- 해당 블로그 포스트는 RAG From Scratch : Coursework
강의 파트 10 - 11 내용을 다루고 있습니다.
| 비디오 | 요약 | 강의 링크 | 슬라이드 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Part 10 (라우팅) | 쿼리를 관련 데이터 소스로 유도하기 위한 논리적 및 의미적 쿼리 라우팅을 다룹니다. | 📌 강의 | 📖 슬라이드 |
| Part 11 (쿼리 구조화) | 자연어 쿼리를 구조화된 쿼리로 변환하여 데이터베이스 상호작용을 효율화하는 방법을 다룹니다. | 📌 강의 | 📖 참고자료 |
Part 10 (라우팅)
-
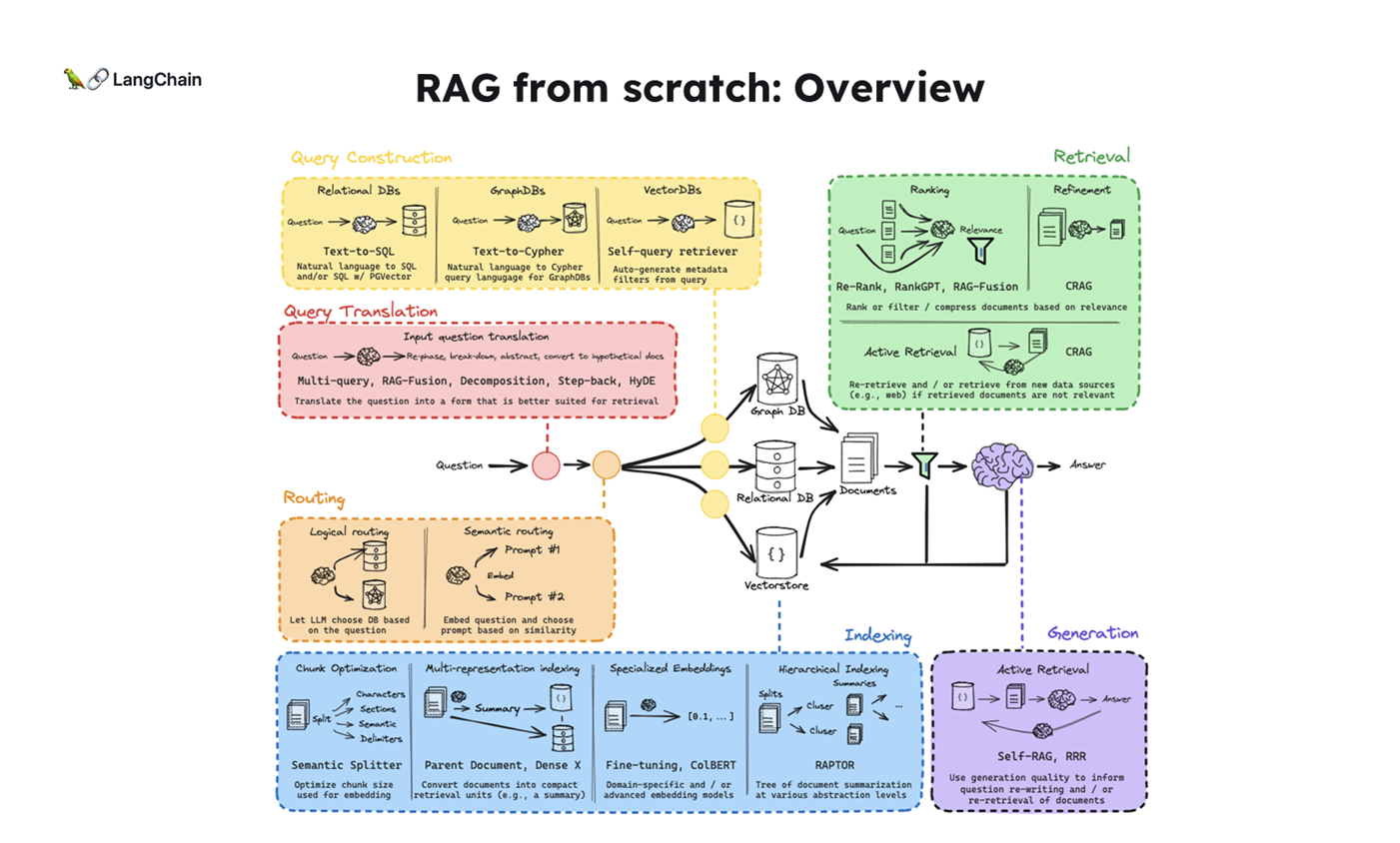
위 그림의 단계에 따라 각 과정의 역할과 개념을 간략하게 설명하겠습니다:
-
Question (질문) : 사용자가 시스템에 입력하는 자연어 형태의 질문입니다. 이는 전체 프로세스의 시작점이 됩니다.
