;
nh = GethValue(ny, nx, dst);
nf = ng + nh;
if (cellDetails[ny][nx].f == INF || cellDetails[ny][nx].f > nf) {
cellDetails[ny][nx].f = nf;
cellDetails[ny][nx].g = ng;
cellDetails[ny][nx].h = nh;
cellDetails[ny][nx].parent_x = x;
cellDetails[ny][nx].parent_y = y;
openList.insert({ nf, { ny, nx } });
}
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
void PrintMap() {
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < COL; ++j) {
std::cout << zmap[i][j];
}
std::cout << '\n';
}
}
std::vector<std::vector<int>> fileload(std::string filepath) {
std::ifstream ifs(filepath);
int col, row, cur = 0;
if (ifs.is_open()) {
ifs >> ROW >> COL;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> result(ROW, std::vector<int>(COL));
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < COL; ++j) {
ifs >> result[i][j];
}
}
return result;
}
return std::vector<std::vector<int>>();
}
int main() { // 0: 빈 공간, 1: 벽, 2: 출발지점, 3: 도착지점
Pair src, dst;
int row, col;
/// 방법1 - 맵정보 직접 입력하기
/*
std::cin >> row >> col;
ROW = row;
COL = col;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> grid(row, std::vector<int>(col));
for(int i=0;i<row;++i){
for(int j=0;j<col;++j){
std::cin >> grid[i][j];
}
}*/
/// 방법2 - 파일로 부터 맵정보 불러오기
std::vector<std::vector<int>> grid = fileload("W:\\MAP.txt");
if (grid.empty()) return -1;
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < COL; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] == 2) {
src = { i, j };
grid[i][j] = 0;
}
if (grid[i][j] == 3) {
dst = { i, j };
grid[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < ROW; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < COL; ++j) {
zmap[i][j] = grid[i][j] + '0';
}
}
if (aStarSearch(grid, src, dst)) PrintMap();
else std::cout << "실패.";
return 0;
}🔥소스코드 설명
💎함수 - isDestination
현재좌표가 도착지점과 일치하다면 참, 아니면 거짓을 반환하는 함수.
💎함수 - isInRange
현재좌표가 전체 맵안에 존재하면 , 아니면 거짓을 반환하는 함수.
💎함수 - isUnBlocked
현재좌표가 벽이아니라면 참, 아니면 거짓을 반환하는 함수.
💎함수 - GethValue
현재좌표로부터 도착지점까지의 거리를 계산하는 함수.
💎함수 - tracePath
backtracking을 이용하여 최단경로를 탐색하는 함수.
💎함수 - aStarSearch
a*알고리즘을 실행하는 함수.
💎함수 - PrintMap
현재 맵의 상태를 출력하는 함수.
💎함수 - fileload
텍스트파일로부터 맵정보를 불러오는 함수.
🔥실행
(0: 빈 공간, 1: 벽, 2: 출발지점, 3: 도착지점)
" MAP1.txt "
(밑에 사진 0과 1위치가 반전됬습니다. 참고바랍니다.)
" MAP2.txt "
MAP2는 썸네일의 맵입니다.
실제 출력해보니까, 저의 코드에서는 썸네일의 경로와는 다른 최단경로를 찾아냈습니다.

와우~!!! 아주 정상적으로 잘됩니다!!
🔥다운로드
✨마치며...
이렇게 A*알고리즘 공부를 해봤습니다.
우선은 저도 처음 제대로 공부해봤는데, 구조익히는거라든지 은근히 배우기 쉬웠습니다.
아시다시피 구조가 bfs + backtracking이랑 매우 비슷했습니다.
이 포스팅을 완료한뒤, 몇번더 직접써보면서 완전히 마스터하고오겠습니다.
궁금한 부분있으면 댓글로 질문주세요.