23.08.04 최초 작성
1. Files of Linux
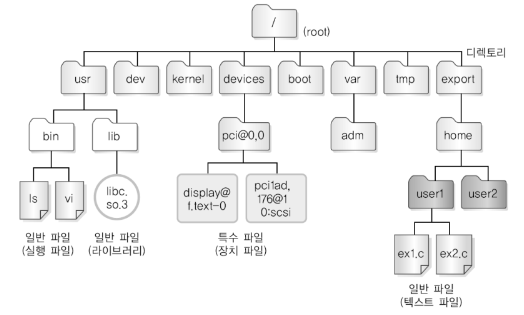
일반 파일 (Regular File) [-]
텍스트 & 바이너리 파일특수 파일 (Special File) [b] [c]
장치와 데이터를 주고 받는 통로디렉토리 [d]
파일의 목록을 저장 하는 파일심볼릭 링크 [s]
이미 존재하는 파일이나 디렉토리에 접근할 수 있는 파일
1.1 Special File
- 데이터 블록이 없으며 장치 번호(종류, 수)를 inode에 저장한다.
1.1.1 Character Device File [c]
- Character 단위 데이터 전송
1.1.2 Block Device File [b]
- Block 단위 데이터 전송
2 File Organization
File Name(Hard Link): 사용자가 파일에 접근할 때 사용Inode: 파일에 대한 정보 저장. 번호를 통해 관리/접근 함 (ls -i를 통해 확인 가능)Data Block: 실제 데이터가 저장된 저장장치의 공간
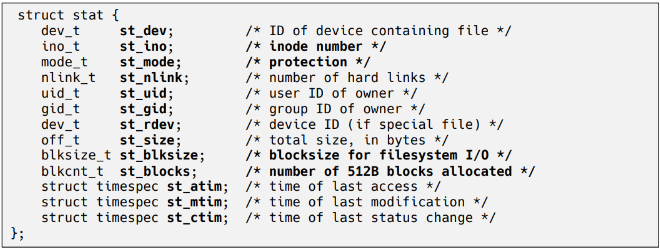
2.1 파일의 정보 확인
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *buf);
int lstat(const char *pathname, struct stat *buf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf);
///
pathname/fd : 파일의 경로 / File Descriptor
buf : 파일의 정보를 저장할 주소
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Error)stat structure의 구조
ex) 예제
t_stat:stat명령어를 통해 얻은 정보 출력
`
#include <sys/sysmacros.h>
#if defined(_AIX)
#define _BSD
#endif
#if defined(__sgi) || defined(__sun) /* Some systems need this */
#include <sys/mkdev.h> /* To get major() and minor() */
#endif
#if defined(__hpux) /* Other systems need this */
#include <sys/mknod.h>
#endif
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "file_perms.h"
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static void
displayStatInfo(const struct stat *sb)
{
printf("File type: ");
switch (sb->st_mode & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFREG: printf("regular file\n"); break;
case S_IFDIR: printf("directory\n"); break;
case S_IFCHR: printf("character device\n"); break;
case S_IFBLK: printf("block device\n"); break;
case S_IFLNK: printf("symbolic (soft) link\n"); break;
case S_IFIFO: printf("FIFO or pipe\n"); break;
case S_IFSOCK: printf("socket\n"); break;
default: printf("unknown file type?\n"); break;
}
printf("Device containing i-node: major=%ld minor=%ld\n",
(long) major(sb->st_dev), (long) minor(sb->st_dev));
printf("I-node number: %ld\n", (long) sb->st_ino);
printf("Mode: %lo (%s)\n",
(unsigned long) sb->st_mode, filePermStr(sb->st_mode, 0));
if (sb->st_mode & (S_ISUID | S_ISGID | S_ISVTX))
printf(" special bits set: %s%s%s\n",
(sb->st_mode & S_ISUID) ? "set-UID " : "",
(sb->st_mode & S_ISGID) ? "set-GID " : "",
(sb->st_mode & S_ISVTX) ? "sticky " : "");
printf("Number of (hard) links: %ld\n", (long) sb->st_nlink);
printf("Ownership: UID=%ld GID=%ld\n",
(long) sb->st_uid, (long) sb->st_gid);
if (S_ISCHR(sb->st_mode) || S_ISBLK(sb->st_mode))
printf("Device number (st_rdev): major=%ld; minor=%ld\n",
(long) major(sb->st_rdev), (long) minor(sb->st_rdev));
printf("File size: %lld bytes\n", (long long) sb->st_size);
printf("Optimal I/O block size: %ld bytes\n", (long) sb->st_blksize);
printf("512B blocks allocated: %lld\n", (long long) sb->st_blocks);
printf("Last file access: %s", ctime(&sb->st_atime));
printf("Last file modification: %s", ctime(&sb->st_mtime));
printf("Last status change: %s", ctime(&sb->st_ctime));
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct stat sb;
Boolean statLink; /* True if "-l" specified (i.e., use lstat) */
int fname; /* Location of filename argument in argv[] */
statLink = (argc > 1) && strcmp(argv[1], "-l") == 0;
/* Simple parsing for "-l" */
fname = statLink ? 2 : 1;