-
Query Translation (쿼리 번역) : 사용자의 자연어 질문을 시스템이 이해할 수 있는 형식으로 변환하는 과정입니다. 이는 자연어 처리 기술을 활용하여 수행됩니다.
-
Routing (라우팅, 이번 챕터📌) : 변환된 쿼리를 적절한 처리 경로나 데이터 소스로 안내하는 과정입니다. 질문의 특성에 따라 최적의 처리 방법을 결정합니다.
-
Query Construction (쿼리 구성) : 라우팅된 정보를 바탕으로 실제 데이터베이스나 검색 엔진에서 사용할 수 있는 형태의 쿼리를 구성합니다.
-
Indexing (인덱싱) : 데이터베이스나 문서 컬렉션에서 효율적인 검색을 위해 데이터를 구조화하고 조직화하는 과정입니다. 이는 주로 시스템 구축 단계에서 수행됩니다.
-
Retrieval (검색) : 구성된 쿼리를 사용하여 인덱싱된 데이터에서 관련 정보를 추출하는 과정입니다. 이 단계에서 질문과 가장 관련성 높은 정보를 찾아냅니다.
-
Generation (생성) : 검색된 정보를 바탕으로 질문에 대한 답변을 생성하는 과정입니다. 이 단계에서는 주로 자연어 생성 기술이 사용됩니다.
-
Answer (답변) : 최종적으로 생성된 답변을 사용자에게 제공합니다. 이는 원래 질문에 대한 응답으로, 자연어 형태로 표현됩니다.
-
-
이 과정은 질문 응답 시스템의 전형적인 파이프라인을 나타내며, 각 단계는 사용자의 질문에 대해 정확하고 관련성 높은 답변을 제공하기 위해 유기적으로 작동합니다.
-
이번 강의는 3. Routing(라우팅)이라는 개념을 설명하고, 두 가지 주요 라우팅 방법인 ① 논리적 라우팅(Logical Routing)과 ② 의미적 라우팅(Semantic Routing)을 다룹니다.
1. 라우팅 개념
-
라우팅(Routing)은 질문을 적절한 데이터 소스로 전달하는 프로세스를 의미합니다.
- RAG(질문-답변 생성 모델)에서 라우팅은 특정 질문을 처리하기 위해 적절한 데이터베이스나 프롬프트에 연결하는 역할을 합니다.
-
다르게 정의해본다면, 라우팅을 아래와 같이 정의해볼 수 있습니다:
정의: 입력된 쿼리나 작업을 적절한 모델이나 처리 경로로 안내하는 과정입니다.목적: 주어진 입력에 가장 적합한 LLM이나 처리 모듈을 선택합니다.작동 방식: 입력의 특성을 분석하여 미리 정의된 규칙이나 학습된 알고리즘을 통해 최적의 처리 경로를 결정합니다.적용: 다양한 LLM을 효율적으로 활용하거나, 특정 도메인에 특화된 모델로 쿼리를 전달하는 데 사용됩니다.
-
예시 시나리오: 사용자가 코딩 관련 질문을 할 때, 시스템은 그 질문을 적절한 프로그래밍 언어 문서(예: Python, JS, Golang)로 라우팅하는 것입니다.
-
라우팅 방법은 크게
논리적 라우팅(Logical Routing)과의미적 라우팅(Semantic Routing)으로 나눌 수 있습니다. 이 두 방법은 다음과 같이 정의되고 구분됩니다:
2.1. 논리적 라우팅 (Logical Routing) 설명
논리적 라우팅 개념
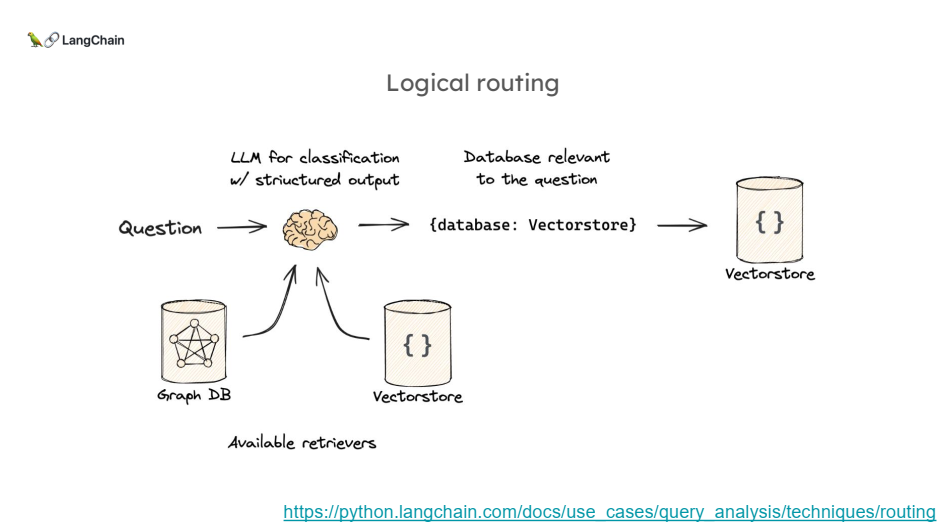
- 논리적 라우팅은 시스템이 다양한 데이터 소스 중 어떤 소스를 사용할지 미리 설정된 규칙에 따라 결정하는 방식입니다.
