Network
“몇 개의 독립적인 장치가 적절한 영역 내에서 적당히 빠른 속도의 물리적 통신 채널을 통하여 서로가 직접 통신할 수 있도록 지원해 주는 데이터 통신 체계”
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers:국제 전기 전자 공학회)
- Network = Net + Work
- 컴퓨터들이 통신 기술을 이용하여 그물망처럼 연결된 통신 이용 형태
Internet
“network of networks” → 네트워크 간의 연결
“Interconnected ISPs”
- ISP (Internet Service Provider) : Internet service를 파는 사업체
ISP+NSP: KT, SKT, LGU+ISP only: LG헬로비전(알뜰폰 사업자)- NSP (Network Service Provider) : Network infrastructure를 파는 사업체
- KT, SKT, LGU+ : 네트워크 망을 임대
Internet의 구성 요소
Network Edge | Access Network | Network Core |
|---|---|---|
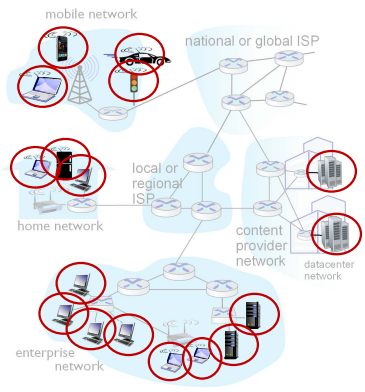 |  |  |
| Hosts : client & servers | Wired/wireless communication links | Interconnected routers |
추가 지식 : IoT
- 핵심 요구사항 : low power & high connectivity
- 5G가 복잡하고 power 소비가 많아서 LPWAN (예, LoRa, SigFox) 기술들이 IoT를 위해 개발됨
- BUT, 최근 5G를 저전력으로 사용할 수 있도록 변경하여 IoT 서비스 지원하는 통신사가 등장함
Protocol
“컴퓨터나 원거리 통신 장비 사이에서 메시지(데이터)를 주고 받는 양식과 규칙의 체계”
- 프로토콜은 두 소프트웨어 모듈 사이의 동작을 정의한 것
- 동작 종류
- 주고 받는 메세지의 형식과 순서 (format & order)
- 주고받기 전후 해야할 일 (action)
- 두 소프트웨어는 반드시 같은 계층에 속한 모듈
- 호스트 A의 L4 계층 소프트웨어 ⇔ 호스트 B의 L5 계층 소프트웨어
X
- 호스트 A의 L4 계층 소프트웨어 ⇔ 호스트 B의 L5 계층 소프트웨어
- 동작 종류
- 엔드 시스템, 패킷 스위치, 인터넷에서의 다른 조각들은 protocol을 운영
Protocol의 구성 요소
- format
- 메시지 내에 어떤 메시지가 보내는 사람 IP 주소인지, 아니면 목적지 IP 주소인지 구분할 수 있는 형식을 정의하는 것
- order
- 메시지를 주고 받는 순서
- action
- 메시지를 보내거나 받을 때 취해야 할 행동
ex) - 보내는 쪽에서 메시지를 적당한 크기로 잘라서 보내야 한다 - 받는 쪽에서는 메시지가 잘라져서 오기 때문에 합쳐야 한다 - 메시지에 에러가 포함되어있는지 확인을 한다
- 메시지를 보내거나 받을 때 취해야 할 행동
TCP/IP
- 인터넷의 근본 프로토콜 (가장 중요함) : TCP/IP
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- IP (Internet Protocol)
- 엔드 시스템과 라우터 사이에서 주고받는 패킷의 유형을 구체화
Internet standards
- IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) : L3/4/5 프로토콜 표준화
- RFC (Request for comments) : IETF가 만드는 문서의 이름 (프로토콜은 RFC 문서로 정의되어있음)
- IEEE : L2 프로토콜 표준화
여기부터 조금씩 수정 중
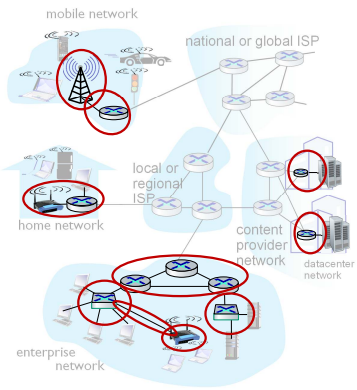
Access Network
“Wired / wireless communication links”
※ 인터넷 사용자(host)를 인터넷에 연결된 다른 access network의 host로 연결해 주는 첫번째 라우터까지를 포함한 네트워크
- 형태 : fiber, copper, radio, satellite
- link capacity
- transmission rate : bandwidth (대역폭)
- 단위 : bps = bits per sec
End System - Edge Router의 연결 방식
| 위치 | 네트워크 종류 |
|---|---|
| 집 | Residential Access Network |
| 학교, 회사, 기관 | Institutional Access Network |