if (fname >= argc || (argc > 1 && strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0))
usageErr("%s [-l] file\n"
" -l = use lstat() instead of stat()\n", argv[0]);
if (statLink) {
if (lstat(argv[fname], &sb) == -1)
errExit("lstat");
} else {
if (stat(argv[fname], &sb) == -1)
errExit("stat");
}
displayStatInfo(&sb);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}2.2 권한 확인
#include <unistd.h>
int access(const char * pathname, int mode);
///
pathname : 파일의 경로
mode : 확인 할 권한 (R_OK, W_OK, X_OK, F_OK -> 파일 존재 여부)
Return
(0 : 권한 있음, -1 : Error 권한 없음 or 파일 없음)2.3 접근권한 변경
#include <sys/stat.h>
int chmod(const char * pathname, mode_t mode);
int fchmod(int fd, mode_t mode);
///
pathname/fd : 파일의 경로 / File Descriptor
mode : 적용하려는 접근 권한
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Error)2.4 파일 소유권 변경
#include <unistd.h>
int chown(const char *pathname, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
int lchown(const char *pathname, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
int fchown(int fd, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
///
pathname/fd : 파일의 경로 / File Descriptor
uid_t owner : 파일에 대한 새로운 소유자의 사용자 ID(-1이면 변경 취소)
gid_t group 파일에 대한 새로운 소유자의 그룹 ID(-1이면 변경 취소)
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Error)2.5 파일 시스템 마운트
mount,umount: 파일 시스템을 마운트 / 해제
#include <sys/mount.h>
int mount(const char *specialfile, const char * dir , const char * filesystemtype, unsigned long rwflag , const void * data);
int umount(const char *specialfile);
int umount(const char *dir);
///
specialfile : 장치 이름
dir : mount/umount 할 경로
filesystemtype : /proc/filesystems 에 정의된 값
MS_RDONLY 1 : 읽기-전용 마운트
MS_NOSUID 2 : suid 그리고 sgid 비트를 무시
MS_NODEV 4 : 특별 파일 장치 접근을 허용하지 않는다
MS_NOEXEC 8 : 프로그램 실행을 허용하지 않는다
MS_SYNC 16 : 쓰기를 일단 동기화
MS_REMOUNT 32 : 마운트된 FS의 플래그를 수정
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Error)3. Directory
File Name들과 File Name이 가리키는 inode 번호를 담고 있는 파일
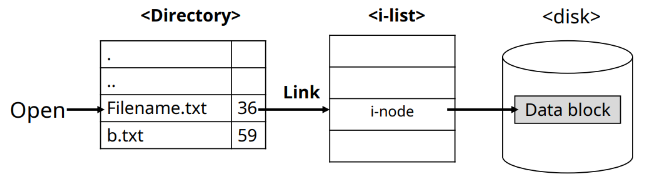
1. Sub Directory : Directory에 포함된 Directory
2. Special Directory : 모든 Directory가 포함하는 Directory들
(. : 최근 Directory, .. : 부모 Directory)
3. Pathname
Absolute Pathname: Root Directory(/)로 시작하는 파일 경로Relative Pathname: Current Directory(.)로 시작하는 파일 경로
3.1 Directory 생성, 삭제, 이름 변경
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int mkdir(const char *pathname, mot_t mode);#include <unistd.h>
int rmdir(const char * pathaname);#include <stdio.h>
int rename(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath);
///
Return
(0 : Sucess, -1 : Fail)3.2 Directory 현재 위치, 이동
#include <unistd.h>
char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size);
///
buf : 현재 디렉토리의 절대 경로를 저장 할 주소
size : 버퍼의 크기
Return : Path가 저장된 buf의 주소
(NULL : Error)#include <unistd.h>
int chdir(const char *path);
///
path : 변경할 Directory의 경로
Return
(0: Success, -1 : Fail)3.3 Directory 정보 검색
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
DIR *opendir(const char * name);
///
name : 열려는 Directory 이름
Return : 열린 Directory의 DIR 포인터
(NULL : Error)#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int closedir(DIR *dirp)
///
dirp : 닫으려는 Directory의 포인터
Return
(0 : Sucess, -1 : Fail)#include <dirent.h>
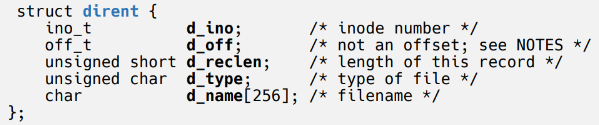
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp) // Directory의 내용을 하나씩 읽어옴
///