- 사용자가 질문을 입력하면 LLM(Large Language Model)은 그 질문이 어느 데이터베이스나 문서 소스와 가장 관련이 있는지 결정하고, 해당 소스로 라우팅하여 답변을 생성합니다.
특징
- 주로 "구조화된 출력"을 사용하여 라우팅을 수행합니다. 즉, 시스템은 질문을 미리 정의된 규칙에 따라 분류하고 그에 맞는 데이터 소스를 선택합니다.
- 질문이 명확히 구분 가능한 주제나 데이터베이스와 관련이 있을 때 매우 적합한 방법입니다.
과정
1. 사용자가 질문을 입력합니다.
2. LLM이 그 질문을 분석하여 미리 설정된 데이터 소스 목록(예: Python 문서, JS 문서 등) 중에서 가장 적합한 소스를 결정합니다.
3. 선택된 데이터 소스를 바탕으로 답변을 생성합니다.
코드 설명
from typing import Literal
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
# Data model
class RouteQuery(BaseModel):
"""Route a user query to the most relevant datasource."""
datasource: Literal["python_docs", "js_docs", "golang_docs"] = Field(
..., description="Given a user question choose which datasource would be most relevant for answering their question",
)
# LLM with function call
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0125", temperature=0)
structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(RouteQuery)
# Prompt 정의
system = """
You are an expert at routing a user question to the appropriate data source.
Based on the programming language the question is referring to, route it to the relevant data source.
"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[("system", system), ("human", "{question}")])
# Define router
router = prompt | structured_llmRouteQuery는 사용자 질문을 적절한 데이터 소스로 라우팅하기 위해 미리 정의된datasource옵션을 포함하는 클래스입니다.Field(...)에서 ...은 Python의 pydantic 라이브러리에서 사용되는 특별한 표현으로, 필드를 필수 필드로 지정하는 것을 의미합니다.- 위 코드에서 datasource 필드는 필수로 제공되어야 하며, 값이 없다면 모델 인스턴스를 생성할 때 오류가 발생합니다.
structured_llm은 LLM이 구조화된 출력 형식을 사용하도록 설정된 LLM입니다.prompt는 시스템이 질문을 처리하고 데이터 소스를 결정하는 방법을 정의하는 템플릿입니다.
# 질문 예시
question = """
Why doesn't the following code work:
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(["human", "speak in {language}"])
prompt.invoke("french")
"""
# LLM이 질문을 분석하여 적절한 데이터 소스를 반환
result = router.invoke({"question": question})result에는 RouteQuery(datasource='python_docs')값이 들어가 있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.- 사용자는 Python 코드와 관련된 질문을 입력했습니다. (question)
- LLM은 미리 설정된 지침에 따라 질문을 분석합니다. (router.invoke({"question": question}))
- LLM은 질문의 맥락이 Python과 관련되어 있음을 감지하고, (router = prompt | structured_llm)
- RouteQuery(datasource='python_docs')라는 구조화된 출력을 생성하여 적절한 데이터 소스를 반환합니다.
# 선택된 데이터 소스에 따라 추가적인 처리 수행
def choose_route(result):
if "python_docs" in result.datasource.lower():
return "chain for python_docs"
elif "js_docs" in result.datasource.lower():
return "chain for js_docs"
else:
return "chain for golang_docs"
# 최종적으로 선택된 경로에 따라 라우팅
full_chain = router | RunnableLambda(choose_route)
full_chain.invoke({"question": question}) # 'chain for python_docs'choose_route()함수는 반환된 데이터 소스를 기반으로 다음 단계에서 어떤 처리를 할지 결정합니다.- 이 예시에서 사용자는 질문을 입력하고, 시스템은 이를 분석하여 적절한 데이터 소스를 선택합니다. 예를 들어, Python과 관련된 질문이라면
python_docs로 라우팅됩니다.
