Analysis of Variance and Design of Experiments (2)
Randomized Block Design (RBD)
CRD와 달리, 실험에서 고려되지 않은 외부요인에 의한 변동을 제어
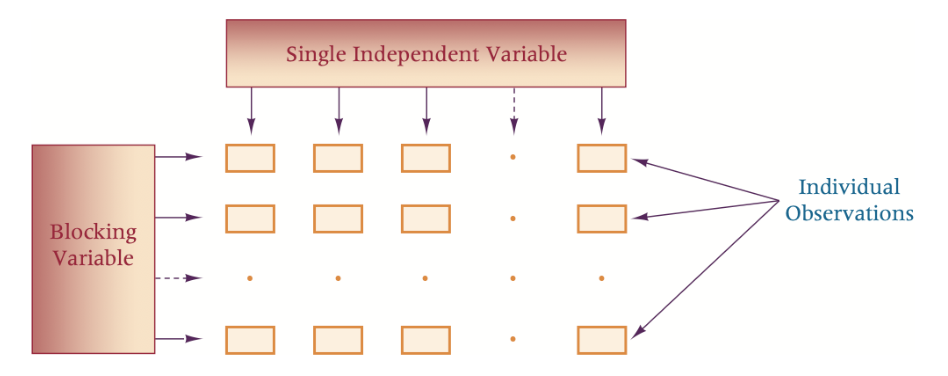
RBD includes a second variable, referred to as a blocking variable, that can be used to control for confounding (or concomitant) variable(교란 변수)
교란변수; Confounding (concomitant) variables: variables that are not being controlled by the analyst in the experiment, but can have an effect on the outcome of the treatment being studied
Blocking variable: a variable that the analyst wants to control, but is not the treatment variable of interest
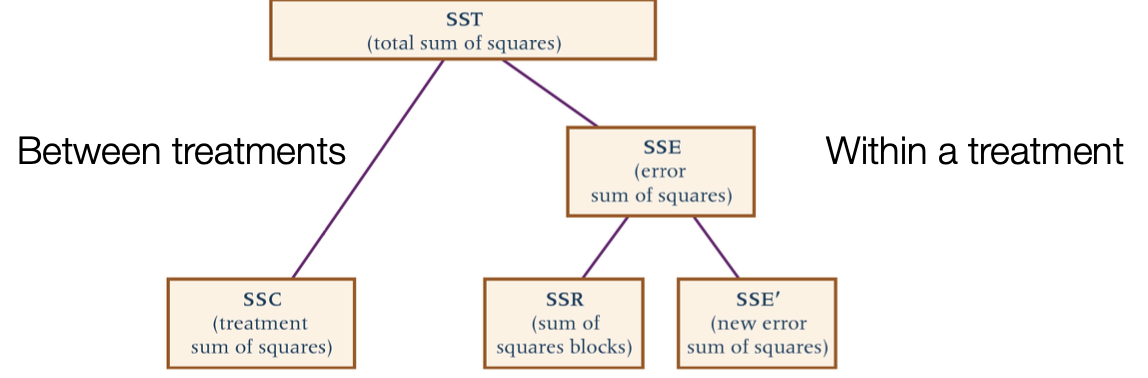
SSC=nj=1∑C(xˉj−xˉ)2SSR=Ci=1∑n(xˉi−xˉ)2SSE′=i=1∑nj=1∑C(xij−xˉj−xˉi+xˉ)2SST=i=1∑nj=1∑C(xij−xˉ)2
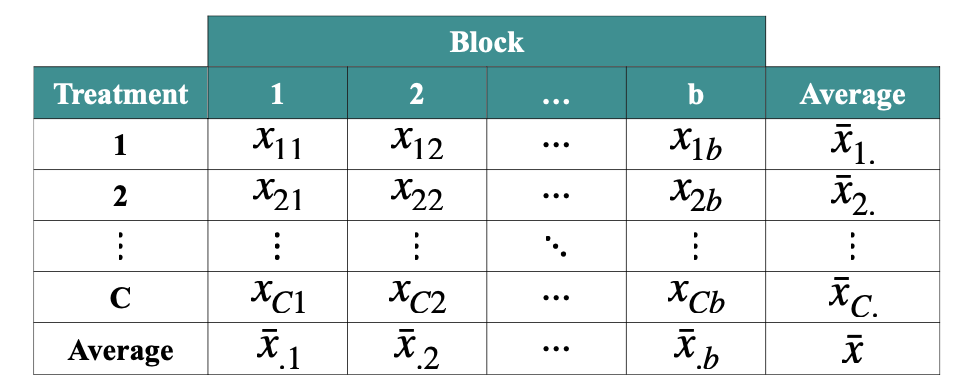
i : block group
j : treatment level
n : number of observations in each treatment level C : number of treatment levels
N=nC : total number of observations
xij : individual observation
xˉi : block mean
xˉj : treatment mean
xˉ : total mean
MSCMSRMSE′=C−1SSC=n−1SSR=N−n−C+1SSE′
Ftreatments Fblocks =MSE′MSC=MSE′MSR
Step 1.
가설을 2개 세운다.
Hypothesis for the treatment effect:
- H0: the mean value is identical for different treatments
- Ha: At least one of the treatment means is different from the others
Hypothesis for the blocking effect:
- H0: the mean value is identical for different blocks
- Ha: At least one of the blocking means is different from the others
Step 2.
compute observed values(SSE, SSR, SST, MSE, ... formula)
Step 3.
conclude the process
1) For treatment
observed value: Ft=MSE′MSC
critical value: Fα,C−1,(C−1)(b−1)=F0.01,2,8
Because the observed value of Ft is greater than the critical F value, the null hypothesis is rejected.
