0. Abstract
- 증강 현실(AR)에서는 virtual assets이 실제 객체 '사이에 위치'하는 것처럼 보이는 것이 중요
구현되어야하는 점
- 가상 요소는 plausible depth ordering (그럴듯한 깊이 순서)에 따라 실제 물질을 가리거나 실제 물질에 의해 가려져야함
- occulsion은 시청자의 카메라가 움직일 때 시간이 지나도 일관되어야 함
⇒ 중간 단계로서 depth-regression의 필요성
- implicit model for depth를 이용해 occlusion mask를 directly 예측함
- input : 1장 이상의 컬러 이미지 & virtual geometry의 알려진 depth
- ScanNetv2 dataset 이용
1. Introduction
3가지의 Contributions
- known depth의 virtual object를 real scene에 합성하는 문제를 binary mask estimation problem으로 frame화
- occlusion evaluation를 위한 metrics 소개
- 경쟁 접근방식들 - 깜빡거리면서 jarring occlusions을 초래함
=> 문제를 segmentation으로 framing해서 temporal smoothing method 사용 가능 -> baseline에 비해 더 smooth prediction
3. Method
목표 : real scenes의 images에 자동적으로 virtual objects를 합성하는 것
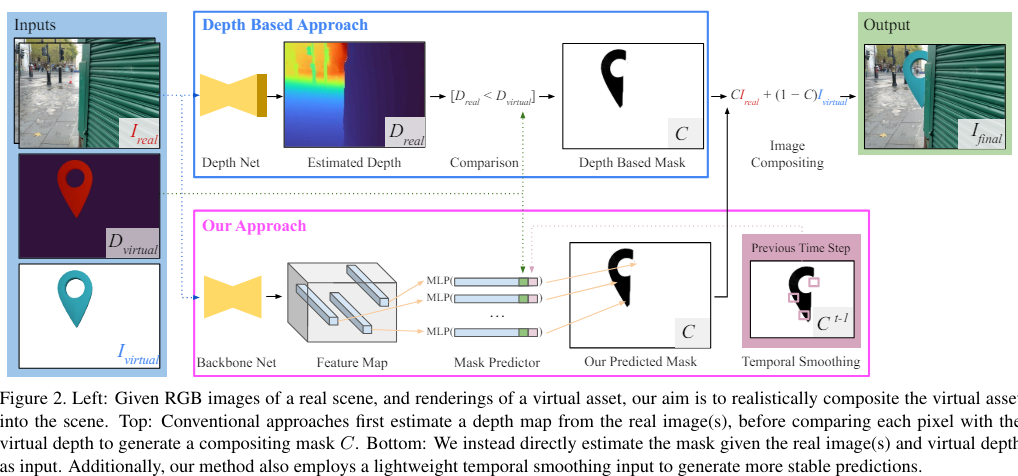
input
- : RGB image
- corresponding camera intrinsics and poses
- : full sequence of
3D virtual object & camera poses로부터 각 frame에 대해 virtual object & associated virtual depth map 의 color rendering을 추출함
3.1 Our approach
Occlusion 단계
- virtual pixel이 보여져야 하는지 or 가려져야 하는지 추정해야함
- final image 생성
-
2개의 image와 per-pixel compositing mask(픽셀 단위의 합성 마스크) 를 안다면 compositing equation으로 설명가능
-
다음 compositing equation은 virtual object에 가려지는 pixel에만 적용돼야함
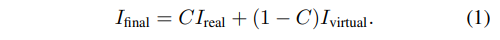
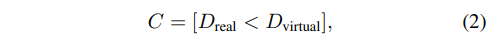
directy predict C 하는 것보다 기존 network 쓰는게 더 좋아보이지만, direct prediction은 가 없으면 수행 불가능
=> 따라서 deep network 로 C를 directly 추정
depth informed mask prediction의 장점
- 각 픽셀 위치에서 binary 'in front vs. behind' 값을 예측
- absolute depth을 regression하기 위해 연속적인 값을 예측하는 기존 방법과의 차이점
3.2 Predicting an occlusion map
architecture
1. Backbone network for image encoding
2. per-pixel MLP
1) Backbone network for image encoding
RGB image -> pixel-aligned feature encoding F with K channels per pixel 으로 매핑해줌
2) Predicting the occlusion mask with an MLP
compositing mask at pixel location 는 3개의 input으로 predict됨
1. image features at , i.e.
2. virtual object depth at , i.e.
3. warped previous temporal prediction at
3.3 Training our network
목표 : network phi의 weight update
training sample
- img 위치 p에서의 training tuple
- 위치 p에서의 virtual depth
- ground truth label y_i = {0,1}
- virtual depth 가 real image의 depth map보다 앞(0)에 있는지, 뒤(1)에 있는지 - previous prediction for 위치 p : C(p)
- 2D상의 위치 p를 image space에서 uniformly 정함
동시에 training-time feature F(p)를 sample - 주어진 image location p에서, p의 camera ray선을 따라서(선상에서) 합성된 virtual depth를 sampling할 수 있음
- D_virtual 이 D_real과 가까이 있을 때(겹쳐있을 때) D_virtual을 가장 선택하기 어렵다
=> 실측 깊이 표면 근처에서 training-time samples 일부를 편향함 - real surface로부터 멀리 떨어진 예측을 하기 위해,
1-q의 확률로 D_Real의 min, max depth 범위 사이에서 training depth를 uniform하게 sampling함
