모든 사진 자료에 관한 출처는 아래 알튜비튜 - 튜터링에 있음을 밝힙니다.
https://github.com/Altu-Bitu/Notice
📚 스택 (stack)
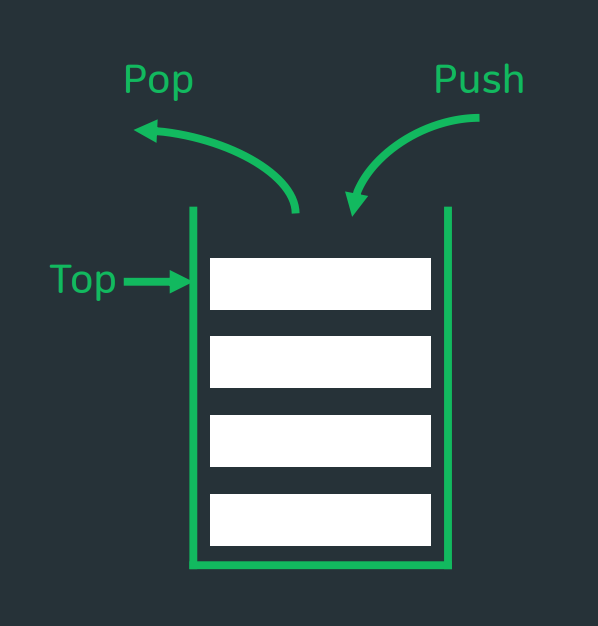
Last in, First out- 자료의
맨 끝위치에서만 모든 연산이 이루어짐 - 따라서 모든 연산에 대한 시간 복잡도는
O(1). - 연산이 이루어지는 위치를
top이라고 하며 삽입은push, 삭제는pop
💡 배열로 크기 3의 stack구현하기
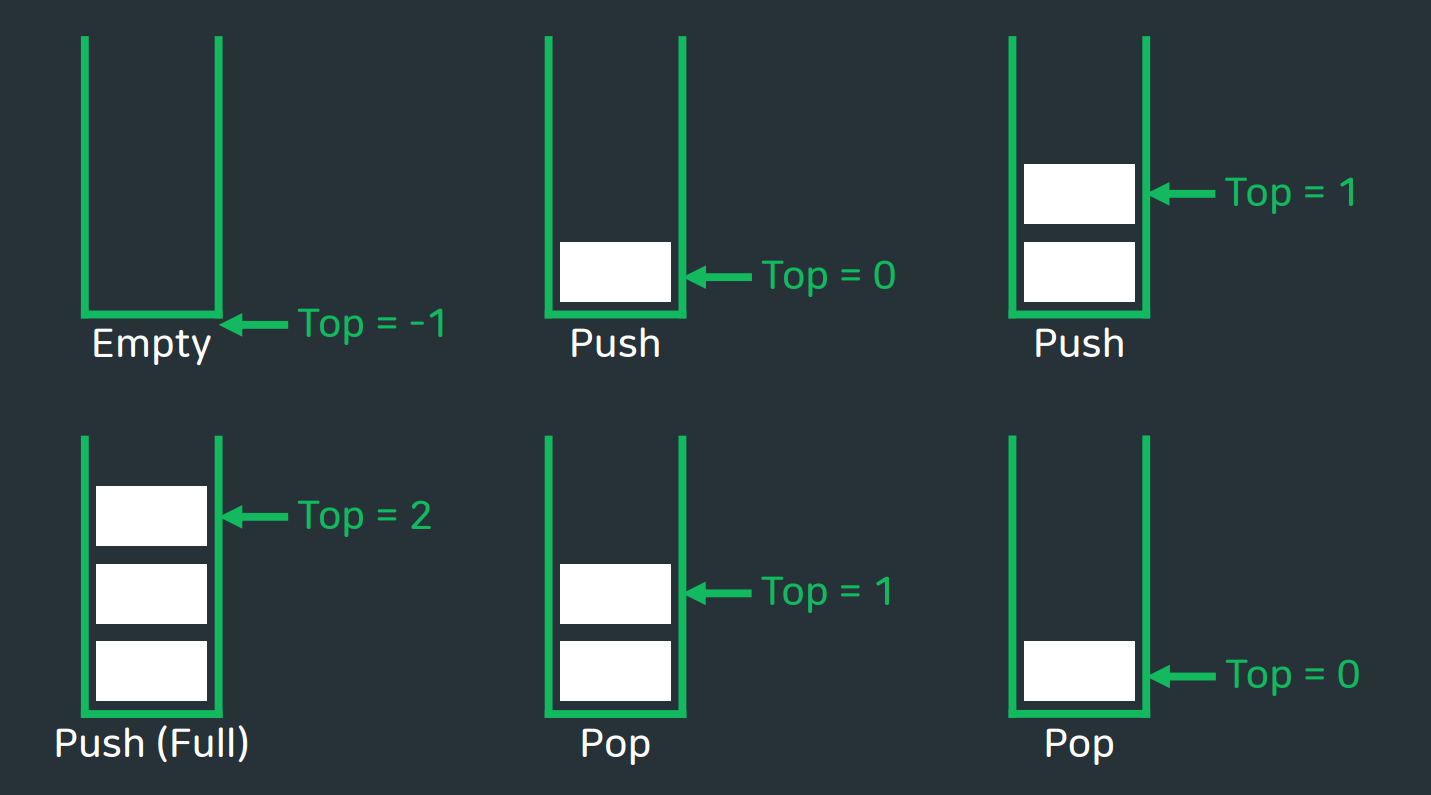
🚩이때 주의할 점은, pop하기 전에 empty체크하기, push하기 전에 full체크하기!
안그럼 index오류가 발생할것이다.
🧾 script [stack]
#include <iostream>
# include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 10000;
int top_pointer = -1; // 스택의 맨 윗 상단을 가리킬 포인터
vector<int> stack_vec(SIZE);
//empty
bool empty() {
return top_pointer == -1;
}
//full
bool full() {
return top_pointer == SIZE - 1; //top포인터가 max로 가리킬수있는 인덱스는 size-1.
}
//push
void push(int k) {
stack_vec[++top_pointer]=k;
}
//pop
int pop() {
//pop 할때 벡터에 있는 값을 실질적으로 삭제시키지 않아도됨.
//어짜피 다음번 push할때 그 인덱스가 사용자가 입력한 값으로 바꿔치기 되기 때문.
return stack_vec[top_pointer--];
}
//size
int size() {
return top_pointer + 1;
}
//top
int top() {
return stack_vec[top_pointer];
}
int main() {
cin.tie(NULL);
ios_base:: sync_with_stdio(false);
int n, k;
string cmd;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
cin >> cmd;
if (cmd == "push") {
cin >> k;
// if (!full())
// push(k);
push(k);
continue;
}
if (cmd == "pop") {
if (empty()) //스택이 비었다면
cout << -1 << '\n';
else {
cout << pop() << '\n';
}
continue;
}
if (cmd == "size") {
cout<< size() << '\n';
continue;
}
if (cmd == "empty") {
cout << empty() << '\n';
continue;
}
if (cmd == "top") {
if (empty())
cout << -1 << '\n';
else
cout << top() << '\n';
continue;
}
}
//스택 순회
while (!empty()) {
cout << top() << ' ';
pop();
}
}📰 [C++ STL] Stack
: c++에서는 **stack 라이브러리**를 제공하므로 그것을 이용한다면 이 모든 것을 일일히 구현할 필요가 없다!
* 멤버함수
-
empty(): 스택이 비어 있으면 true를, 비어 있지 않으면 false를 반환 -
size(): 스택에 원소가 몇개 있는지 -
top(): 스택의 가장 상단에 위치한 값 가져오기. -
push(k): k를 스택 최상단에 삽입 -
pop(): 스택에서 가장 위에 있는 값을 빼고 가져오기.
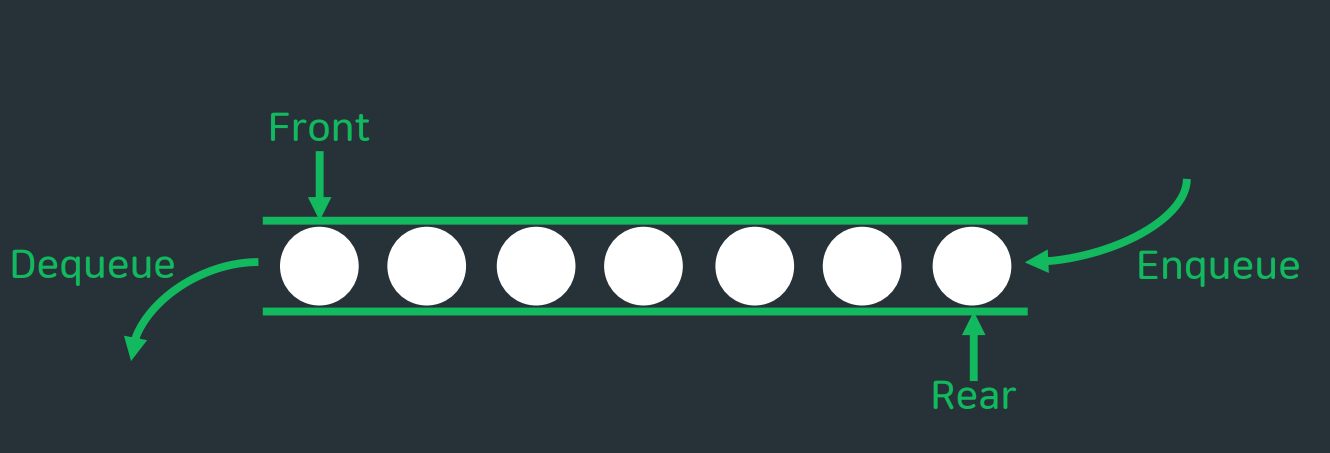
💠 큐 (Queue)
- FIFO (
First In, First Out) - 자료의 앞에서(front) 삭제, 끝(end)에서 삽입연산이 이루어짐.
- 모든연산에 대한 시간복잡도는
O(1) - 삭제가 이루어지는 위치를
front, 삽입이 이루어지는 위치를rear라고 부름 - 삽입은
enqueue, 삭제는dequeue
💡 배열로 크기 3의 큐 구현하기
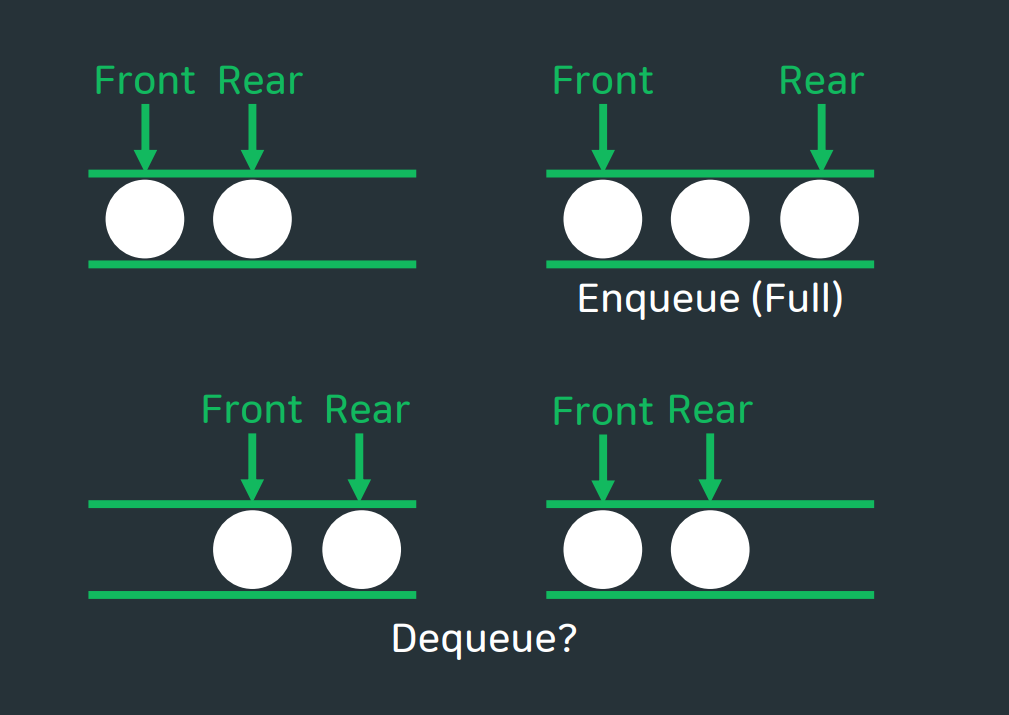
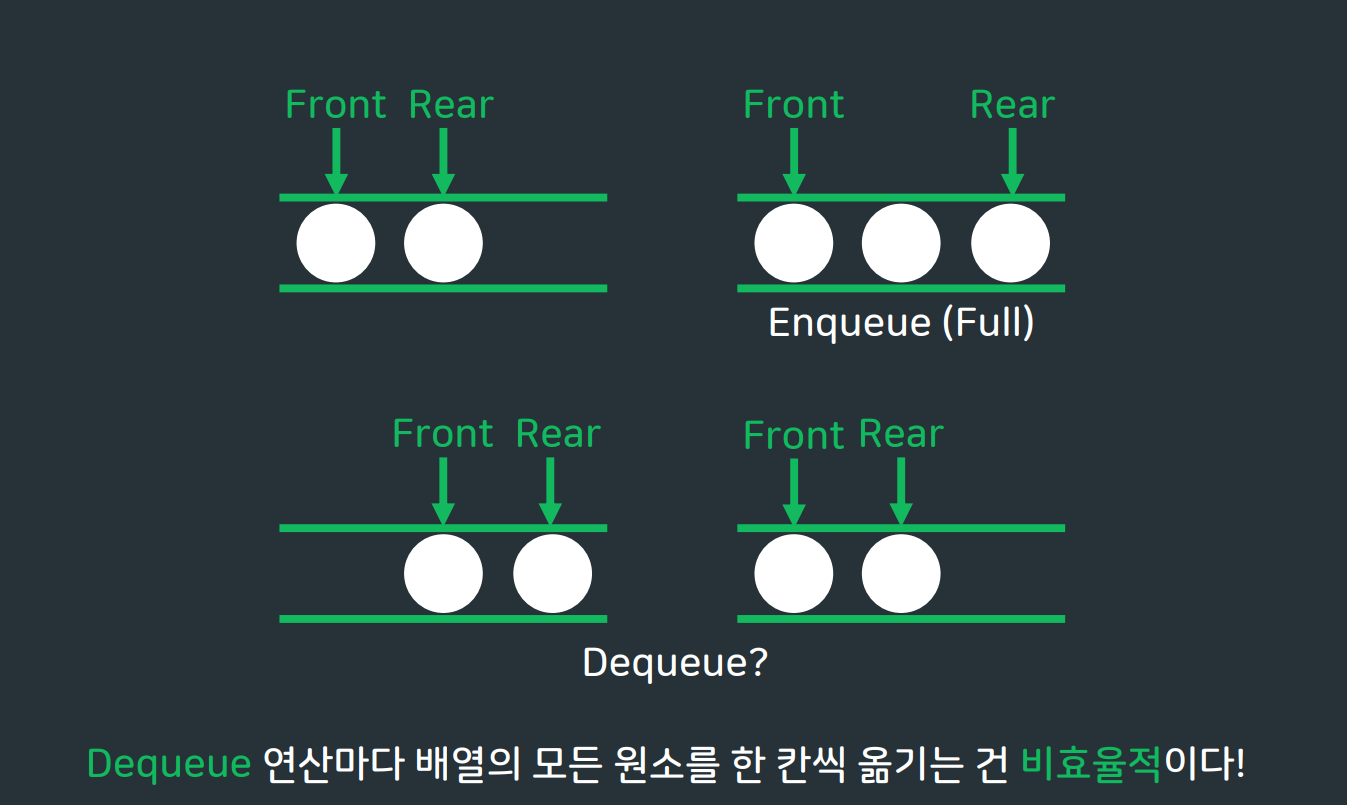
선형큐는 데이터들을 앞으로 당겨주는 과정이 필요하다.
그리고 이러한 선형 큐의 문제점을 보완하기 위한 자료구조로서 원형큐를 이용한다!
🔄 원형 큐
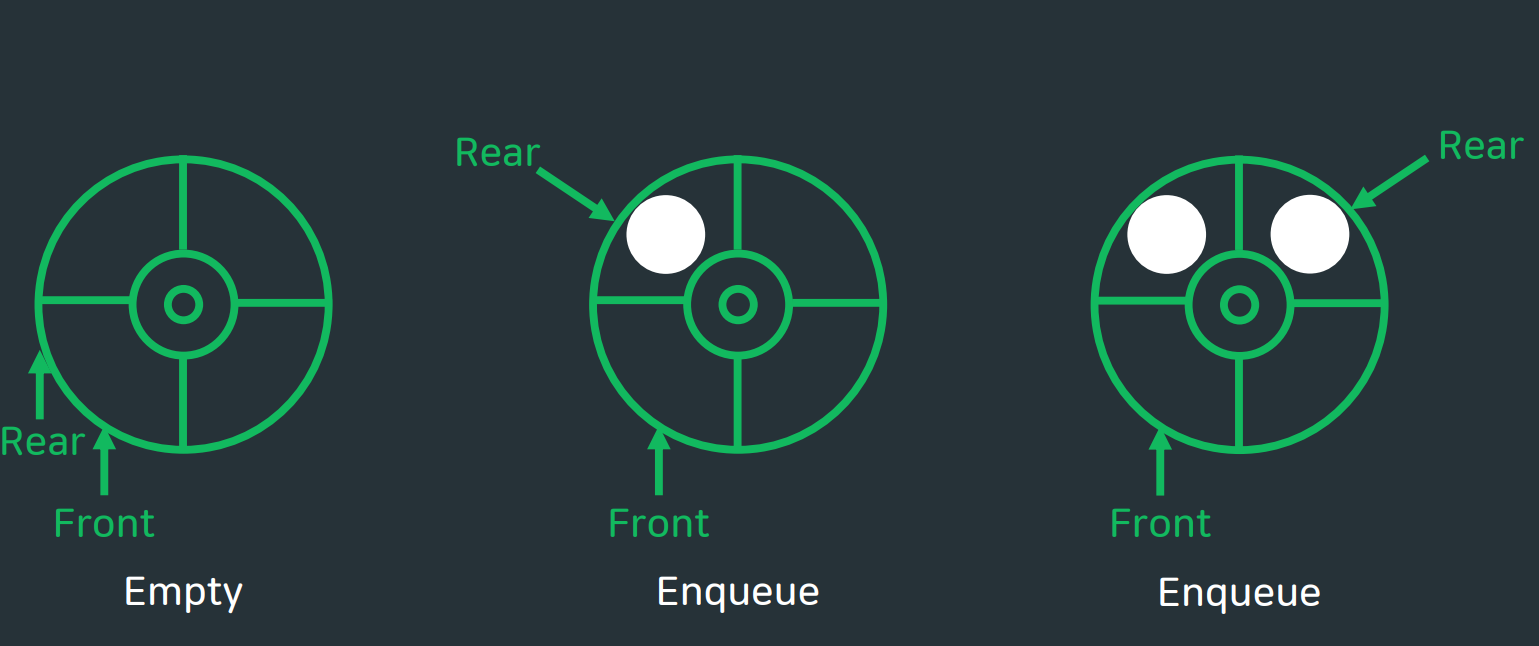
Front = Rear인채로 시작하여 큐에 값을 넣을때 rear의 포인터를 1증가 시키고 그 위치에 데이터 삽입이 이루어진다. 큐가 비어있게 된다면 rear와 front는 같은 위치를 가리킨다.
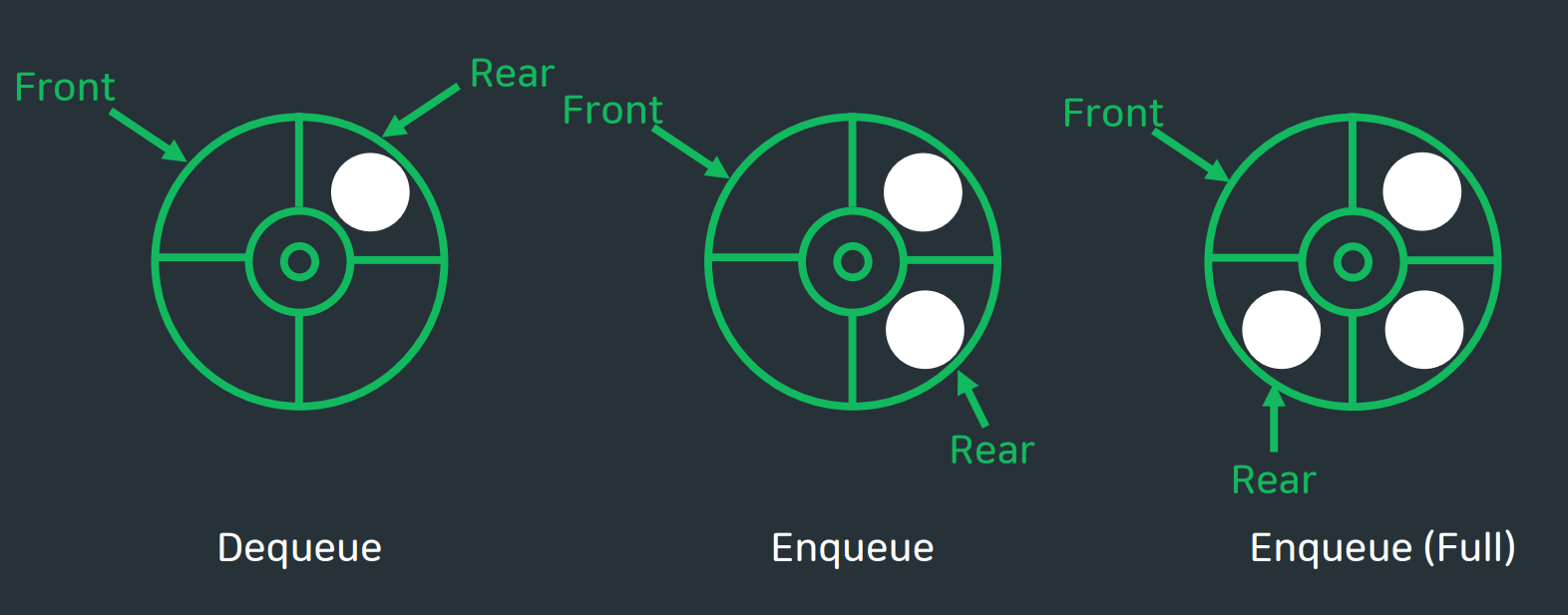
값을 삭제할때에는 front의 포인터를 1증가 시키고 그 위치의 데이터를 배열에서 삭제시켜 가지고 온다. 이때 배열의 포화상태 여부를 판단하기 위하여 배열의 1칸은 항상 비워둔다.
❓ 원형큐에서 Full의 의미?
그리고 맨 마지막 그림이 원형큐의 포화상태를 나타낸 그림인데 ' 한칸이 비었는데 왜 Full상태이지?' 하고 의아해할 수 있다. 잘 생각해보면 앞에서 Front == Rear 인 상태를 공백상태로 보기로 했으므로, 한칸을 비우지 않고 큐를 꽉채운다면 큐가 공백상태인지, 포화상태인지 구별할 수 없다. 따라서 Front뒤에 바로 REAR가 올때, 즉 (Rear +1)%SIZE == Front 라는 수식이 성립할때를 원형큐가 Full상태인것으로 해야 두 상태를 구분지을수 있다.
🧾 script [queue]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 10001;
int front_pointer = 0, rear_pointer = 0;
vector<int> queue_vec(SIZE);
//empty
bool empty() {
return front_pointer == rear_pointer; // front rear가 같은곳을 가리킬때 큐가 비어있다.
}
//full
bool full() {
return (rear_pointer + 1) % SIZE == front_pointer;
}
//push
void push(int k) {
rear_pointer = (rear_pointer + 1) % SIZE; //rear포인터를 먼저 하나 증가시키고
queue_vec[rear_pointer] = k; //그위치에 k를 삽입
}
//pop
int pop() {
front_pointer = (front_pointer + 1) % SIZE; //front포인터를 먼저 하나 증가시키고
return queue_vec[front_pointer]; // 그위치에 있는 값 반환.
//이때 어짜피 비어있는 상태로 치기때문에 값을 굳이 삭제해줄필요 X
}
//size
int size() { //rear = 1, front = 2
int tmp = (rear_pointer - front_pointer);
//front가 더 큰값이 나올수가 있나?
//-> front가 rear포인터를 추월할 순 없지만, 한바퀴를 다돌면 index가 0으로 초기화되므로 단순히 front>rear 가 되는 경우의 수는 가능함.
if (tmp < 0)
tmp += SIZE;
return tmp;
}
//front
int front() { //가장 나중에 들어온 값.
int tmp = (front_pointer + 1) % SIZE; //단순히 맨 앞 값을 가져오기만 하는것이므로 front를 증가시킬 필요 X
return queue_vec[tmp];
}
//back
int back() { //가장 최근에 들어온 값.
return queue_vec[rear_pointer]; //rear포인터가 가리키는 값이 가장 최근에 들어온값.
}
int main() {
cin.tie(NULL);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n, k;
string cmd;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
cin >> cmd;
if (cmd == "push") {
cin >> k;
if (!full()) //라이브러리 사용시 필요 없음
push(k);
continue;
}
if (cmd == "pop") {
if (empty())
cout << -1 << '\n';
else {
cout << pop() << '\n';
}
continue;
}
if (cmd == "size") {
cout << size() << '\n';
continue;
}
if (cmd == "empty") {
cout << empty() << '\n';
continue;
}
if (cmd == "front") {
if (empty())
cout << -1 << '\n';
else
{
cout << front() << '\n';
}
continue;
}
if (cmd == "back") {
if (empty())
cout << -1 << '\n';
else
cout << back() << '\n';
continue;
}
}
/*
* 큐 순회
*
while (!empty()) {
cout << front() << ' ';
pop();
}
*/
}
📰 [C++ STL] Queue
: c++에서는 Queue 라이브러리 또한 제공하므로 우리는 이미 만들어진것을 활용하기만 하면 된다!
* 멤버함수

-
empty(): 큐가 비어 있으면 true를, 비어 있지 않으면 false를 반환 -
size(): 큐요소의 총 개수를 반환 -
front(): 맨 앞 (가장 처음으로 들어온) 원소 리턴 -
back(): 맨 뒤 (가장 최근에 들어온) 원소 리턴 -
push(k): k를 큐에 맨뒤에 삽입 -
pop(): 큐에서 가장 앞에 있는 요소를 빼고 출력 -
emplace(): 값을 만드는 생성자 인수를 전달해주면 그 인수들로 새로 원소가 들어갈 장소에 바로 원소를 생성
-> 즉, 들어갈 값(또는 struct)을 생성자로 생성한 다음에 그것을 복사해 새로 컨테이너에 넣는 메모리 낭비를 막음.
🔰 덱 (Deque)
- Double - Ended Queue
stack+queue- 자료의
양끝에서 연산이 이루어짐 - 모든 연산에 대한 시간 복잡도는
O(1)
🧾 script [Deque]
: queue와 동일한 양상을 띠지만 기능이 두개(pop_back,push_front) 추가됨!
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 10001;
int front_pointer = 0, rear_pointer = 0;
vector<int> queue_vec(SIZE);
//empty
bool empty() {
return front_pointer == rear_pointer; // front rear가 같은곳을 가리킬때 큐가 비어있다.
}
//full
bool full() {
return (rear_pointer + 1) % SIZE == front_pointer;
}
//push
void push_back(int k) {
rear_pointer = (rear_pointer + 1) % SIZE; //rear포인터를 먼저 하나 증가시키고
queue_vec[rear_pointer] = k; //그위치에 k를 삽입
}
//pop
int pop_front() { // 큐에서의 default pop
front_pointer = (front_pointer + 1) % SIZE; //front포인터를 먼저 하나 증가시키고
return queue_vec[front_pointer]; // 그위치에 있는 값 반환.
//이때 어짜피 비어있는 상태로 치기때문에 값을 굳이 삭제해줄필요 X
}
//size
int size() {
int tmp = (rear_pointer - front_pointer);
if (tmp < 0)
tmp += SIZE;
return tmp;
}
//front
int front() { //가장 나중에 들어온 값.
int tmp = (front_pointer + 1) % SIZE; //단순히 맨 앞 값을 가져오기만 하는것이므로 front를 증가시킬 필요 X
return queue_vec[tmp];
}
//back
int back() { //가장 최근에 들어온 값.
return queue_vec[rear_pointer]; //rear포인터가 가리키는 값이 가장 최근에 들어온값.
}
//덱에 추가되는 기능 두가지
//1. 가장 뒤쪽에서 빼기 -> rear 출력 및 rear --
int pop_back() {
int temp = rear_pointer--;
// index 에러 방지.
if (rear_pointer < 0)
{
rear_pointer += SIZE;
}
return queue_vec[temp];
}
//2. 가장 앞쪽에 수 삽입하기 -> front출력 및 front --
void push_front(int k) {
int temp = front_pointer--;
// index 에러 방지.
if (front_pointer < 0)
{
front_pointer += SIZE;
}
queue_vec[temp] = k;
}
int main() {
cin.tie(NULL);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n, k;
string cmd;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
cin >> cmd;
if (cmd == "push_front") {
cin >> k;
if (!full())
push_front(k);
continue;
}
if (cmd == "push_back") {
cin >> k;
if (!full()) //라이브러리 사용시 필요 없음
push_back(k);
continue;
}
if (cmd == "pop_front") {
if (empty())
cout << -1 << '\n';
else {
cout << pop_front() << '\n';
}
continue;
}
if (cmd == "pop_back") {
if (empty())
cout << -1 << '\n';
else
cout << pop_back() << '\n';
continue;
}
if (cmd == "size") {
cout << size() << '\n';
continue;
}
if (cmd == "empty") {
cout << empty() << '\n';
continue;
}
if (cmd == "front") {
if (empty())
cout << -1 << '\n';
else
{
cout << front() << '\n';
}
continue;
}
if (cmd == "back") {
if (empty())
cout << -1 << '\n';
else
{
cout << back() << '\n';
}
continue;
}
}
/*
* 덱 순회
*
while (!empty()) {
cout << front() << ' ';
pop();
}
*/
}
📰 [C++ STL] Deque
- 🎗🛠🔗🔎🧾📒📃📜📄📑📰♐⚜🔰💠🔂🔁🔄🔛