At least one of the population means of the treatment level is not the same as the others
2) For Blocking
observed value: Fb=MSE′MSB
critical value: Fα,b−1,(C−1)(b−1)=F0.01,4,8
Because the observed value of Fb is greater than the critical F value, the blocking effect is significant.
추가적으로, ANOVA table을 다음과 같이 작성할 수 있다.
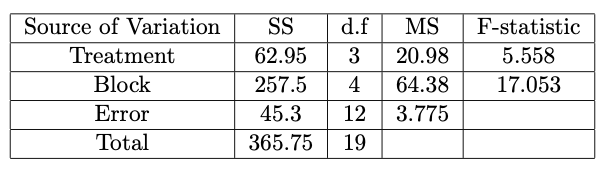
blocking 없는 F value는 F=MSEMSC로 구할 수 있다.
Two-way ANOVA
: test the effect of two independent variables (or factors) on one dependent variable
- 예를 들어, 하나 이상의 요인(factor: 자동차 등급과 제조사)에 의해 종속변수가 결정되는 경우
- Factorial: all possible combinations of the levels of the factors are investigated
- interaction effect를 고려해야 한다.
- 조건: Each sample must be i.i.d. from a normally distributed population / Each population must have the same variance
SSR=nCi=1∑R(xˉi−xˉ)2SSC=nRj=1∑C(xˉj−xˉ)2SSI=ni=1∑Rj=1∑C(xˉij−xˉi−xˉj+xˉ)2SSE=i=1∑Rj=1∑Ck=1∑n(xijk−xˉij)2SST=i=1∑Rj=1∑Ck=1∑n(xijk−xˉ)2
i : row treatment level
j : column treatment level
k : cell member
n : number of observations per cell
C : number of column treatments
R : number of row treatments
xijk : individual observation
xˉij : cell mean
xˉi : row mean
xˉj : column mean
xˉ : total mean
MSR=R−1SSRMSC=C−1SSCMSI=(R−1)(C−1)SSIMSE=RC(n−1)SSE
FR=MSEMSRFC=MSEMSCFI=MSEMSI
Two-way ANOVA: Table

ex. DATA
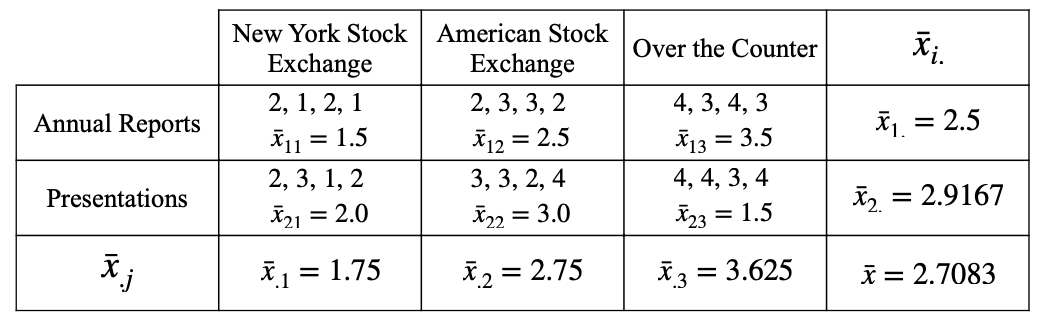
Step 1.
각 행/열에 대해 평균을 전부 구한다.
1) Test for interaction effect:
H0 : There is no interaction effect between Treatment 1 and Treatment 2.
Ha : There exists an interaction effect between Treatment 1 and Treatment 2.
2) Test for Treatment 1 effect:
H0 : μX=μY
Ha : At least one row mean is different.
3) Test for Treatment 2 effect:
H0 :μA=μB=μC=μD
Ha : At least one column mean is different.
Step 2.
observed values(formula)를 전부 구하고 two-way anova를 작성한다.
필요한 critical values:
FR=Fα,R−1,RC(n−1)
FC=Fα,C−1,RC(n−1)
FI=Fα,(R−1)(C−1),RC(n−1)
Step 3.
observed value < critical value: not significant, fail to reject H0
observed value > critical value: significant, reject H0
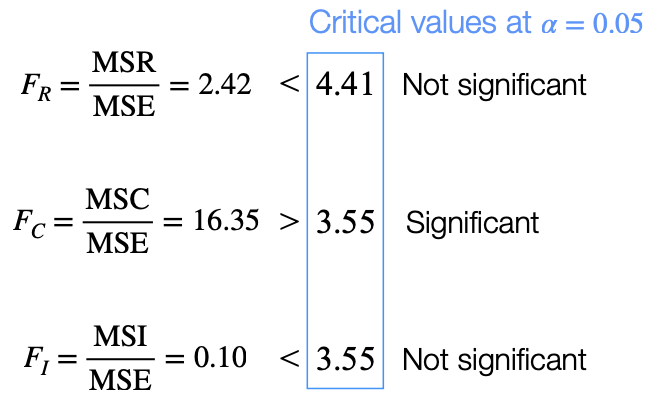
3개의 가설에 대해 H0 reject 할 수 있는지/ 가능하다면 significant different in means for Treatment i(또는 interaction effect) 라고 conclude한다.






