PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation [CVPR 2017]
논문 리뷰
논문 원문 링크 : https://arxiv.org/pdf/1612.00593
0. Abstract
- point cloud : geometric data 구조 중 중요한 형태임
- irregular한 format 때문에, 대부분 연구자들은 regular한 3D voel grid 또는 image들의 집합으로 변환해서 사용함
- 하지만 이렇게 하면 data가 불필요하게 부피가 커지고, 문제가 발생함
- 이 논문에선 point cloud를 direct하게 consume할 수 있는 neural network인 'PointNet'을 디자인함
- PointNet : object classification, part segmentation, scene semantic parsing에 이르는 다양한 적용을 위한 통합 아키텍쳐를 제공함
- PointNet은 단순하지만, 매우 효율적 & 효과적임
- 실험적으로 최첨단 기술과 동등하거나 그 이상의 강력한 성능을 보여줌
- 이론적으로 네트워크가 무엇을 학습했는지, 네트워크가 input perturbation & corruption에 왜 강력한지에 대해 분석했음
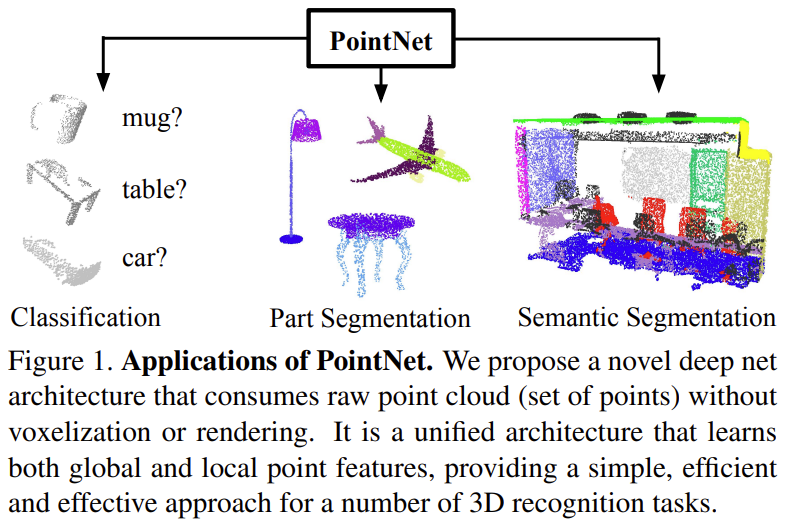
1. Introduction
- point cloud나 mesh는 정해진 format이 없기 때문에, 대부분 연구자들은 regular한 3D voel grid 또는 image들의 집합으로 변환한 뒤, 딥러닝 모델에 집어 넣음
<단점>
- resulting data가 불필요하게 부피가 커지고
- data의 natural invariances을 가리는 quantization 문제가 생길 수 있음
=> input으로 point clound를 이용한 모델인 PointNet을 제안함
- 단순한 point들의 집합이므로 permutation에 invariant 불변해야하고. rigid motion에도 invariant해야 함
(point들이 어떤 순서의 변수로 오던 달라지는 것이 없고, point들 집합 전체를 회전하거나 이동시킨다고 해서 3D 형체가 달라지는 것은 아니기 때문)
Key Contributions
- 3D에서 unordered point set들을 다루기에 적합한 딥러닝 아키텍처를 디자인함
- 3D shape classification, shape part segmentation, scene semantic parsing tasks을 수행할 수 있는 모델임
- 모델의 stability & efficiency에 대한 실험적 / 이론적 분석함