- 이 예시에서 사용자는 질문을 입력하고, 시스템은 이를 분석하여 적절한 데이터 소스를 선택합니다. 예를 들어, Python과 관련된 질문이라면
2.2. 의미적 라우팅 (Semantic Routing) 설명
의미적 라우팅 개념
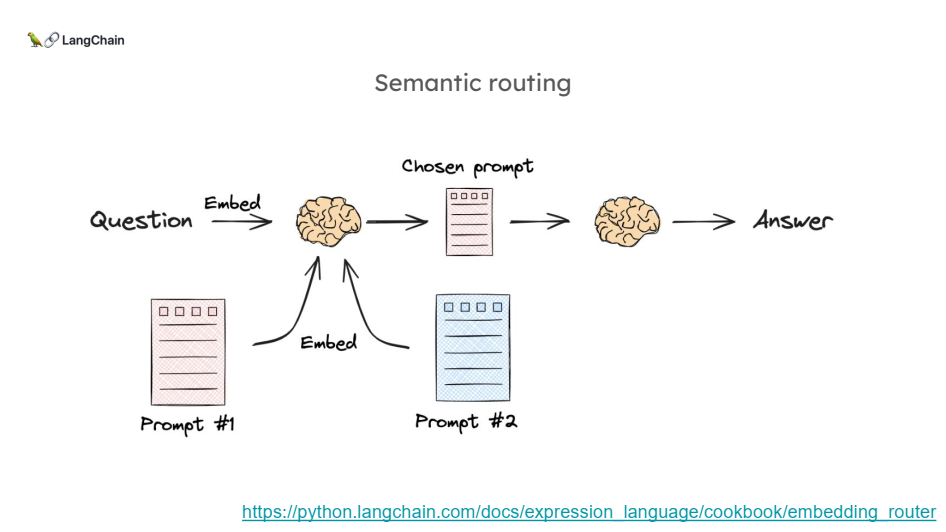
- 의미적 라우팅은 질문과 여러 프롬프트 간의 의미적 유사성을 기반으로 적합한 프롬프트를 선택하는 방식입니다.
- 여기서 질문과 프롬프트는 임베딩(벡터화)된 후 유사도를 계산하여, 가장 유사한 프롬프트를 선택합니다.
특징
- 질문과 프롬프트 간의 의미적 유사성을 바탕으로 라우팅을 수행합니다.
- 미리 정의된 데이터베이스가 아니라, 질문의 의미를 파악해 가장 적합한 프롬프트를 선택하는 방식입니다.
- 질문이 단순한 정보 조회가 아니라, 의미적으로 유사한 여러 가능성을 고려해야 할 때 적합합니다.
과정
1. 사용자가 질문을 입력하면 시스템이 그 질문을 임베딩(벡터화)합니다.
2. 시스템은 여러 프롬프트 중에서 질문과 가장 유사한 프롬프트를 선택합니다.
3. 선택된 프롬프트에 따라 답변을 제공합니다.
코드 설명
from langchain.utils.math import cosine_similarity
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambda, RunnablePassthrough
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
# 두 가지 프롬프트 정의
physics_template = """You are a very smart physics professor. \
You are great at answering questions about physics in a concise and easy to understand manner. \
When you don't know the answer to a question you admit that you don't know.
Here is a question:
{query}"""
math_template = """You are a very good mathematician. You are great at answering math questions. \
You are so good because you are able to break down hard problems into their component parts, \
answer the component parts, and then put them together to answer the broader question.- 물리학 프롬프트와 수학 프롬프트 두 가지가 주어지며, 시스템이 질문을 분석한 후 적합한 프롬프트를 선택합니다.
Here is a question:
{query}"""
# 프롬프트 임베딩
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
prompt_templates = [physics_template, math_template]
prompt_embeddings = embeddings.embed_documents(prompt_templates)OpenAIEmbeddings()를 사용하여 질문과 프롬프트를 임베딩합니다.cosine_similarity()함수를 사용하여 질문과 프롬프트 간의 유사도를 계산하고, 가장 유사한 프롬프트를 선택합니다.