dirp : 읽으려는 Directory의 포인터
Return : 현재 읽어온 항목의 dirent 구조체를 가리키는 포인터
(NULL : 더이상 읽을 항목이 없음)- dirent 구조체
ex) 예제
list_dir: 디렉토리 안의 파일 목록 출력
#if defined(__APPLE__)
/* Darwin requires this header before including <dirent.h> */
#include <sys/types.h>
#endif
#include <dirent.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static void /* List all files in directory 'dirpath' */
listFiles(const char *dirpath)
{
DIR *dirp;
struct dirent *dp;
Boolean isCurrent; /* True if 'dirpath' is "." */
isCurrent = strcmp(dirpath, ".") == 0;
dirp = opendir(dirpath);
if (dirp == NULL) {
errMsg("opendir failed on '%s'", dirpath);
return;
}
/* For each entry in this directory, print directory + filename */
for (;;) {
errno = 0; /* To distinguish error from end-of-directory */
dp = readdir(dirp);
if (dp == NULL)
break;
if (strcmp(dp->d_name, ".") == 0 || strcmp(dp->d_name, "..") == 0)
continue; /* Skip . and .. */
if (!isCurrent)
printf("%s/", dirpath);
printf("%s\n", dp->d_name);
}
if (errno != 0)
errExit("readdir");
if (closedir(dirp) == -1)
errMsg("closedir");
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc > 1 && strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s [dir-path...]\n", argv[0]);
if (argc == 1) /* No arguments - use current directory */
listFiles(".");
else
for (argv++; *argv; argv++)
listFiles(*argv);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
3.4 Directory Offset
#include <dirent.h>
long telldi(DIR *dirp); // 현재 offset 반환
void seekdir(DIR *dirp, long loc); // offset을 loc으로 이동
void rewinddir(DIR *dirp); // offset을 0으로 변경
///
loc : 이동 할 위치4. Link
- Hard Link : 디렉토리의 파일 이름과 inode를 매핑해 놓은 것. 다른 파일 시스템에 있는 inode에 대한 Hard Link는 불가능하다. Hard Link의 갯수는 링크의 갯수이며 링크의 갯수가 0이 될 시 파일이 삭제된다. (확장자 명은 *.ln)
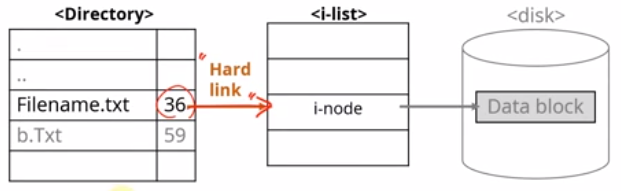
#include <unistd.h>
int link(const char *existing, const char *new);
///
existing : 기존 파일 경로
new : 새로 생성할 링크의 경로
Return
(0 : Sucess, -1 : Fail)- Soft Link(Symbolic Link) : 실제 파일의 경로명을 저장하는 파일. 다른 파일 시스템의 inode를 Link 할 수 있다. (확장자 명은 *.sym)
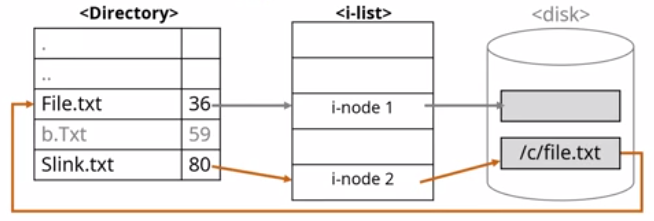
#include <unistd.h>
int symlink(const char *name1, const char * name2);
///
name1 : 기존 파일의 경로
name2 : 새로 생성할 링크의 경로
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Fail)4.1 Removing a Link
# include <unistd.h>
int unlink(const char *pathname); // Directory에 사용 불가
///
pathname : 삭제하려는 HardLink의 경로
Return
(0 : Sucess, -1 : Fail)# include <unistd.h>
int remove(const char * pathname); // 비어있는 Directory에 사용 가능
///
pathname : 삭제하려는 HardLink의 경로
Return
(0 : Sucess, -1 : Fail)4.2 Symbolic Link의 정보 가져오기
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int lstat(const char *pathname, struct stat *buf);
// Symbolic Link File 자체의 파일 정보를 가져옴
// stat : Symbolic Link가 가리키는 파일의 정보를 가져옴
///
pathname : 읽어오려는 Symbolic Link의 경로
buf : 파일의 정보를 담을 공간
Return
(0 : Sucess, -1 : Fail)#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t readlink(const char *pathname, char *buf, size_t bufsize);
///
pathname : 읽어오려는 Symbolic Link의 경로
buf / bufsize : 데이터를 저장할 buffer의 주소 및 읽을 크기
Return : 읽은 byte 수
(-1 : Error)#include <limits.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
char* realpath(const char *path, char *resolved_path);
///
pathname : Symbolic Link File의 경로
resolved_path : 결과 값을 저장할 buffer
Return : 결과가 저장된 buffer의 포인터
(NULL : Error)