- 네트워크에서 학습하고 선택된 3D feature에 대한 illustrate - 성능에 대해 직관적인 설명 가능
2. Related Work
Point Cloud Features
Deep Learning on 3D Data
Deep Learning on Unordered Sets
3. Problem Statement
- point cloud : 3D point들의 집합{| }으로 표현됨, 각 point 는 좌표 & feature channel(color, normal)의 벡터
=> 여기서는 만 사용하겠음
-
object classification task의 input point cloud로는 shape으로부터 sampling되거나, scene point cloud에서 사전에 segmented 된 것을 사용
- our model은 k개의 class에 대해 k개의 score들을 가짐
-
sementic segmentation task의 input은
- part region segmentation을 위한 single object이거나,
- object region segmentation을 위한 3D scene의 sub-volume임
- our model은 n개의 point와 m개의 semantic sub category에 대해 n × m개의 score들을 가짐
4. Deep Learning on Point Sets
4.1. Properties of Point Sets in
input : 유클리디안 space에서 point들의 subset
3가지 주요 특성을 가짐
- Unordered : point cloud는 특정 순서가 없는 point들의 집합, N개의 3D point set을 이용하는 network는 N!개의 입력 조합에 대해 invariant해야 함
- Interaction among points :
- point들이 distance metric이 있는 space에 있으므로, 근처의 point들은 의미 있는 subset을 형성함
- 따라서 근처의 point들로부터 local structure를 포착할 수 있어야하고, local structure로부터 combinatorial interaction을 포착할 수 있어야함
- Invariance under transformations : point들이 다같이 rotate / translate해도 global point cloud category 나 point들의 segmentation이 변경돼선 안 됨
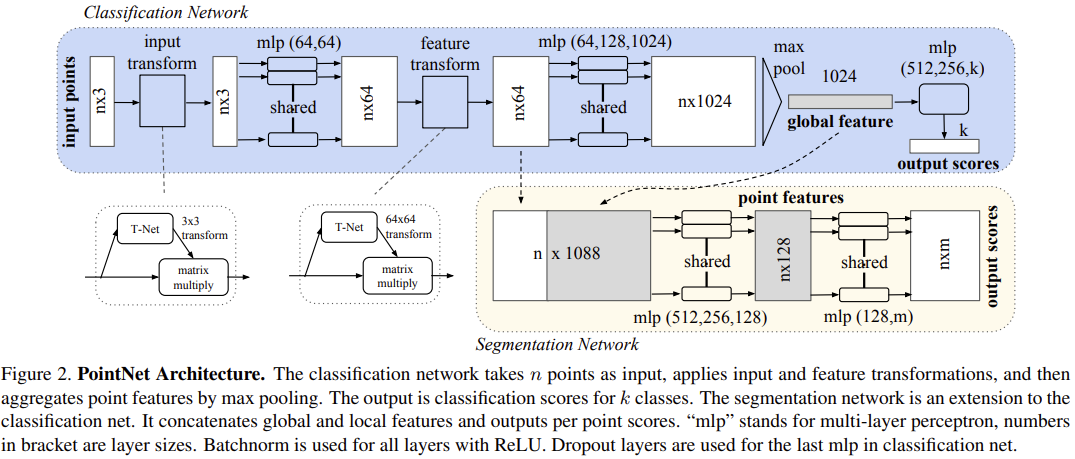
4.2. PointNet Architecture
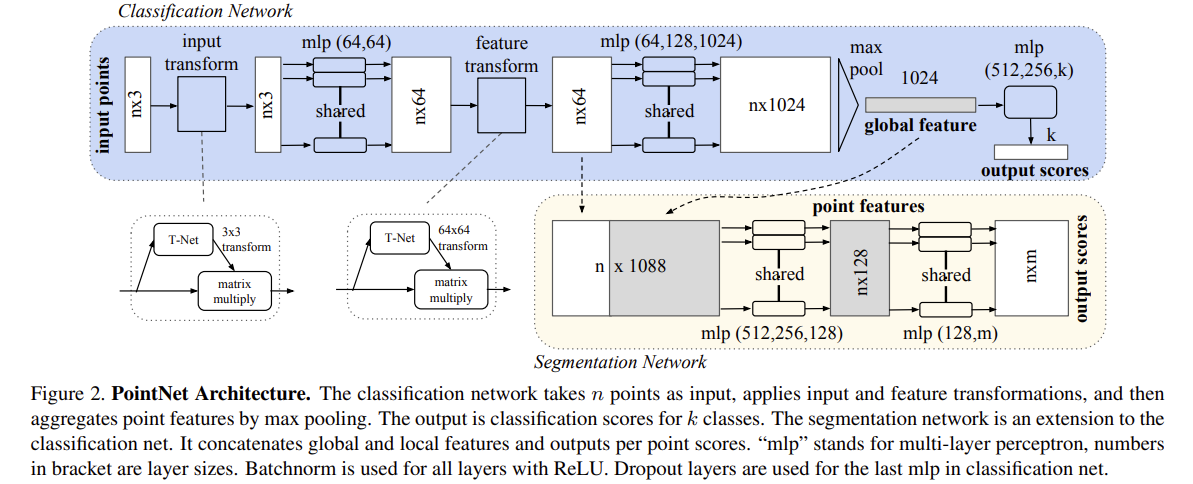
