
Chapter 14. Secure HTTP
(해석 또는 이해가 잘못된 부분이 있다면 댓글로 편하게 알려주세요.)
✏️ 원문 번역
Server Certificates
SSL supports mutual authentication, carrying server certificates to clients and carrying client certificates back to servers. But today, client certificates are not commonly used for browsing. Most users don’t even possess personal client certificates. A web server can demand a client certificate, but that seldom occurs in practice.
-
SSL은 상호 인증을 지원합니다.
-
서버의 인증서는 클라이언트에, 클라이언트의 인증서는 서버에 전달할 수 있습니다.
-
하지만 오늘날 클라이언트 인증서는 브라우징에서 일반적으로 사용되지 않습니다.
-
대부분의 사용자가 개인적인 클라이언트 인증서를 가지고 있지 않습니다.
-
웹 서버가 클라이언트 인증서를 요청할 수는 있지만 실제로 그런 일은 거의 발생하지 않습니다.
On the other hand, secure HTTPS transactions always require server certificates. When you perform a secure transaction on a web server, such as posting your credit card information, you want to know that you are talking to the organization you think you are talking to. Server certificates, signed by a well-known authority, help you assess how much you trust the server before sending your credit card or personal information.
-
반면 안전한 HTTPS 트랜잭션은 항상 서버의 인증서를 필요로 합니다.
-
웹 서버와 신용카드 정보 등록과 같은 보안 트랜잭션을 수행할 때 사용자는 자신이 정말 통신하고자 한 그 기관과 통신하고 있는지 확인하고 싶어합니다.
-
공신력 있는 인증기관에 의해 서명된 서버 인증서는 사용자의 신용카드 정보나 개인정보를 전송하기 전 서버의 신뢰도를 평가하는 데 도움을 줍니다.
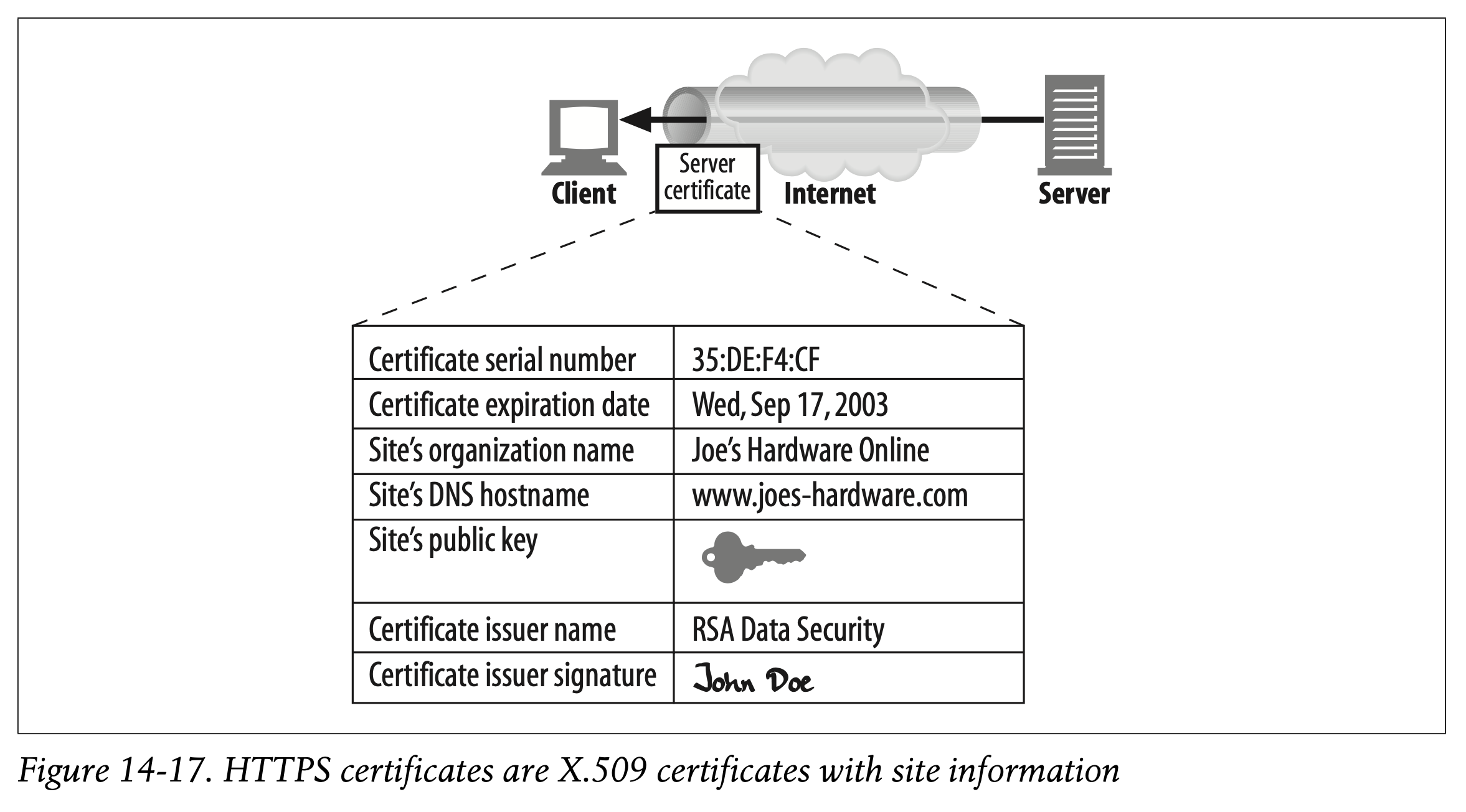
The server certificate is an X.509 v3–derived certificate showing the organization’s name, address, server DNS domain name, and other information (see Figure 14-17). You and your client software can examine the certificate to make sure everything seems to be on the up-and-up.
