23.08.04 최초 작성
1. Linux System Information
- 시스템에 설치된 운영체제에 관한 정보
- 호스트명 정보
- 하드웨어 종류에 관한 정보
- 하드웨어에 따라 사용할 수 있는 자원의 최댓값
2. System Info. 가져오기
#include <sys/utsname.h>
int uname (struct utsname *buf);
///
buf : 읽을 정보를 저장할 공간
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Error)- utsname 구조체

#include <unistd.h>
int sysinfo (struct sysinfo *info);
///
info : 읽을 정보를 저장할 sysinfo 구조체
Return
(0 : Sucess, -1 : Error)-sysinfo 구조체

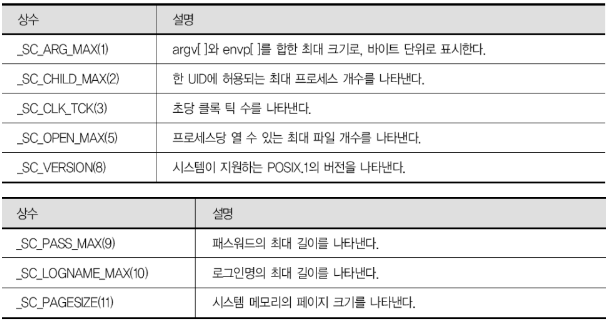
2.1 Resource Info. 가져오기
#include <unistd.h>
long sysconf (int name);
///
name : 검색할 정보를 나타냄
Return : 요청한 정보의 값
(-1 : Error)-name의 종류
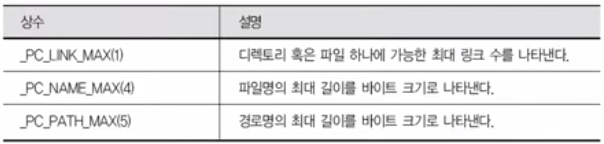
2.2 File & Directory Resource Info. 가져오기
#include <unistd.h>
long fpathconf (int fd, int name);
long pathconf (const char *path, int name);
//
fd / path : 정보를 읽어올 디렉토리 or 파일
name : 검색할 정보를 나타냄
Return : 읽어온 정보 값
(-1 : Error)- name의 종류
3. User Information
- UID : 사용자에게 부여된 ID 번호
- Login Name : 문자 형태의 사용자 이름 (UID 와 매핑됨)
3.1 프로세스 입장에서 User ID
- Real User ID (RUID) : 최초에 프로세스를 실행한 User ID
- Effective User ID(EUID) : 현재 프로세스가 행사하는 UID (권한)
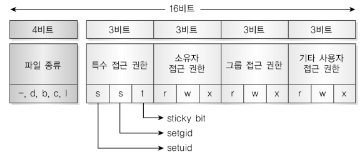
실행파일의 setuid = 1인 경우 해당 파일의 소유자의 UID가 EUID가 됨 - Saved User ID (SUID) : 프로세스 최초의 EUID
3.2 UID Gettign / Setting
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
uid_t getuid (void);
uid_t geteuid (void);
///
Return : uid / euid 를 가져옴#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int seteuid (uid_t uid); // 일반 사용자는 RUID or SUID로만 설정 가능
///
uid : EUID로 설정하려는 uid 3.3 Reading passwd File
/etc/passwd file : 사용자에 대한 기본 정보가 들어 있는 파일
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pwd.h>
struct passwd *getpwnam (const char *name);
struct passwd *getpwuid (uid_t uid);
///
uid / name : passwd file에서 정보를 읽어 올 사용자
Return : 해당 사용자에 대한 passwd structure가 저장된 포인터
(-1 : NULL)- passwd 구조체
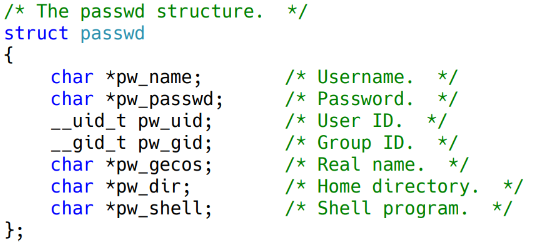
/etc/shadow file : 암호화 된 사용자 정보 (password를 암호화 해서 저장)
#include <shadow.h>
struct spwd *getspent (void); // /etc/shadow 파일의 패스워드 정보를 순차적으로 읽어옴
void setspent (void); // /etc/shadow 파일의 File Offset을 처음으로 되돌림
void endspent (void); // /etc/shadow 파일을 닫음4. Group ID
- Real Group :
- Effective Group :
- Saved Group :
4.1 Group Info.
/etc/group : 그룹 정보를 가지고 있는 파일
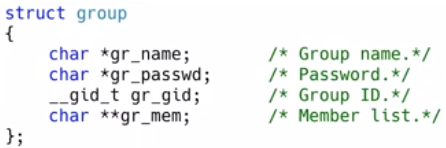
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <grp.h>
struct group *getgrnam (const char *name);
struct group *getgrgid (gid_t gid);
struct group *getgrent (void); // /etc/group 파일의 그룹 정보를 순차적으로 읽어옴
void setgrent (void); // /etc/group 파일의 File Offset을 되감음
void endgrent (void);// /etc/group 파일을 닫음
///
name : 검색하려는 그룹명 ID
gid : 검색하려는 그룹의 ID5. Time Information
5.1 Time in Linux
- 1970.01.01 0시 0분 0초 기준
- 현재까지 경과한 시간을 초 단위로 저장
5.2 Getting / Setting Time
#include <sys/time.h>
time_t time (time_t *tloc);
///
tloc : 얻어온 초를 저장할 주소
Return : 얻어온 초
(-1 : Error)#include <sys/time.h>
int gettimeofday (struct timeval *tv, struct time zone *tz);
int settimeofday (const struct timeval *tv, const struct timezone *tz);
///
tv : 읽어온 시간을 저장할 timeveal 구조체
tz : NULL 사용
Return
(0 : Success, -1 : Fail)- timeval 구조체
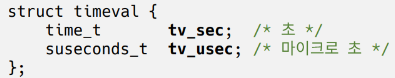
#include <time.h>
void tzset (void);
///
현재 지역의 시간대로 시간대를 설정 함- 전역 변수에 정보가 저장 됨

