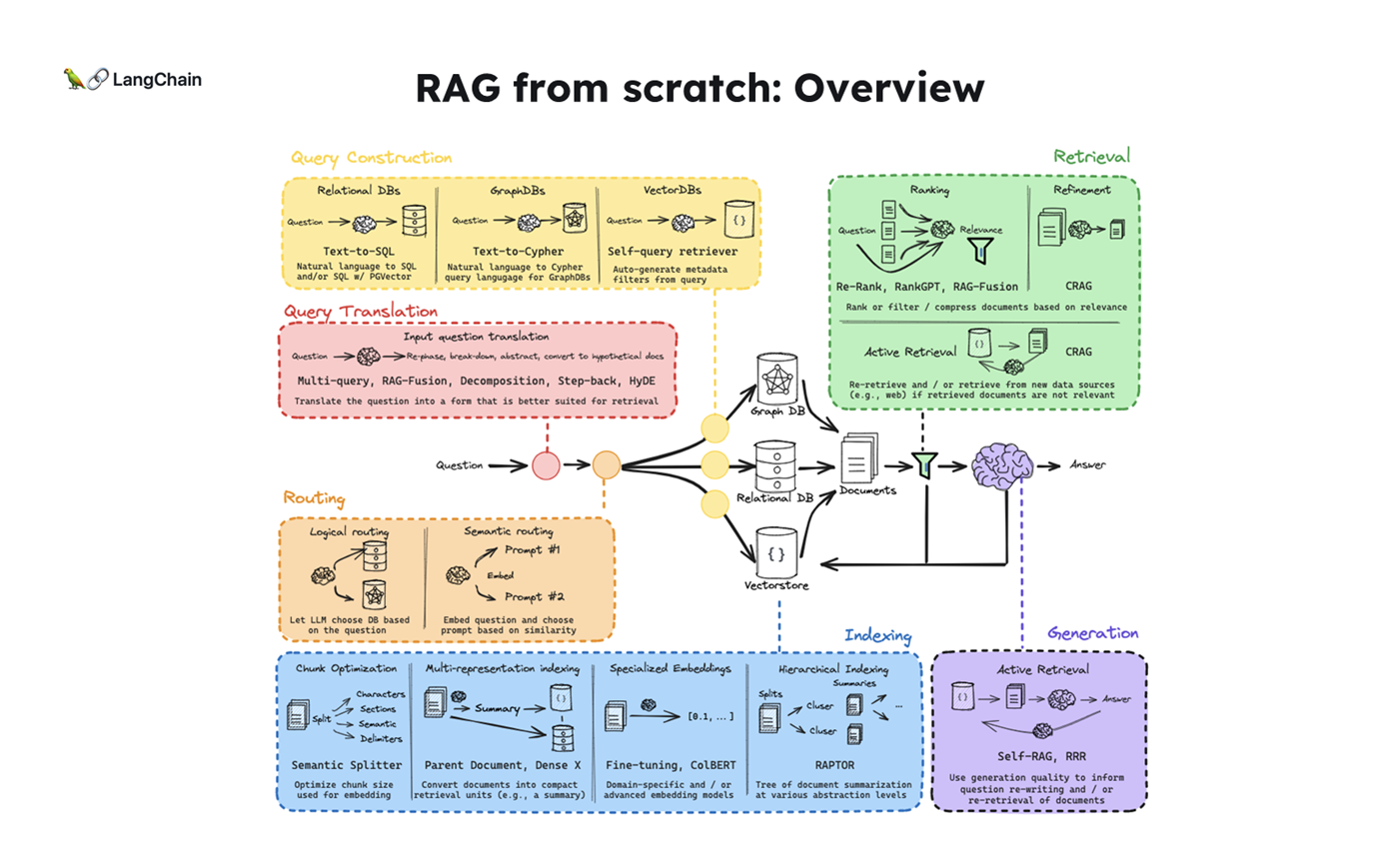
- 해당 블로그 포스트는 RAG From Scratch : Coursework
강의 파트 5 - 9 내용을 다루고 있습니다.
| 비디오 | 요약 | 강의 링크 | 슬라이드 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Part 5 (다중 쿼리) | 다양한 문서 검색을 위해 쿼리 재작성 기법을 설명합니다. | 📌 강의 | 📖 슬라이드 |
| Part 6 (RAG Fusion) | 여러 검색 결과를 결합하여 향상된 랭킹을 제공하는 RAG Fusion을 소개합니다. | 📌 강의 | 📖 슬라이드 |
| Part 7 (분해) | 복잡한 질문을 세분화된 하위 질문으로 나누어 상세한 답변을 제공하는 방법을 논의합니다. | 📌 강의 | 📖 슬라이드 |
| Part 8 (단계적 후퇴) | 근본적인 이해를 이끌어내는 추상적 질문을 생성하는 단계적 후퇴 프롬프팅을 탐구합니다. | 📌 강의 | 📖 슬라이드 |
| Part 9 (HyDE) | 인덱스 문서와 더 잘 일치하도록 가설적 문서를 생성하는 HyDE 기법을 소개합니다. | 📌 강의 | 📖 슬라이드 |
Part 5 (다중 쿼리)
- 해당 강의는 RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation) 파이프라인의 첫 번째 단계인 "Query Translation(쿼리 변환)"에 대해 다루고 있습니다.
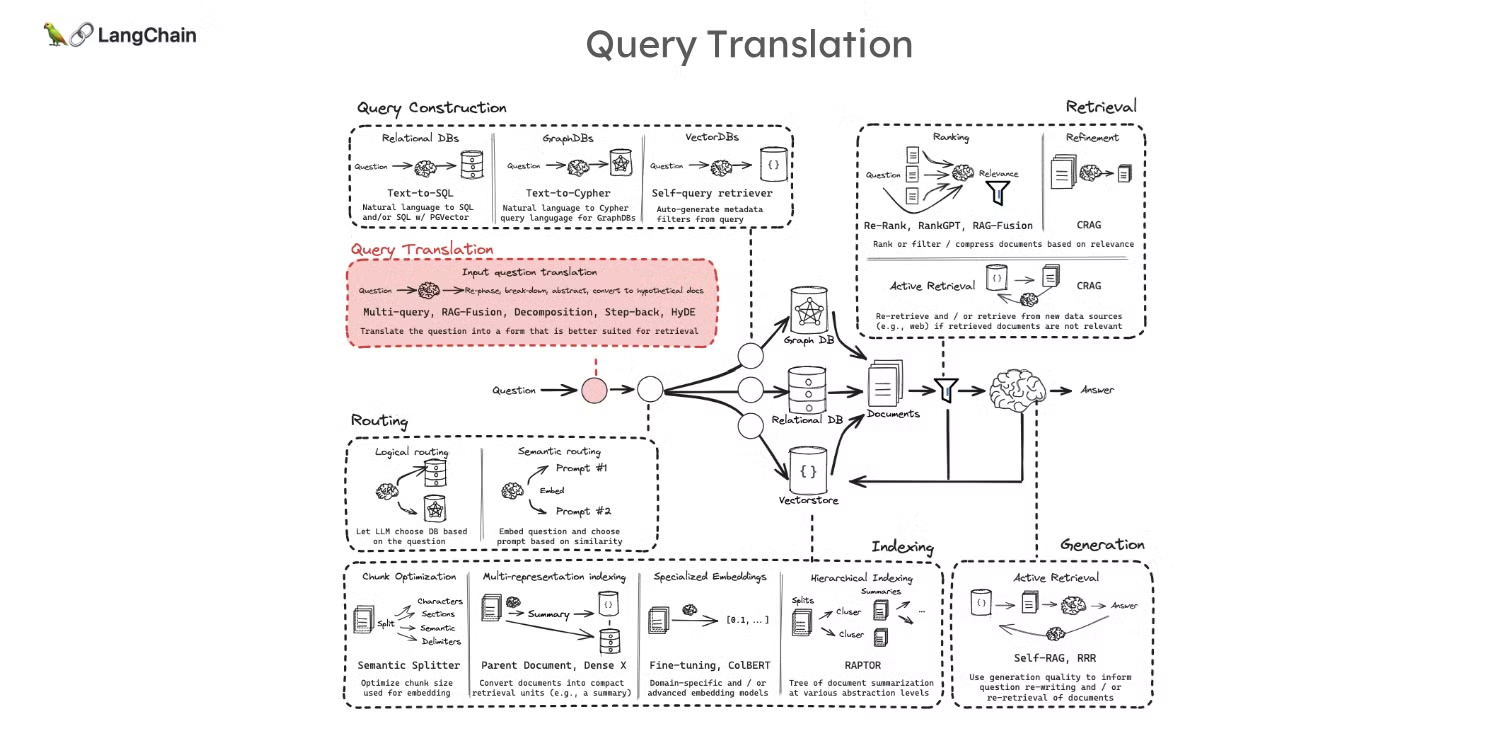
- Query Translation: 사용자가 작성한 질문이 모호하거나 제대로 구조화되지 않은 경우, 문서에서 의미적 유사성을 기준으로 검색하는 과정에서 원하는 문서를 찾지 못할 수 있습니다. 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 질문을 다양한 관점에서 재작성하여 보다 효과적으로 문서를 검색하는 방법이 필요합니다.
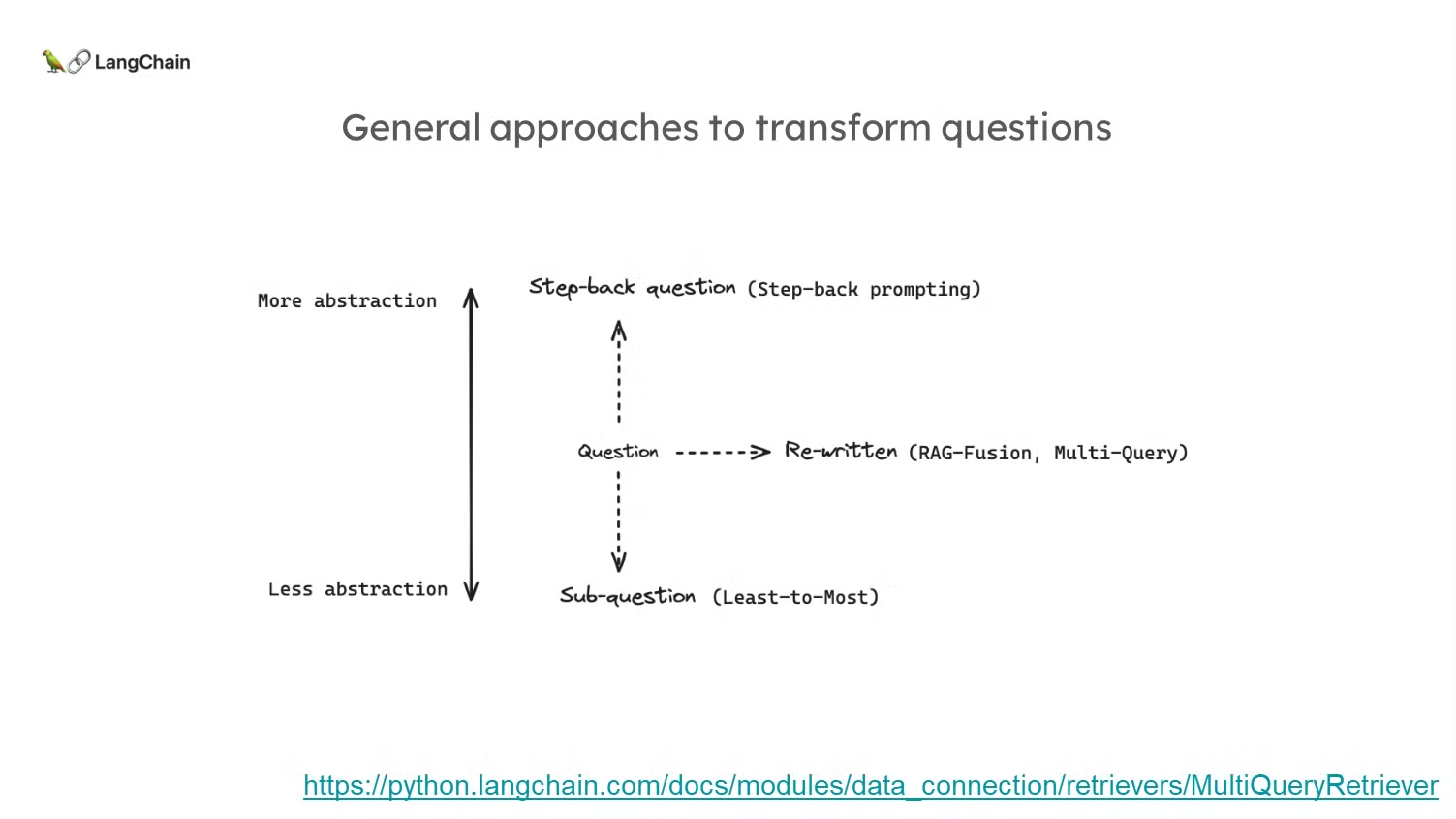
- 아래 3가지 기법은 대표적인 Query Translation의 3가지 기법으로 이들은 각각 다르게 질문을 변형하여 검색 성능을 향상시키는 기법으로, 기본적으로 원래 질문을 재구성하거나 변형하는 방식이라는 공통점을 가지고 있습니다.
