0. Tree
그래프와 더불어 하나보다 많은 후행자를 가지는 비선형 리스트(Non linear list)의 한 종류로 root로부터 뻗어나가는 형태를 지니는 자료구조이다.
- 구성요소
Node: 그림에서 원으로 표현된 것.
Branch: 화살표로 표현된 것. C에서 리스트로 구현시에는 포인터가 해당 역할은 한다.
degree: indegree(자신을 가리키는 branch) + outdegree(자신이 가리키는 branch)- 용어
leaf: outdegree가 0인 맨 끝의 Node들
internal node: root, leaf를 제외한 내부 노드
(자료에 따라 root를 internal node에 포함하는 경우도 있음.)
parent & child: 부모&자식 관계 ex. 8은 3과 10의 parent
ancestor & descendant
sibling: 자신과 같은 레벨에 있는 Node
level: root로부터의 거리. root의 레벨을 0으로 계산.
height: 노드 중 가장 높은 레벨 + 1
(자료에 따라 노드 중 가장 높은 레벨을 높이로 보는 경우도 있음.)
subtree: 부분 집합과 유사한 개념
1. Binary Search Tree
후행자를 최대 2개 지니는 이진 트리(Binary Tree)이면서 다음과 같은 조건을 충족시키는 탐색에 특화된 트리이다.
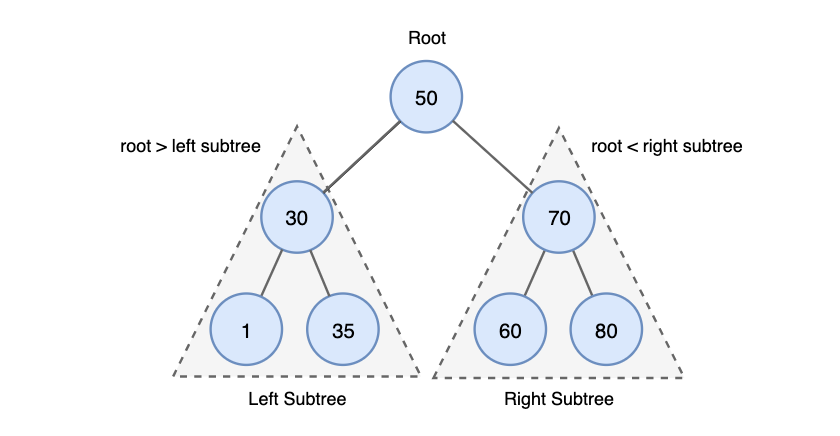
root의 왼쪽의 노드들은 root보다 작은 값을 가지며, 오른쪽의 노드들은 root보다 큰 값을 지닌다. 재귀적으로 Subtree들도 똑같은 특성을 지닌다.
앞서 말한대로 이는 search에 특화된 구조이다. search 알고리즘 중에서 이진 탐색(binary search) 알고리즘은 O(lg N)의 시간복잡도를 지니는 매우 빠른 알고리즘인데, 해당 이진 트리 구조에서는 이진 탐색이 아주 쉽게 가능하게 된다.
다만, 삭제가 어렵다는 문제가 있다. 삭제 대상 노드가 자식이 없거나 한 쪽만 자식을 가지고 있는 경우, 기존에 선형 리스트의 삭제 작업과 동일하지만, 양쪽에 자식을 지니고 있는 경우 문제가 발생한다. 가령 상단 이미지의 트리에서 50을 삭제하고자 할 경우, 어떤 노드가 50의 자리를 대체할 것이냐는 문제가 발생한다.
이를 해결하는 방법에는 크게 2가지가 있다. 좌측의 max node 35를 root로 올리는 방법과 우측의 min node 60을 위로 올리는 방법이다. 이 두 방법을 이용시 이진 탐색 트리의 특성을 유지하며 삭제를 진행할 수 있다. 이렇듯 이진 탐색 트리는 삭제가 복잡하다는 단점이 있다.