5.3 시간 변환 - tm structure
시간 정보를 사람이 이해하기 편한 초단위 형태로 변환하는 함수 제공
- tm 구조체
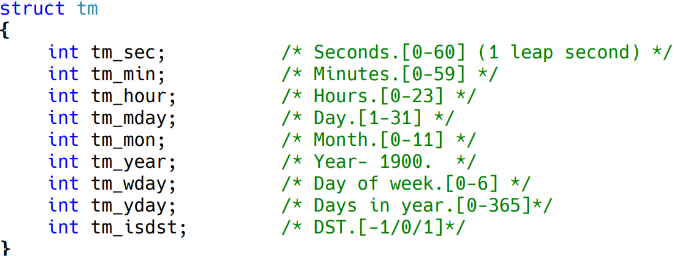
#include <time.h>
struct tm *gmtime (const time_t *timep); // UTC 기준으로 초를 tm으로 변환
struct tm *localtime (const time_t *timep); // Local Time 기준으로 초를 tm으로 변환
time_t mktime (struct tm *tm); // tm을 초로 변환5.4 Printing Time
#include <time.h>
char *ctime (const time_t *timep);
char *asctime (const struct tm *tm);
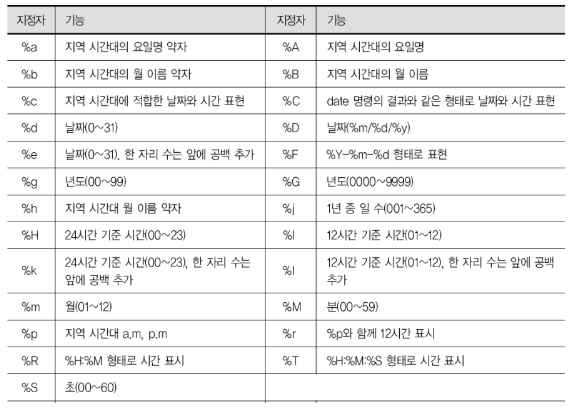
// 요일 월 일 시:분:초 년도 형태로 Return#include <time.h>
size_t strftime (char *s, size_t max, const char *format, const struct tm *tm);
///
s : 시간 정보를 저장 할 배열 주소
max : s의 크기
format : 출력 형식
timeptr : 출려갈 시간 정보를 저장한 구조체
Return : print문처럼 정보를 출력- 포멧 지정자