- Query Rewriting(쿼리 재작성): 질문을 다양한 관점에서 다시 작성하여 검색 성능을 높이는 방식입니다. 예를 들어, 다중 쿼리(multi-query) 기법은 여러 가지 방식으로 질문을 변환하여 검색된 문서의 다양성과 정확성을 높이려는 방법입니다.
- Sub-questions(하위 질문 생성): 복잡하거나 추상적인 질문을 더 작고 구체적인 하위 질문으로 분해하는 방법입니다. 이를 통해 더 정확하고 세부적인 문서를 검색할 수 있습니다. Google의 "least-to-most" 기법은 복잡한 질문을 더 작은 단계로 나누어 해결하는 대표적인 방식입니다.
- Abstract Query(추상적인 질문 생성): 질문을 더 높은 수준으로 추상화하여, 일반적이거나 광범위한 문서를 검색하는 방법입니다. "Stepback prompting" 기법은 질문을 한 단계 더 높은 추상화 수준으로 변환하여 보다 넓은 범위의 문서를 검색하는 것을 목표로 합니다.
- 아래 3가지 기법은 대표적인 Query Translation의 3가지 기법으로 이들은 각각 다르게 질문을 변형하여 검색 성능을 향상시키는 기법으로, 기본적으로 원래 질문을 재구성하거나 변형하는 방식이라는 공통점을 가지고 있습니다.
- 본 강의는 “1. Query Rewriting(쿼리 재작성)” 기법 중 하나에 속하는
Multi-query(다중 쿼리)에 중점을 두고 설명합니다.- 여기서 다루는 핵심 개념은 사용자의 질문을 여러 형태로 변환하여 문서 검색 성능을 개선하는 방법입니다.
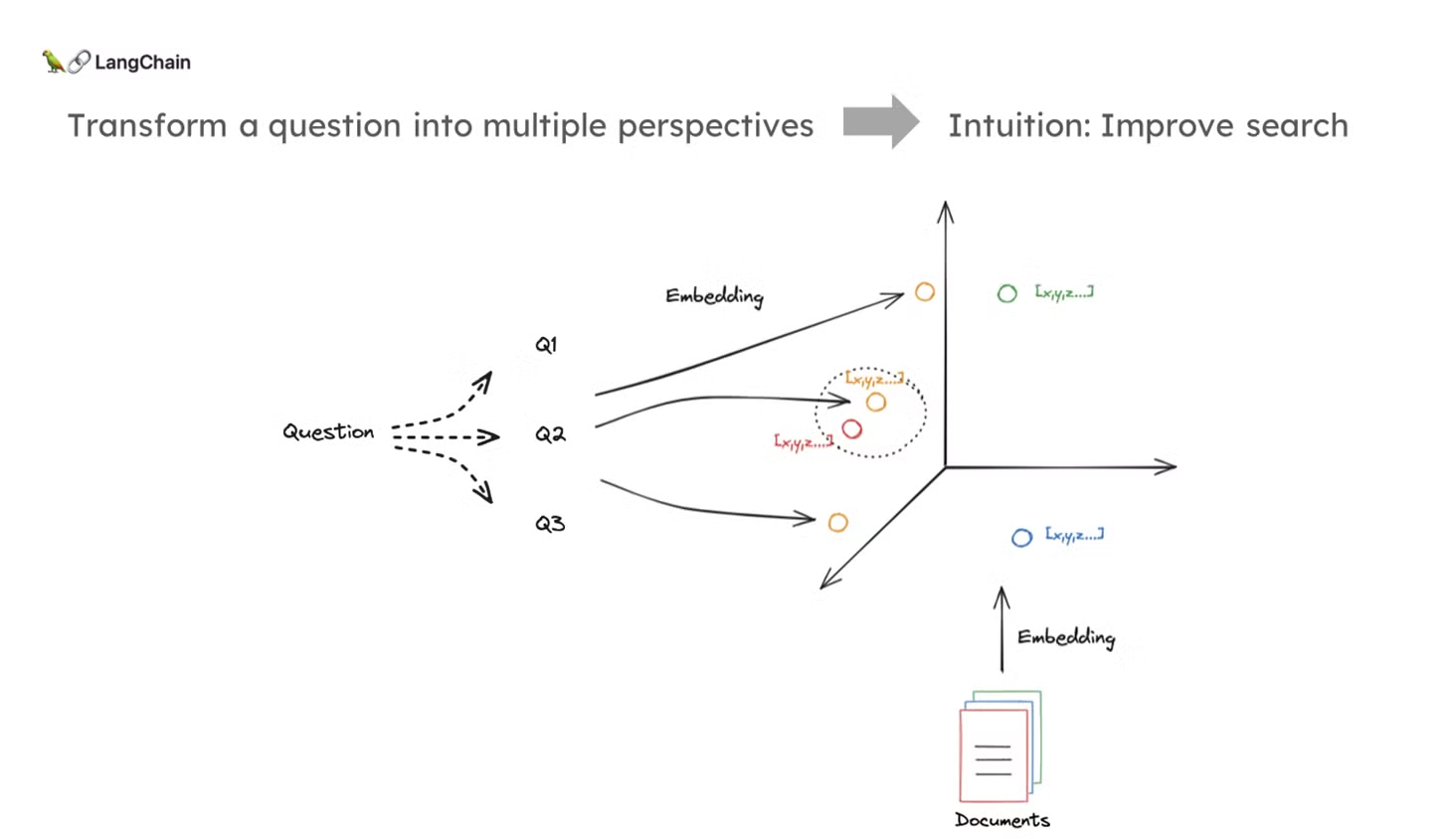
- Multi-Query 접근 방식
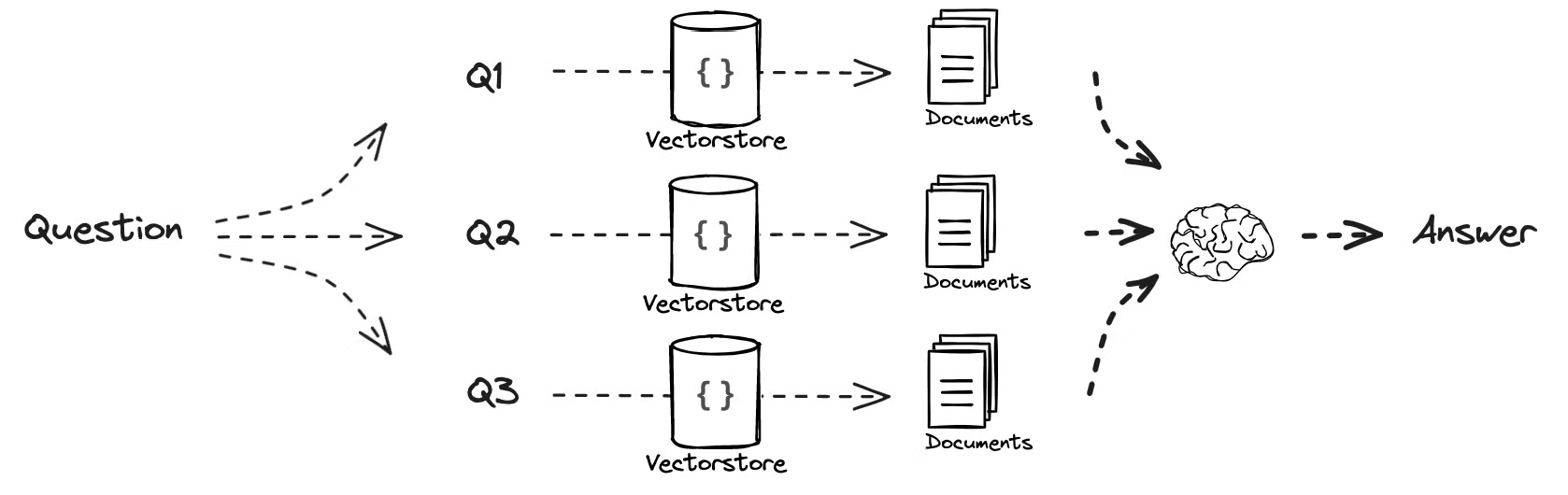
- 다중 쿼리 방식의 기본적인 직관은 질문을 여러 가지 형태로 변환하여 다양한 관점에서 검색을 수행하는 것입니다.
- 이는 문서와 질문이 고차원 임베딩 공간에서 잘 정렬되지 않을 경우, 질문을 재작성하여 해당 문서를 더 잘 검색할 수 있도록 하는 전략입니다.
- 즉, 질문을 여러 방식으로 다시 작성함으로써 검색 성능을 향상시키는 것입니다.
코드 시연
- 이 방식은 여러 재작성된 질문을 독립적으로 검색한 후, 각 검색 결과를 통합하여 더 신뢰성 있는 검색 결과를 도출하는 방식입니다.
-
블로그 문서 로드 및 벡터 스토어 생성/검색 준비
import bs4 from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma loader = WebBaseLoader( web_paths=("https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",), bs_kwargs=dict( parse_only=bs4.SoupStrainer( class_=("post-content", "post-title", "post-header") ) ), ) blog_docs = loader.load() text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder( chunk_size=300, chunk_overlap=50 ) splits = text_splitter.split_documents(blog_docs) vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(documents=splits, embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings()) retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()- 블로그 데이터를 웹에서 가져와
bs4를 이용해 파싱한 후, 해당 데이터를 분할하여 벡터 스토어에 인덱싱합니다. - 분할된 문서를 벡터 스토어에 저장하고, 검색을 위한 설정을 수행합니다.
- 블로그 데이터를 웹에서 가져와
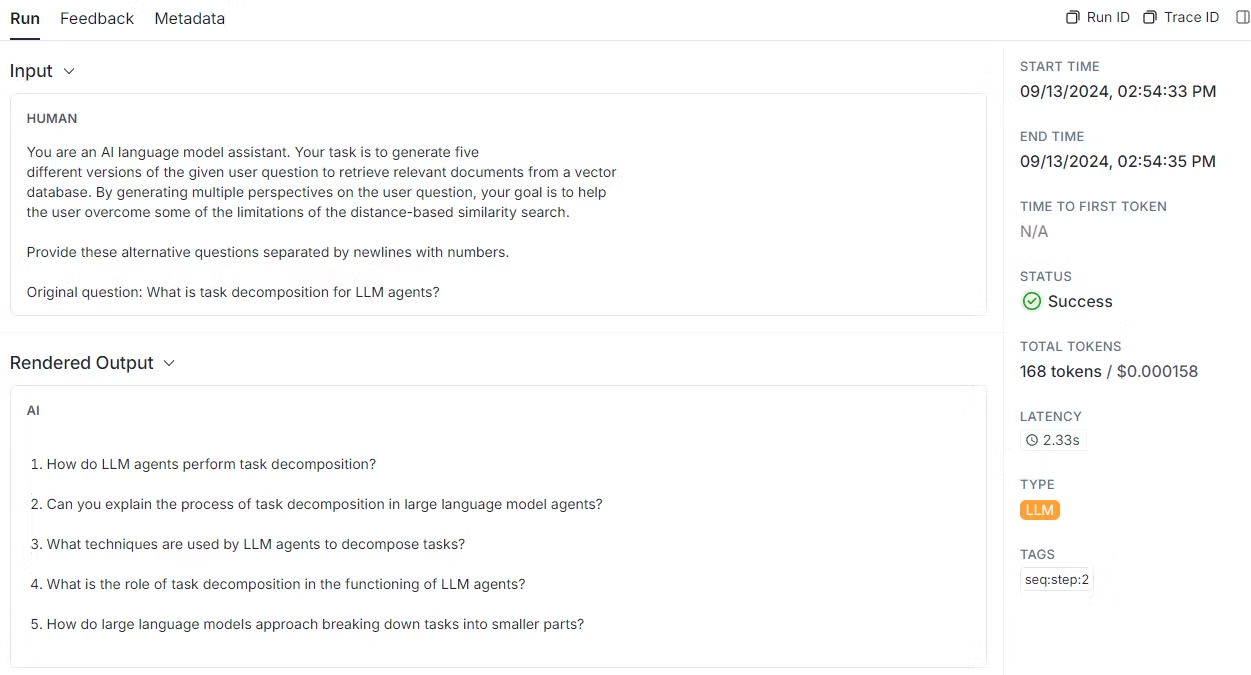
- 다중 쿼리 생성을 위한 프롬프트 정의:
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
template = """
You are an AI language model assistant.
Your task is to generate five different versions of the given user question to retrieve relevant documents from a vector database.
By generating multiple perspectives on the user question, your goal is to help the user overcome some of the limitations of the distance-based similarity search.
Provide these alternative questions separated by newlines.
Original question: {question}
"""
prompt_perspectives = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)- 질문을 다양한 방식으로 다시 작성하는 다중 쿼리 생성용 프롬프트를 정의합니다.
- (해석) 당신은 AI 언어 모델 어시스턴트입니다. 주어진 사용자 질문의 다섯 가지 버전을 생성하여 벡터 데이터베이스에서 관련 문서를 검색하는 것이 작업의 목표입니다. 사용자 질문에 대한 여러 관점을 생성함으로써 사용자가 거리 기반 유사성 검색의 한계를 극복할 수 있도록 돕는 것이 목표입니다. 새 줄로 구분하여 다음 대체 질문을 제공합니다.