int BST_Insert(TREE* pTree, void* dataInPtr, void (*callback)(void*))
{
NODE* newNode = _makeNode(dataInPtr);
if (!newNode) return 0; //overflow
if (pTree->root == NULL)
{
pTree->root = newNode;
(pTree->count)++;
return 1;
}
int ret = _insert(pTree->root, newNode, pTree->compare, callback);
if (ret == 1) {
(pTree->count)++;
return ret;
}
else if (ret == 2) {
free(newNode);
return ret;
}
free(newNode);
return 0; //Insertion failed
}
static NODE* _makeNode(void* dataInPtr)
{
NODE* n = (NODE*)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
if (!n) return NULL;
n->dataPtr = dataInPtr;
n->left = NULL;
n->right = NULL;
return n;
}
static int _insert(NODE* root, NODE* newPtr, int (*compare)(const void*, const void*), void (*callback)(void*))
{
int cmp_res = compare(newPtr->dataPtr, root->dataPtr);
if (cmp_res < 0) {
//find insert Loc
if (root->left == NULL) {
root->left = newPtr;
return 1;
}
//recursion
else return _insert(root->left, newPtr, compare, callback);
}
else if (cmp_res > 0) {
//find insert Loc
if (root->right == NULL) {
root->right = newPtr;
return 1;
}
//recursion
else return _insert(root->right, newPtr, compare, callback);
}
//find duplicated & execute callback function
else if (cmp_res == 0) {
callback(root->dataPtr);
return 2;
}
return 0; // failure
}
void* BST_Delete(TREE* pTree, void* keyPtr)
{
if (pTree->root == NULL) return NULL;
void* dataout = NULL;
pTree->root = _delete(pTree->root, keyPtr, &dataout, pTree->compare);
if (dataout != NULL) (pTree->count)--;
return dataout;
}
static NODE* _Rsmallest(NODE* rightSub_root) {
NODE* pLoc = rightSub_root;
while (pLoc && pLoc->left != NULL) {
pLoc = pLoc->left;
}
return pLoc;
}
static NODE* _delete(NODE* root, void* keyPtr, void** dataOutPtr, int (*compare)(const void*, const void*))
{
if (!root) return NULL;
int cmp_res = compare(keyPtr, root->dataPtr);
if (cmp_res < 0) {
root->left = _delete(root->left, keyPtr, dataOutPtr, compare);
}
else if (cmp_res > 0) {
root->right = _delete(root->right, keyPtr, dataOutPtr, compare);
}
else // found
{
if (root->left == NULL) {
NODE* temp = root->right;
*dataOutPtr = root->dataPtr;
free(root);
return temp;
}
else if (root->right == NULL) {
NODE* temp = root->left;
*dataOutPtr = root->dataPtr;
free(root);
return temp;
}
// two child case
NODE* temp = _Rsmallest(root->right);
void* dataTemp;
dataTemp = temp->dataPtr; //루트랑 right min value swap
temp->dataPtr = root->dataPtr;
root->dataPtr = dataTemp;
root->right = _delete(root->right, temp->dataPtr, dataOutPtr, compare); //right subtree의 rightmin 삭제
}
return root;
}
void* BST_Search(TREE* pTree, void* keyPtr)
{
if (pTree->root == NULL) return NULL;
NODE* foundNode = _search(pTree->root, keyPtr, pTree->compare);
return foundNode->dataPtr;
}
static NODE* _search(NODE* root, void* keyPtr, int (*compare)(const void*, const void*))
{
if (!root) return NULL;
int cmp_res = compare(keyPtr, root->dataPtr);
if (cmp_res < 0) {
return _search(root->left, keyPtr, compare);
}
else if (cmp_res > 0) {
return _search(root->right, keyPtr, compare);
}
else if (cmp_res == 0) return root;
}하지만, 이진 탐색 트리의 가장 큰 문제점은 삭제가 아니다. 최악의 경우, 선형 리스트와 다를 바 없어진다는 점이다.
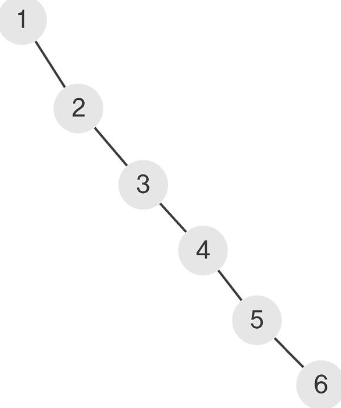
이렇게 unbalanced한 트리가 될 경우, 선형 리스트에서 탐색하는 것과 다를 바가 없어지기에, 이진 탐색 트리로서의 장점이 없어지게 된다. 이 치명적인 단점을 보완한 것이 균형 잡힌 트리 AVL Tree이다.
3. AVL Tree(Adelson-Velsky and Landis Tree)
AVL Tree는 이진 탐색 트리의 장점을 항상 유지할 수 있도록 보완한 트리이다. 삽입, 삭제 과정에서 트리가 unbalance할 경우 다신 균형 잡힌 트리가 되도록 수정을 가하는 것이다. 그만큼 삽입, 삭제 과정이 복잡해진다는 단점은 있으나, 탐색에 특화된 장점을 항상 유지할 수 있는 것이다.
