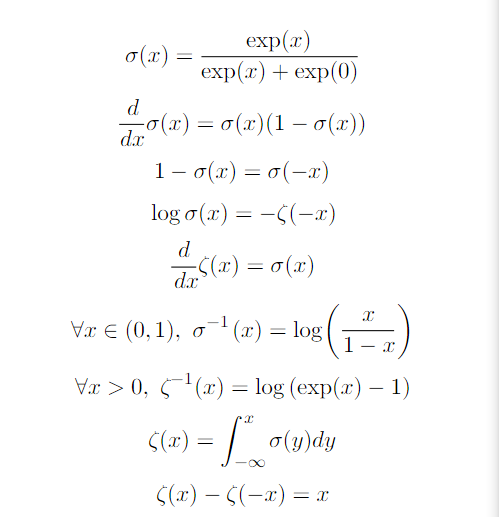Here, some common probability distributions that are useful in machine learning context are introduced.
Bernoulli Distribution
The Bernoulli distribution is a distribution over a single binary random variable.
A single binary random variable means that a variable has only two values, 0 and 1. The Bernoulli distribution has a single parameter φ which is the probability of X being equal to 1.
Properties of the Bernoulli Distribution
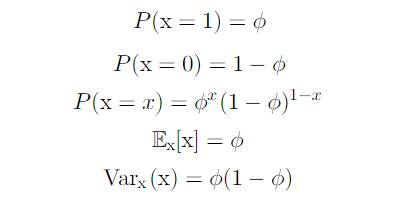
Multinoulli Distribution
The multinoulli distribution, also called the categorical distribution, is a distribution over a single discrete variable with k finite states. The probability of each state is seperately specified.
The multinoulli distribution is parametrized by a vector p.
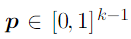
The probability of the k-th state is not in the vector but is given by
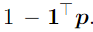
We do not usually need to compute the expectation or variance since multinoulli-distributed random variables often do not have numerical values.
It is easy to confuse the multinoulli distribution with the multinomial distribution.
The multinomial distribution is a distribution over vectors in {0, . . . , n}^k representing how many times each of the k categories is visited when n samples are drawn from a multinoulli distribution.
In other words, the multinomial distribution gives the probability of any particular combination of numbers of successes for the various categories for n independent trials, which leads to a success for exactly one of k categories, with each category having a given fixed success probability. The multinoulli distribution is a special case of the multinomial distribution where n = 1.
Gaussian Distribution
THe Gaussian distribution is also known as the normal distribution.
It is the most commonly used distribution over real numbers.
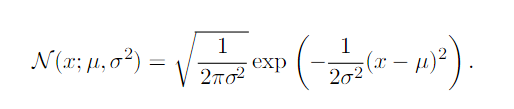
To efficiently evaluate the distribution, we use a parameter β to control the precision(inverse variance) of the distribution.
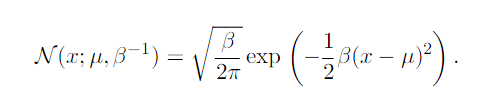
There are two reasons that the normal distribution is a good choice.
1) The central limit theorem shows that the sum of many independent random variables is approximately normally distributed.
2) Among the probability distributions with the same variance,the normal distribution encodes the maximum amount of uncertainty over the real numbers.
The multivariate normal distribution is the generalized version of the normal distribution with n random variables.
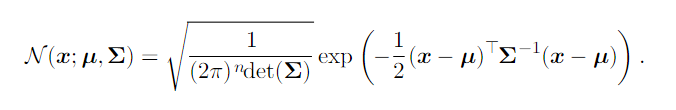
The parameter Σ, is the covariance matrix. To efficiently evaluate the distribution, we can use a precision matrix β instead, which is an inverse matrix of Σ.
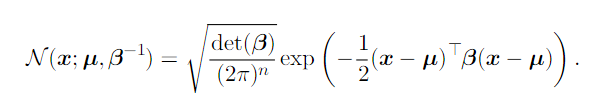
Exponential Distribution
The exponential distribution is the probability distribution of the time between events in a Poisson point process, i.e., a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate. It is a particular case of the gamma distribution.
The exponential distribution assigne probability of zero to all negative values of x.
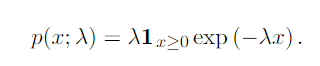
Laplace Distribution
The Laplace distribution, also called the double exponential distribution, has a sharp peak of probability mass at an arbitrary point µ. The difference between two independent identically distributed exponential random variables is governed by a Laplace distribution.
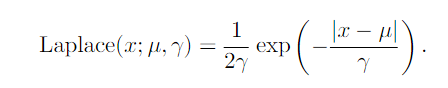
Dirac Distribution
The dirac distribution has all the mass clustered around a single point
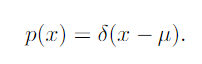
The Dirac delta function is a generalized function that is defined in terms of its properties when integrated. The Dirac delta function is the limit point of a series of functions that put less and less density on all points other than zero. In other words, it is zero valued everywhere except zero.
Empirical Distribution
The empirical distribution puts probability mass 1/m on each of the m points forming a given data set or collection of samples.
A common use of the Dirac delta distribution is as a component of an empirical distribution over continuous variables.
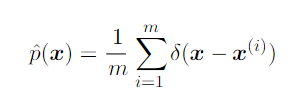
For discrete variables, an empirical distribution can be conceptualized as a multinoulli distribution with a probability associated with each possible input value that is simply equal to the empirical frequency of that value in the training set. The empirical distribution is the probability density that maximizes the likelihood of the training data.
Logistic Sigmoid Function
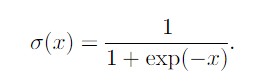
The logistic sigmoid is commonly used to produce the φ parameter of the Bernoulli distribution because its range is (0,1).
The sigmoid function saturates and kills gradients for a large positive/negative values, becoming insensitive to small changes in input.
Softplus Function
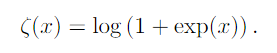
The softplus function can be used to produce β or σ because its range is (0,∞).
The softplus is a smooth, softened version of the positive part function ζ(x).
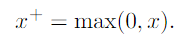 .
.
This is the counterpart of the negative part function ζ(−x).
Useful Properties