- (해석) 당신은 AI 언어 모델 어시스턴트입니다. 주어진 사용자 질문의 다섯 가지 버전을 생성하여 벡터 데이터베이스에서 관련 문서를 검색하는 것이 작업의 목표입니다. 사용자 질문에 대한 여러 관점을 생성함으로써 사용자가 거리 기반 유사성 검색의 한계를 극복할 수 있도록 돕는 것이 목표입니다. 새 줄로 구분하여 다음 대체 질문을 제공합니다.
- 다중 쿼리를 이용한 검색 및 문서 통합:
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.load import dumps, loads
generate_queries = (
prompt_perspectives
| ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
| StrOutputParser()
| (lambda x: x.split("\n"))
)
def get_unique_union(documents: list[list]):
""" Unique union of retrieved docs """
flattened_docs = [dumps(doc) for sublist in documents for doc in sublist]
unique_docs = list(set(flattened_docs))
return [loads(doc) for doc in unique_docs]
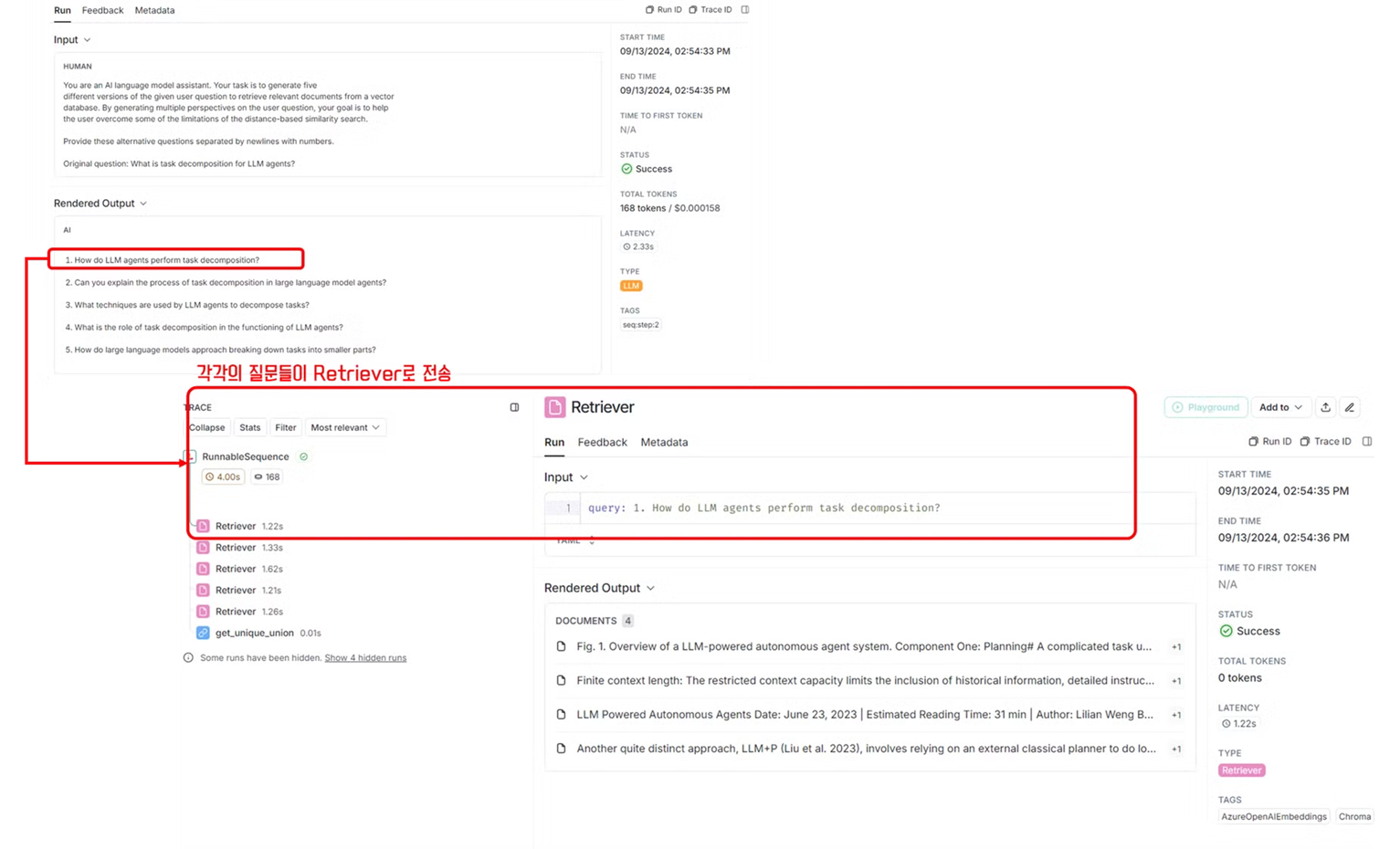
retrieval_chain = generate_queries | retriever.map() | get_unique_union
question = "What is task decomposition for LLM agents?"
docs = retrieval_chain.invoke({"question":question})
len(docs)
-
생성된 여러 질문을 이용해 독립적인 검색을 수행하고, 그 결과를 통합하여 중복되지 않는 문서를 반환합니다.
-
generate_queries: 주어진 질문에 대해 여러 관점의 쿼리를 생성합니다.
a. ChatOpenAI 모델을 통해 프롬프트를 처리합니다.
b. StrOutputParser로 모델의 출력을 파싱합니다.
c. 결과를 개행 문자(\n)로 분할하여 여러 쿼리로 만듭니다.
-
retriever: 생성된 쿼리를 사용하여 문서를 검색합니다.
a.retriever.map()을 사용하여 각 생성된 쿼리에 대해 문서를 검색합니다.
-
get_unique_union: 검색된 문서들 중 중복을 제거합니다.
a.
get_unique_union함수를 사용하여 검색된 모든 문서에서 중복을 제거합니다.unique_docs = list(set(flattened_docs)): 집합(set)을 사용해 중복을 제거한 후, 다시 원래 형식으로 변환합니다.
b.
dumps와loads를 사용함으로써, Document 객체의 내용을 기반으로 중복을 제거하고, 다시 원래의 객체 형태로 복원할 수 있습니다.- 이는 특히 복잡한 객체 구조를 가진 Document 클래스를 다룰 때 유용합니다.
-
- 최종 RAG(질문 + 문서):
from operator import itemgetter
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
template = """
Answer the following question based on this context:
{context}
Question:
{question}
"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
# retrieval_chain = generate_queries | retriever.map() | get_unique_union
final_rag_chain = (
{"context": retrieval_chain,
"question": itemgetter("question")}
| prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
final_rag_chain.invoke({"question":question})
- 검색된 문서를 바탕으로 질문에 대한 답을 생성하는 최종 RAG 체인을 정의합니다.
retrieval_chain이 컨텍스트를 제공합니다.itemgetter("question")가 입력에서 질문을 추출합니다.- 이 두 요소가 프롬프트 템플릿에 삽입됩니다.
- 완성된 프롬프트가 LLM에 전달되어 응답을 생성합니다.
💡
itemgetter함수에 대해서 더 알아보자
itemgetter함수:operator모듈의itemgetter는 딕셔너리나 시퀀스에서 특정 키나 인덱스의 값을 추출하는 callable 객체를 생성합니다.- 여기서는
itemgetter("question")이 사용되어, 입력 딕셔너리에서 "question" 키의 값을 추출합니다.
itemgetter와.invoke의 상호작용:final_rag_chain.invoke({"question": question})가 호출될 때,itemgetter("question")는 이 입력 딕셔너리에서 "question" 키의 값을 추출합니다.- 이 추출된 값은 체인의 "question" 부분에 전달됩니다.
- 체인 내에서의 역할:
{"context": retrieval_chain, "question": itemgetter("question")}에서 "question" 키에itemgetter("question")이 할당됩니다.- 이는 입력 딕셔너리의 "question" 값을 그대로 전달하는 역할을 합니다.
- 전체 과정:
.invoke({"question": question})가 호출되면, 이 딕셔너리가 체인에 입력됩니다.itemgetter("question")는 이 딕셔너리에서 "question" 값을 추출합니다.- 추출된 값은 프롬프트 템플릿의 {question} 부분을 채우는 데 사용됩니다.
Part 6 (RAG Fusion)
- 이 강의는 RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation) 파이프라인의 "Query Translation(쿼리 변환)" 두 번째 방법인 RAG Fusion에 대해 설명합니다.
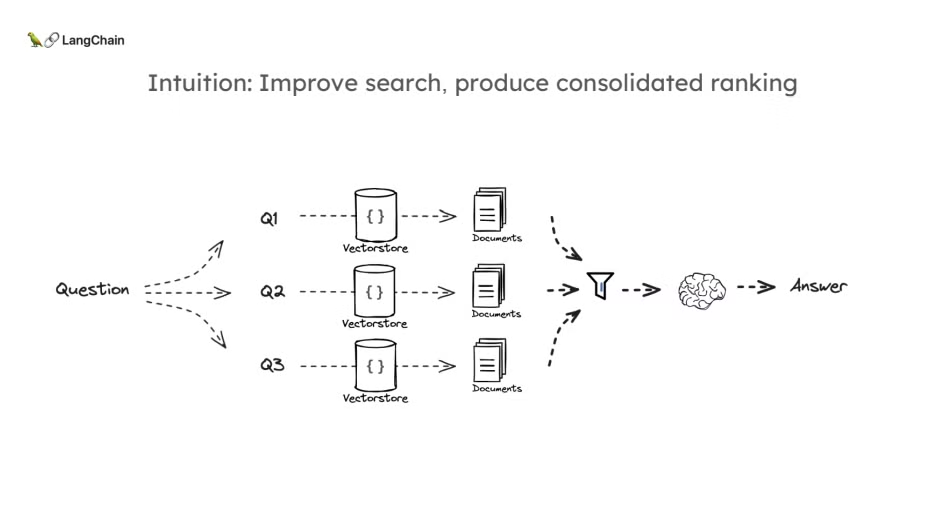
- RAG Fusion은 다중 쿼리와 검색 결과를 통합하는 과정에서 중요한 기법으로, Reciprocal Rank Fusion(RRF)을 사용하여 검색된 문서를 재정렬하는 방식입니다.
- 이전에 챕터 5에서 설명한 다중 쿼리 방법에서는 사용자의 질문을 여러 형태로 변환한 후, 각 변환된 질문으로 독립적인 검색을 수행했습니다.
- RAG Fusion도 기본적으로 같은 구조를 따르지만, Reciprocal Rank Fusion(RRF)이라는 기법을 사용하여 검색 결과를 보다 효율적으로 결합하고 재정렬합니다.
- RRF의 핵심 개념은 여러 개의 독립적인 문서 리스트에서 각 문서의 랭킹을 계산하고, 상호 순위를 기반으로 문서들의 최종 순위를 결정하는 것입니다.
RAG Fusion의 직관
RAG Fusion의 기본 원리는 다중 쿼리 방법과 유사하게 여러 번의 검색을 통해 각 질문에 대한 문서 리스트를 생성한 후, RRF 알고리즘을 통해 각 문서의 순위를 합산하여 최종 순위가 높은 문서를 선택하는 방식입니다. 이를 통해 각각의 독립적인 검색 결과를 최적화하여 최종 문서를 구성할 수 있습니다.
- 다중 쿼리 생성: 하나의 질문에 대해 여러 변형된 쿼리를 생성합니다. 예를 들어, "인공지능의 발전"이라는 질문에 대해 "AI의 미래", "기계 학습의 역사" 등 다양한 쿼리를 생성할 수 있습니다.
- 개별 검색 수행: 각 변형된 쿼리로 독립적인 검색을 수행합니다. 즉, 하나의 쿼리가 아니라 여러 쿼리로 검색을 진행하여 더 다양한 검색 결과를 얻습니다.
- RRF 적용: 이렇게 얻은 여러 검색 결과를 RRF 방식으로 통합합니다. 각 문서의 순위를 기반으로 점수를 매기고, 상위 문서에 더 높은 가중치를 부여하면서 최종 순위를 재정렬합니다.
- 결과 통합: 재정렬된 문서들을 최종 컨텍스트로 사용하여 LLM에 입력합니다. LLM은 이 문서들을 바탕으로 최종 답변을 생성합니다.
Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF)
- 순위 기반 접근 (Ranking-based Approach)
RRF는 검색 결과를 "점수"가 아닌 "순위"에 기반해 통합합니다. 이는 검색 결과에서 각 문서가 몇 번째로 중요한지(순위)를 매기고, 이를 활용해 최종적으로 어떤 문서가 더 중요한지를 판단합니다.
- 왜 순위가 중요한가?
- 일반적으로 검색 결과는 점수(해당 문서가 얼마나 관련성이 높은지 평가한 값)를 기반으로 나열되는데, 문제는 검색 알고리즘마다 이 점수 스케일이 다를 수 있다는 것입니다.
- 예를 들어, 하나의 검색 엔진은 0에서 1까지 점수를 매기고, 다른 엔진은 0에서 100까지 점수를 줄 수 있습니다. 이렇게 스케일이 다르면 단순히 점수를 기반으로 검색 결과를 통합하기 어렵습니다.
- 반면, 순위는 각 검색 엔진에서 매겨진 순서 그대로 활용하기 때문에 스케일 문제를 해결할 수 있습니다.
