🔪소개및 개요
🔴임시공지
본 포스팅은 미완성 포스팅입니다.
계속 만들어지는 중입니다.
예상 완성일은 2021-08-06입니다.
🔴 미완성요소 🔴
🔴 MCMF
🔴 네트워크유량이 사용된 알고리즘 문제들 예제
🔴 추가설명
🔴 이분매칭
💎개요
본 포스팅에서는 알고리즘 문제풀이에서 사용하는 몇가지 네트워크유량과 관련된 기본적인 요소들을 종류별로 작성할것입니다.
이 글은 어디까지나 저의 개인적인 노트, 정리같은것이기 때문에 이론들을 깊게 설명하는것은 하지 않겠습니다.
소스코드는 c++ , c# 사용하겠습니다.
💎참고
💎개발환경
2021-07-27기준 Windows10 Home 사용했으며, 컴파일러는 MSVC, GCC를 사용했습니다.
c++버전은 17사용했습니다.
c#버전은 .Net6.0이랑 .Net4.72사용했습니다.
🔪네트워크 유량
💎포드-풀커슨
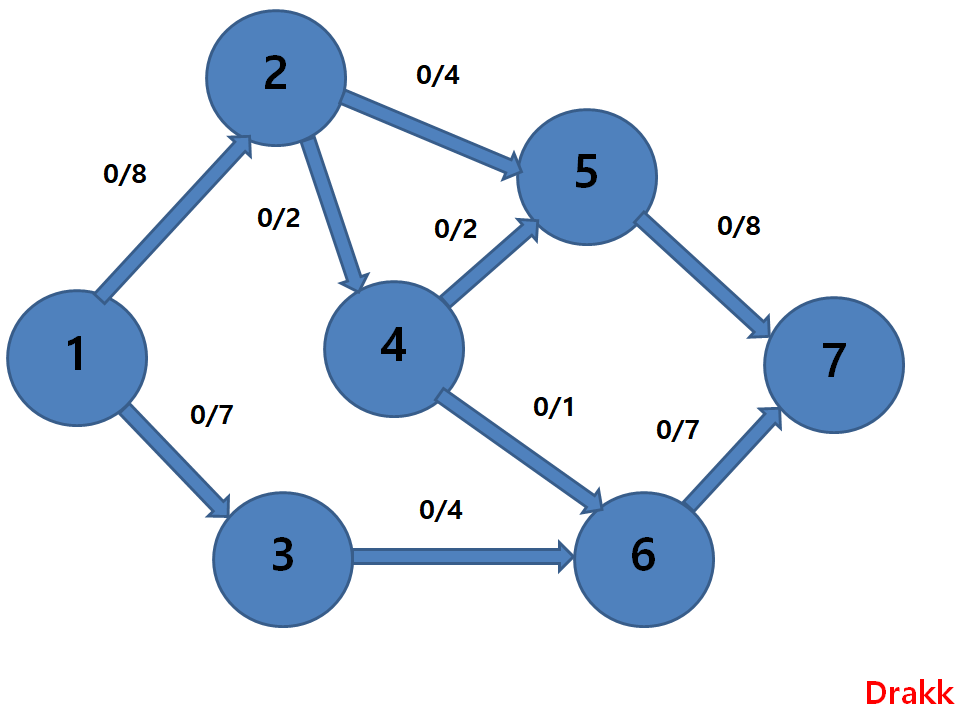
포드-풀커슨 알고리즘은 네트워크 유량을 해결하는데 사용되는 가장 기본적인 알고리즘입니다.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
constexpr int MAX = 7 + 1;
constexpr int INF = 987654321;
std::vector<int> adj[MAX];
int c[MAX][MAX], f[MAX][MAX];
void makeGraph(int a, int b, int cost) {
adj[a].push_back(b);
adj[b].push_back(a);
c[a][b] = cost;
c[b][a] = 0;
}
int FordFulkerson(int start, int end) {
int result = 0;
while (true) {
std::vector<int> dist(MAX, -1);
std::queue<int> q;
q.push(start);
while (!q.empty()) {
int current = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < adj[current].size(); ++i) {
int next = adj[current][i];
if (c[current][next] - f[current][next] > 0 && dist[next] == -1) {
dist[next] = current;
q.push(next);
if (next == end)
break;
}
}
}
if (dist[end] == -1)
break;
int flow = INF;
for (int i = end; i != start; i = dist[i])
flow = std::min(flow, c[dist[i]][i] - f[dist[i]][i]);
for (int i = end; i != start; i = dist[i]) {
f[dist[i]][i] += flow;
f[i][dist[i]] -= flow;
}
result += flow;
}
return result;
}
int main() {
makeGraph(1, 2, 8);
makeGraph(1, 3, 7);
makeGraph(2, 4, 2);
makeGraph(3, 6, 4);
makeGraph(2, 5, 4);
makeGraph(4, 5, 2);
makeGraph(4, 6, 1);
makeGraph(5, 7, 8);
makeGraph(6, 7, 7);
std::cout << FordFulkerson(1, 7);
}C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace NetworkFlow
{
class Program
{
private const int MAX = 7 + 1;
private const int INF = 987654321;
static private List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>();
private static int[,] c = new int[MAX, MAX];
private static int[,] f = new int[MAX, MAX];
static private void makeGraph(int a, int b, int cost)
{
adj[a].Add(b);
adj[b].Add(a);
c[a, b] = cost;
c[b, a] = 0;
}
static private int FordFulkerson(int start, int end)
{
int result = 0;
while (true)
{
List<int> dist = new List<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; ++i) dist.Add(-1);
Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>();
q.Enqueue(start);
while(q.Count > 0)
{
int current = q.Dequeue();