#define BALANCING
#include <stdlib.h> // malloc
#include <stdio.h>
#include "avlt.h"
#define max(x, y) (((x) > (y)) ? (x) : (y)) //left sub, right sub height 비교에 이용.
// internal function
// return height of the (sub)tree from the node (root)
static int getHeight(NODE* root) {
int lheight = ((root->left != NULL) ? (root->left->height) : 0);
int rheight = ((root->right != NULL) ? (root->right->height) : 0);
return max(lheight, rheight) + 1;
}
// internal function
// Exchanges pointers to rotate the tree to the right
// updates heights of the nodes
// return new root
static NODE* rotateRight(NODE* root)
{
NODE* left_sub = root->left;
root->left = left_sub->right;
left_sub->right = root;
root->height = getHeight(root);
left_sub->height = getHeight(left_sub);
return left_sub;
}
// internal function
// Exchanges pointers to rotate the tree to the left
// updates heights of the nodes
// return new root
static NODE* rotateLeft(NODE* root)
{
NODE* right_sub = root->right;
root->right = right_sub->left;
right_sub->left = root;
root->height = getHeight(root);
right_sub->height = getHeight(right_sub);
return right_sub;
}
// internal functions (not mandatory)
// used in AVLT_Insert
// return pointer to root
static NODE* _insert(NODE* root, NODE* newPtr, int (*compare)(const void*, const void*), void (*callback)(void*), int* duplicated)
{
int cmp_res = compare(newPtr->dataPtr, root->dataPtr);
//duplicated
if (cmp_res == 0) {
*duplicated = 1;
callback(root->dataPtr);
}
else if (cmp_res > 0) {
if (!root->right) //insert right
{
root->right = newPtr;
(newPtr->height)++;
root->height = getHeight(root);
return root;
}
else {
root->right = _insert(root->right, newPtr, compare, callback, duplicated);
//after insert, update height of root
root->height = getHeight(root);
}
}
else
{
if (!root->left) //insert left
{
root->left = newPtr;
(newPtr->height)++;
root->height = getHeight(root);
return root;
}
else {
root->left = _insert(root->left, newPtr, compare, callback, duplicated);
//after insert, update height of root
root->height = getHeight(root);
}
}
if (*duplicated) return root; //rebalancing isn't necessary
else {
//check balance of (sub)tree
int lheight = ((root->left != NULL) ? (root->left->height) : 0);
int rheight = ((root->right != NULL) ? (root->right->height) : 0);
int diff = lheight - rheight;
if (diff > 1) //main Tree Left High (LL, RL)
{
NODE* left_sub = root->left;
lheight = ((left_sub->left != NULL) ? (left_sub->left->height) : 0);
rheight = ((left_sub->right != NULL) ? (left_sub->right->height) : 0);
int sub_diff = lheight - rheight;
if (sub_diff >= 0) return rotateRight(root); // LL case
else { //RL case;
root->left = rotateLeft(root->left);
root->height = getHeight(root);
return rotateRight(root);
}
}
else if (diff < -1) //main Tree Right high (LR, RR)
{
NODE* right_sub = root->right;
