
🌳 Tree Data Structure
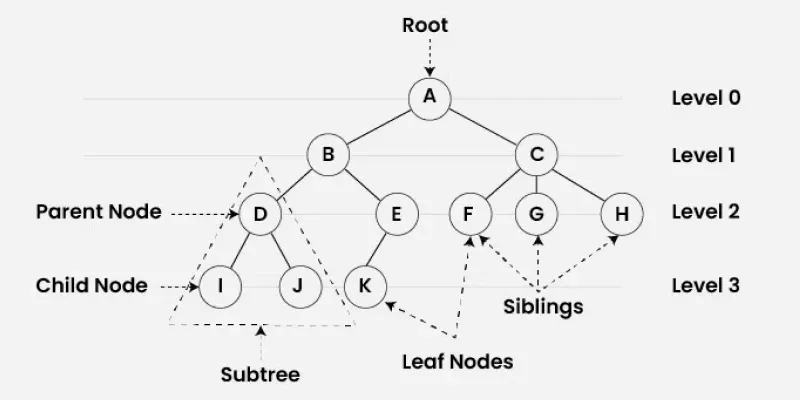
Tree는 비선형 구조로 원소들 간에 1:n 관계를 가지는 자료구조입니다. 상위 원소에서 하위 원소로 내려가면서 확장되는 트리(나무)모양의 구조이기 때문에, Tree라고 합니다.
-
개념:
-
계층적(hierarchical) 구조를 가지며, 최상위의 하나의 루트(root) 노드에서 시작해 여러 갈래(branch)를 거쳐 리프(leaf) 노드들로 뻗어 나가는 구조
-
루트를 제외한 모든 노드는 정확히 하나의 부모(parent) 노드로부터 오는 단 하나의 들어오는 간선(incoming edge)를 갖는다 (단방향)
-
루트에서 각 노드까지의 경로(path)는 유일하며, 이는 트리의 계층적 특성을 보장
-
-
정의:
한 개 이상의 노드로 이루어진 유한 집합이며, 다음 조건을 만족합니다.- 노드 중 최상위 노드를 루트(root)라 한다.
- 나머지 노드들은 n(n>=0)개의 분리 집합 T1, ..., TN으로 분리될 수 있다.
- 이들 T1, ..., TN 은 각각 하나의 트리가 되며(재귀적 정의) 루트의 부 트리(subtree)라 한다.
-
기본 용어 및 표기:
단어 뜻 노드(node) 트리를 구성하는 기본 단위로, 일반적으로 값을 나타내는 키(key)를 가짐엣지(edge) 두 노드를 연결하는 선(간선) 루트(root) 부모가 없는 최상위 노드 부모(parent)·자식(children) 어떤 노드 A에서 뻗어나간 엣지로 연결된 노드 B가 있을 때, A를 부모, B를 자식이라 함 형제(sibling) 같은 부모를 공유하는 노드들 경로(path) 여러 노드가 차례로 연결된 순서 부분트리(subtree) 트리 내의 어떤 노드와 그 아래로 뻗어 있는 모든 노드들로 이루어진 작은 트리 레벨(level) 루트가 0레벨, 그 자식들은 1레벨, ...과 같이 각 노드의 깊이를 나타냄 높이(height) 루트에서 가장 먼 리프 노드까지의 레벨
이진 트리(Binary Tree)
- 개념:
- 트리의 각 노드가 최대 두 개의 자식만 갖도록 제한한 것을 이진트리라고 함
- 이진 트리는 구현과 탐색 알고리즘이 단순해, 다양한 응용에 폭넓게 사용됨
- 트리 순회(Tree Traversal):
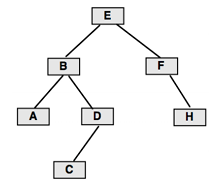
순회(Traversal)란, Tree의 각 노드를 중복되지 않게 전부 방문하는 것을 말합니다.