classification network & segmentation network는 구조에서 상당히 많은 부분을 공유함
classification network
- input : n개의 point들
- input transform & feature transform 적용
- max pooling으로 point features 집계함
- ouput : k개 class에 대한 classification scores
segmentation network
: classification net의 extension
- global & local features를 이어붙임
- output : point별 score
“mlp” = multi-layer perceptron, 괄호 안의 숫자는 각 layer의 크기
모든 layer 에 대해 Batchnorm & ReLU 사용됨
classification net의 마지막 mlp에서 Dropout layer 사용됨
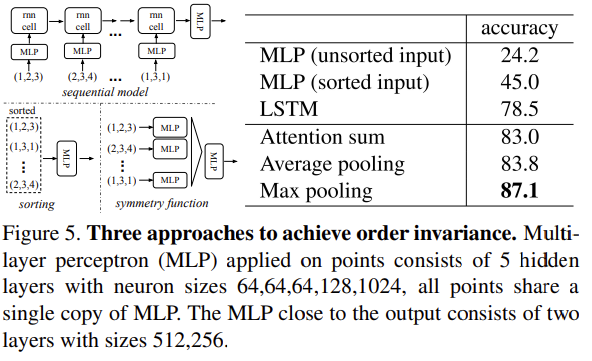
Symmetry Function for Unordered Input
< model을 input permutation에 대해 invariant하게 만들 3가지 전략 >
1) sort input into a canonical order
: 간단해보일 수 있지만, 고차원 공간에서는 ordering이 point perturbation(순열)에 대해서 stable 하지 않음
2) RNN을 학습시킬 때 input을 sequence 처럼 다룸, 단 모든 permutation에 대해 training data를 augment함
- point set을 sequential signal로 고려
- 무작위로 순열 조합된 sequence으로 RNN을 학습시켜서, RNN이 input 순서에 불변해지기를 바라는 것이 주요 아이디어
- 하지만 'OrderMatters' 논문에서 order를 무시를 할 수 없다는 것을 보였음
-> 결국은 RNN이 작은 수의 input에 대해서는 어느정도 robustness를 보여줄 수 있지만 point cloud처럼 수만개의 data에 대해서는 좋은 성능을 보여줄수 없음
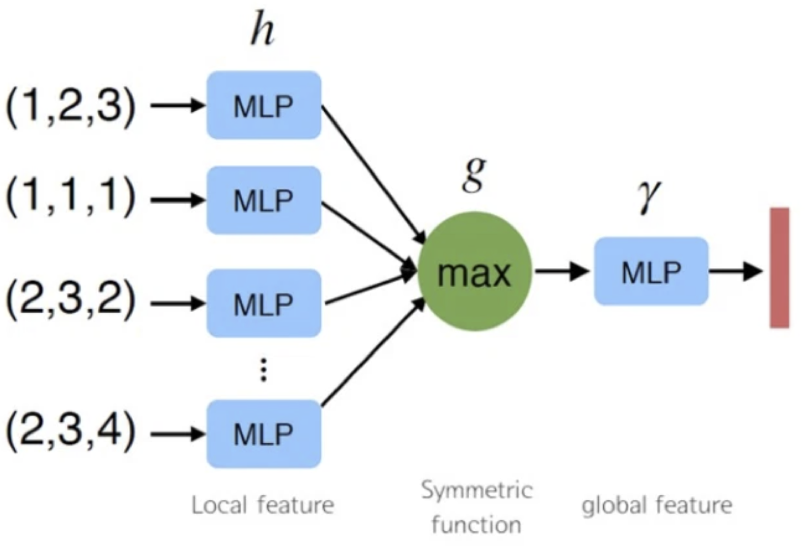
3) use a simple symmetric function to aggregate the information from each point [채택]
- 아이디어 : set에서 변형된 요소들에 symmetric(대칭) 함수를 적용하여 point set에 대한 general function(모델 전체를 함수 수식으로 표현했을 때)를 근사하는 것
[논문에서 찾고자 하는 symmetric function의 general한 표현]
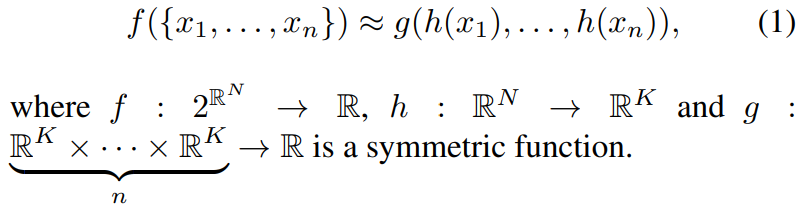