# 질문을 적합한 프롬프트로 라우팅
def prompt_router(input):
query_embedding = embeddings.embed_query(input["query"])
similarity = cosine_similarity([query_embedding], prompt_embeddings)[0]
most_similar = prompt_templates[similarity.argmax()]
print("Using MATH" if most_similar == math_template else "Using PHYSICS")
return PromptTemplate.from_template(most_similar)
chain = (
{"query": RunnablePassthrough()}
| RunnableLambda(prompt_router)
| ChatOpenAI()
| StrOutputParser()
)
print(chain.invoke("What's a black hole"))- 시스템은 선택된 프롬프트를 기반으로 답변을 제공합니다.
- 예를 들어, 질문이 "블랙홀은 무엇인가?"라면 아래와 같이 물리학 관련 프롬프트가 선택되고 답변을 제공하게 됩니다.
Using PHYSICS
A black hole is a region in space where the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape from it. This occurs because a significant amount of mass has been compressed into a very small area.
The boundary around a black hole is called the event horizon, and once something crosses this boundary, it cannot escape. Black holes can be formed from the remnants of massive stars that have ended their life cycles in a supernova explosion and collapsed under their own gravity.
They are fascinating objects that challenge our understanding of physics, particularly in the realms of general relativity and quantum mechanics.(정리) 논리적 라우팅 vs 의미적 라우팅 비교
