
1. 정의
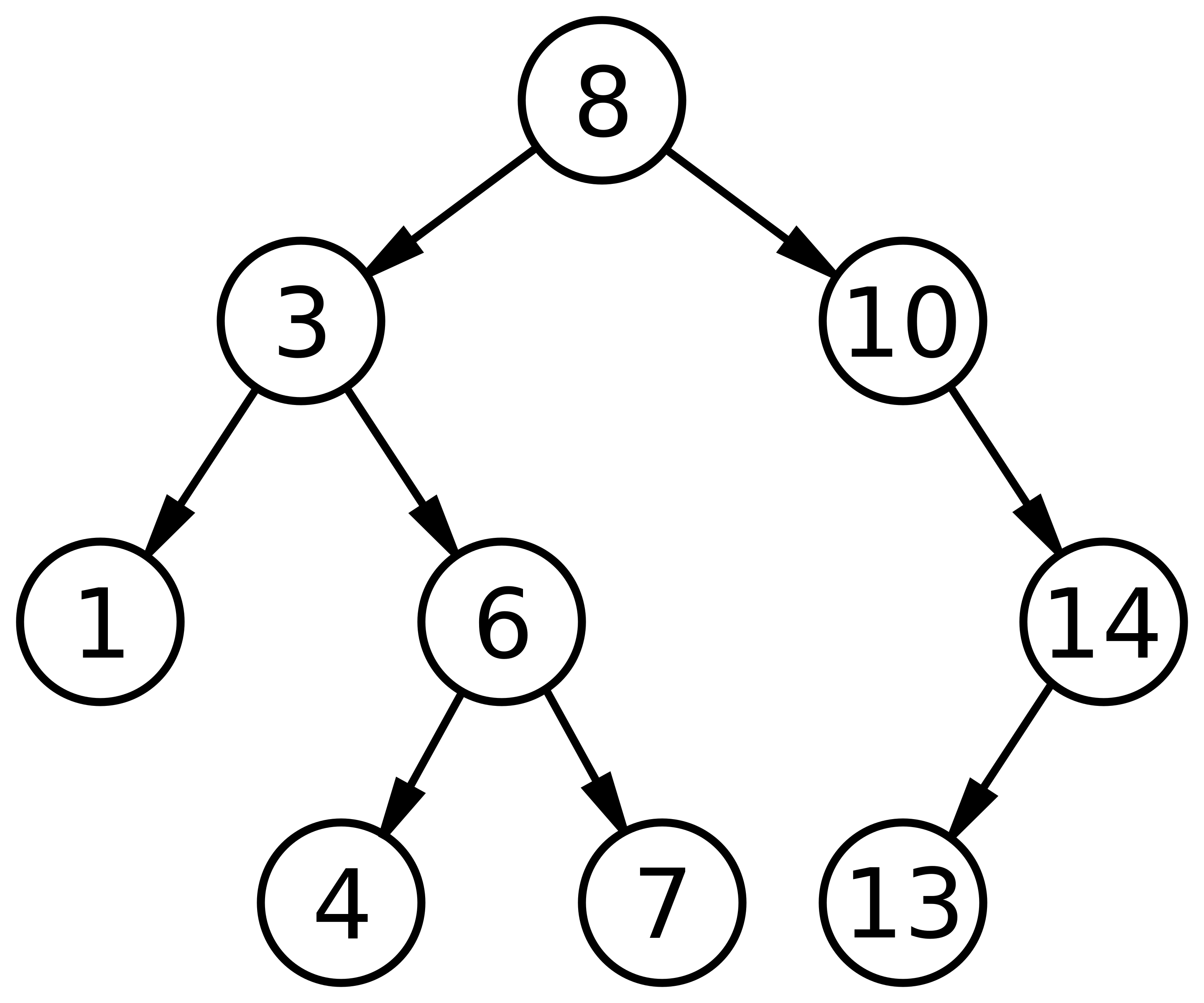
이진 탐색 트리(BST, Binary Search Tree)는 bst property를 만족하는 트리 자료구조입니다.
bst property란?