- RRF 점수 계산 방식
-
RRF에서 각 문서의 점수는 다음과 같이 계산됩니다:
-
여기서 k는 작은 상수(일반적으로 60 정도),
rank(d)는 문서 d가 각 검색 결과에서 차지한 순위입니다. 순위가 높을수록, 즉 더 상위에 랭크된 문서일수록 점수가 높아집니다. -
이 공식이 어떻게 작동하는지 예를 들어보겠습니다:
- 검색 결과에서 어떤 문서가 첫 번째 순위에 있으면, 점수는 , 즉 약 0.016입니다.
- 두 번째 순위라면, 점수는 , 즉 약 0.0157이 됩니다.
- 이처럼 순위가 낮아질수록 점수가 줄어드는 것을 알 수 있습니다. 그래서 상위에 랭크된 문서가 더 큰 영향을 미치게 됩니다.
코드 시연
1. RAG Fusion용 프롬프트 정의 및 다중 쿼리 생성
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
template = """
You are a helpful assistant that generates multiple search queries based on a single input query. \n
Generate multiple search queries related to: {question} \n
Output (4 queries):
"""
prompt_rag_fusion = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
generate_queries = (
prompt_rag_fusion
| ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
| StrOutputParser()
| (lambda x: x.split("\n"))
)
- 다중 쿼리 생성:
- ChatPromptTemplate을 사용하여 입력 질문을 바탕으로 여러 검색 쿼리를 생성하도록 프롬프트를 설계했습니다.
- 체인 구성:
- prompt_rag_fusion | ChatOpenAI | StrOutputParser() 순으로 체인을 구성하여 프롬프트 실행, LLM 응답 생성, 문자열 파싱을 수행합니다.
- 리스트로 변환:
(lambda x: x.split("\n"))부분이 LLM의 출력을 줄바꿈을 기준으로 분리하여 리스트로 만듭니다.
2. Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) 함수 정의 및 검색 수행
from langchain.load import dumps, loads
def reciprocal_rank_fusion(results: list[list], k=60):
""" Reciprocal_rank_fusion that takes multiple lists of ranked documents
and an optional parameter k used in the RRF formula """
# Initialize a dictionary to hold fused scores for each unique document
fused_scores = {}
# Iterate through each list of ranked documents
for docs in results:
# Iterate through each document in the list, with its rank (position in the list)
for rank, doc in enumerate(docs):
# Convert the document to a string format to use as a key (assumes documents can be serialized to JSON)
doc_str = dumps(doc)
# If the document is not yet in the fused_scores dictionary, add it with an initial score of 0
if doc_str not in fused_scores:
fused_scores[doc_str] = 0
# Retrieve the current score of the document, if any
previous_score = fused_scores[doc_str]
# Update the score of the document using the RRF formula: 1 / (rank + k)
fused_scores[doc_str] = previous_score + 1 / (rank + k)
# Sort the documents based on their fused scores in descending order to get the final reranked results
reranked_results = [
(loads(doc), score)
for doc, score in sorted(fused_scores.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
]
# Return the reranked results as a list of tuples, each containing the document and its fused score
return reranked_results
retrieval_chain_rag_fusion = generate_queries | retriever.map() | reciprocal_rank_fusion
docs = retrieval_chain_rag_fusion.invoke({"question": question})
len(docs)- RRF 알고리즘을 구현하여, 여러 개의 독립적인 검색 결과 리스트에서 문서를 통합하고 순위를 계산합니다.
- 이중 for 문을 통해 각각 result와 docs를 돌면서 등장하는 문서의 순서에 따라 점수를 매깁니다.
- (참고) 이전에 개념에서 살펴봣던 것처럼 RRF의 score는 다음과 같습니다:
- 재 등장한 문서에 대해서는 이전 score(previous score)에 현재 스코어(current score)를 더해주는 형태로 진행합니다
- 생성된 쿼리를 통해 독립적인 검색을 수행하고, 그 결과를 RRF 알고리즘을 통해 재정렬합니다.
3. 최종 RAG 체인 정의
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
template = """Answer the following question based on this context:
{context}
Question: {question}
"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
final_rag_chain = (
{"context": retrieval_chain_rag_fusion,
"question": itemgetter("question")}
| prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
final_rag_chain.invoke({"question":question})
- 검색된 문서를 바탕으로 질문에 대한 답을 생성하는 최종 RAG 체인을 정의합니다.
요약
- RAG Fusion은 다중 쿼리를 이용해 검색된 문서들을 Reciprocal Rank Fusion(RRF) 알고리즘을 사용하여 재정렬하고, 그 결과를 바탕으로 최종 답변을 생성하는 방법입니다.
- RRF는 다양한 검색 결과를 하나로 통합하여, 각 문서의 중요도를 순위로 환산하고 최적의 문서를 선택하는 데 유리한 알고리즘입니다.
- 이 방법은 특히 여러 개의 벡터 스토어에서 동시에 검색하거나, 다양한 형태의 질문에 대해 검색을 수행할 때 유용하게 사용할 수 있습니다.
중간 정리
- 지금까지
멀티쿼리 기법과RAG Fusion에 대해서 살펴봤는데요. 한번 정리하고 넘어가보도록 하겠습니다. - 두 기법 모두 검색 성능을 향상시키는 데 효과적이지만, RAG Fusion은 결과의 품질 개선에 더 중점을 두는 반면, 멀티쿼리 기법은 검색 범위 확대에 더 초점을 맞춥니다.
- 상황에 따라 적절한 기법을 선택하거나 두 기법을 결합하여 사용할 수 있습니다.
RAG Fusion
- 쿼리 생성: 원본 쿼리를 기반으로 LLM을 사용해 여러 개의 관련 쿼리를 생성합니다.
- 검색 과정: 생성된 여러 쿼리로 각각 검색을 수행합니다.
- 결과 통합: Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) 알고리즘을 사용하여 여러 검색 결과를 통합하고 재정렬합니다.
- 장점: 다양한 관점의 쿼리를 통해 더 포괄적인 검색 결과를 얻을 수 있으며, RRF를 통해 결과의 품질을 향상시킵니다.
멀티쿼리 기법 (Multi-Query Retriever)
- 쿼리 생성: 원본 쿼리를 기반으로 LLM을 사용해 여러 개의 관련 쿼리를 생성합니다.
- 검색 과정: 생성된 여러 쿼리로 각각 검색을 수행합니다.
- 결과 통합: 검색된 모든 문서를 단순히 합치거나, 중복을 제거하여 통합합니다.
- 장점: 단일 쿼리보다 더 다양한 관련 문서를 검색할 수 있어 recall이 향상됩니다.
Part 7 (분해)
- 이 강의는 RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation) 파이프라인의 "Query Translation(쿼리 변환)" 중 세 번째 방법인 Decomposition(질문 분해)에 대해 설명합니다.
문제 정의 및 접근 방법
- Decomposition(질문 분해)는 복잡한 질문을 여러 하위 질문으로 나누어 각각을 독립적으로 해결한 후, 최종적으로 통합하여 답변을 제공하는 방식입니다.
- 이전 방법들인 다중 쿼리(Multi-query)와 RAG Fusion에서는 질문을 여러 방식으로 변환(rewrite-question)하여 검색 성능을 개선하려 했습니다.
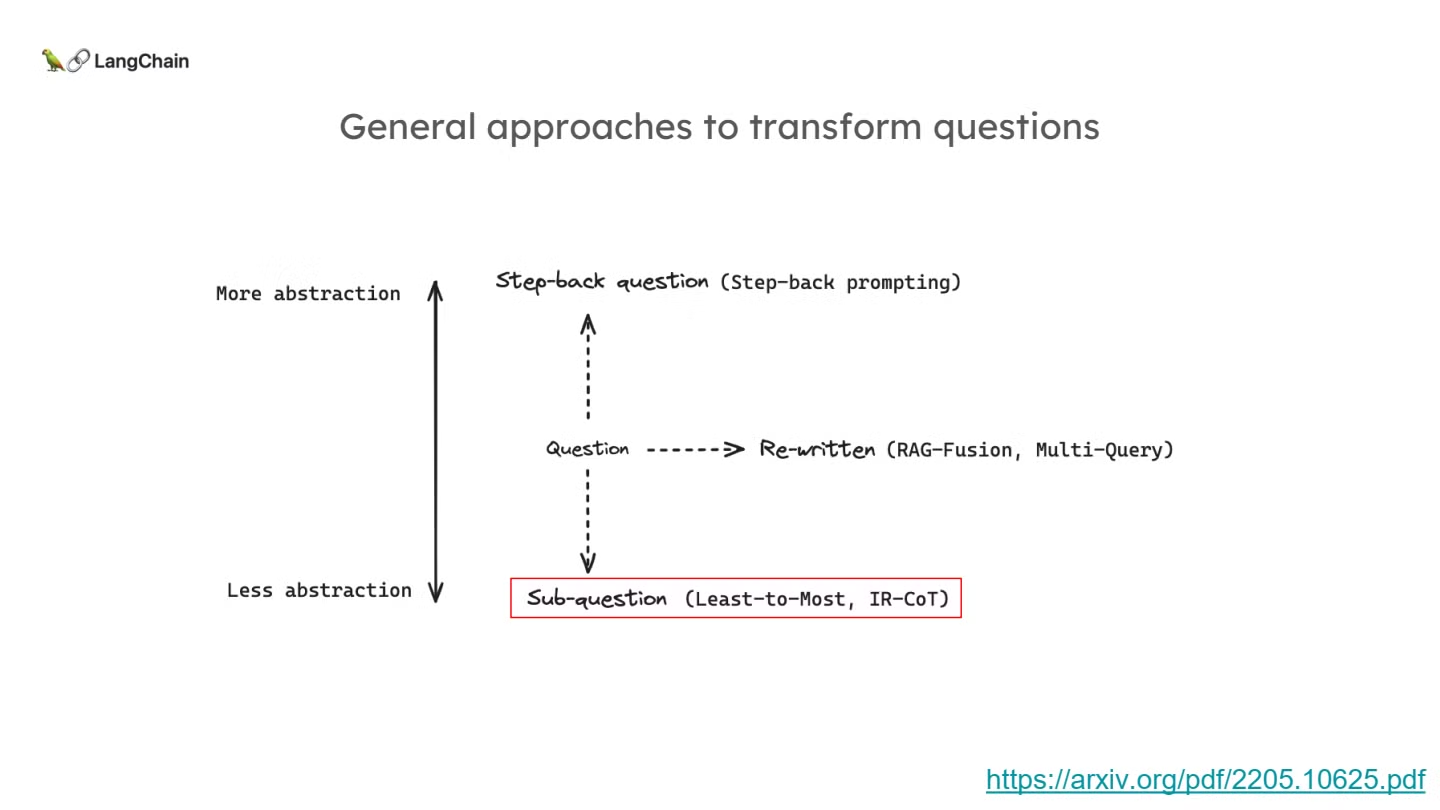
- Decomposition 방식, 다른 이름으로는 sub-question방식은 기존 질문을 하위 문제로 분해하여 각 문제를 순차적으로 해결하는 접근입니다.
- 이 방법은 주로 복잡한 문제나 질문을 해결할 때 유용하며, 각각의 하위 질문을 독립적으로 해결하면서 이전 질문의 답을 바탕으로 다음 질문을 해결하는 방식입니다.
- 주요 연구 및 방법론으로는 “Least-to-Most”와 “IT-CoT”기법이 있습니다.

- 논문: Least-to-Most Prompting Enables Complex Reasoning in Large Language Models
- 최소-최대 프롬프팅(Least-to-Most Prompting)은 복잡한 문제를 해결하기 위해 문제를 더 작은 하위 문제로 나눈 후, 각 하위 문제를 순차적으로 해결하는 방법입니다.
- 이전 하위 문제의 답을 바탕으로 다음 하위 문제를 해결하는 방식으로, 대형 언어 모델이 어려운 문제를 더 쉽게 해결할 수 있게 합니다.
- Chain-of-Thought(연쇄적 사고 프롬프팅)와 같은 기존 기법은 더 어려운 문제를 해결하는 데 한계가 있었으나, 최소-최대 프롬프팅은 이러한 문제를 해결할 수 있도록 설계되었습니다.
- 논문: Interleaving Retrieval with Chain-of-Thought Reasoning for Knowledge-Intensive Multi-Step Questions
- IRCoT는 다단계 질문에 답할 때, 정보 검색과 Chain-of-Thought(COT) 추론을 상호 보완적으로 결합하는 방법입니다.
- 모델이 답을 도출하는 중간 단계에서 필요한 정보를 지속적으로 검색해 오고, 검색된 정보를 바탕으로 새로운 CoT 단계를 생성하여 이를 반복적으로 개선합니다.
- 단계별로 필요한 정보를 검색하고, 추론 과정을 통해 얻은 정보를 바탕으로 추가 검색을 수행하는 방식으로 복잡한 질문에 대한 답변을 개선합니다.