| 구분 | 논리적 라우팅 (Logical Routing) | 의미적 라우팅 (Semantic Routing) |
|---|---|---|
| 라우팅 기준 | 미리 정의된 데이터 소스 목록에 기반 | 질문과 프롬프트 간의 의미적 유사성에 기반 |
| 데이터 소스 선택 | LLM이 데이터 소스 목록에서 적합한 소스를 선택 | 질문의 의미를 분석해 가장 유사한 프롬프트나 데이터를 선택 |
| 주요 활용 | 데이터 소스나 자료가 명확히 구분되어 있는 경우 사용 | 다양한 의미를 포함하는 질문에 대해 유연한 답변 제공 |
| 실제 예시 | 프로그래밍 문서, 라이브러리 문서 등 특정 주제의 DB | 특정 도메인에 관련된 여러 의미가 혼재된 질문에 대한 답변 선택 |
| 적합한 상황 | 질문이 어느 DB에서 처리될지 미리 명확한 경우 | 질문이 다양한 의미로 해석될 수 있을 때 적합 |
- 위 테이블 비교를 통해,
- 논리적 라우팅은 미리 설정된 규칙에 따라 적절한 데이터 소스를 선택하는 반면,
- 의미적 라우팅은 질문의 의미적 유사성을 기반으로 라우팅이 이루어진다는 차이점을 이해할 수 있습니다.
Part 11 (쿼리 구조화)
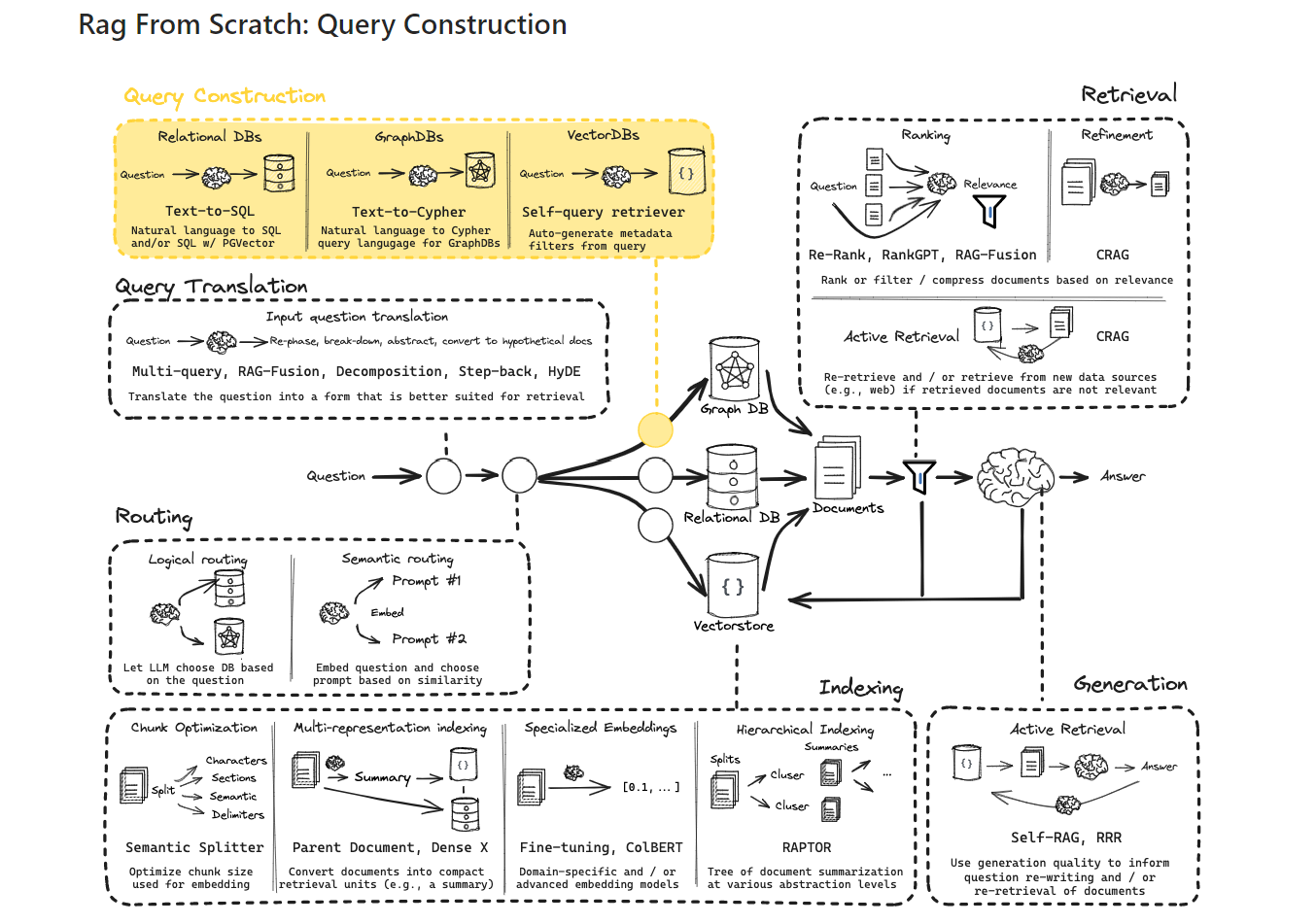
-
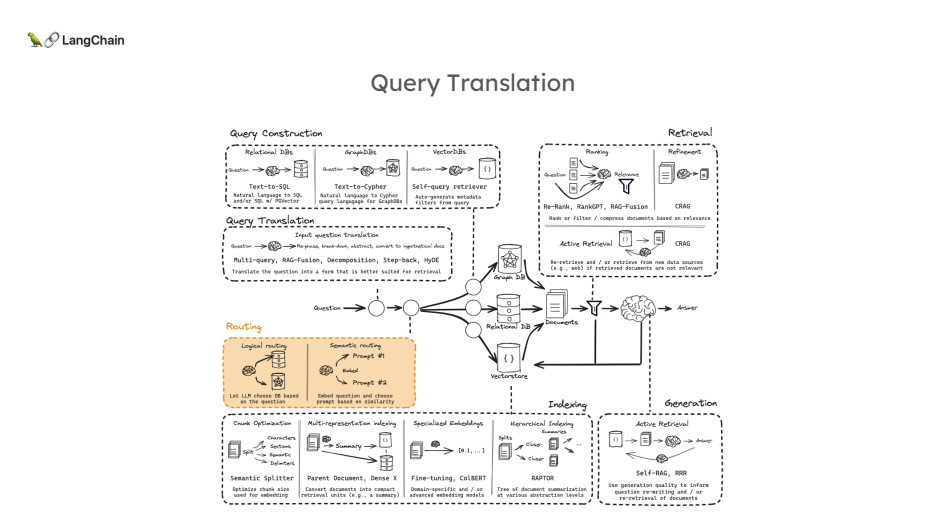
위 그림의 단계에 따라 각 과정의 역할과 개념을 간략하게 설명하겠습니다:
-
Question (질문) : 사용자가 시스템에 입력하는 자연어 형태의 질문입니다. 이는 전체 프로세스의 시작점이 됩니다.
-
Query Translation (쿼리 번역) : 사용자의 자연어 질문을 시스템이 이해할 수 있는 형식으로 변환하는 과정입니다. 이는 자연어 처리 기술을 활용하여 수행됩니다.
-
Routing (라우팅) : 변환된 쿼리를 적절한 처리 경로나 데이터 소스로 안내하는 과정입니다. 질문의 특성에 따라 최적의 처리 방법을 결정합니다.
-
Query Construction (쿼리 구성, 이번 챕터📌) : 라우팅된 정보를 바탕으로 실제 데이터베이스나 검색 엔진에서 사용할 수 있는 형태의 쿼리를 구성합니다.
-
Indexing (인덱싱) : 데이터베이스나 문서 컬렉션에서 효율적인 검색을 위해 데이터를 구조화하고 조직화하는 과정입니다. 이는 주로 시스템 구축 단계에서 수행됩니다.