- Breadth first traversal:
- 같은 레벨을 먼저 순회
- E > B > F > A > D > H > C
- Depth first traversal:
- 최대한 깊게 순회
- Preorder(전위): root > left child > right child
- E > B > A > D > C > F > H
- Inorder(중위): left child > root > right child
- A > B > C > D > E > F > H
- Postorder(후위): left child > right child > root
- A > C > D > B > H > F > E
Priority Queues with Binary Heaps
핵심 개념
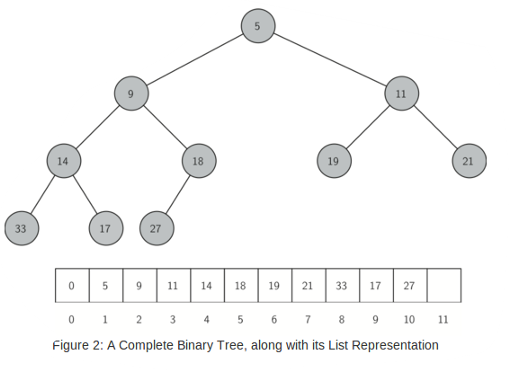
-
완전 이진 트리(Complete Binary Tree):
- 마지막 레벨을 제외한 모든 레벨이 꽉 차 있고, 마지막 레벨의 노드들은 왼쪽부터 채워짐
- 배열(리스트) 하나로 표현 가능
- 부모 인덱스
i - 왼쪽 자식
2*i - 오른쪽 자식
2*i+1 - (1-based indexing 기준)
- 부모 인덱스
-
힙 속성(Heap Order Property):
-
A가 B의 부모노드이면, A의 키값과 B의 키값 사이에는 항상 일정한 대소관계가 성립하는 것
-
키값의 대소관계는 오로지 부모노드와 자식노드 간에만 성립하며, 형제노드 사이에서는 일정한 대소관계가 정해지지 않음
-
최소 힙(min-heap): 부모의 키 <= 자식의 키
-
최대 힙(max-heap): 부모의 키 >= 자식의 키
-
Binary Heap ADT
-
데이터(Data):
변수 설명 currentSize 힙의 현재 크기 heapList 아이템을 저장할 리스트 -
기능(Operators):
연산 설명 시간 복잡도 isEmpty()힙이 비어 있는지 검사 size()요소(노드) 개수 반환 insert(key)새 키 삽입 후 up-heap 수행 deleteMin()루트 삭제 후 down-heap 수행 buildHeap(a)1-based 배열로 변환 후 각 내부 노드 down-heap
Priority Queue Implementation
-
isEmpty():
bool isEmpty() { return currentSize == 0; } -
size():
int size() { return currentSize; } -
insert(key):