- 이러한 개념들을 종합해서 아래와 같읍 decomposition 컨셉을 그려볼 수 있습니다:
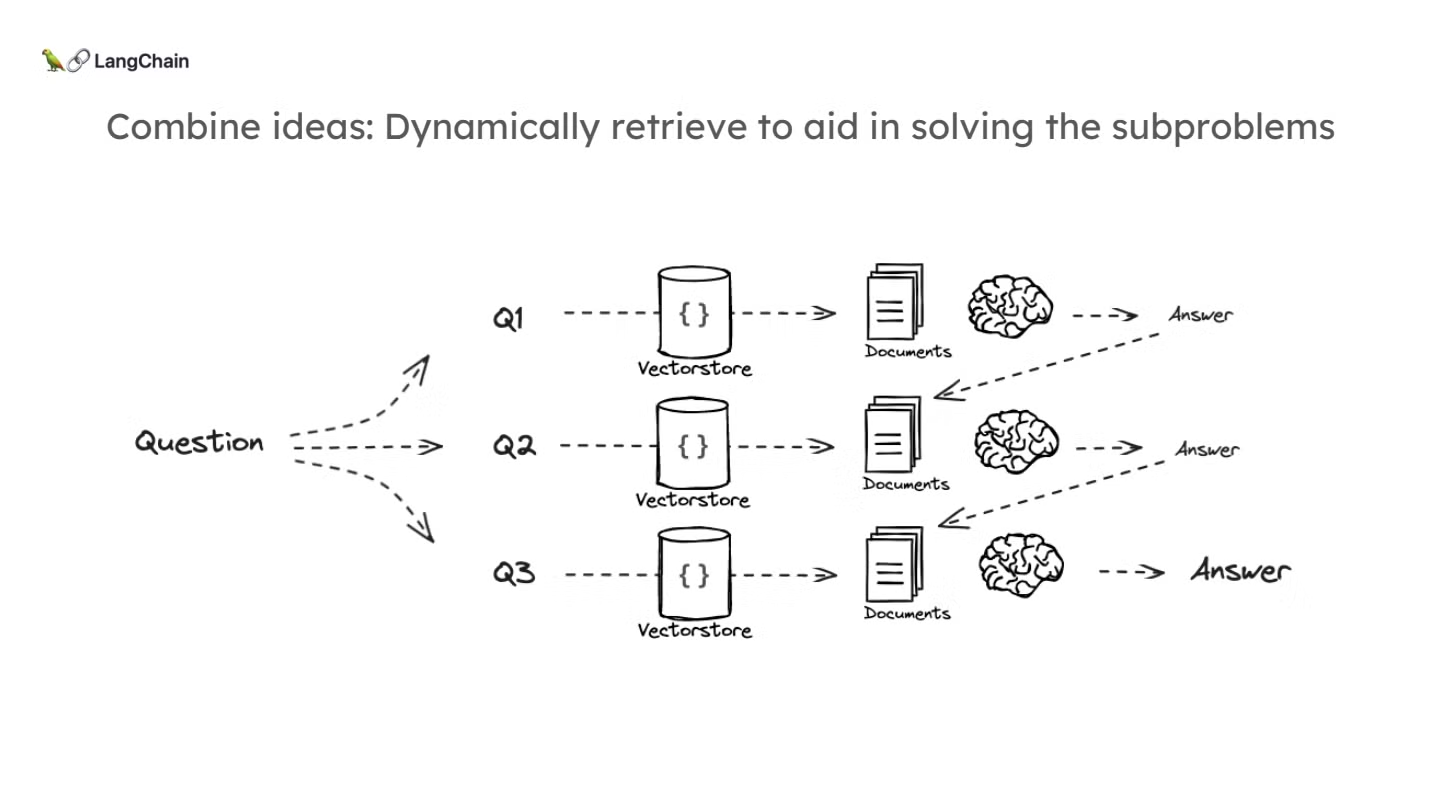
Decomposition 방식의 직관
- Decomposition 방식에서는 질문을 작게 나누어 더 쉽게 해결할 수 있는 하위 문제로 분해하고, 각각의 문제에 대해 독립적으로 검색 및 답변을 진행합니다.
- 이 과정에서 이전 질문의 답변을 다음 질문에 사용하여 점진적으로 문제를 해결합니다. 이를 통해, 복잡한 문제를 체계적으로 해결할 수 있습니다.
코드 시연
1. Decomposition용 프롬프트 정의 / LLM을 이용한 하위 질문 생성
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
# prompt template for decomposition
template = """
You are a helpful assistant that generates multiple sub-questions related to an input question. \n
The goal is to break down the input into a set of sub-problems / sub-questions that can be answers in isolation. \n
Generate multiple search queries related to: {question} \n
Output (3 queries):
"""
prompt_decomposition = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
generate_queries_decomposition = (
prompt_decomposition
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
| (lambda x: x.split("\n"))
)
# 예시 질문
question = "What are the main components of an LLM-powered autonomous agent system?"
questions = generate_queries_decomposition.invoke({"question":question})- 입력된 질문을 하위 질문으로 분해하기 위한 프롬프트를 정의합니다.
- 프롬프트를 사용하여 입력된 질문을 하위 질문으로 분해하고, 이를 리스트로 변환합니다.
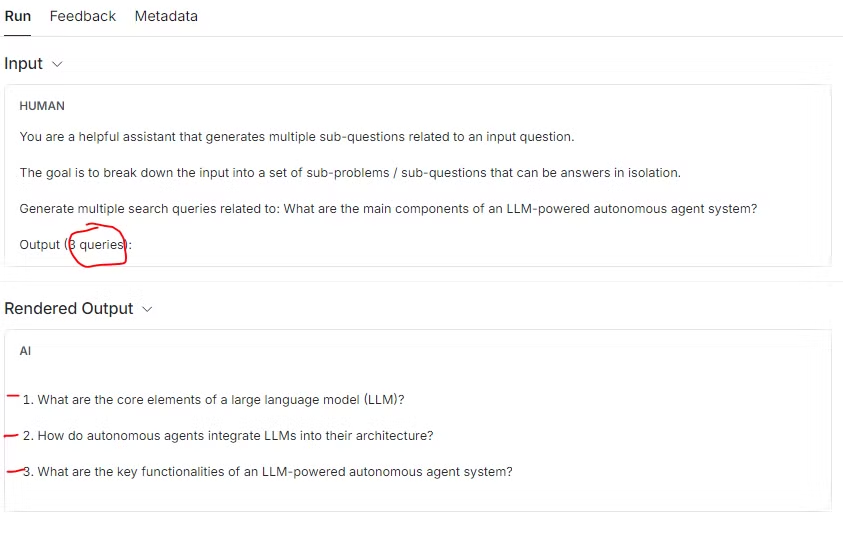
-
위 예시를 보면, generate_queries_decomposition를 통해서 “LLM 기반 자율 에이전트 시스템의 주요 구성 요소는 무엇인가요?” 이라는 질문이 아래와 같이 3가지 질문으로 분해되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다:
- '1. 대형 언어 모델(LLM)의 핵심 요소는 무엇인가요?
- '2. 자율 에이전트는 어떻게 LLM을 아키텍처에 통합하나요?'
- '3. LLM 기반 자율 에이전트 시스템의 주요 기능은 무엇인가요?'
2. 하위 질문별로 답변 생성 및 연속적인 처리
from operator import itemgetter
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
# prompt template for RAG
template = """
Here is the question you need to answer:
\n --- \n {question} \n --- \n
Here is any available background question + answer pairs:
\n --- \n {q_a_pairs} \n --- \n
Here is additional context relevant to the question:
\n --- \n {context} \n --- \n
Use the above context and any background question + answer pairs to answer the question: \n {question}
"""
decomposition_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
def format_qa_pair(question, answer):
"""
Format question and answer pairs for inclusion in the prompt
"""
formatted_string = ""
formatted_string += f"Question: {question}\nAnswer: {answer}\n\n"
return formatted_string.strip()
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
# Initialize an empty string to accumulate question-answer pairs
q_a_pairs = ""
for q in questions:
rag_chain = (
{
"context": itemgetter("question") | retriever,
"question": itemgetter("question"),
"q_a_pairs": itemgetter("q_a_pairs")
}
| decomposition_prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
answer = rag_chain.invoke({"question": q, "q_a_pairs": q_a_pairs})
q_a_pair = format_qa_pair(q, answer)
q_a_pairs = q_a_pairs + "\n---\n" + q_a_pair
-
위에서 생성된 3개의 하위 질문에 대해 순차적으로 검색을 수행하고, 이전 질문의 답변을 다음 질문에 활용하여 점진적으로 해결해 나갑니다.
q_a_pair = format_qa_pair(q, answer)를 통해 이전 답변을 감싸고, rag_chain.invoke({"question": q, "q_a_pairs":q_a_pairs}) 시에 넣어줌으로써 이전 답변을 현재 답변을 해줄때 참고할 수 있게 해줍니다.
-
(예시) 2번째 프롬프트 Input
# 2번 질문의 답변을 위해 q_a_pair로 1번 Question과 Answer를 참고하고 있음 { "question": "2. How do autonomous agents integrate LLMs into their architecture?", "q_a_pairs": "\n---\nQuestion: 1. What are the core elements of a large language model (LLM)?\n Answer: The core elements of a large language model (LLM) include:\n\n1. **Architecture**: The foundational design of the LLM, typically involving layers of neural networks such as transformers. This architecture determines how the model processes and generates language.\n\n2. **Training Data**: The corpus of text data used to train the model. This data is crucial for the model to learn language patterns, grammar, facts, and even some reasoning capabilities.\n\n3. **Training Process**: The method by which the model learns from the training data, often involving techniques like supervised learning, unsupervised learning, or reinforcement learning. This process includes fine-tuning and adjusting the model's parameters to improve its performance.\n\n4. **Tokenization**: The process of breaking down text into smaller units (tokens) that the model can understand and process. Tokenization is essential for handling different languages, special characters, and various text structures.\n\n5. **Context Handling**: The mechanism by which the model understands and maintains the context of a conversation or text. This includes managing the finite context length and using techniques like attention mechanisms to focus on relevant parts of the input.\n\n6. **Memory**: Systems that allow the model to store and recall information beyond the immediate context window. This can involve techniques like vector stores and retrieval systems to access a larger knowledge pool.\n\n7. **Inference Mechanism**: The process by which the model generates responses based on the input it receives. This includes the model's ability to perform tasks like text generation, translation, summarization, and more.\n\n8. **Optimization and Planning**: For advanced applications, LLMs may include components for planning, breaking down tasks into subgoals, and refining actions based on self-reflection and feedback.\n\nThese elements work together to enable the LLM to perform a wide range of language-related tasks effectively." } -
최종 답변: 1 → 2 → 3에 대해서 순차적으로 답변 해가면서 고도화해간 답변입니다.
-
내용을 보니 얼추 맞는 것 같습니다.
The essential technologies supporting an LLM-powered autonomous agent include:
-
Large Language Models (LLMs):
- Natural Language Interface: LLMs serve as the core controller or "brain" of the system, enabling the agent to understand, generate, and parse instructions and responses through natural language interactions. This interface facilitates communication between the LLM and external components such as memory systems, planning modules, and tools.
-
Planning Technologies:
- Task Decomposition: Techniques like Chain of Thought (CoT) and Tree of Thoughts (ToT) are used to break down complex tasks into smaller, manageable subgoals. This helps the agent plan and execute tasks step-by-step.
- Reflection and Refinement: The agent performs self-criticism and self-reflection to learn from past actions, refine strategies, and improve the quality and efficiency of its outputs.
-
Memory Systems:
- Finite Context Length Handling: Due to the finite context length limitation of LLMs, mechanisms such as vector stores and retrieval are employed to access a larger knowledge pool and overcome context capacity constraints.
- Retrieval Models: These models surface relevant context based on factors like recency, importance, and relevance to inform the agent's behavior and decision-making processes.
- Reflection Mechanism: This involves synthesizing memories into higher-level inferences that guide future behavior, generating summaries of past events for better decision-making.
-
Inter-Agent Communication:
- The LLM generates natural language statements to facilitate communication between different agents within the system, triggering new actions and responses based on the shared information.
-
Environment Interaction:
- The LLM translates reflections and environmental information into actionable plans, considering relationships between agents and observations to optimize both immediate and long-term actions.
-
Proof-of-Concept Implementations:
- Examples like AutoGPT, GPT-Engineer, and BabyAGI demonstrate the potential of LLM-powered autonomous agents, highlighting the integration of LLMs with other system components to handle complex tasks and improve over time through continuous learning and refinement.
Together, these technologies enable LLM-powered autonomous agents to plan, learn, adapt, and interact effectively, supporting their function as powerful general problem solvers.
-
3. 하위 질문별로 답변 생성 및 연속적인 처리
- (고집) 하지만, 원본 질문은 Key components를 묻는거였으므로, essential technologies라고 답하는 것은 만족스럽지 않습니다.
- 이에 한번 더 원본 질문을 참조하는 프롬프트를 만들어서 호출해보도록 하겠습니다.