-
서버 인증서는 X.509 v3-derived 인증서를 사용합니다.
-
인증서는 기관명, 주소, 서버의 DNS 도메인 이름, 그 밖의 다른 정보들로 구성되어 있습니다. (Figure 14-17)
-
사용자와 사용자의 클라이언트 소프트웨어는 인증서를 검사하여 모든 것이 정상적인지 확인할 수 있습니다.
Site Certificate Validation
SSL itself doesn’t require you to examine the web server certificate, but most modern browsers do some simple sanity checks on certificates and provide you with the means to do more thorough checks. One algorithm for web server certificate validation, proposed by Netscape, forms the basis of most browser’s validation techniques. The steps are:
-
SSL이 웹 서버의 인증서를 검사하는 과정을 필수적으로 요구하는 것은 아니지만, 대부분의 현대 브라우저에서는 간단한 Sanity Check를 통하여 인증서를 철저히 확인할 수 있는 수단을 제공합니다.
-
Netscape에 의해 제안된 웹 서버 인증서 검증 알고리즘은 대부분의 브라우저 검증 기술에서 사용되고 있습니다.
Date check
First, the browser checks the certificate’s start and end dates to ensure the certificate is still valid. If the certificate has expired or has not yet become active, the certificate validation fails and the browser displays an error.
Date Check
-
먼저 브라우저는 증명서의 발급일시와 만료일시를 확인한 후 해당 증명서가 유효한지 확인합니다.
-
인증서가 만료되었거나 아직 활성화되지 않은 경우 인증서 검증에 실패하며 브라우저가 에러를 표시합니다.
Signer trust check
Every certificate is signed by some certificate authority (CA), who vouches for the server. There are different levels of certificate, each requiring different levels of background verification. For example, if you apply for an e-commerce server certificate, you usually need to provide legal proof of incorporation as a business.
Signer Trust Check
-
모든 증명서는 CA에 의해 서명되며, CA는 서버를 보증합니다.
-
서로 다른 수준의 인증서는 서로 다른 수준의 백그라운드 증명을 요구합니다.
-
예를 들어 전자상거래 인증서를 발급하려 하는 경우 사용자는 법인 설립에 대한 법적 증명 자료를 제공해야 합니다.
Anyone can generate certificates, but some CAs are well-known organizations with well-understood procedures for verifying the identity and good business behavior of certificate applicants. For this reason, browsers ship with a list of signing authorities that are trusted. If a browser receives a certificate signed by some unknown (and possibly malicious) authority, the browser usually displays a warning. Browsers also may choose to accept any certificates with a valid signing path to a trusted CA. In other words, if a trusted CA signs a certificate for “Sam’s Signing Shop” and Sam’s Signing Shop signs a site certificate, the browser may accept the certificate as deriving from a valid CA path.
-
누구나 인증서를 발급할 수 있지만 CA 중에는 간단하게 이해할 수 있는 신원 증명 절차와 좋은 기업 혜택을 제공하는 공신력 있는 기관들도 있습니다.
-
따라서 브라우저는 신뢰할 수 있는 서명 기관의 목록을 전달합니다.
-
만약 브라우저가 알려지지 않은 기관(혹은 악성일 가능성이 있는 기관)에 의해 서명된 인증서를 받았다면 일반적으로 경고창을 띄웁니다.
-
신뢰할 수 있는 CA까지 유효한 서명 체인을 가진 임의의 인증서의 경우 브라우저가 허용할 수 있습니다.
-
즉 신뢰할 수 있는 CA가 "Sam's Signing Shop"을 서명하고 Sam's Signing Shop이 사이트의 증명서를 서명하고 있다면, 브라우저는 해당 인증서를 유효한 CA 체인으로부터 파생된 것으로 간주합니다.
Signature check
Once the signing authority is judged as trustworthy, the browser checks the certificate’s integrity by applying the signing authority’s public key to the signature and comparing it to the checksum.
Signature Check
- CA가 사이트의 신뢰성을 판단하고 나서 브라우저는 인증서의 무결성을 확인하기 위해 서명 기관의 public key을 signature에 적용하여 checksum과 대조해볼 수 있습니다.
Site identity check
To prevent a server from copying someone else’s certificate or intercepting their traffic, most browsers try to verify that the domain name in the certificate matches the domain name of the server they talked to. Server certificates usually contain a single domain name, but some CAs create certificates that contain lists of server names or wildcarded domain names, for clusters or farms of servers. If the hostname does not match the identity in the certificate, user-oriented clients must either notify the user or terminate the connection with a bad certificate error.