for(int i = 0; i < adj[current].Count; ++i)
{
int next = adj[current][i];
if(c[current, next] - f[current, next] > 0 && dist[next] == -1)
{
dist[next] = current;
q.Enqueue(next);
if (next == end)
break;
}
}
}
if (dist[end] == -1)
break;
int flow = INF;
for (int i = end; i != start; i = dist[i])
flow = Min(flow, c[dist[i], i] - f[dist[i], i]);
for (int i = end; i != start; i = dist[i])
{
f[dist[i], i] += flow;
f[i, dist[i]] -= flow;
}
result += flow;
}
return result;
}
static private int Min(int a, int b)
{
return a < b ? a : b;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; ++i)
adj.Add(new List<int>());
makeGraph(1, 2, 8);
makeGraph(1, 3, 7);
makeGraph(2, 4, 2);
makeGraph(3, 6, 4);
makeGraph(2, 5, 4);
makeGraph(4, 5, 2);
makeGraph(4, 6, 1);
makeGraph(5, 7, 8);
makeGraph(6, 7, 7);
Console.WriteLine(FordFulkerson(1, 7));
}
}
}💎in-out 분할정점 최대유량
in-out 분할정점 최대유량은 한 정점 안에서 두개의 정점으로 분할되는 정점을 말합니다. 이러한 정점들의 최대유량을 포드풀커슨알고리즘과 결합합니다.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
constexpr int N = 7;
constexpr int MAX = (N + 1) * 2;
constexpr int OUT = (N + 1);
constexpr int INF = 987654321;
std::vector<int> adj[MAX];
int c[MAX][MAX], f[MAX][MAX];
void makeGraph(int a, int b, int cost) {
adj[a + OUT].push_back(b);
adj[b].push_back(a + OUT);
c[a + OUT][b] = cost;
c[b][a + OUT] = 0;
adj[b + OUT].push_back(a);
adj[a].push_back(b + OUT);
c[b + OUT][a] = cost;
c[a][b + OUT] = 0;
}
int FordFulkerson(int start, int end) {
int result = 0;
while (true) {
std::vector<int> dist(MAX, -1);
std::queue<int> q;
q.push(start);
while (!q.empty()) {
int current = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < adj[current].size(); ++i) {
int next = adj[current][i];
if (c[current][next] - f[current][next] > 0 && dist[next] == -1) {
dist[next] = current;
q.push(next);
if (next == end)
break;
}
}
}
if (dist[end] == -1)
break;
int flow = INF;
for (int i = end; i != start; i = dist[i])
flow = std::min(flow, c[dist[i]][i] - f[dist[i]][i]);
for (int i = end; i != start; i = dist[i]) {
f[dist[i]][i] += flow;
f[i][dist[i]] -= flow;
}
result += flow;
}
return result;
}
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
adj[i].push_back(i + OUT);
adj[i + OUT].push_back(i);
c[i][i + OUT] = 1;
c[i + OUT][i] = 0;
}
makeGraph(1, 2, 8);
makeGraph(1, 3, 7);
makeGraph(2, 4, 2);
makeGraph(3, 6, 4);
makeGraph(2, 5, 4);
makeGraph(4, 5, 2);
makeGraph(4, 6, 1);
makeGraph(5, 7, 8);
makeGraph(6, 7, 7);
std::cout << FordFulkerson(1 + OUT, 7);
}
이번에 C#은 WinForm Framework로 해봤습니다.