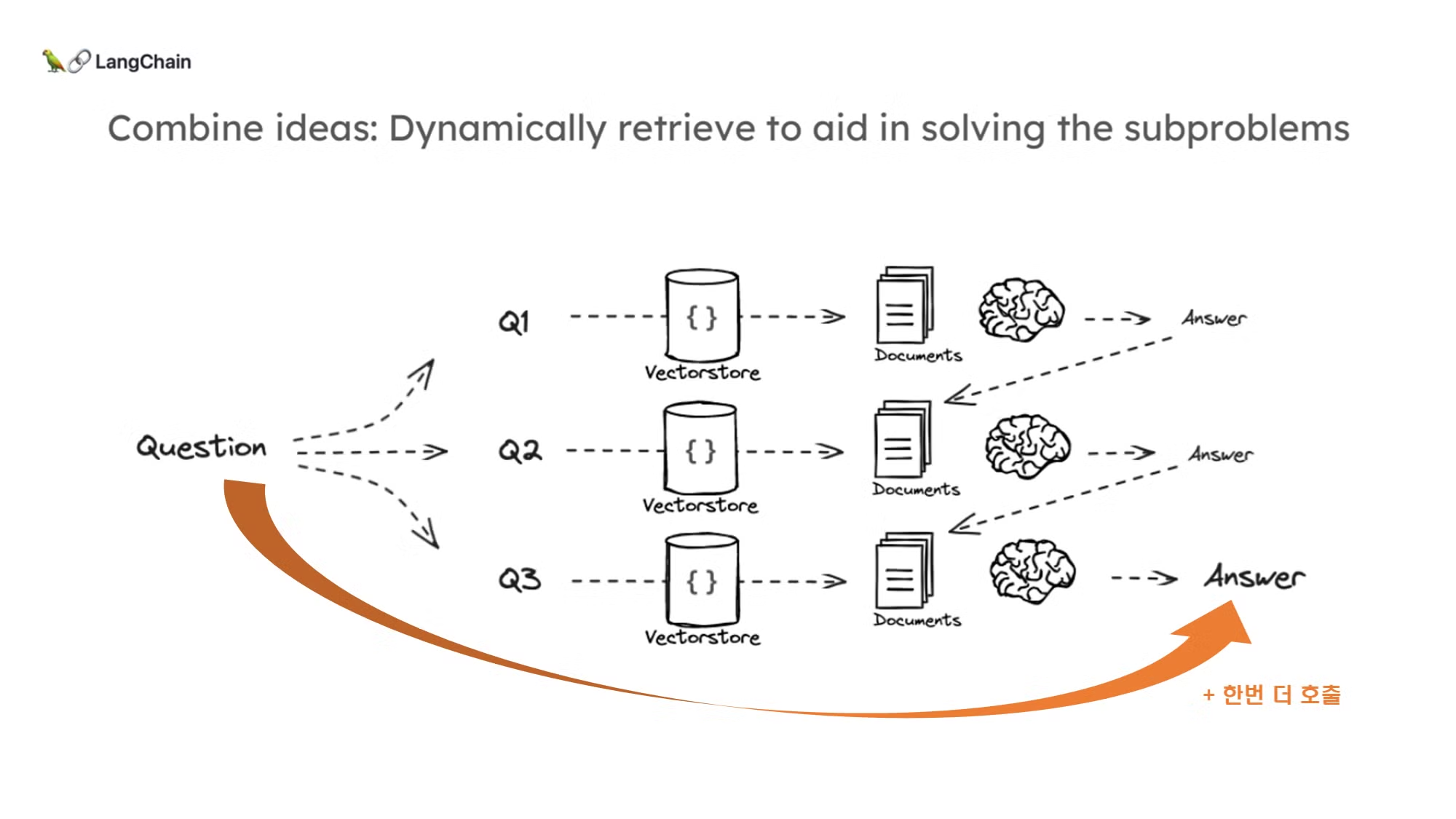
# After processing sub-questions and accumulating q_a_pairs
final_prompt_template = """
You are a knowledgeable assistant.
Here is the original question:
{original_question}
Here are the relevant question and answer pairs that may help you:
{q_a_pairs}
Using the information above, please provide a detailed and comprehensive answer to the original question.
"""
final_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(final_prompt_template)
# Reuse or initialize the LLM
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
# Create the chain
final_chain = (
final_prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
# Invoke the chain to get the final answer
final_answer = final_chain.invoke({"original_question": question, "q_a_pairs": q_a_pairs})
print("Final Answer:\n", final_answer)
답변:
Final Answer:
# Main Components of an LLM-Powered Autonomous Agent System
- An LLM-powered autonomous agent system integrates a variety of technologies and modules to enable the agent to plan, learn, adapt, and interact with its environment and other agents effectively. Below are the main components of such a system:
## 1. Large Language Models (LLMs)
- Core Controller: The LLM acts as the brain of the system, driving the core functionalities. It understands, generates, and parses instructions and responses through natural language interactions.
## 2. Natural Language Interface
- Communication: This interface allows for natural language interactions between the LLM and external components such as memory systems and planning modules. It facilitates effective communication and information exchange within the system.
## 3. Planning
- Task Decomposition: Techniques like Chain of Thought (CoT) and Tree of Thoughts (ToT) are used to break down complex tasks into smaller, manageable subgoals. This helps in planning and executing tasks step-by-step.
- Reflection and Refinement: The agent can perform self-criticism and self-reflection over past actions, learning from mistakes, and refining its approach for future tasks. This continuous improvement enhances the quality and efficiency of the agent's outputs.
## 4. Memory Systems
- Finite Context Length Handling: Due to the finite context length limitation of LLMs, mechanisms such as vector stores and retrieval models are employed to access a larger knowledge pool.
- Retrieval Models: These models surface relevant context based on factors like recency, importance, and relevance to inform the agent's behavior and decision-making processes.
- Reflection Mechanism: This involves synthesizing memories into higher-level inferences that guide future behavior. It generates summaries of past events and uses them for better decision-making.
## 5. Inter-Agent Communication
- Natural Language Statements: The LLM generates natural language statements to facilitate communication between different agents within the system. This enables the sharing of information, triggering new actions and responses.
## 6. Environment Interaction
- Actionable Plans: The LLM translates reflections and environmental information into actionable plans. It takes into account the relationships between agents and observations to optimize both immediate and long-term actions.
## 7. Proof-of-Concept Implementations
- Examples: Implementations like AutoGPT, GPT-Engineer, and BabyAGI demonstrate the potential and capabilities of LLM-powered autonomous agents. These examples highlight the integration of LLMs with other system components to handle complex tasks and improve over time through continuous learning and refinement.
# Summary
An LLM-powered autonomous agent system is composed of several key components that work together to enable sophisticated functionalities. The Large Language Model (LLM) serves as the core controller, interfacing with other modules through a natural language interface. The planning module uses techniques like Task Decomposition and Reflection and Refinement to manage tasks efficiently. Memory systems overcome the finite context length of LLMs by employing vector stores and retrieval models, aiding in better decision-making. Inter-agent communication and environment interaction modules ensure seamless information exchange and actionable planning. Proof-of-concept implementations illustrate the practical applications and continuous improvement potential of these systems. Together, these components create a robust framework for autonomous agents capable of complex problem-solving and adaptive learning.(참고) 모든 하위 질문에 대한 답변을 개별적으로 처리
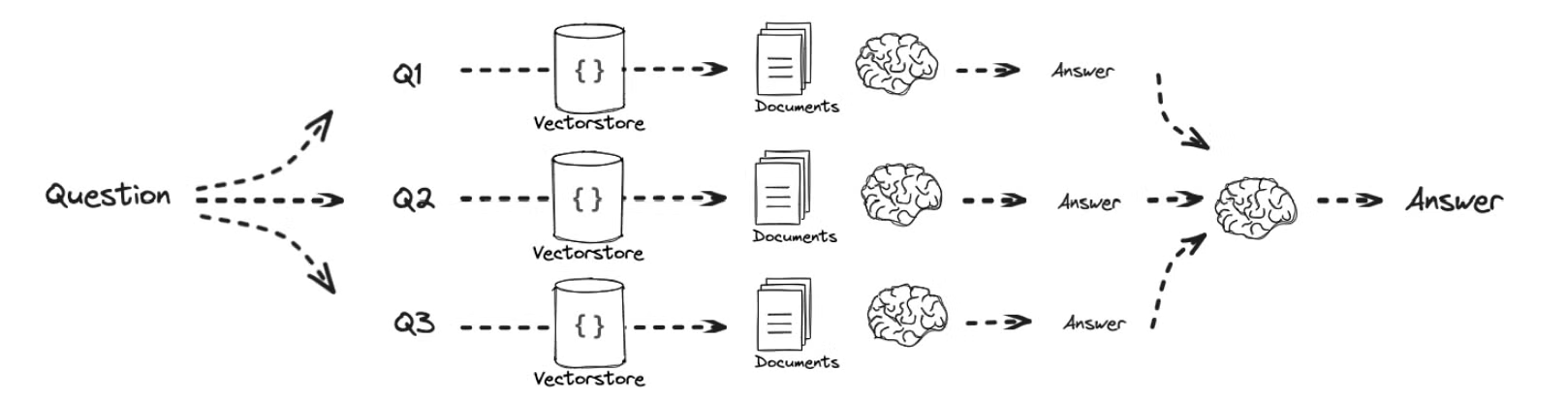
- 위에서는 순차적으로 질문에 대해서 답변을 각 하위 질문에 대해 순차적으로 답변을 생성하고 이를 종합하여 최종 답변을 생성합니다.
- 반면에 해당 예시는 각각 하위 질문에 대한 답변을 생성 후 이를 종합하여 최종 답변을 생성합니다.
from langchain import hub
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough, RunnableLambda
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
# RAG 프롬프트
prompt_rag = hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt")
def retrieve_and_rag(question, prompt_rag, sub_question_generator_chain):
"""하위 질문에 대한 RAG 수행"""
sub_questions = sub_question_generator_chain.invoke({"question":question})
rag_results = []
for sub_question in sub_questions:
retrieved_docs = retriever.get_relevant_documents(sub_question)
answer = (prompt_rag | llm | StrOutputParser()).invoke({"context": retrieved_docs,
"question": sub_question})
rag_results.append(answer)
return rag_results, sub_questions
answers, questions = retrieve_and_rag(question, prompt_rag, generate_queries_decomposition)
def format_qa_pairs(questions, answers):
"""질문과 답변을 포맷팅"""
formatted_string = ""
for i, (question, answer) in enumerate(zip(questions, answers), start=1):
formatted_string += f"Question {i}: {question}\nAnswer {i}: {answer}\n\n"
return formatted_string.strip()
context = format_qa_pairs(questions, answers)
# 최종 RAG 프롬프트
template = """Here is a set of Q+A pairs:
{context}
Use these to synthesize an answer to the question: {question}
"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
final_rag_chain = (
prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
final_rag_chain.invoke({"context":context,"question":question})
답변: 관점이 다르게 답하지만 전 이전 버전의 대답이 좀 더 제 취향인걸로😎
Question: 'What are the main components of an LLM-powered autonomous agent system?'
Answer:
An LLM-powered autonomous agent system is composed of several key components that work together to enable the agent's functionality. These include:
1. Hardware Components: The primary hardware components consist of the large language model (LLM) itself, memory storage for managing historical data and interactions, and processing units capable of handling the intensive computational demands required for planning and task decomposition.
2. Software Frameworks: Essential software frameworks for building such a system include AutoGPT, GPT-Engineer, and BabyAGI. These frameworks are proof-of-concept demos that illustrate how LLMs can serve as the core controller of autonomous agents, handling tasks such as planning, task decomposition, and self-reflection to continually improve their performance.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP) Modules: NLP modules act as the interface between the LLM and other external components like memory and tools. They enable the agent to parse and understand model outputs, which is crucial for effective task decomposition, planning, and interaction with other system components. However, managing the reliability of these outputs is critical, as errors can impact the agent's performance.
Together, these hardware and software components form a cohesive system that supports the complex functionalities required for an autonomous agent to operate effectively.요약
- Decomposition 방식은 복잡한 질문을 여러 하위 질문으로 분해하여 각각을 독립적으로 해결한 후, 최종 답변을 제공하는 방법입니다.
- 이 과정에서 이전 질문의 답변을 다음 질문에 활용하여 점진적으로 문제를 해결하는 방식이 핵심입니다.
- 이를 통해 복잡한 문제를 체계적으로 해결하고, 검색 성능을 향상시킬 수 있습니다.
Part 8 (단계적 후퇴)
- 이 강의는 RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation) 파이프라인의 "Query Translation(쿼리 변환)" 중 네 번째 방법인 Step Back(스텝백) 프롬프팅에 대해 설명합니다.
- Step Back 기법은 질문을 더 추상적인 수준으로 변환하여 문서 검색 성능을 개선하는 방법입니다.
문제 정의 및 접근 방법
- 이전 기법들인 Multi-query와 RAG Fusion은 질문을 여러 관점에서 다시 쓰거나, 질문을 하위 문제로 분해하여 각각을 해결하는 방법에 중점을 두었습니다. 그러나 Step Back 방식은 질문을 더 추상적인 질문으로 변환하여 고차원적인 개념을 중심으로 검색을 수행하는 것이 특징입니다.
- 논문 "Take a Step Back: Evoking Reasoning via Abstraction in Large Language Models"에서는 대형 언어 모델(LLM)의 추론 능력을 향상시키기 위한 새로운 프롬프트 기법인 Step-Back Prompting을 제안합니다.