왼쪽 서브트리(sub tree)의 키 값 < 노드의 키 값 < 오른쪽 서브 트리(sub tree)의 키 값
2. 이진 탐색 트리의 ADT(Abstract Data Type)와 구현
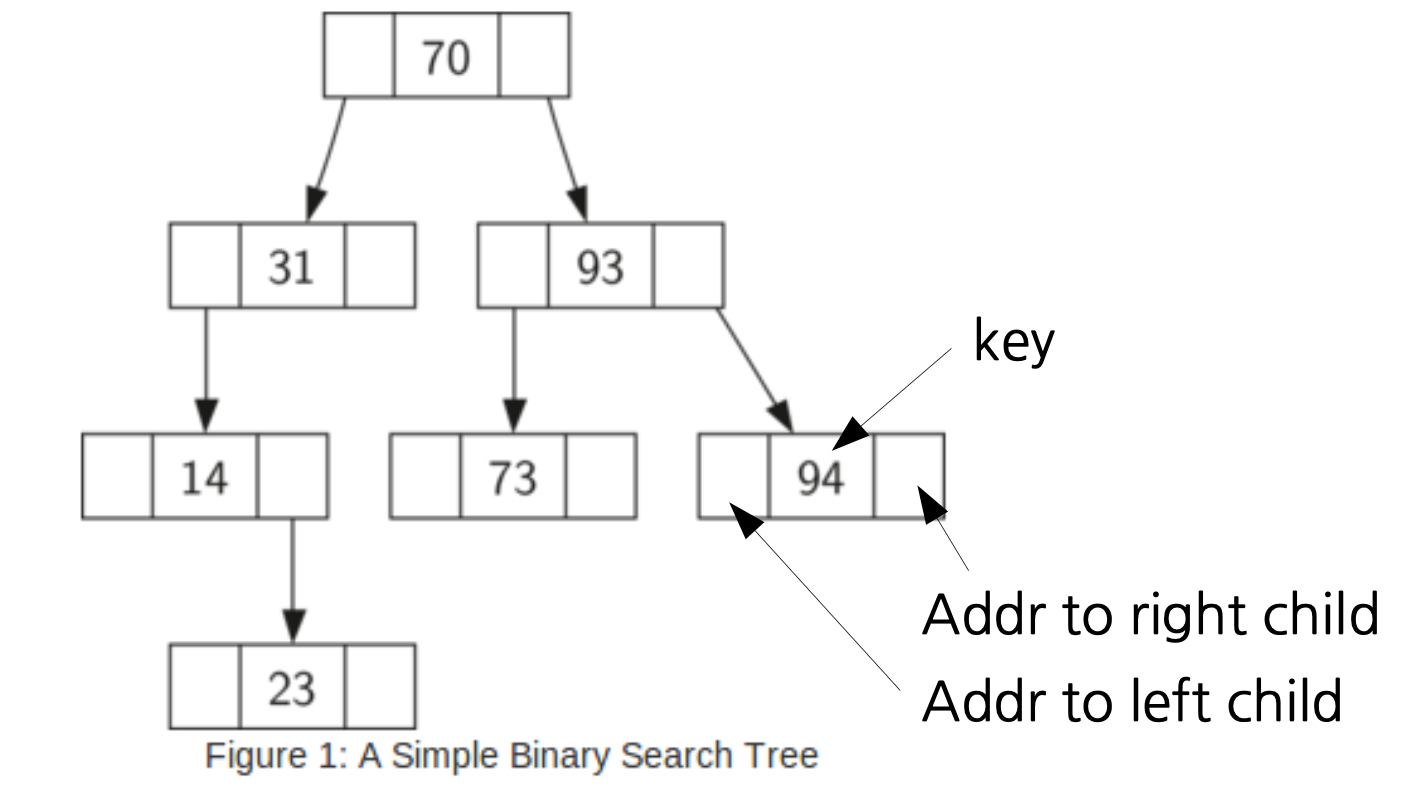
📦 데이터
key: 비교 연산을 수행하기 위해 사용하는 값 (중복되지 않아야 함)value: 키와 연관된 데이터 (필수는 아님)left: 왼쪽 자식 노드right: 오른쪽 자식 노드
따라서 다음과 같이 트리의 노드를 나타내는 구조체를 선언할 수 있습니다.
struct TreeNode
{
int key;
string value;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int k, string v)
{
key = k;
value = v;
left = nullptr;
right = nullptr;
}
};참고로 구조체도 클래스와 같이 생성자를 둘 수 있습니다.