설정화면은 이렇습니다.
"ClickMe!"라는 라벨을 누르면 최대유량이 나오게끔 했습니다.
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace inOut
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private const int N = 7;
private const int MAX = (N + 1) * 2;
private const int OUT = N + 1;
private const int INF = 987654321;
static private List<List<int>> adj = new List<List<int>>();
private static int[,] c = new int[MAX, MAX];
private static int[,] f = new int[MAX, MAX];
static private void makeGraph(int a, int b, int cost)
{
adj[a + OUT].Add(b);
adj[b].Add(a + OUT);
c[a + OUT, b] = cost;
c[b, a + OUT] = 0;
adj[b + OUT].Add(a);
adj[a].Add(b + OUT);
c[b + OUT, a] = cost;
c[a, b + OUT] = 0;
}
static private int FordFulkerson(int start, int end)
{
int result = 0;
while (true)
{
List<int> dist = new List<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; ++i) dist.Add(-1);
Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>();
q.Enqueue(start);
while (q.Count > 0)
{
int current = q.Dequeue();
for (int i = 0; i < adj[current].Count; ++i)
{
int next = adj[current][i];
if (c[current, next] - f[current, next] > 0 && dist[next] == -1)
{
dist[next] = current;
q.Enqueue(next);
if (next == end)
break;
}
}
}
if (dist[end] == -1)
break;
int flow = INF;
for (int i = end; i != start; i = dist[i])
flow = Min(flow, c[dist[i], i] - f[dist[i], i]);
for (int i = end; i != start; i = dist[i])
{
f[dist[i], i] += flow;
f[i, dist[i]] -= flow;
}
result += flow;
}
return result;
}
static private int Min(int a, int b)
{
return a < b ? a : b;
}
static private void Init()
{
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; ++i)
adj.Add(new List<int>());
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i)
{
adj[i].Add(i + OUT);
adj[i + OUT].Add(i);
c[i, i + OUT] = 1;
c[i + OUT, i] = 0;
}
makeGraph(1, 2, 8);
makeGraph(1, 3, 7);
makeGraph(2, 4, 2);
makeGraph(3, 6, 4);
makeGraph(2, 5, 4);
makeGraph(4, 5, 2);
makeGraph(4, 6, 1);
makeGraph(5, 7, 8);
makeGraph(6, 7, 7);
}
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Init();
}
private void label1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
label1.Text = FordFulkerson(1 + OUT, 7).ToString();
}
}
}💎최소비용 최대유량 (MCMF)
미완성(현재 만드는중입니다!)
C++
C#
💎이분매칭
이분매칭은 어떠한 정점과 다른정점을 일련의 순서에 맞게 매치시키는 알고리즘입니다.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
constexpr int MAX = 4;
constexpr int INF = 987654321;
std::vector<int> adj[MAX + 1];
int dist[MAX + 1];
bool visit[MAX + 1];
bool dfs(int start) {
for (int i = 0; i < adj[start].size(); ++i) {
int next = adj[start][i];
if (visit[next])
continue;
visit[next] = true;
if (dist[next] == 0 || dfs(dist[next])) {
dist[next] = start;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int BipartiteMatching() {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= MAX; ++i) {
std::fill(visit, visit + MAX + 1, false);
if (dfs(i))
++result;
}
return result;
}
int main() {
adj[1].push_back(1);
adj[1].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(1);
adj[3].push_back(4);
adj[4].push_back(3);
int result = BipartiteMatching();
std::cout << result << '\n';
for (int i = 1; i <= MAX; ++i) {
if (dist[i] != 0)
std::cout << dist[i] << " =>> " << i << '\n';
}
}C#