lheight = ((right_sub->left != NULL) ? (right_sub->left->height) : 0);
rheight = ((right_sub->right != NULL) ? (right_sub->right->height) : 0);
int sub_diff = lheight - rheight;
if (sub_diff <= 0) return rotateLeft(root); //RR case
else { //LR case
root->right = rotateRight(root->right);
root->height = getHeight(root);
return rotateLeft(root);
}
}
else return root; //balanced
}
}
// used in AVLT_Destroy
static void _destroy(NODE* root, void (*callback)(void*))
{
//post order deletion LRN
if (root->left != NULL) _destroy(root->left, callback);
if (root->right != NULL) _destroy(root->right, callback);
callback(root->dataPtr);
free(root);
}
static NODE* _Rsmallest(NODE* rightSub_root) {
NODE* pLoc = rightSub_root;
while (pLoc && pLoc->left != NULL) {
pLoc = pLoc->left;
}
return pLoc;
}
// used in AVLT_Delete
// return pointer to root
static NODE* _delete(NODE* root, void* keyPtr, void** dataOutPtr, int (*compare)(const void*, const void*))
{
if (!root) return NULL;
int cmp_res = compare(keyPtr, root->dataPtr);
if (cmp_res < 0) root->left = _delete(root->left, keyPtr, dataOutPtr, compare);
else if (cmp_res > 0) root->right = _delete(root->right, keyPtr, dataOutPtr, compare);
else{ //found
NODE* temp = NULL;
if (root->left == NULL) {
temp = root->right;
*dataOutPtr = root->dataPtr;
free(root);
return temp;
}
else if (root->right == NULL) {
temp = root->left;
*dataOutPtr = root->dataPtr;
free(root);
return temp;
}
// two child case
temp = _Rsmallest(root->right);
void* dataTemp;
dataTemp = temp->dataPtr; //루트랑 right min value swap
temp->dataPtr = root->dataPtr;
root->dataPtr = dataTemp;
root->right = _delete(root->right, temp->dataPtr, dataOutPtr, compare); //right subtree의 rightmin 삭제
}
//height verification
if (root != NULL) root->height = getHeight(root);
return root;
}
// used in AVLT_Search
// Retrieve node containing the requested key
// return address of the node containing the key
// NULL not found
static NODE* _search(NODE* root, void* keyPtr, int (*compare)(const void*, const void*))
{
if (!root) return NULL;
int cmp_res = compare(keyPtr, root->dataPtr);
if (cmp_res > 0) return _search(root->right, keyPtr, compare);
else if (cmp_res < 0) return _search(root->left, keyPtr, compare);
else return root;
}
// used in AVLT_Traverse
static void _traverse(NODE* root, void (*callback)(const void*))
{
//traverse inorder
if (root->left != NULL) _traverse(root->left, callback);
callback(root->dataPtr);
if (root->right != NULL) _traverse(root->right, callback);
}
// used in AVLT_TraverseR
static void _traverseR(NODE* root, void (*callback)(const void*))
{
//reverse inorder
if (root->right != NULL) _traverseR(root->right, callback);
callback(root->dataPtr);
if (root->left != NULL) _traverseR(root->left, callback);
}
// used in printTree
static void _inorder_print(NODE* root, int level, void (*callback)(const void*))
{