⚙️ 연산
1. 삽입(Insert)
- 새로운 키가 부모 노드의 키보다 작으면 왼쪽 서브트리로 삽입
- 새로운 키가 부모 노드의 키보다 크면 오른쪽 서브트리로 삽입
트리 구조는 재귀적으로 서브트리에 접근하면 됩니다. 삽입하려는 키 값이 bst property를 만족하도록 노드를 이동합니다.
void Insert(TreeNode* cur, int key, string value)
{
// 왼쪽
if (key < cur->key)
{
if (cur->left == nullptr)
cur->left = new TreeNode(key, value);
else
Insert(cur->left, key, value);
}
// 오른쪽
else
{
if (cur->right == nullptr)
cur->right = new TreeNode(key, value);
else
Insert(cur->right, key, value);
}
}2. 탐색(Search)
- 현재 노드의 키와 탐색 키를 비교
- 탐색 키가 현재 노드의 키보다 작으면 왼쪽 서브트리 탐색
- 탐색 키가 현재 노드의 키보다 크면 오른쪽 서브트리 탐색
삽입 연산과 크게 다르지 않습니다. 이진 탐색을 하는 것처럼 노드를 이동합니다.
void Search(TreeNode* cur, int key)
{
if (key < cur->key)
{
if (cur->left == nullptr)
cout << "tree hasn't key : " << key << '\n';
else
Search(cur->left, key);
}
else if (key > cur->key)
{
if (cur->right == nullptr)
cout << "tree hasn't key : " << key << '\n';
else
Search(cur->right, key);
}
else
cout << "value : " << cur->value << '\n';
}3. 삭제(Delete)
삭제 연산은 노드를 삭제하고 서브 트리를 루트에 연결하는 작업이 필요합니다. 이때 노드를 삭제하는 세 가지 케이스가 있습니다.
- Case1 : 삭제할 노드가 리프 노드(자식이 없는 경우)
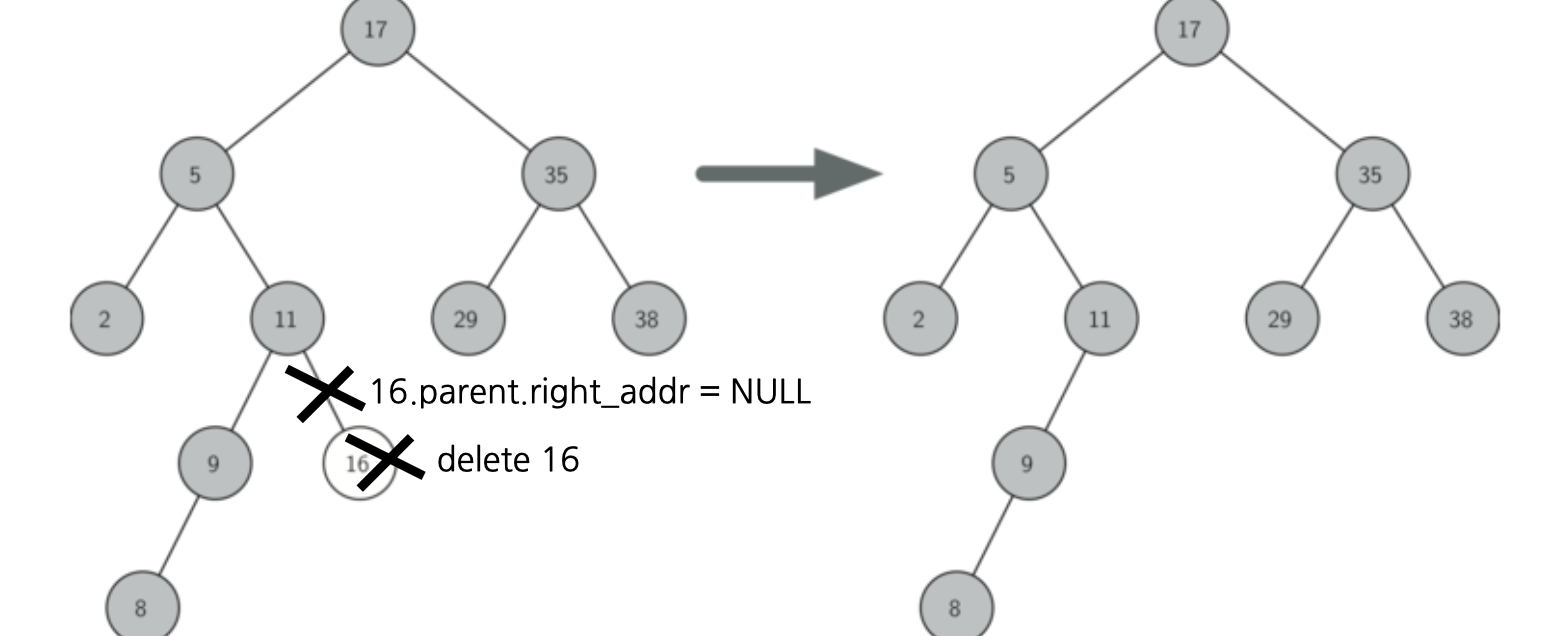
삭제하려는 노드를 delete(메모리 반납)하고, 해당 엣지(Edge)를 널(nullptr)로 초기화 합니다.
