CSS의 position 속성을 이용하여 HTML 요소를 원하는 위치에 배치할 수 있다.
position 속성은 HTML 문서 상에서 요소가 배치되는 방식을 결정한다.
position 속성은 요소의 정확한 위치 지정을 위해서 ✔ top, left, bottom, right ✔ 속성과 함께 사용된다.
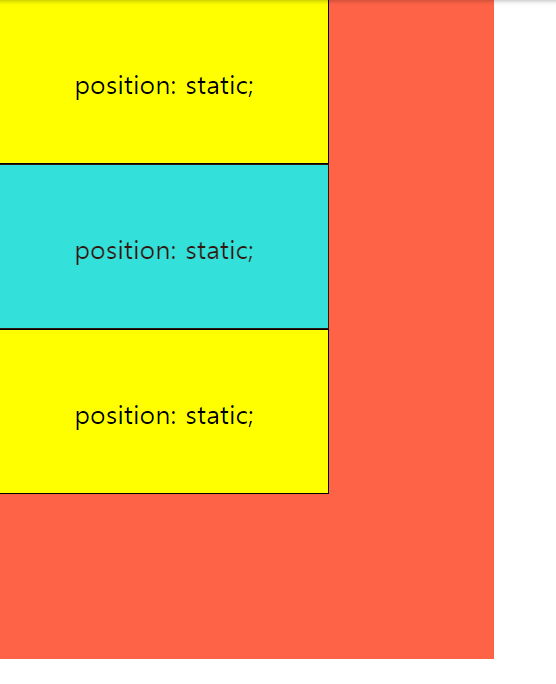
1) position: static (디폴트)
position 속성이 static인 요소는 HTML 문서 상에서 원래 있어야하는 위치에 배치한다.
즉, 요소들이 HTML에 작성된 순서 그대로 브라우저 화면에 표시된다.
top, left, bottom, right 속성값은 position 속성이 static일 때는 무시된다.
<main>
<div>첫 번째 요소</div>
<div>두 번째 요소</div>
<div>세 번째 요소</div>
</main>
main {
width: 300px;
height: 400px;
background: tomato;
}
div { // default : static
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid;
background: yellow;
text-align: center;
line-height: 100px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
div:nth-of-type(2) {
position: static; // static
background: cyan;
opacity: 0.8;
}
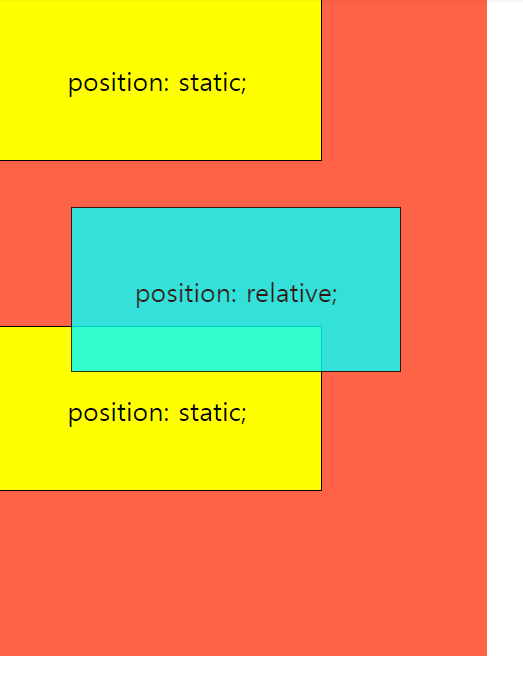
2) position: relative
요소를 원래 위치를 기준으로 상대적(relative)으로 배치해준다.
top, bottom, left, right 속성을 이용해서, 요소가 원래 위치에 있을 때의 상하좌우로 부터 얼마나 떨어지게 할지를 지정한다.
예를 들어, 두 번째 div 요소의 position 속성을 relative로 변경하고, 요소의 원래 위치로 부터 위에서 28px, 왼쪽에서 48px 떨어지도록 top과 left 속성을 설정해 보자.
div:nth-of-type(2) {
position: relative; // relative
top: 28px;
left: 48px;
background: cyan;
opacity: 0.8;
}
3) position: absolute
position 속성을 absolute로 지정하면 사실 전혀 절대적(absolute)으로 요소를 배치해주지 않는다.
pposition 속성이 absolute일 때 해당 요소는 배치 기준을 자신이 아닌 상위 요소에서 찾는다. DOM 트리를 따라 올라가다가 position 속성이 ❗ "static이 아닌 첫 번째 상위 요소" ❗가 해당 요소의 배치 기준으로 설정된다.
➡ 대부분의 경우, 부모 요소(가장 가까운 상위 요소)를 기준으로 top, left, bottom, right 속성을 적용해야하기 때문에 어떤 요소의 display 속성을 absolute로 설정하면, 부모 요소의 display 속성을 relative로 지정해주는 것이 관례이다.