Site Identity Check
-
서버가 다른 인증서를 복사하거나 인증서 트래픽을 가로채는 것을 방지하기 위해 대부분의 브라우저는 인증서 내부의 도메인 이름과 통신중인 서버의 도메인 이름이 일치하는지 검증합니다.
-
보통 서버의 인증서에는 하나의 도메인 이름이 포함되어 있지만, 일부 CA는 서버 클러스터나 팜을 표현하기 위해 여러 개의 서버명이나 와일드카드 된 도메인 이름으로 구성된 목록을 포함하는 인증서를 생성할 수도 있습니다.
-
만약 호스트명이 인증서의 정보와 일치하지 않는 경우 사용자 지향적인 클라이언트는 사용자에게 이 사실을 알리거나 bad certificate 에러와 함께 서버와의 연결을 종료해야 합니다.
Virtual Hosting and Certificates
It’s sometimes tricky to deal with secure traffic on sites that are virtually hosted (multiple hostnames on a single server). Some popular web server programs support only a single certificate. If a user arrives for a virtual hostname that does not strictly match the certificate name, a warning box is displayed.
-
가상 호스팅(단일 서버에 여러 호스트명 존재)된 사이트들에 대하여 보안 트래픽을 처리하는 것은 상당히 까다로울 수 있습니다.
-
몇몇 인기 있는 웹 서버 프로그램은 단일 인증서만 지원하기도 합니다.
-
만약 사용자가 인증서에 명시된 이름과 정확히 일치하지 않는 가상 호스트명으로 요청을 전송한다면 경고창이 표시됩니다.
For example, consider the Louisiana-themed e-commerce site Cajun-Shop.com. The site’s hosting provider provided the official name cajun-shop.securesites.com. When users go to https://www.cajun-shop.com, the official hostname listed in the server certificate (*.securesites.com) does not match the virtual hostname the user browsed to (www.cajun-shop.com), and the warning in Figure 14-18 appears.
-
예를 들어 Louisiana를 테마로 한 전자상거래 사이트 Cajun-Shop.com를 생각해봅시다.
-
사이트의 호스팅 제공자는 cajun-shop.securesites.com이라는 공식 명칭을 제공하고 있습니다.
-
사용자가 https://www.cajun-shop.com 에 요청을 전송하는 경우, 서버 인증서에 나열된 공식적인 호스트명과 사용자가 브라우징한 가상 호스트명이 일치하지 않습니다.
-
따라서 Figure 14-18과 같이 경고창이 표시됩니다.

To prevent this problem, the owners of Cajun-Shop.com redirect all users to cajun-shop.securesites.com when they begin secure transactions. Cert management for virtually hosted sites can be a little tricky.
-
문제를 해결하기 위해서는 Cajun-Shop.com의 소유자가 보안 트랜잭션을 시작하려는 모든 사용자를 cajun-shop.securesites.com으로 리디렉션 시켜야 합니다.
-
가상 호스팅된 사이트에 대한 인증서 관리는 조금 더 까다롭습니다.
✏️ 요약
Certificates Supported by SSL
: SSL은 상호 인증 기능 제공을 제공하고 있다
- 서버 인증서 : 안전한 HTTP 트랜잭션에서 서버의 신뢰성을 평가하기 위해 사용
- 클라이언트 인증서 : 안전한 HTTP 트랜잭션에서 클라이언트의 신뢰성을 평가하기 위해 사용 (일반적으로 사용 X)
Site Certificate Validation
[1] 인증서 발급일시 & 만료일시 확인
- 브라우저가 웹 서버 인증서의 발급일시와 만료일시를 검토하여 유효 여부를 확인하는 과정
- 인증서가 만료되었거나 활성화되지 않은 경우 에러 표시
[2] 신뢰할 수 있는 CA가 발급한 인증서인지 확인
- 브라우저가 신뢰할 수 있는 CA로부터 인증서를 발급 받았는지 확인하는 과정
- 신뢰할 수 있는 CA 체인이 웹 서버 인증서를 서명하고 있다면 문제 발생 X
- 알려지지 않은 기관으로부터 웹 서버 인증서를 전달받았다면 경고창 표시
[3] CA's Signature 확인 (Integrity Check)
- CA의 Public Key를 통해 인증서의 Signature를 복호화함으로써 전달받은 인증서에 변조가 발생했는지 확인하는 과정
[4] 도메인 일치 여부 확인 (MITM 및 인증서 복사 방지)
- 인증서 내부의 도메인 이름과 통신중인 서버의 이름이 일치하는지 확인하는 과정
- 가상 호스팅 -> 인증서에 등록되지 않은 도메인으로 접근 시 등록된 도메인으로 리디렉션한 후 일치 여부 확인
✏️ 감상
HTTP 읽으면서 웹 보안을 하도 많이 봤더니
보안 시험 진짜 만점 받고 왔습니다
ㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋ 맛있네요,,