- h : multi-layer perceptron(mlp)로 이뤄진 neural network
- g : max pooling 함수
n개의 point가 mlp로 이루어진 function에 input으로 각각 들어가고, output으로 나온값들은 max pooling함
=> point들이 어떤 순서로 모델에 들어가더라도 max pooling을 거치고 나오는 결과값은 동일함
=> unordered 문제 해결
- mlp의 경우 layer size에 맞춰서 node가 있다고 할 때, 이 node들이 weight를 sharing함
-> input으로 들어오는 값들에 대해 같은 weight를 가짐 - max pooling이 전체 point data에서 max라는 특수한 정보를 가져오므로, point들 간 정보를 얻을 수 있음
Local and Global Information Aggregation
-
point segmentation은 point의 local and global 정보의 combination이 필요함
-
모델 아키텍처에서 Segmentation Network 부분으로 해결함
- global point cloud feature 벡터를 계산하고, 각 point feature에 global feature를 concatenate(이어붙임)해서 per point feature에 feed back함
- 합쳐진 point feature를 기반으로 새로운 per point feature를 추출함 => local & global 정보를 모두 인식해서 추출하게 됨
➡ local geometry & global semantic에 의존하는 per point quantities를 예측할 수 있게 됨
Joint Alignment Network
- point cloud에 geometric transformation이 일어나도 semantic labeling 결과는 변하지 않아야함(invariant)
[Our method에서의 해결 방법]
-
T-net이라는 mini network으로 affine transformation matrix을 예측함
-
input point의 좌표에 해당 affine transformation 적용
-
이 network를 통과했는데도 semantic labeling이 그대로 나온다면 invariant하다고 볼 수 있음
-
T-net 구조 ?
The mininetwork itself resembles the big network and is composed
by basic modules of point independent feature extraction,
max pooling and fully connected layers.