➡ position: absolute인 요소는 HTML 문서 상에서 독립되어 앞뒤에 나온 요소와 더 이상 상호작용을 하지 않게 된다.
main {
position: relative; // 부모는 relative
width: 300px;
height: 400px;
background: tomato;
}
div:nth-of-type(2) {
position: absolute; // 자식은 absolute
bottom: 8px;
right: 16px;
background: cyan;
opacity: 0.8;
} 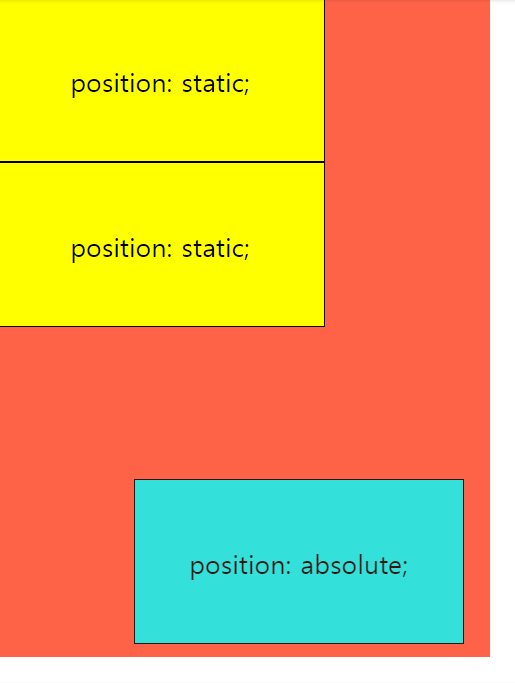
-> main 요소의 우측 하단에 배치되었다.
-> 첫 번째 요소 아래에 바로 세 번째 요소가 배치된다.
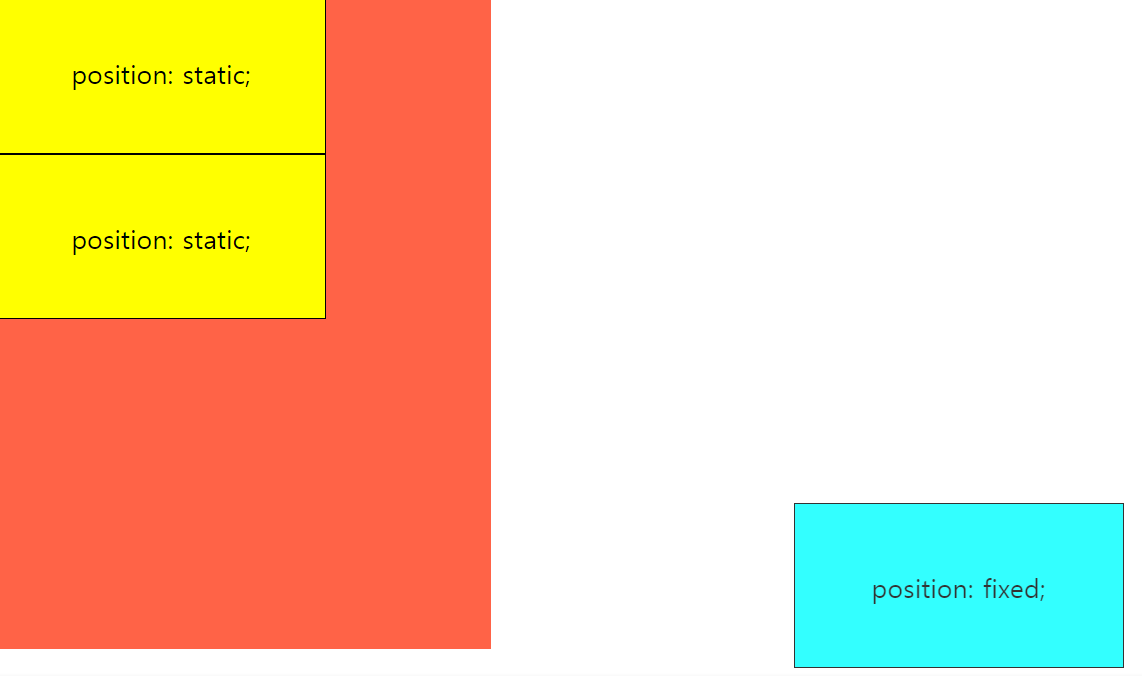
4) position: fixed
position 속성을 fixed로 지정하면 요소를 항상 고정된(fixed) 위치에 배치할 수 있다.
화면을 위아래로 스크롤하더라도 브라우저 화면의 특정 부분에 고정되어 움직이지 않는 UI 는 이러한 방식을 이용한 것 !
fixed 속성값의 배치 기준이 자신이나 부모 요소가 아닌 뷰포트(viewport), 즉 브라우저 전체화면이기 때문이다.
top, left, bottom, right 속성은 각각 브라우저 상단, 좌측, 하단, 우측으로 부터 해당 요소가 얼마나 떨어져있는지를 결정한다
div:nth-of-type(2) { position: fixed; // fixed bottom: 8px; right: 16px; background: cyan; opacity: 0.8; }
position: fixed인 요소도 position: absolute인 요소와 마찬가지로 HTML 문서 상에서 독립되어 앞뒤에 나온 요소와 더 이상 상호작용을 하지 않는다.