클래스
클래스(class)란 객체를 정의하는 틀 또는 설계도와 같은 의미로 사용된다.
인스턴스
클래스에 소속된 개별적인 객체로써,
클래스를 사용하기 위해서는 우선 클래스 타입의 객체를 선언해야 한다.
클래스로부터 객체를 선언하는 과정을 클래스의 인스턴스 화라고 한다.
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> //max 함수 사용
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
// public과 private로 접근 정의
public:
//동작 정의(이를 멤버함수라고 합니다)
double getAvg();
int getMaxScore();
void setMathScore(int math) {
// this-> 로 표시해야 할 것
this->math = math;
}
void setEngScore(int eng) {
this->eng = eng;
}
void setKorScore(int kor) {
this->kor = kor;
}
int getMathScore() {
return this->math;
}
int getEngScore() {
return this->eng;
}
int getKorScore() {
return this->kor;
}
private:
//데이터 정의(이를 멤버변수라고 합니다.)
int kor;
int eng;
int math;
};
// getter와 setter로 Student 내부의 private 정보에 접근 가능
int main() {
Student s;
Student v;
int kor;
int eng;
int math;
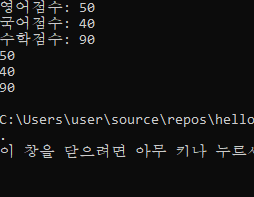
cout << "영어점수: ";
cin >> eng;
cout << "국어점수: ";
cin >> kor;
cout << "수학점수: ";
cin >> math;
s.setEngScore(eng);
s.setKorScore(kor);
s.setMathScore(math);
cout << s.getEngScore() << endl;
cout << s.getKorScore() << endl;
cout << s.getMathScore() << endl;
}
// private에 접근
//double Student::getAvg()
//{
// return (kor + eng + math) / 3.0;
//}
//
//int Student::getMaxScore()
//{
// return max(max(kor, eng), math);
//}
//
//int main()
//{
// Student s;
// s.getAvg();
//
// return 0;
//}
// 접근 방식 1 ==> Class명::
//double Student::getAvg()
//{
// return (kor + eng + math) / 3.0;
//}
//int Student::getMaxNum()
//{
// return max(max(kor, eng), math);
// // 다른 방법 return max({ kor, eng, math });
//}하나의 클래스로부터 여러개의 인스턴스를 생성할 수 있고 각 인스턴스는 독립된 메모리 공간에 저장된 자신만의 필드를 가진다.
그렇지만 해당 클래스의 모든 메소드(getEngScore 등)는 해당 클래스에 생성된 모든 인스턴스가 공유한다.
getter와 setter
일반적으로 Student내의 선언된 함수를 사용하기 위해서는 그냥 간단하게 Student::함수명()의 방식으로 처리할 수도 있으나
main에서 직접 인스턴스를 선언하여 인스턴스 내의 메소드를 불러오는 방식으로 사용할 수도 있다.(s.함수명())
그리고 클래스 내부에서 public과 private를 통해서 내부,외부에서의 접근을 제한할 수도 있는데 만약 private로 외부에서의 접근을 제한하였을 때 어떻게 외부에서 이를 사용할 수 있을까??
이를 해결하는 것이 getter와 setter이다.
위쪽의 코드에서 보면 public(외부,내부에서 제한없이 접근 가능) 으로 선언된 getter와 setter변수를 통해서 내부에 private로 선언되어 외부에서 접근이 불가능한 변수인 kor,eng,math에 대해서 접근 및 조작이 가능하게끔 설계가 되어있다.
이를 직접 실행해보면
이렇게 실제로 접근 및 조작이 가능하게 되는 것을 알 수 있다.
생성자
생성자는 클래스의 객체가 생성되었을 때 객체를 초기화하는 목적으로 실행하는 함수이다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person {
public:
string name;
int age;
// 기본 생성자
Person() {
name = "Unknown";
age = 0;
}
void display() {
cout << "Name: " << name << ", Age: " << age << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Person p; // 기본 생성자 호출
p.display();
return 0;
}여기서 Person() {} 안에 기본 생성자로써 아무런 인자를 넣지 않고 값을 초기화하며 객체의 인스턴스가 main에서 생성될 때 호출되어 내부 변수 값을 초기화 한다.
기본 생성자뿐만 아니라 인자값을 받아서 초기화하거나 값이 없을 경우 초기화 값을 지정해주는 것도 있다.
// 매개변수가 있는 생성자
Person(string n, int a) {
name = n;
age = a;
}
// 기본 매개변수가 있는 생성자
// 매개변수에 값이 들어올 경우 해당 값으로 초기화
Person(string n = "DefaultName", int a = 18) {
name = n;
age = a;
}헤더 파일로 클래스를 정하고 이를 include하여 처리하기
위에서 사용하던 class 파일들을 헤더파일로 만들고 난 후,
#ifndef STUDENT_H_
#define STUDENT_H_
class Student
{
public:
//값이 주어지지 않을경우 기본값을 할당하는 생성자
Student(int math = 32, int eng = 17, int kor = 52)
{
this->math = math;
this->eng = eng;
this->kor = kor;
}
double getAvg();
int getMaxScore();
//동작 정의(이를 멤버함수라고 합니다)
void setMathScore(int math)
{
this->math = math;
}
void setEngScore(int eng)
{
this->eng = eng;
}
void setKorScore(int math)
{
this->math = math;
}
int getMathScore() { return math; }
int getEngScore() { return eng; }
int getKorScore() { return kor; }
private:
//데이터 정의(이를 멤버변수라고 합니다.)
int kor;
int eng;
int math;
};
#endif내부에 class파일을 정의한다.
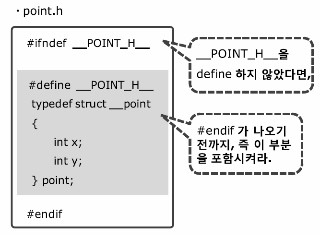
이때 #ifndef는 구조체의 중복 정의를 막기 위해서 사용하는 문법이다.
문제 풀이
- 배터리 문제
#ifndef BATERY_H_
#define BATERY_H_
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Batery {
public:
Batery(int energy = 100) {
this->energy = energy;
}
int getBatery() {
return energy;
}
void printBatery() {
cout << "현재 남은 배터리 잔량: " << energy << endl;
}
void setBatery(int energy) {
this->energy = energy;
}
void useBatery() {
if (energy < 5) {
energy = 0;
}
else {
energy -= 5;
}
}
void chargeBatery() {
if (energy + 7 > 100) {
energy = 100;
}
else {
energy += 7;
}
}
private:
int energy;
int limit = 100;
};
#endif
------ Battery.cpp -------
int main() {
Batery b;
b.printBatery();
cout << "배터리 사용" << endl;
b.useBatery();
b.printBatery();
cout << "배터리 충전" << endl;
b.chargeBatery();
b.printBatery();
cout << "배터리 설정" << endl;
b.setBatery(10);
b.printBatery();
}
- 두 분수의 곱셉을 할 수 있는 클래스 만들기
#ifndef Operator_h_
#define Operator_h_
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Operator {
public:
// 최대 공약수 구하기(유클리드 호제법)
int gcd(int a, int b) {
while (b != 0) {
int temp = b;
b = a % b;
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
Operator() {
numerator = 0;
denominator = 1;
}
Operator(int numerator, int denominator) {
this->numerator = numerator;
this->denominator = denominator;
}
void display() {
cout << numerator << "/" << denominator << endl;
}
// 기약분수(분모와 분자의 공약수가 1뿐인 분수)로 만들기
void simplify() {
int num = gcd(numerator, denominator);
numerator /= num;
denominator /= num;
}
// return 값 = Operator ==> 자료형
Operator multifly(Operator& other) {
int resultNum = numerator * other.numerator;
int resultDeno = denominator * other.denominator;
Operator result(resultNum, resultDeno);
result.simplify();
return result;
}
private:
int numerator;
int denominator;
};
#endif // !Operator_h_
#include <iostream>
#include "operator.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
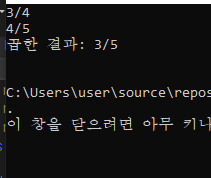
Operator o1(3, 4);
Operator o2(4, 5);
o1.display();
o2.display();
Operator result = o1.multifly(o2);
cout << "곱한 결과: ";
result.display();
cout << endl;
}