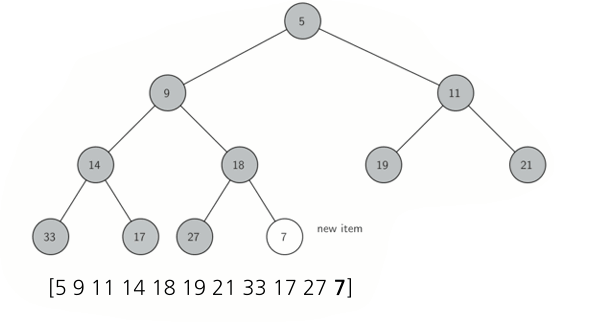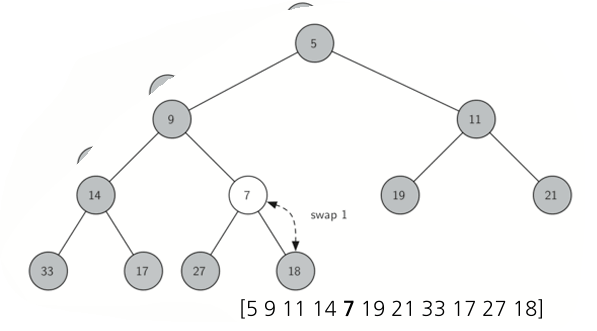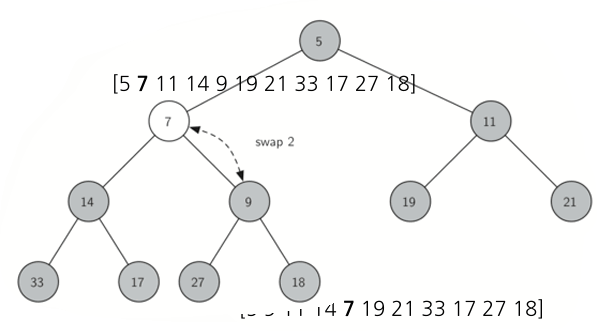
//새 키 삽입 후 up-heap 수행 bool insert(int key) { heapArray[++currentSize] = key; upHeap(currentSize); return true; } void upHeap(size_t idx) { while (idx > 1) { size_t parent = idx / 2; if (heapArray[parent] < heapArray[idx]) swap(heapArray[parent], heapArray[idx]); else break; idx = parent; } }- delMin():
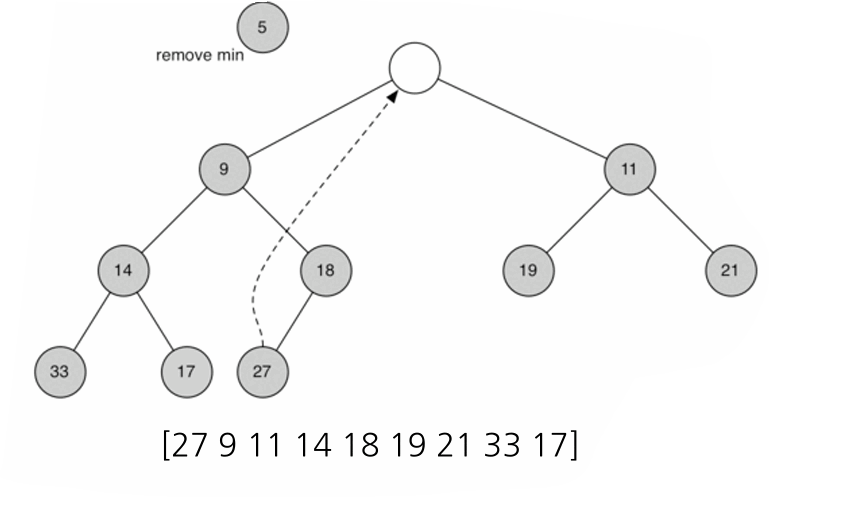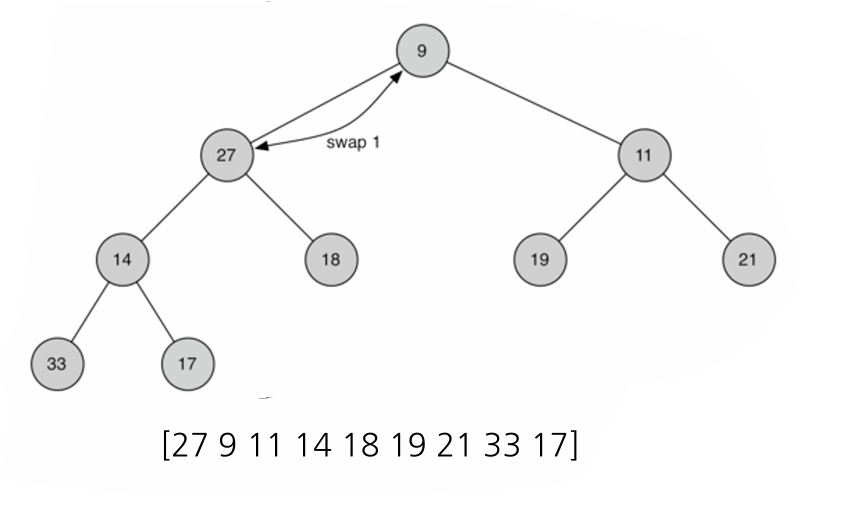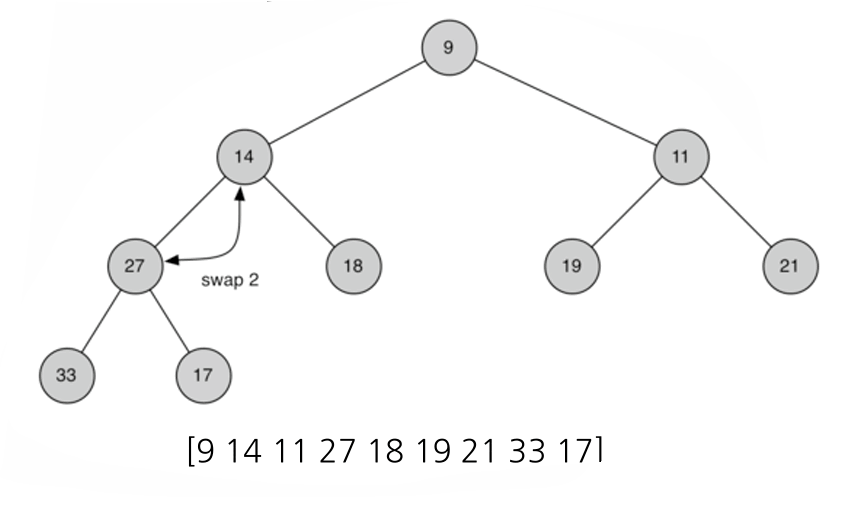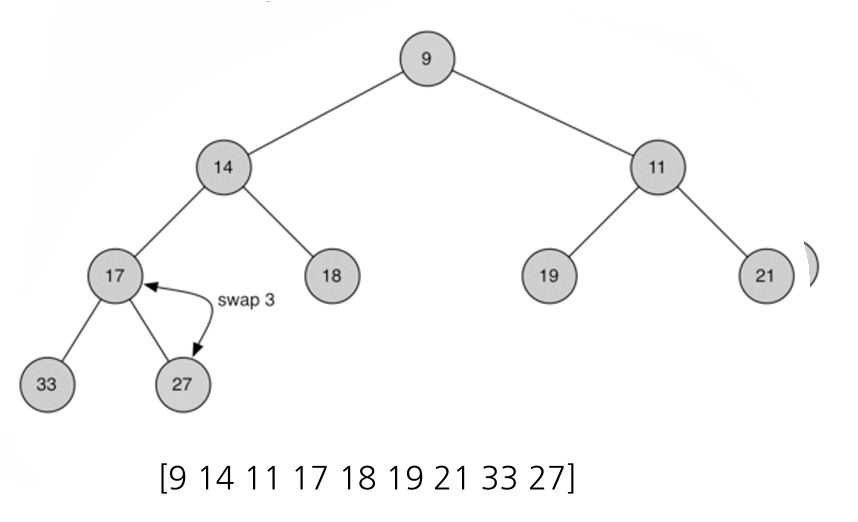
- delMin():
int delMin() {
int retval = heapList[1];
heapList[1] = heapList[currentSize];
currentSize--;
heapList.pop_back();
downHeap(1);
return retval;
}
void downHeap(int i) {
while (i * 2 <= currentSize) {
int mc = minChild(i);
if (heapList[i] > heapList[mc]) swap(heapList[i], heapList[mc]);
i = mc;
}
}- buildHeap(a):
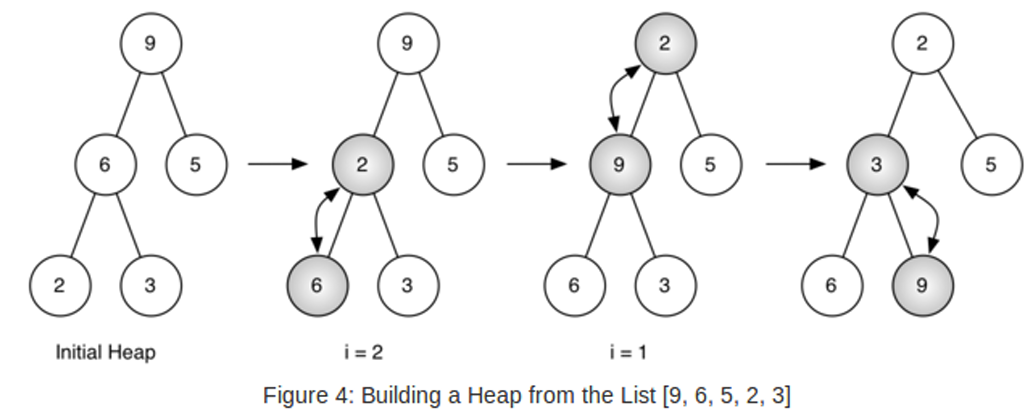
bool buildHeap(vector<int>& alist) {
currentSize = alist.size();
alist.insert(alist.begin(), 0);
heapList = alist;
// 마지막 부모 노드(n/2)부터 루트(1)까지
for (int i = alist.size() / 2; i > 0; i--) {
downHeap(i);
}
return true;
}(참고) max-heap 구현
class MaxHeap {
static constexpr size_t MAX_N = 100000; //힙 최대 사이즈 설정
size_t currentSize = 0;
int heapArray[MAX_N + 1] = { 0, };
void swap(int& a, int& b) { int tmp = a; a = b; b = tmp; }
void upHeap(size_t idx) {
while (idx > 1) {
size_t parent = idx / 2;
if (heapArray[parent] < heapArray[idx]) swap(heapArray[parent], heapArray[idx]);
else break;
idx = parent;
}
}
void downHeap() {
size_t parent = 1;
size_t large = parent;
size_t left = parent * 2;
size_t right = parent * 2 + 1;
while (1) {
if (left <= currentSize && heapArray[left] > heapArray[large]) large = left;
if (right <= currentSize && heapArray[right] > heapArray[large]) large = right;
//현재가 가장 크면 더 이상 down-heap을 하지 않음
if (large == parent) break;
else {
swap(heapArray[parent], heapArray[large]);
parent = large;
left = large * 2;
right = large * 2 + 1;
}
}
}
public:
MaxHeap() { memset(heapArray, 0, sizeof(heapArray)); }
//힙 사이즈 리턴
size_t size() { return currentSize; }
//새 키 삽입 후 up-heap 수행
bool insert(int key) { heapArray[++currentSize] = key; upHeap(currentSize); return true; }
//루트값 리턴(최댓값)
int top() { assert(currentSize != 0); return heapArray[1]; };
//루트값 삭제 후 down-heap 수행
bool pop() { assert(currentSize != 0); heapArray[1] = heapArray[currentSize--]; downHeap(); return true; }
};
출처
- 전공 강의
- GFG