-
Retrieval (검색) : 구성된 쿼리를 사용하여 인덱싱된 데이터에서 관련 정보를 추출하는 과정입니다. 이 단계에서 질문과 가장 관련성 높은 정보를 찾아냅니다.
-
Generation (생성) : 검색된 정보를 바탕으로 질문에 대한 답변을 생성하는 과정입니다. 이 단계에서는 주로 자연어 생성 기술이 사용됩니다.
-
Answer (답변) : 최종적으로 생성된 답변을 사용자에게 제공합니다. 이는 원래 질문에 대한 응답으로, 자연어 형태로 표현됩니다.
-
-
이번 강의에서는 Query Construction (or Structuring)(쿼리 구조화)에 대해 다룹니다. 쿼리 구조화는 자연어로 된 질문을 특정 데이터베이스나 도메인에 맞는 구조화된 쿼리로 변환하는 과정을 설명합니다. 특히 벡터 스토어에서 메타데이터 필터를 사용하여 질의를 처리하는 방법에 중점을 둡니다.
1. 쿼리 구조화 개념
-
쿼리 구조화는 사용자가 자연어로 묻는 질문을 메타데이터 필터를 사용하여 보다 구체적으로 변환하는 과정입니다.
-
예를 들어, 사용자가 "2024년 이후에 게시된 Lang Chain 관련 비디오를 찾아주세요"라고 질문할 경우, 이 질문은 메타데이터 필터로 변환되어 벡터 스토어에 적합한 쿼리로 만들어집니다.
2. 쿼리 구조화의 주요 흐름
2.1. 자연어 질문 → 구조화된 쿼리:
-
사용자가 자연어로 질문을 입력하면, LLM이 해당 질문을 분석하여 메타데이터 필터(예: 날짜, 조회수, 비디오 길이)를 사용해 데이터베이스 검색에 적합한 구조화된 쿼리로 변환합니다.
- 예시: 유튜브 비디오 데이터를 로드하고 메타데이터 필터 적용
- 링크 : Self-reflective RAG with LangGraph: Self-RAG and CRAG
from langchain_community.document_loaders import YoutubeLoader # https://youtu.be/pbAd8O1Lvm4 docs = YoutubeLoader.from_youtube_url( "https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pbAd8O1Lvm4", add_video_info=True ).load() docs[0].metadata- 위 코드는 YouTube에서 비디오를 로드하고 해당 비디오의 메타데이터(예: 제목, 조회수, 게시일)를 가져오는 예시입니다.
2.2. 메타데이터 필터 사용:
-
벡터 스토어에서 사용 가능한 메타데이터 필터를 기반으로 자연어 질문을 처리합니다.
-
필터로는 조회수, 게시일, 비디오 길이 등이 있으며, 이를 통해 보다 세밀한 검색을 할 수 있습니다. (
view_count,publish_date,length등을 필터로 사용하여 검색할 수 있습니다.)-
아래는 위에서 호출한 영상의 정보입니다.
{'source': 'pbAd8O1Lvm4', 'title': 'Self-reflective RAG with LangGraph: Self-RAG and CRAG', 'description': 'Unknown', 'view_count': 23406, 'thumbnail_url': 'https://i.ytimg.com/vi/pbAd8O1Lvm4/hq720.jpg', 'publish_date': '2024-02-07 00:00:00', 'length': 1058, 'author': 'LangChain'}
-
2.3. LLM과 함수 호출:
-
구조화된 쿼리의 스키마: 이 스키마는 검색할 비디오의 메타데이터 필터(예: 조회수, 게시일, 비디오 길이)를 정의합니다.
import datetime from typing import Literal, Optional, Tuple from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field class TutorialSearch(BaseModel): """Search over a database of tutorial videos about a software library.""" content_search: str = Field( ..., description="Similarity search query applied to video transcripts.", ) title_search: str = Field( ..., description=( "Alternate version of the content search query to apply to video titles. " "Should be succinct and only include key words that could be in a video " "title." ), ) min_view_count: Optional[int] = Field( None, description="Minimum view count filter, inclusive. Only use if explicitly specified.", ) max_view_count: Optional[int] = Field( None, description="Maximum view count filter, exclusive. Only use if explicitly specified.", ) earliest_publish_date: Optional[datetime.date] = Field( None, description="Earliest publish date filter, inclusive. Only use if explicitly specified.", ) latest_publish_date: Optional[datetime.date] = Field( None, description="Latest publish date filter, exclusive. Only use if explicitly specified.", ) min_length_sec: Optional[int] = Field( None, description="Minimum video length in seconds, inclusive. Only use if explicitly specified.", ) max_length_sec: Optional[int] = Field( None, description="Maximum video length in seconds, exclusive. Only use if explicitly specified.", ) def pretty_print(self) -> None: for field in self.__fields__: if getattr(self, field) is not None and getattr(self, field) != getattr( self.__fields__[field], "default", None ): print(f"{field}: {getattr(self, field)}")-
LLM은 함수 호출을 사용하여 자연어 질문을 처리하고, 이를 JSON 형식의 구조화된 객체로 변환하여 반환합니다. 이 객체는 검색 쿼리로 바로 사용할 수 있습니다.
structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(TutorialSearch)에 앞에 설정해둔 TutorialSearch으로 출력하도록 정의해둡니다.
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI # Create the Prompt Template: system = """You are an expert at converting user questions into database queries. You have access to a database of tutorial videos about a software library for building LLM-powered applications. Given a question, return a database query optimized to retrieve the most relevant results.""" prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", system), ("human", "{question}")]) # Initialize the Language Model (LLM) llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0125", temperature=0) structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(TutorialSearch) # Prompt and LLM into a Query Analyzer query_analyzer = prompt | structured_llm -
2.4. User Question 처리:
-
앞에서 정의한
prompt와query_analyzer를 바탕으로 User Question을 처리합니다.- prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", system), ("human", "{question}")])
- query_analyzer = prompt | structured_llm
-
아래와 같은 형태로 question을 처리해줍니다.
query_analyzer.invoke({"question": "your question"}).pretty_print()프롬프트 생성: 사용자 질문을 프롬프트에 삽입합니다.LLM 처리: LLM이 프롬프트를 읽고 TutorialSearch 구조에 맞는 출력을 생성합니다.구조화된 출력: 결과를 TutorialSearch 객체로 파싱하고 출력합니다.
예시: 사용자가 다음과 같은 질문을 한다고 가정합니다:
"2023년 6월 이후에 게시된 LangChain에 관한 영상 중 10분 이하의 영상을 보여줘."-
이 자연어 질문을 LLM(대형 언어 모델)과 쿼리 분석 체인(query analyzer)을 사용해,
TutorialSearch와 같은 데이터 모델로 변환할 수 있습니다.class TutorialSearch(BaseModel): content_search: str = None title_search: str = None earliest_publish_date: Optional[date] = None latest_publish_date: Optional[date] = None min_length_sec: Optional[int] = None max_length_sec: Optional[int] = None min_view_count: Optional[int] = None max_view_count: Optional[int] = None -
여기서 사용자 질문을 변환하면 다음과 같은
TutorialSearch객체가 생성될 수 있습니다:TutorialSearch( content_search='LangChain', title_search='LangChain', earliest_publish_date=datetime.date(2023, 6, 1), max_length_sec=600 # 10분을 초 단위로 변환한 값 ) -
이 구조화된 쿼리는 이제 메타데이터 필터링에 사용됩니다. 예를 들어:
earliest_publish_date필드는2023년 6월 1일 이후에 게시된 영상만 필터링합니다.max_length_sec필드는10분 이하의 영상만 필터링합니다.content_search와title_search필드는 LangChain이라는 키워드가 포함된 콘텐츠나 제목을 찾습니다.
-
이 쿼리를 사용하여 메타데이터 필터링을 적용하면, 조건에 맞는 영상만을 반환할 수 있습니다.
2.5. 추가 예시
- 자연어 질문: "2023년에 게시된 chat langchain 비디오"
- 질의문:
query_analyzer.invoke( {"question": "videos on chat langchain published in 2023"} ).pretty_print() - 구조화된 쿼리 출력:
content_search: chat langchain title_search: 2023 earliest_publish_date: 2023-01-01 latest_publish_date: 2023-12-31
- 질의문:
- 자연어 질문: "2024년 이전에 게시된 chat langchain 비디오"
- 질의문:
query_analyzer.invoke( {"question": "videos that are focused on the topic of chat langchain that are published before 2024"} ).pretty_print() - 구조화된 쿼리 출력:
content_search: chat langchain title_search: chat langchain latest_publish_date: 2023-12-31
- 질의문:
- 자연어 질문: "5분 이하의 멀티모달 모델 관련 비디오"
- 질의문:
query_analyzer.invoke( {"question": "how to use multi-modal models in an agent, only videos under 5 minutes"} ).pretty_print() - 구조화된 쿼리 출력:
content_search: multi-modal models agent title_search: multi-modal models agent max_length_sec: 300
- 질의문:
