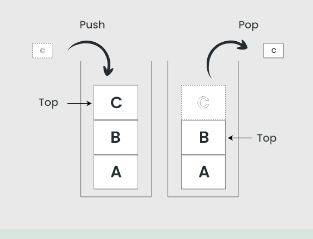
1. Stack: LIFO(Last In First Out)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define PUSH 1
#define POP 2
#define SIZE 3
#define EMPTY 4
#define TOP 5
typedef struct stack {
int* arr;
int memsize;
int count;
int top_idx;
}STACK;
STACK* createStack() {
STACK* s = (STACK*)malloc(sizeof(STACK));
s->arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 100);
s->memsize = 100;
s->count = 0;
int top_idx = -1;
return s;
}
void destroyStack(STACK* stack) {
free(stack->arr);
free(stack);
}
int push(STACK* stack, int input_data)
{
if ((stack->count) >= (stack->memsize))
{
stack->memsize += 100;
stack->arr = (int*)realloc(stack->arr, (stack->memsize)*sizeof(int));
}
(stack->arr)[(stack->count)] = input_data;
stack->top_idx = stack->count;
stack->count += 1;
return 1;
}
int pop(STACK* stack)
{
if (stack->count == 0) return -1;
int pop_data = (stack->arr)[(stack->top_idx)];
(stack->arr)[(stack->top_idx)] = 0;
stack->top_idx -= 1;
stack->count -= 1;
return pop_data;
}
int size(STACK* stack) {
return stack->count;
}
int empty(STACK* stack) {
if (stack->count == 0) return 1;
else return 0;
}
int top(STACK* stack) {
if (stack->count == 0) return -1;
return (stack->arr)[(stack->top_idx)];
}
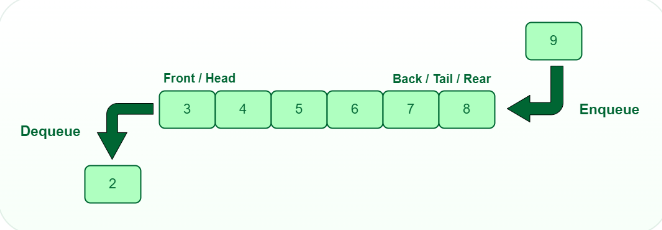
2. Queue: FIFO(First In First Out)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define PUSH 1
#define POP 2
#define SIZE 3
#define EMPTY 4
#define FRONT 5
#define BACK 6
typedef struct queue {
int count;
int* arr;
int front_idx, rear_idx;
int size;
} Q;
Q* createQ() {
Q* new_Q = (Q*)malloc(sizeof(Q));
if (new_Q == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
new_Q->arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 100);
if (new_Q->arr == NULL) {
free(new_Q);
return NULL;
}
new_Q->count = 0;
new_Q->front_idx = -1;
new_Q->rear_idx = -1;
new_Q->size = 100;
return new_Q;
}
void destroyQ(Q* q) {
free(q->arr);
free(q);
}
void Enqueue(Q* q, int input_data) {
if (q->count == 0) {
(q->arr)[0] = input_data;
q->front_idx = 0;
q->rear_idx = 0;
q->count += 1;
}
else {
q->count += 1;
if ((q->count) >= (q->size)) {
q->size += 100;
q->arr = realloc(q->arr, sizeof(int) * (q->size));
}
q->rear_idx += 1;
if (q->rear_idx >= (q->size)) {
q->rear_idx = 0;
}
(q->arr)[q->rear_idx] = input_data;
}
}
int Dequeue(Q* q) {
int dataout;
if (q->count == 0) return -1;
else if (q->count == 1) {
dataout = (q->arr)[q->front_idx];
q->front_idx = -1;
q->rear_idx = -1;
q->count -= 1;
}
else {
dataout = (q->arr)[q->front_idx];
(q->arr)[q->front_idx] = 0;
q->front_idx += 1;
if (q->front_idx >= (q->size)) {
q->front_idx = 0;
}
q->count -= 1;
}
return dataout;
}
int sizeQ(Q* q) {
return q->count;
}
int is_empty(Q* q) {
if (q->count == 0) return 1;
else return 0;
}
int Qfront(Q* q) {
if (q->count == 0) return -1;
else return (q->arr)[q->front_idx];
}
int Qrear(Q* q) {
if (q->count == 0) return -1;
else return (q->arr)[q->rear_idx];
}