if (cur->left == nullptr && cur->right == nullptr)
{
// case1 : deletion of a node without children
// 그냥 삭제
delete cur;
return nullptr;
}- Case2 : 삭제할 노드가 자식 노드 하나만 있는 경우
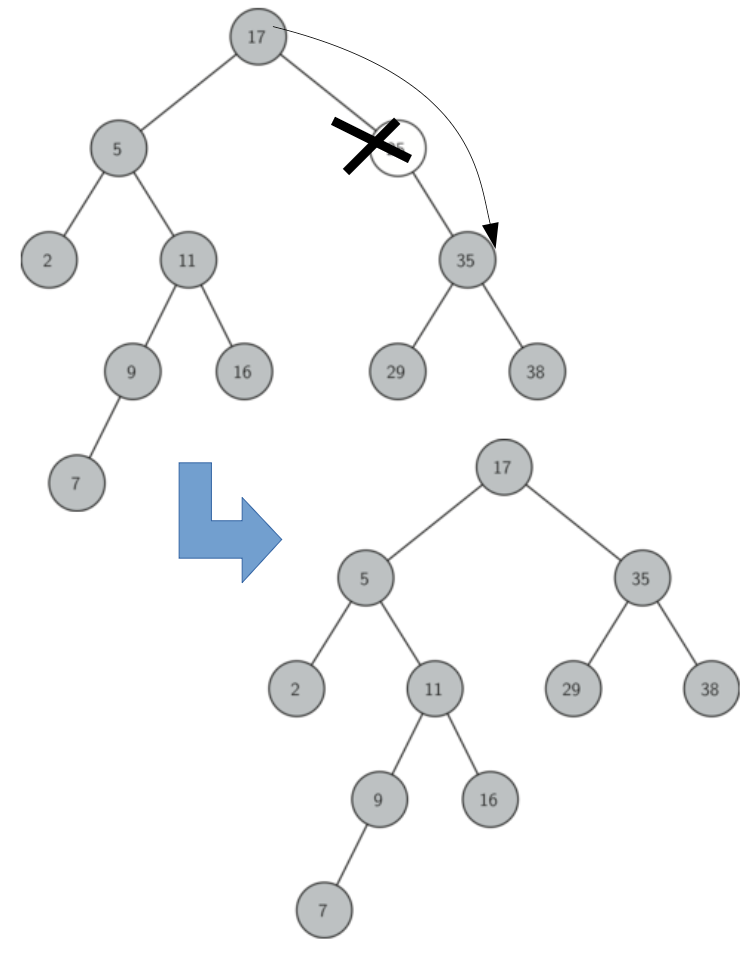
자식 노드를 현재 노드의 위치로 변경합니다. 위 그림에서는 17의right가 35를 가리키도록 재귀를 타고 목표 노드로 간 다음 35의 주소를 리턴합니다.
else if (cur->right == nullptr)
{
// case2 : deletion of a node with one child
// 왼쪽만 있는 경우
// 왼쪽을 부모 노드에 잇는다
TreeNode* tmp = cur->left;
delete cur;
return tmp;
}
else if (cur->left == nullptr)
{
// case2 : deletion of a node with one child
// 오른쪽만 있는 경우
// 오른쪽을 부모 노드에 잇는다
TreeNode* tmp = cur->right;
delete cur;
return tmp;
}- Case3 : 삭제할 노드가 자식 노드 두 개가 있는 경우
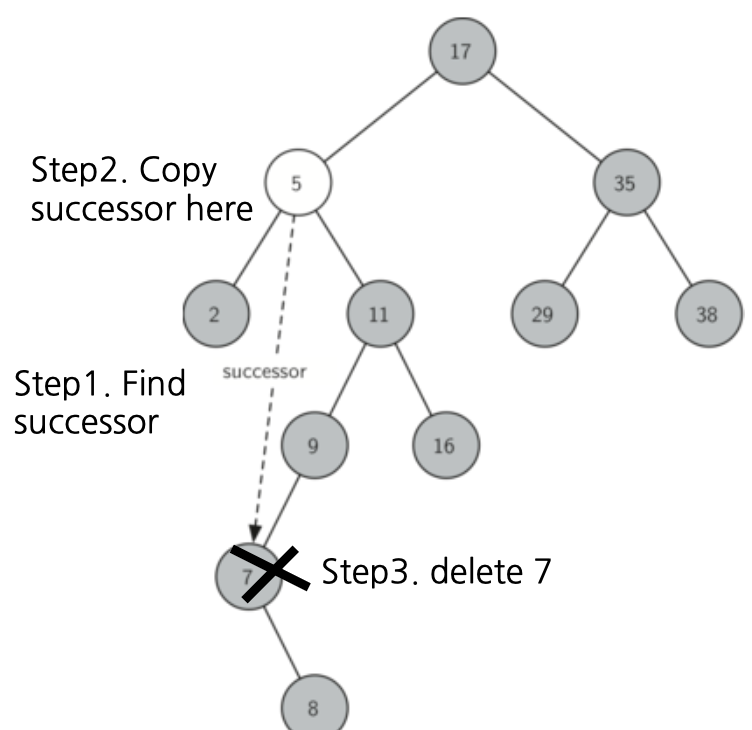
Step1. 후속자(Successor)를 찾습니다.
여기서 후속자는 오른쪽 서브트리에서 키 값이 가장 작은 노드입니다. 후속자는 키 값이 현재 노드의 left보다는 크고, right보다는 작은데, 항상 자식이 하나이거나 없습니다. 때문에 case1이나 case2의 프로세스대로 삭제를 수행할 수 있습니다.
Step2. 후속자의 key와 value를 삭제하고자 하는 노드로 복사합니다.
Step3. 후속자를 삭제합니다.
이 과정은 case1 또는 case2의 과정으로 완료될 수 있습니다.
else
{
// case3 : deletion of a node with two children
// Step1. Find the successor(Successor has one or no child)
// The minimal key node on the right subtree of the node to delete
// (or the maximal key node on the left subtree of the node to delete)
TreeNode* tmp = FindMin(cur->right);
// Step2. Copy of successor to the node to delete
cur->key = tmp->key; cur->value = tmp->value;
// Step3. Delete the successor
// This process can be done by deletion of case
cur->right = Delete(cur->right, tmp->key);
} 4. 최소값(Find Minimum)
트리에서 가장 작은 키를 가진 노드를 찾습니다. 왼쪽 자식이 없을 때, 해당 노드가 최소값입니다.
TreeNode* FindMin(TreeNode* root)
{
while (root->left != nullptr)
root = root->left;
return root;
}5. 최대값(Find Maximum)
트리에서 가장 큰 키를 가진 노드를 찾습니다. 오른쪽 자식이 없을 때, 해당 노드가 최대값입니다.
TreeNode* FindMax(TreeNode* root)
{
while (root->right != nullptr)
root = root->right;
return root;
}6. 중위 순회(Inorder Traversal)
트리를 중위 순회하여 정렬된 키를 반환합니다.
- 왼쪽 서브트리 -> 현재 노드 -> 오른쪽 서브트리
void Inorder(TreeNode* root)
{
Inorder(root->left);
cout << "key : " << root->key << " value : " << root->value << '\n';
Inorder(root->right);
}7. 높이 (Height)
트리의 높이를 반환합니다.