if (root != NULL) {
if (root->right != NULL) _inorder_print(root->right, level + 1, callback);
for (int i = 0; i < level; i++) printf("\t");
callback(root->dataPtr);
if (root->left != NULL) _inorder_print(root->left, level + 1, callback);
}
}
// used in AVLT_Insert
static NODE* _makeNode(void* dataInPtr)
{
NODE* new_node = (NODE*)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
if (!new_node) return NULL;
new_node->height = 0; //Initialize height to zero
new_node->left = NULL;
new_node->right = NULL;
new_node->dataPtr = dataInPtr;
return new_node;
}
TREE* AVLT_Create(int (*compare)(const void*, const void*))
{
TREE* new_tree = (TREE*)malloc(sizeof(TREE));
if (!new_tree) return NULL;
new_tree->root = NULL;
new_tree->count = 0;
new_tree->compare = compare;
return new_tree;
}
void AVLT_Destroy(TREE* pTree, void (*callback)(void*))
{
if (pTree->root != NULL) _destroy(pTree->root, callback);
free(pTree);
}
int AVLT_Insert(TREE* pTree, void* dataInPtr, void (*callback)(void*))
{
int duplicated = 0;
NODE* new_node = _makeNode(dataInPtr);
if (!new_node) return 0;
//_insert, makenode, rotate
//empty tree
if (!pTree->root) {
pTree->root = new_node;
pTree->root->height = 1;
(pTree->count)++;
return 1;
}
pTree->root = _insert(pTree->root, new_node, pTree->compare, callback, &duplicated);
pTree->root->height = getHeight(pTree->root);
if (duplicated) {
free(new_node);
return 2;
}
else {
(pTree->count)++;
return 1;
}
}
void* AVLT_Delete(TREE* pTree, void* keyPtr)
{
if (!pTree->root) return NULL;
void* dataoutPtr = NULL;
pTree->root = _delete(pTree->root, keyPtr, &dataoutPtr, pTree->compare);
if (dataoutPtr != NULL) {
if (pTree->root != NULL) {
pTree->root->height = getHeight(pTree->root);
}
(pTree->count)--;
}
return dataoutPtr;
}
void* AVLT_Search(TREE* pTree, void* keyPtr)
{
if (!pTree->root) return NULL;
NODE* dataLoc = _search(pTree->root, keyPtr, pTree->compare);
if (dataLoc) return dataLoc->dataPtr;
else return NULL;
}
void AVLT_Traverse(TREE* pTree, void (*callback)(const void*)){
if (pTree->root != NULL) _traverse(pTree->root, callback);
else fprintf(stdout, "EMPTY TREE\n");
}
void AVLT_TraverseR(TREE* pTree, void (*callback)(const void*))
{
if (pTree->root != NULL) _traverseR(pTree->root, callback);
else fprintf(stdout, "EMPTY TREE\n");
}
void printTree(TREE* pTree, void (*callback)(const void*))
{
int level = 0;
if (pTree->root != NULL) _inorder_print(pTree->root, level, callback);
else fprintf(stdout, "EMPTY TREE\n");
}
int AVLT_Count(TREE* pTree)
{
return pTree->count;
}
int AVLT_Height(TREE* pTree)
{
if (pTree->root != NULL) return getHeight(pTree->root);
else return 0;
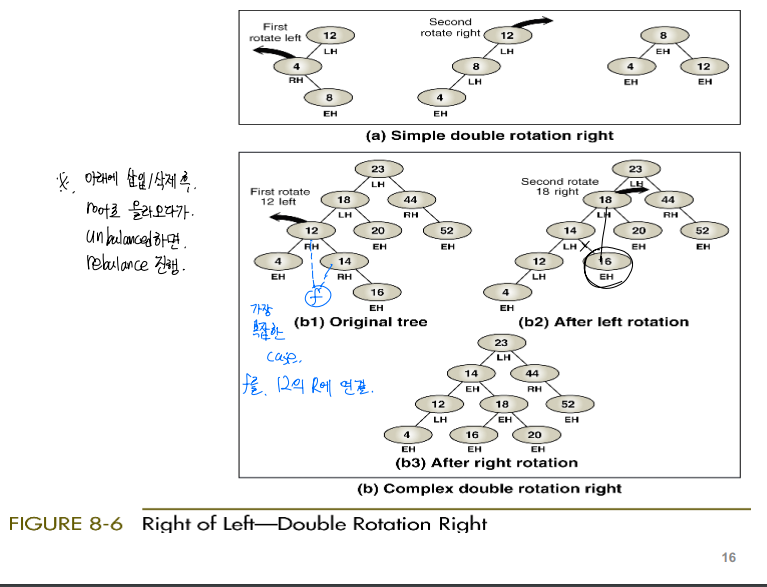
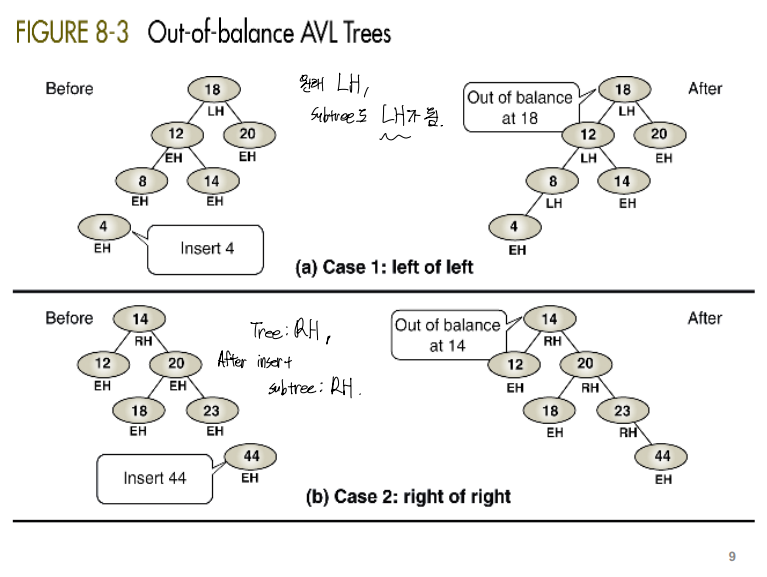
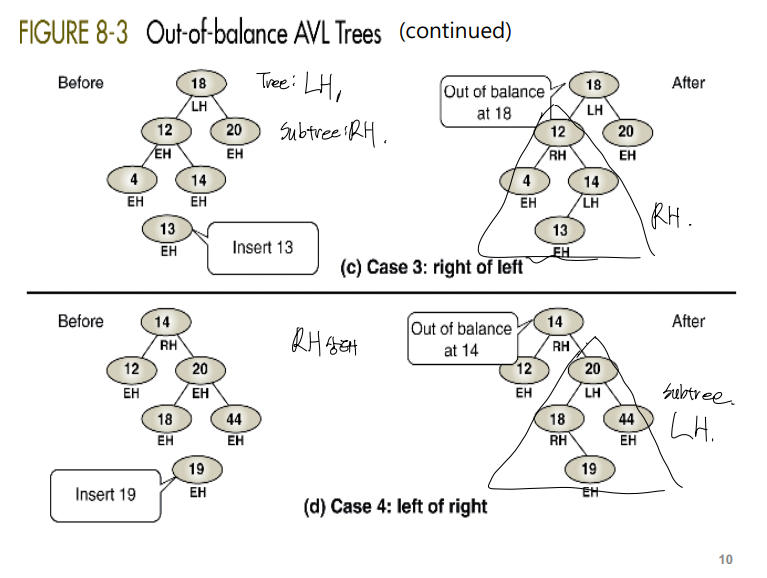
}Balancing 작업을 해줘야 하는 경우는 크게 4 case로 구분된다. (LL, LR, RR, RL)
-
RR, LL Case
이 두 케이스의 경우, 비교적 쉽게 수정이 가능하다.