이 아이디어는 feature space의 alignment로 확장할 수 있음
다른 input point cloud으로부터 나온 feature들과 align하기 위한 feature transformation matrix을 예측하기 위해, point feature에 또다른 alignment network를 적용함
(two joint alignment network인 이유)
feature space에서의 transformation matrix는 spatial transform matrix보다 훨씬 고차원이라서, optimization이 훨씬 어려움
=> regularization term을 추가했더니 훨씬 stable하고, performance 나아짐
- feature transformation matrix가 orthogonal matrix에 가까워지도록 식을 설정함
- orthogonal transformation가 input에 대한 정보를 잃지 않기 때문
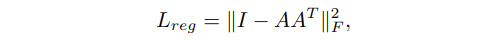
- A = mini-network로부터 예측된 feature alignment matrix
4.3. Theoretical Analysis
Universal approximation
5. Experiment
5.1. Applications
3D Object Classification
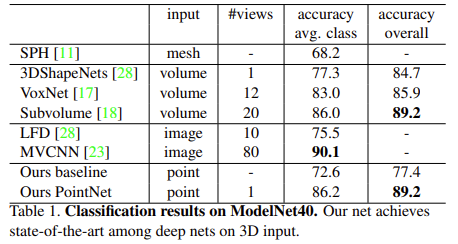
- ModelNet40 데이터셋에 대해 model 평가함
- input point cloud : mesh faces에서 1024개 point들을 uniformly sampling함
- 그후 unit sphere으로 normalize함
- 학습시킬 때 data augmentation을 위해 up-axis를 따라 랜덤하게 회전 시키거나, point의 position값에 Gaussian noise를 추가함
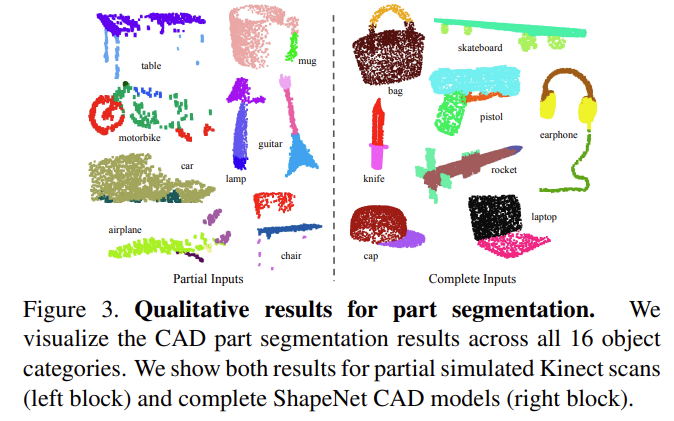
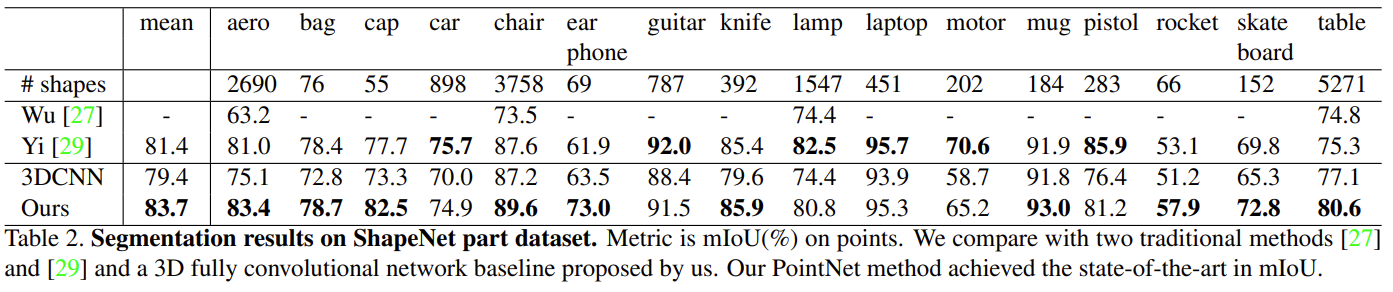
3D Object Part Segmentation
- per-point classification problem으로 고려함
- Metric : mean IoU(%) on point
- 각 카테고리 C의 각 shape S에 대해서 shape의 mIoU를 계산한 후 카테고리별로 평균 냄 : mIoU는 겹치는 point개수로 계산함
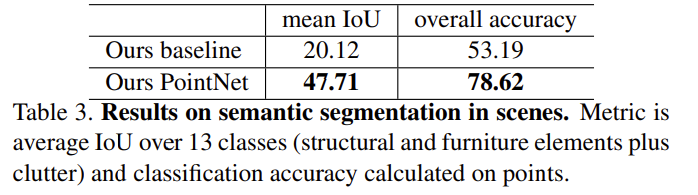
Semantic Segmentation in Scenes
- part segmentation에서 semantic scene segmentation으로의 확장은 쉬움
- point label이 object part label 대신 semantic object class가 되면 됨
- Stanford 3D semantic parsing dataset 사용
- 각 point : 9차원 벡터로 표현 (XYZ, RGB, normalized location)
- 추가로 had craft point features로써 local point density, local curvature, normal을 추가해서 총 12차원 벡터로 baseline과 our method 성능 비교함
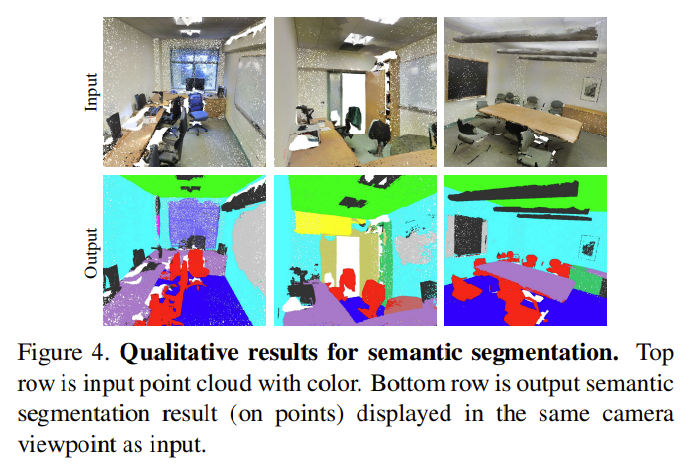

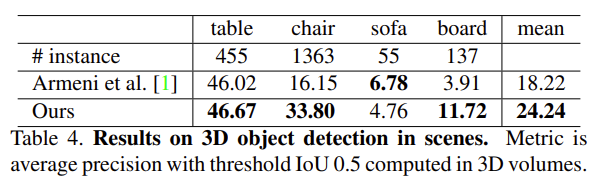
3D object detection system
- semantic segmentation output을 기반으로 object proposal을 위한 connected component 을 이용한 3D object detection system 만듦
5.2. Architecture Design Analysis
- 위에서 설명한 unordered data set에 대한 strategy들을 다 시험해봄
Comparison with Alternative Order-invariant Methods
- max pooling vs. average pooling vs. attention 중 max pooling이 가장 성능 높았음
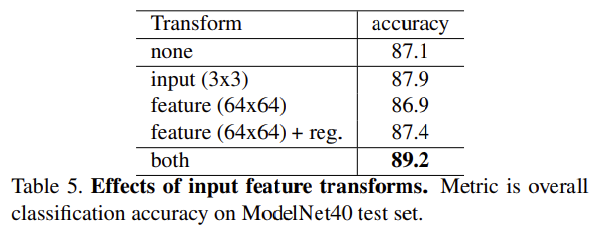
Effectiveness of Input and Feature Transformations
positive effects of our input and feature transformations (for alignment)
- regularization loss도 고차원 transform에 효과 있었음
Robustness Test
- MVCNN & 3D CNN은 성능은 좋지만 convolution layer 때문에 연산량이 많음
- 그러나 pointNet은 시간 복잡도가 O(N)이라서 효율적