Records
Record필요한 이유는 아래 예제를 보면 알 수 있다.
List<Object> getLocInfo() => ["Seoul", 31]
void main(){
final locInfo = getLocInfo();
String place= locInfo [0] as String;
int address= locInfo [1] as int;
print("$place $address")- 타입 캐스팅을 해줘야하며 실수할 확률이 있음
- 별도 클래스를 구현하면 코드가 길어지고 비효율적Record를 사용하면 이렇게 간단해진다
(String, int) getLocInfo() => ("Seoul", 31)
void main(){
final locInfo = getLocInfo();
String place= locInfo.$1
int address= locInfo.$2
print("$place $address")
Record 문법
(int, String, {bool a, int b}) record = (1, a: true, "3", b:4)Pattern
- 패턴이란?
- 데이터 구조를 분해하거나, 비교하는데 사용되는 문법
- 패턴매칭이란?
- 입력값의 패턴을 인식하여 해당 패턴에 맞는 처리를 수행하는 기능
- 가장 기본적 패턴매칭 예제
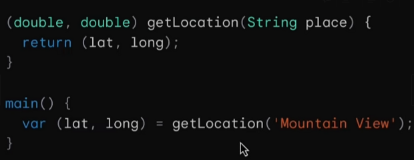
- lat, lang 두개의 값을 return 받아서 한꺼번에 사용가능
(double, double) getLocation(String place){
return (lat, long);
}
main(){
var(lat, long) = getLocation("Mountain View");
}패턴매칭을 활용하여 아래처럼 간결한switch문도 쓸 수 있다!
- swtich문에 Square, Circle 클래스를 던져주면 그에맞는 값 계산
sealed class Shape {}
class Square implements Shape {
final double length;
Square(this.length);
}
class Circle implements Shape {
final double radius;
Circle(this.radius);
}
double calculateArea(Shape shape) => switch (shape) {
Square(length: var l) => l * l,
Circle(radius: var r) => math.pi * r * r
};Class Modifier
쉽게 말하면, class 용도 구분 키워드가 추가되었다는 뜻!
처음부터 지원됐어야 할 기능이 늦게서야 지원된다는 생각이 있음
-
class Modifier왜 필요한가?
- 사용자들이 implement해서 사용하던 부모 클래스에 새 멤버를 추가하는것도 breaking changes. 이를 방지하기 위해 “please dont implement this class”주석을 사용하지만 충분치 않음
==⇒ 구현과 상속을 금지함으로써 기존 사용자들에게 변경없이 새 멤버 추가가능. 확장 및 발전이 훨씬 쉬워짐 - 클래스의 의도를 명확히 전달할 수 있음
- 사용자들이 implement해서 사용하던 부모 클래스에 새 멤버를 추가하는것도 breaking changes. 이를 방지하기 위해 “please dont implement this class”주석을 사용하지만 충분치 않음
-
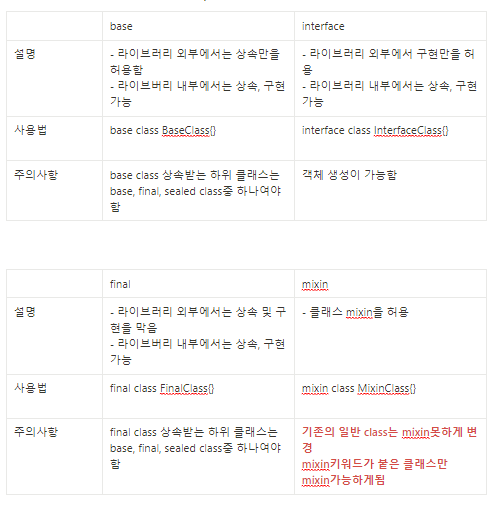
가능한 키워드들
- base
- interface
- final
- mixin
- sealed
-
설명
(참고 .Dart에서 라이브러리의 범위는 “part of”를 포함한 단일 파일!)
base 사용 예시
// Library a.dart
base class Vehicle {
void moveForward(int meters) {
// ...
}
}
// Library b.dart
import 'a.dart';
// Can be constructed
Vehicle myVehicle = Vehicle();
// Can be extended
base class Car extends Vehicle {
int passengers = 4;
// ...
}
// ERROR: Cannot be implemented
base class MockVehicle implements Vehicle {
@override
void moveForward() {
// ...
}
}interface 사용 예시
// Library a.dart
interface class Vehicle {
void moveForward(int meters) {
// ...
}
}
// Library b.dart
import 'a.dart';
// Can be constructed
Vehicle myVehicle = Vehicle();
// ERROR: Cannot be inherited
class Car extends Vehicle {
int passengers = 4;
// ...
}
// Can be implemented
class MockVehicle implements Vehicle {
@override
void moveForward(int meters) {
// ...
}
}final 사용예시
// Library b.dart
import 'a.dart';
// Can be constructed
Vehicle myVehicle = Vehicle();
// ERROR: Cannot be inherited
class Car extends Vehicle {
int passengers = 4;
// ...
}
class MockVehicle implements Vehicle {
// ERROR: Cannot be implemented
@override
void moveForward(int meters) {
// ...
}
}sealed 사용 예시
- 하위 타입들을 모두 알기 쉽다
- switch문에서 빼먹은거없이 모든 하위 타입을 다루고있는지 확인 가능
- sealed클래스는 인스턴스화가 불가능해서 암묵적으로 abstract. 그러나 sealed클래스의 하위 클래스는 인스턴스화 가능
// Library a.dart
interface class Vehicle {
void moveForward(int meters) {
// ...
}
}
// Library b.dart
import 'a.dart';
// Can be constructed
Vehicle myVehicle = Vehicle();
// ERROR: Cannot be inherited
class Car extends Vehicle {
int passengers = 4;
// ...
}
// Can be implemented
class MockVehicle implements Vehicle {
@override
void moveForward(int meters) {
// ...
}
}mixin
- mixin클래스에 있는 기능을 with 키워드로 다른 클래스에서 사용가능
abstract mixin class Musician {
// No 'on' clause, but an abstract method that other types must define if
// they want to use (mix in or extend) Musician:
void playInstrument(String instrumentName);
void playPiano() {
playInstrument('Piano');
}
void playFlute() {
playInstrument('Flute');
}
}
class Virtuoso with Musician { // Use Musician as a mixin
void playInstrument(String instrumentName) {
print('Plays the $instrumentName beautifully');
}
}
class Novice extends Musician { // Use Musician as a class
void playInstrument(String instrumentName) {
print('Plays the $instrumentName poorly');
}
}참고

안녕하세요 잘 읽었습니다. sealed 타입에 관한 예시가 interface 예시와 같네요 ㅎㅎ