추상화를 통한 추론 개선: Step-Back Prompting은 모델이 문제를 직접 해결하기 전에, 먼저 문제를 한 단계 뒤로 물러나서 추상화된 고수준 개념이나 원리를 도출하도록 유도합니다. 이러한 추상화 단계는 모델이 복잡한 문제에서 세부적인 오류를 줄이고 더 높은 정확도로 추론할 수 있게 합니다.다양한 도메인에의 적용: 이 기법은 물리학, 화학, 시간 지식 질문(TimeQA), 다단계 추론(Multi-Hop Reasoning) 등 다양한 작업에 적용 가능하며, 이를 통해 학습된 원리를 다양한 상황에 응용할 수 있음을 보여줍니다.성능 비교: Step-Back Prompting은 다른 기법들, 특히 Chain-of-Thought(CoT)나 Take-a-Deep-Breath(TDB) 프롬프트와 비교하여, 추론 작업에서 일관되게 더 나은 성능을 보였습니다.
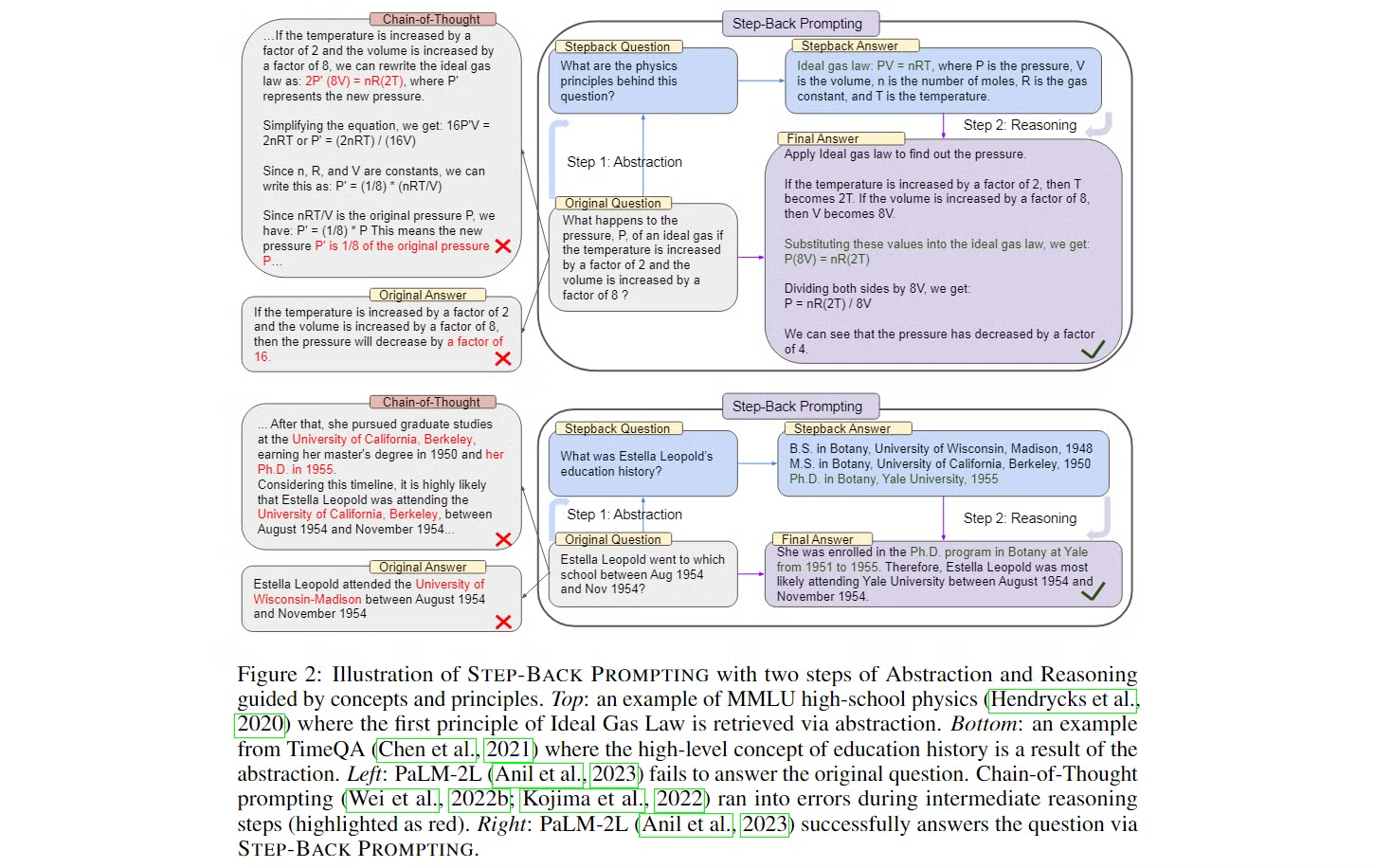
-
Figure 2는 두 가지 작업(물리학 문제와 시간 기반 질문)에 대해 Step-Back Prompting을 어떻게 적용하는지를 보여줍니다. 각각의 예시에서 모델은 문제를 해결하기 위해 "Step-Back" 질문을 생성하고, 이를 바탕으로 추론을 진행합니다.
-
물리학 문제 (MMLU 물리학 예시)
문제: "이상 기체의 압력 P는 온도가 2배로 증가하고 부피가 8배로 증가하면 어떻게 변하는가?"
- 원래 접근 방식: 모델이 처음에 문제를 직관적으로 풀려고 시도합니다. 여기서 Chain-of-Thought(CoT) 방식으로 중간 단계에서 몇 가지 오류가 발생할 수 있습니다.
- Step-Back Prompting의 적용: Step-Back Prompting은 먼저 "① 이 문제의 기본 물리 법칙은 무엇인가?"라는 추상적인 질문을 하도록 유도합니다.
- 이 질문을 통해 모델은 ② 이상 기체 법칙 (Ideal gas law, PV=nRT)을 회상하게 되고, 이를 바탕으로 문제를 해결하는 과정을 이어갑니다.
- 추상화 단계: "이상 기체 법칙"이라는 물리학의 기본 원리를 추출합니다.
- 추론 단계: 이상 기체 법칙을 적용하여, 온도와 부피 변화에 따른 압력 변화를 계산합니다. 결과적으로 압력은 16분의 1로 줄어듭니다.
- 이 질문을 통해 모델은 ② 이상 기체 법칙 (Ideal gas law, PV=nRT)을 회상하게 되고, 이를 바탕으로 문제를 해결하는 과정을 이어갑니다.
이 과정에서 Step-Back Prompting을 통해 모델은 세부적인 계산에서 오류를 피하고, 추상적인 원리로부터 올바른 답을 도출할 수 있게 됩니다.
-
시간 기반 질문 (TimeQA 예시)
문제: "Estella Leopold는 1954년 8월에서 11월 사이에 어느 학교에 다녔는가?"
- 원래 접근 방식: 모델은 주어진 특정 시간 범위 내에서 Estella Leopold의 교육 기록을 바로 찾으려고 시도합니다. CoT 방식으로 중간 단계에서 시간 범위 제한으로 인해 오류가 발생할 수 있습니다.
- Step-Back Prompting의 적용: Step-Back Prompting은 먼저 "Estella Leopold의 교육 기록은 무엇인가?"라는 보다 추상적인 질문을 생성하게 합니다. 이를 통해 모델은 그녀의 전반적인 교육 기록을 회상하고, 이를 바탕으로 특정 시간 범위에 대한 정답을 추론합니다.
- 추상화 단계: "Estella Leopold의 전반적인 교육 이력"이라는 고수준 개념을 도출합니다.
- 추론 단계: 이 추상화된 교육 이력을 기반으로, 1954년 8월부터 11월까지 그녀가 Yale University에서 박사 과정을 밟고 있었다는 결론을 도출합니다.
이 예시에서 Step-Back Prompting은 세부적인 시간 제한에서 발생할 수 있는 오류를 피하고, 보다 넓은 관점에서 문제를 해결할 수 있도록 도와줍니다.
-
Step Back 기법의 직관
- Step Back 방식에서는 기존 질문을 기반으로 더 추상적인 질문을 생성하여, 두 가지 질문(원래 질문과 추상화된 질문)을 동시에 검색하고, 그 결과를 바탕으로 최종 답변을 도출합니다.
- 이는 특히 개념적인 지식을 바탕으로 검색해야 하는 도메인에서 유용하며, 문서의 내용이 특정 질문에 대한 답을 직접 제공하지 않을 경우 더 일반적인 문서를 검색하여 보완할 수 있습니다.
코드 시연
1. Few-shot 예시 생성
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate, FewShotChatMessagePromptTemplate
# fewshot
examples = [
{
"input": "Could the members of The Police perform lawful arrests?",
"output": "What can the members of The Police do?",
},
{
"input": "Jan Sindel’s was born in what country?",
"output": "What is Jan Sindel’s personal history?",
},
]
example_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("human", "{input}"),
("ai", "{output}"),
]
)
few_shot_prompt = FewShotChatMessagePromptTemplate(
example_prompt=example_prompt,
examples=examples,
)
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
(
"system",
"""
You are an expert at world knowledge. Your task is to step back and paraphrase a question to a more generic step-back question, which is easier to answer.
Here are a few examples:
""",
),
few_shot_prompt,
("user", "{question}"),
]
)
generate_queries_step_back = prompt | ChatOpenAI(temperature=0) | StrOutputParser()- Step Back 프롬프팅을 위한 예시(few-shot examples)를 제공하여, 모델이 원래 질문을 어떻게 추상적인 질문으로 변환할지 학습시킵니다.
- 원래 질문(original question)을 기반으로 추상적인 질문을 생성하는 프롬프트(*논문 사용 프롬프트)를 정의합니다.
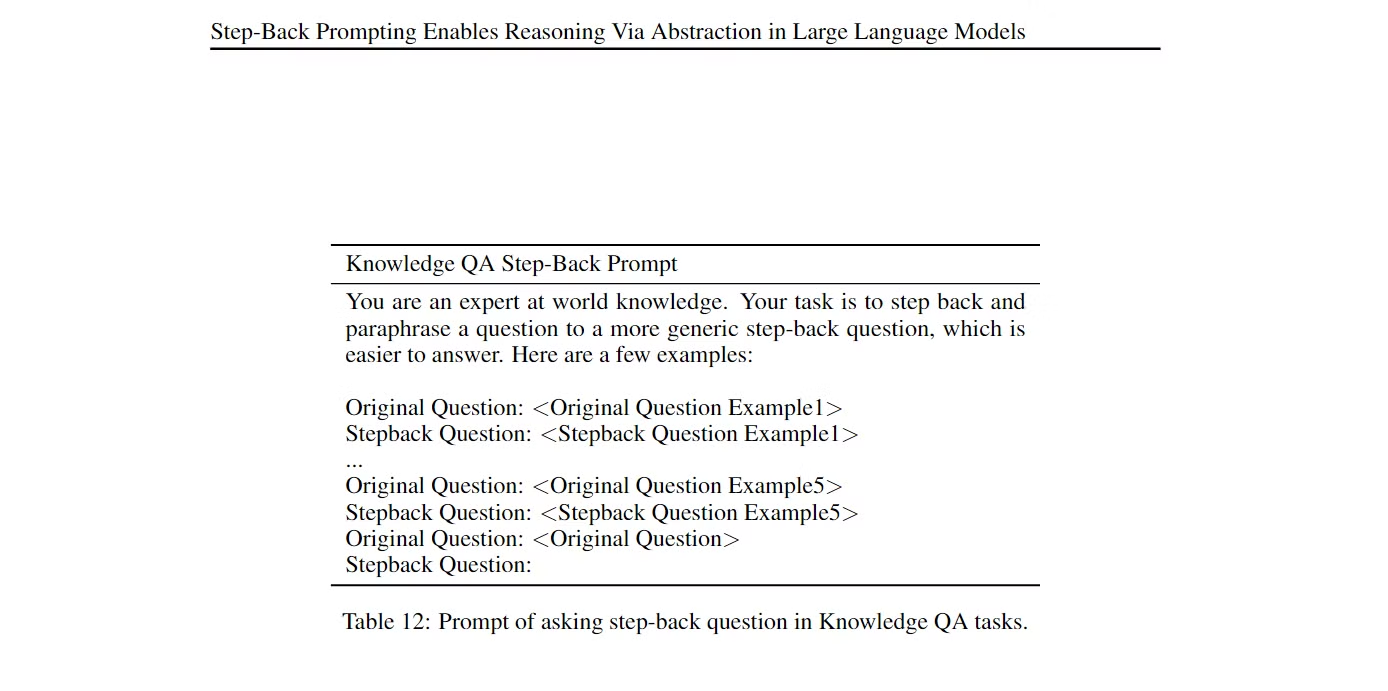
2. Step Back 질문 생성 및 검색 & 답변 생성
question = "What is task decomposition for LLM agents?"
generate_queries_step_back.invoke({"question": question})- "What is task decomposition for LLM agents?"라는 question의 step-back question으로 다음 답변이 나옴.
'How do LLM agents handle complex tasks?'- 이 질문을 통해 LLM 에이전트가 복잡한 작업을 해결하는 전반적인 전략이나 방식을 묻고, 구체적인 세부 사항보다는 고수준의 개념을 이해하려는 목적을 담고 있습니다.
- 이 방식으로 Step-Back 질문을 적용하면 세부적인 작업 분해(task decomposition)의 구체적인 방법보다는, 전체적인 작업 처리 방식에 대한 답변을 도출할 가능성이 높습니다.
response_prompt_template = """
You are an expert of world knowledge. I am going to ask you a question.
Your response should be comprehensive and not contradicted with the following context if they are relevant.