- 루트 노드에서 가장 깊은 리프 노드까지의 경로 길이를 반환
int getHeight(TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftSubTreeheight = getHeight(root->left);
int rightSubTreeheight = getHeight(root->right);
return max(leftSubTreeheight, rightSubTreeheight) + 1;
}
8. 노드 개수 계산 (Count Nodes)
트리의 총 노드 개수를 반환합니다.
int getLen(TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftSubTreeLen = getLen(root->left);
int rightSubTreeLen = getLen(root->right);
return leftSubTreeLen + rightSubTreeLen + 1;
}3. BST 복잡도 분석
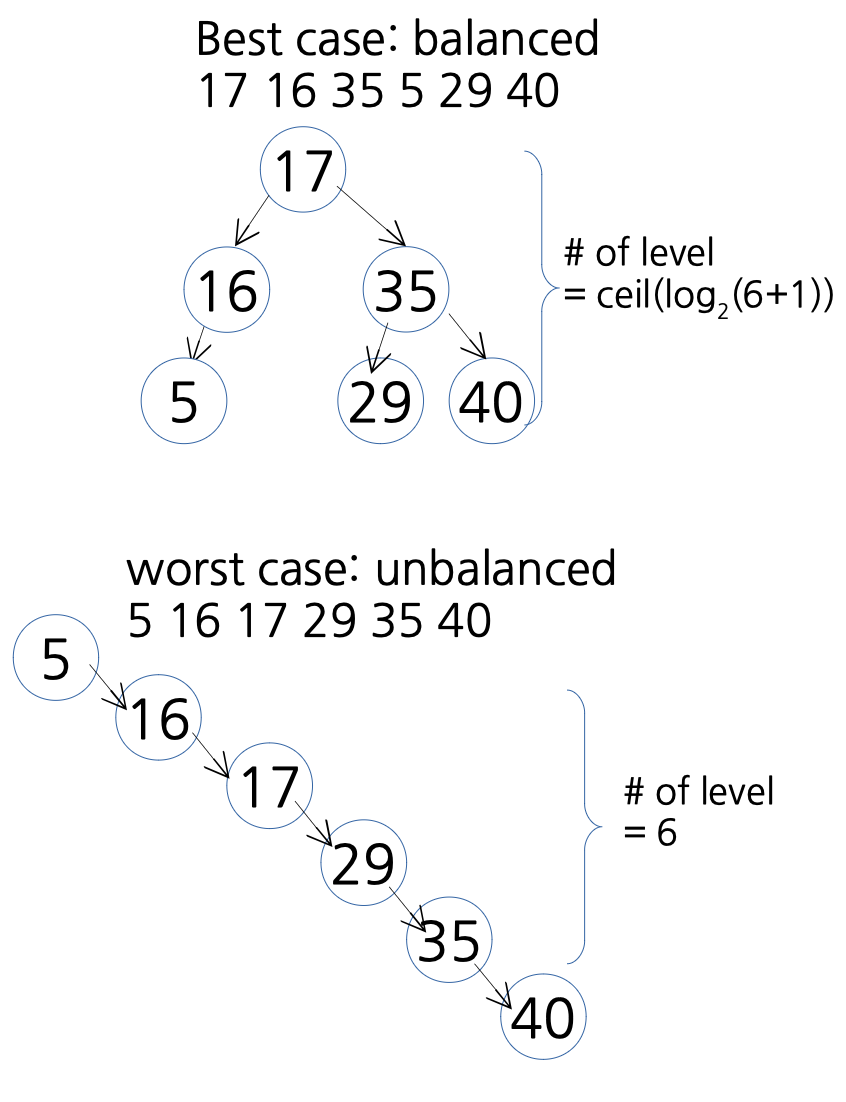
삽입(Insertion)의 복잡도 :
- Best :
- Wort :
탐색(Search)의 복잡도 :
- Best :
- Wort :
삭제(Deletion)의 복잡도 :
- Best :
- Wort :
의 시간복잡도로는 트리 자료구조를 사용하는데 이득이 없습니다. 시간복잡도를 으로 줄이기 위해, 균형 이진 탐색 트리(Balanced Binary Search Tree)가 존재합니다. 이는 다음 시간에 다뤄보도록 하겠습니다.
4. 전체 코드 및 테스트 코드
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
int key;
string value;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode(int k, string v)
{
key = k;
value = v;
left = nullptr;
right = nullptr;
}
};
void Insert(TreeNode* cur, int key, string value)
{
// 왼쪽
if (key < cur->key)
{
if (cur->left == nullptr)
cur->left = new TreeNode(key, value);
else
Insert(cur->left, key, value);
}
// 오른쪽
else
{
if (cur->right == nullptr)
cur->right = new TreeNode(key, value);
else
Insert(cur->right, key, value);
}
}
void Search(TreeNode* cur, int key)
{
if (key < cur->key)
{
if (cur->left == nullptr)
cout << "tree hasn't key : " << key << '\n';
else
Search(cur->left, key);
}
else if (key > cur->key)
{
if (cur->right == nullptr)
cout << "tree hasn't key : " << key << '\n';
else
Search(cur->right, key);
}
else
cout << "value : " << cur->value << '\n';
}
TreeNode* FindMin(TreeNode* root)
{
while (root->left != nullptr)
root = root->left;
return root;
}
TreeNode* FindMax(TreeNode* root)
{
while (root->right != nullptr)
root = root->right;
return root;
}
TreeNode* Delete(TreeNode* cur, int key)
{
if (cur == nullptr) {
cout << "tree hasn't key : " << key << '\n';
return cur;
}
if (key < cur->key)
cur->left = Delete(cur->left, key);
else if (key > cur->key)
cur->right = Delete(cur->right, key);
else
{
if (cur->left == nullptr && cur->right == nullptr)
{
// case1 : deletion of a node without children
// 그냥 삭제
delete cur;
return nullptr;
}
else if (cur->right == nullptr)
{
// case2 : deletion of a node with one child
// 왼쪽만 있는 경우
// 왼쪽을 부모 노드에 잇는다
TreeNode* tmp = cur->left;
delete cur;
return tmp;
}
else if (cur->left == nullptr)
{
// case2 : deletion of a node with one child
// 오른쪽만 있는 경우
// 오른쪽을 부모 노드에 잇는다
TreeNode* tmp = cur->right;
delete cur;
return tmp;
}
else
{
// case3 : deletion of a node with two children
// Step1. Find the successor(Successor has one or no child)
// The minimal key node on the right subtree of the node to delete
// (or the maximal key node on the left subtree of the node to delete)
TreeNode* tmp = FindMin(cur->right);
// Step2. Copy of successor to the node to delete
cur->key = tmp->key; cur->value = tmp->value;
// Step3. Delete the successor
// This process can be done by deletion of case
cur->right = Delete(cur->right, tmp->key);
}
}
return cur;
}
void Inorder(TreeNode* root)
{
Inorder(root->left);
cout << "key : " << root->key << " value : " << root->value << '\n';
Inorder(root->right);
}
int getHeight(TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftSubTreeheight = getHeight(root->left);
int rightSubTreeheight = getHeight(root->right);
return max(leftSubTreeheight, rightSubTreeheight) + 1;
}
int getLen(TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int leftSubTreeLen = getLen(root->left);
int rightSubTreeLen = getLen(root->right);
return leftSubTreeLen + rightSubTreeLen + 1;
}
int main()
{
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(8, "root");
Insert(root, 3, "뭘");
Insert(root, 10, "적을까");
Insert(root, 1, "뭐적지");
Insert(root, 6, "귀찮노");
Insert(root, 14, "음음");
Insert(root, 4, "아무거나");
Insert(root, 7, "뭐징");
Insert(root, 13, "ㅋㅋ");
Search(root, 13);
int len = getLen(root);
cout << "tree의 길이 : " << len << '\n';
int height = getHeight(root);
cout << "tree의 높이 : " << height << '\n';
Delete(root, 4);
len = getLen(root);
cout << "tree의 길이 : " << len << '\n';
height = getHeight(root);
cout << "tree의 높이 : " << height << '\n';
Delete(root, 7);
len = getLen(root);
cout << "tree의 길이 : " << len << '\n';
height = getHeight(root);
cout << "tree의 높이 : " << height << '\n';
Delete(root, 13);
len = getLen(root);
cout << "tree의 길이 : " << len << '\n';
height = getHeight(root);
cout << "tree의 높이 : " << height << '\n';
return 0;
}