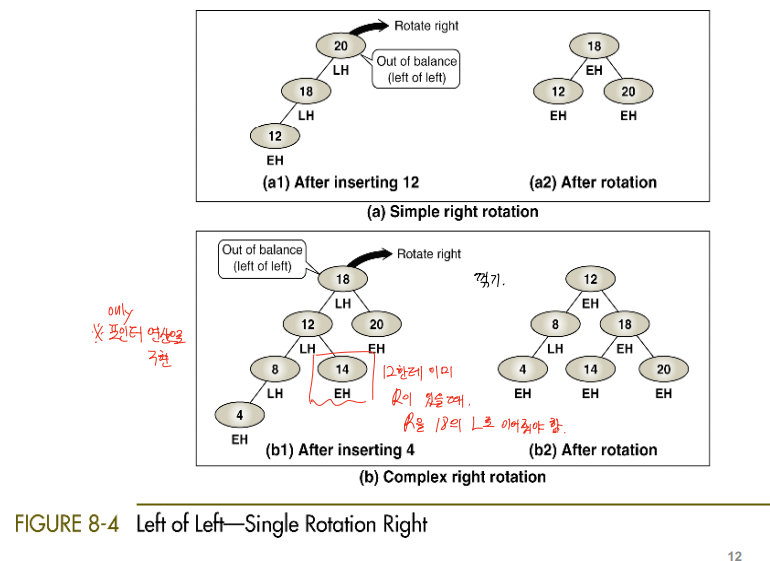
가령, 위 사진처럼 LL case일 때는 오른쪽으로 한 번 회전시켜주면 된다. 다만, (b)처럼 새롭게 root의 자리가 되어야 할 노드인 12의 오른쪽에 자식이 있다면 이를 12의 right child가 될 18의 left child로 넘겨줘야 한다. RR case의 경우 정확히 이와 반대로 작업해주면 된다.
// internal function
// return height of the (sub)tree from the node (root)
static int getHeight(NODE* root) {
int lheight = ((root->left != NULL) ? (root->left->height) : 0);
int rheight = ((root->right != NULL) ? (root->right->height) : 0);
return max(lheight, rheight) + 1;
}
// internal function
// Exchanges pointers to rotate the tree to the right
// updates heights of the nodes
// return new root
static NODE* rotateRight(NODE* root)
{
NODE* left_sub = root->left;
root->left = left_sub->right;
left_sub->right = root;
root->height = getHeight(root);
left_sub->height = getHeight(left_sub);
return left_sub;
}
// internal function
// Exchanges pointers to rotate the tree to the left
// updates heights of the nodes
// return new root
static NODE* rotateLeft(NODE* root)
{
NODE* right_sub = root->right;
root->right = right_sub->left;
right_sub->left = root;
root->height = getHeight(root);
right_sub->height = getHeight(right_sub);
return right_sub;
}unbalanced 여부를 파악하기 위해서는 계속해서 node별 height를 업데이트 해줘야하기에 getheight() 함수를 이용해 수정이 가해질 때마다 업데이팅 해주고 있다.
RL, LR Case
나머지 두 케이스의 경우 약간 번거롭긴 하지만 한번씩 더 rotating 작업을 진행해줘야 한다. 가령, RL case일 때는 left subtree에서 rotate left 작업을 수행해, LL case로 바꿔준 후 rotate right를 해주는 것이다. LR case이면 이와 반대로 subtree에서 오른쪽으로 회전시켜 RR case를 만들어 준 후, 왼쪽으로 회전시켜주면 된다.