Otherwise, ignore them if they are not relevant.
# {normal_context}
# {step_back_context}
# Original Question: {question}
# Answer:
"""
response_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(response_prompt_template)
chain = (
{
# 원래 질문에 대한 검색
"normal_context": RunnableLambda(lambda x: x["question"]) | retriever,
# Step Back 질문에 대한 검색
"step_back_context": generate_queries_step_back | retriever,
"question": lambda x: x["question"],
}
| response_prompt
| ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
| StrOutputParser()
)
chain.invoke({"question": question})
- 원래 질문을 기반으로 추상적인 질문을 생성한 후, 그 질문을 바탕으로 검색을 수행합니다.
- 원래 질문과 Step Back 질문을 모두 사용하여 각각의 검색 결과를 합치고, 최종 답변을 도출하는 프롬프트를 정의합니다.
요약
- Step Back(스텝백) 방식은 원래 질문을 더 추상적인 수준으로 변환하여 검색 성능을 향상시키는 방법입니다.
- 이 기법은 원래 질문이 너무 구체적일 때, 더 일반적인 질문을 생성하여 더 넓은 범위의 정보를 검색하고, 그 결과를 결합하여 최종 답변을 생성합니다.
- 특히, 개념적인 지식을 바탕으로 검색이 필요한 도메인에서 유용하며, 문서의 구조가 개념적 내용과 구체적 내용으로 나뉘는 경우 효과적입니다.
Part 9 (HyDE)
- 이 강의는 RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation) 파이프라인의 "Query Translation(쿼리 변환)" 중 다섯 번째 방법인 HyDE (Hypothetical Document Embeddings)에 대해 설명합니다.

- 해당 논문은 “Precise Zero-Shot Dense Retrieval without Relevance Labels”라는 제목을 가진 논문으로, 핵심적으로 Hypothetical Document Embeddings (HyDE) 기법을 제안합니다.
- HyDE는 쿼리와 관련된 "가상 문서(Hypothetical Document)"를 생성하여 문서 검색을 수행하는 방법입니다. 이 가상 문서는 실제로 존재하지 않는 문서로, 학습된 언어 모델(예: InstructGPT)을 통해 생성됩니다.
- HyDE의 주요 단계는 다음과 같습니다:
가상 문서 생성: 쿼리가 주어졌을 때, 언어 모델이 해당 쿼리에 답변하는 가상의 문서를 작성합니다. 이 가상 문서는 쿼리와 관련된 내용을 담고 있지만, 사실이 아닐 수도 있습니다.문서 임베딩: 가상 문서는 대조 학습을 거친 인코더(예: Contriever)를 통해 임베딩 벡터로 변환됩니다. 이 임베딩 벡터는 가상 문서에서 불필요한 세부 사항을 걸러내고, 쿼리와 관련된 실제 문서들을 검색할 수 있도록 돕습니다.문서 검색: 최종적으로, 임베딩 벡터를 이용해 코퍼스 내의 실제 문서들과의 벡터 유사도를 계산하고, 가장 유사한 문서들을 검색합니다.
문제 정의 및 접근 방법
- RAG의 기본 흐름에서는 질문과 문서를 임베딩하여 임베딩 공간에서의 유사성을 기반으로 문서를 검색합니다.
- 하지만 질문과 문서는 매우 다른 유형의 텍스트 객체입니다.
- Why ⇒ ? 문서는 일반적으로 길고 밀도가 높은 정보로 구성된 반면, 질문은 짧고 사용자에 의해 비구조적으로 작성될 수 있습니다.
- 하지만 질문과 문서는 매우 다른 유형의 텍스트 객체입니다.
- HyDE의 핵심 아이디어는 질문을 가상의 문서로 변환하여 문서 임베딩 공간에 매핑하는 것입니다. (아래 그림 참고)
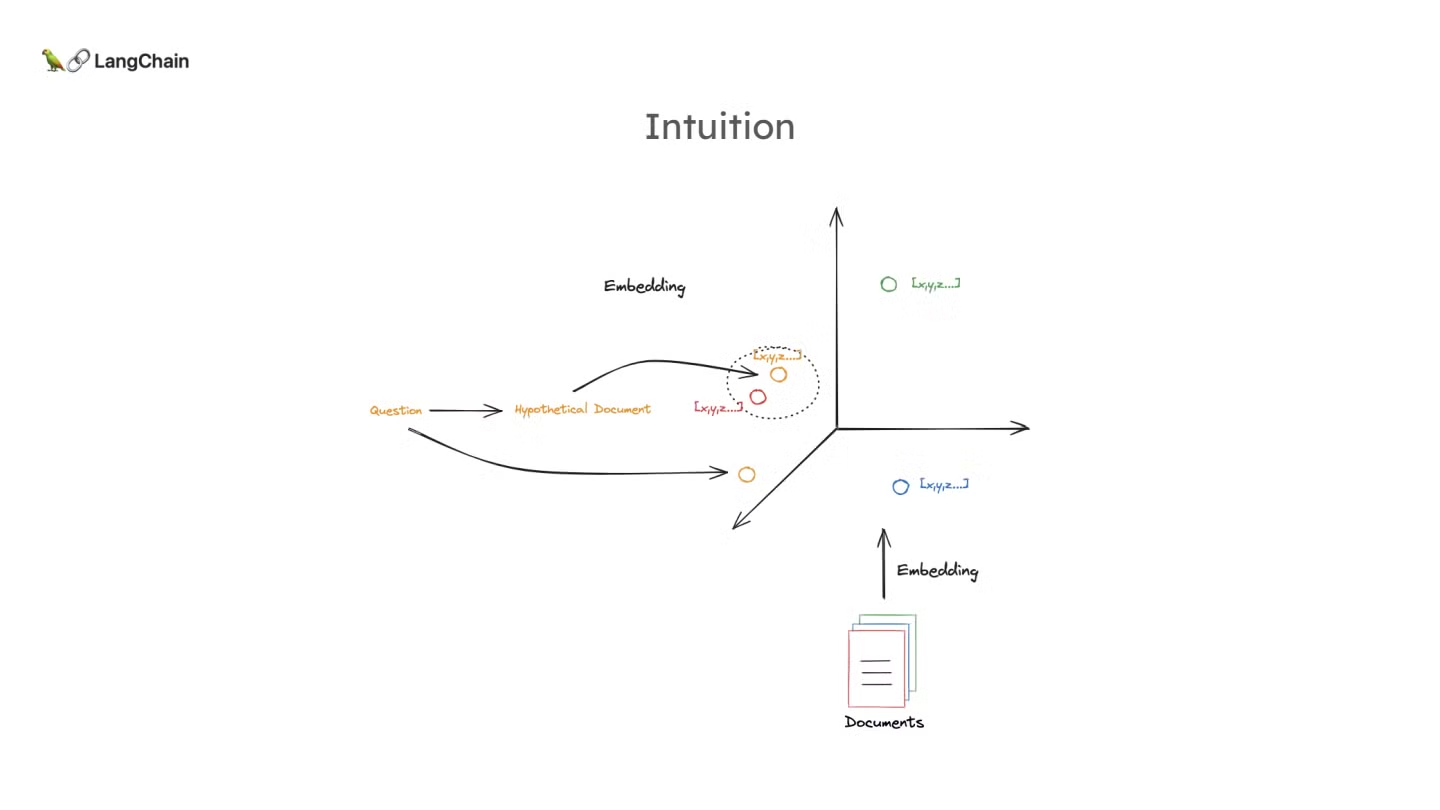
- 즉, 기존처럼 질문을 바로 임배딩을 시켜서 검색하는 대신, 가상의 문서를 생성하여 검색에 활용하는 것입니다.
- 이 방법을 통해 질문의 임베딩이 부족할 수 있는 경우에도 가상의 문서가 더 유사한 실제 문서와 잘 일치할 수 있도록 합니다.
- 왜 가상의 문서가 질문보다 더 원본 문서와 가까워질 수 있는가?
- 가상의 문서는 원래 질문보다 더 많은 정보와 맥락을 포함할 수 있기 때문에, 관련된 실제 문서와 더 가까운 벡터 공간에 위치하게 됩니다.
- 이는 가상 문서가 질문에서 부족한 부분을 보완하고, 언어 모델의 학습된 패턴을 활용해 더 풍부한 관련 정보를 생성하기 때문입니다.
- 이로 인해 가상 문서를 사용하는 것이 원래 질문을 직접 사용하는 것보다 더 나은 검색 결과를 도출할 수 있게 됩니다.
코드 시연
1. HyDE를 위한 문서 생성 프롬프트 정의 및 생성
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
template = """
Please write a scientific paper passage to answer the question
Question: {question}
Passage:
"""
prompt_hyde = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
generate_docs_for_retrieval = (
prompt_hyde | ChatOpenAI(temperature=0) | StrOutputParser()
)
# 예시 질문
question = "What is task decomposition for LLM agents?"
generate_docs_for_retrieval.invoke({"question":question})
- 질문을 바탕으로 가상의 과학적 문서를 생성하는 프롬프트를 정의합니다.
- 원래 질문을 기반으로 가상의 문서를 생성합니다. 엄청 그럴 듯하게 논문 구조로 작성된 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
Title: Task Decomposition for Large Language Model (LLM) Agents
Abstract:
Task decomposition for Large Language Model (LLM) agents refers to the systematic process of breaking down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable subtasks, which can be sequentially or concurrently addressed by the model. This methodology aims to enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and overall performance of LLMs when faced with multifaceted queries or tasks. This passage explores the principles, methodologies, and implications of task decomposition in the context of LLM agents.
Introduction:
Large Language Models (LLMs), such as GPT-4, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in natural language understanding, generation, and various other language-related tasks. However, their performance can be significantly improved through the strategic application of task decomposition. By dividing a complex task into discrete, manageable components, LLM agents can process information more effectively, reduce cognitive load, and minimize errors.
Principles of Task Decomposition:
Task decomposition is grounded in several key principles:
1. Modularity: Breaking down a task into independent or semi-independent modules allows for parallel processing and simplifies error identification and correction.
2. Hierarchy: Establishing a hierarchical structure where higher-level tasks are decomposed into lower-level subtasks ensures a coherent and organized approach to problem-solving.
3. Sequential Dependency: Understanding the dependencies between subtasks enables the LLM to process them in the correct order, ensuring that intermediate results are correctly utilized in subsequent steps.
Methodologies:
There are various methodologies for task decomposition, each tailored to specific types of tasks and LLM capabilities:
1. Top-Down Decomposition: This approach begins with the overarching task and progressively breaks it down into smaller subtasks. For example, answering a complex question might involve identifying key concepts, gathering relevant information, synthesizing data, and constructing a coherent response.
2. Bottom-Up Decomposition: Conversely, this method starts with identifying fundamental subtasks and gradually combines them to form a solution to the larger task. This can be useful in tasks where the basic components are well understood, but their integration is complex.
3. Hybrid Decomposition: Combining top-down and bottom-up approaches can provide a balanced strategy, leveraging the strengths of both methods to handle diverse tasks effectively.
Implications for LLM Performance:
The adoption of task decomposition has several implications for the performance of LLM agents:
1. Enhanced Accuracy: By focusing on smaller, more manageable subtasks, LLMs can provide more precise and accurate responses, reducing the likelihood of errors that may occur when tackling complex tasks holistically.
2. Improved Efficiency: Decomposing tasks allows for parallel processing, which can significantly speed up task completion and optimize resource utilization.
3. Scalability: Task decomposition facilitates the scaling of LLM applications to handle increasingly complex and diverse tasks, making them more versatile and robust.
Conclusion:
Task decomposition is a vital strategy for optimizing the performance of LLM agents. By breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable components, LLMs can improve their accuracy, efficiency, and scalability. As LLM technology continues to evolve, the principles and methodologies of task decomposition will play an increasingly important role in harnessing the full potential of these powerful models.
Keywords: Task decomposition, Large Language Models, LLM agents, modularity, hierarchical structure, sequential dependency, top-down decomposition, bottom-up decomposition, hybrid decomposition.2. 생성된 가상 문서를 사용한 문서 검색
# 검색 체인
retrieval_chain = generate_docs_for_retrieval | retriever
retireved_docs = retrieval_chain.invoke({"question":question})
retireved_docs
- 생성된 가상의 문서를 바탕으로 해당 문서와 관련이 높은 문서들을 검색합니다.
3. 검색된 문서를 바탕으로 최종 답변 생성
# RAG 프롬프트
template = """Answer the following question based on this context:
{context}
Question: {question}
"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
final_rag_chain = (
prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
# 최종 RAG 체인 실행
final_rag_chain.invoke({"context":retireved_docs,"question":question})
- 검색된 문서들을 바탕으로 원래 질문에 대한 최종 답변을 생성합니다.
요약
- HyDE(Hypothetical Document Embeddings)는 질문을 가상의 문서로 변환한 후, 해당 문서를 이용해 검색을 수행하는 방법입니다.
- 질문이 직접 검색에 적합하지 않을 때, 가상의 문서가 문서 임베딩 공간에서 더 유사한 문서를 찾는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
- 이 방식은 특히 질문이 짧거나 구조가 명확하지 않은 경우에 유용하며, 도메인에 맞게 가상 문서 생성 프롬프트를 조정할 수 있다는 장점이 있습니다.