| 기지국 | Mobile Access Network |
Access Network의 종류
Residential network
≈ home access network
1. DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
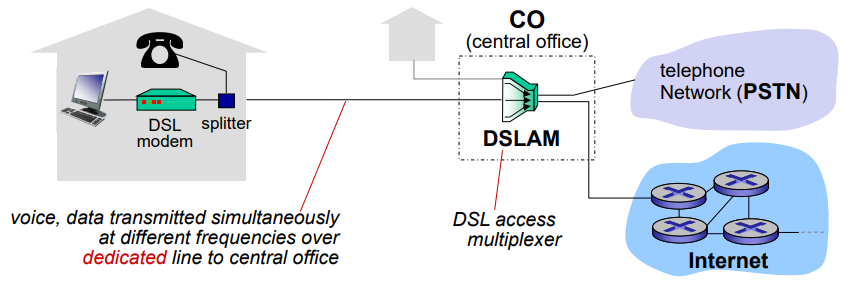
- DSL은 dedicated line을 이용
- 각 집에서 CO의 DSLAM으로 따로 연결이 되어 있어 다른 집과 데이터가 공유되지 않아 충돌하지 않음
- DSL modem은 CO에 위치한 DSLAM(Digital Subscriber Line access multiplexer)과 데이터를 교환하기 위해 기존 전화선(꼬임쌍선형식; Twisted pair copper wires)을 이용
-
DSL modem
- 컴퓨터의 디지털신호를 아날로그신호로 변환
-
splitter
-
DSL modem을 거쳐 온 컴퓨터의 데이터와 전화의 음성을 서로 다른 주파수로 CO의 DSLAM에 보냄
전화 telephone net; PSTN 음성 인터넷 Internet 데이터
-
-
- 전송률 : asymmetric
- upstream : 사용자 딴에서 보내는 데이터 (업로드); 전송률 낮음
- downstream : 사용자 딴에서 받는 데이터 (다운로드); 전송률 높음 (다운로드 빈도 수가 더 많아서)
- ADSL은 집과 CO까지의 거리가 멀수록 데이터 속도(bps)가 떨어짐
2. HFC (Hybrid fiber coax)
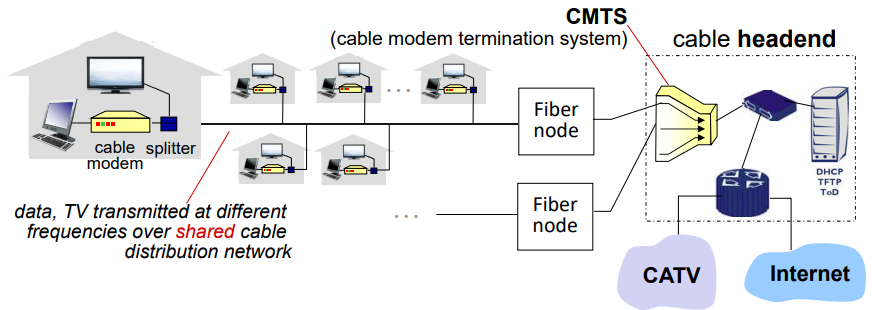
-
Cable Network
-
exploits cable TV network
- Coaxial cable
- Optical fiber cables
-
여러 집이 coaxial cable의 속도를 하는 기술
-
CO쪽에는 fiber가 사용되어 hybrid fiber coax라고 함
-
케이블망이 활성화 되지 않아 국내에서는 크게 성장하지 못함
-
asymmetric: up to 40Mbps~1.2Gbps downstream
transmission rate, 30~100 Mbps upstream transmission rate -
network of cable, fiber attaches homes to ISP router
- homes share access network to cable headend
- unlike DSL, which has dedicated access to central office
3. FTTH (Fiber To The Home)
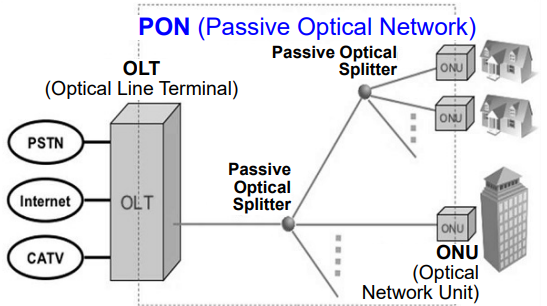
-
uses optical fiber cables up to home to provide Gbps
-
국내에서는 2005년 KT에서 FTTH라는 이름으로 서비스를 시작하였으나, 아파트 관리사무소(혹은 아파트동)까지만 fiber가 들어오고 집과 관리사무소 사이는 Ethernet 기술을 사용하는 (이를 광랜 서비스라 함) 즉, FTTB (Fiber To The Building) + Ethernet to Home 도 있음
-
Provides an optical fiber path from the CO directly to the home.
- Potentially provide Internet access rates in the gigabits per second range.
-
Two optical-distribution network (ODN) architecture
- Active Optical Network (AON) – switched Ethernet
- Passive Optical Network (PON) – passive Splitter
4. 5G FWA (Fixed Wireless Access)
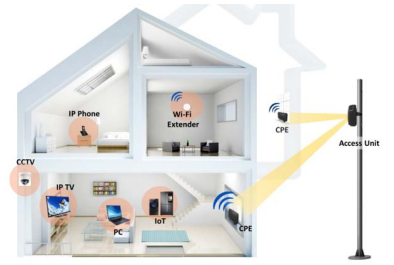
- provides Gbps with less rollout costs and lower OPEX.
- Significantly lower rollout costs, and lower OPEX.
- Used as a way to expand the edges of their current service footprints with a reliable, cost-effective approach
- offers up to Gbps broadband experience, helping operators
provide fiber-like broadband services.
Enterprise network
1. Ethernet (wired access)
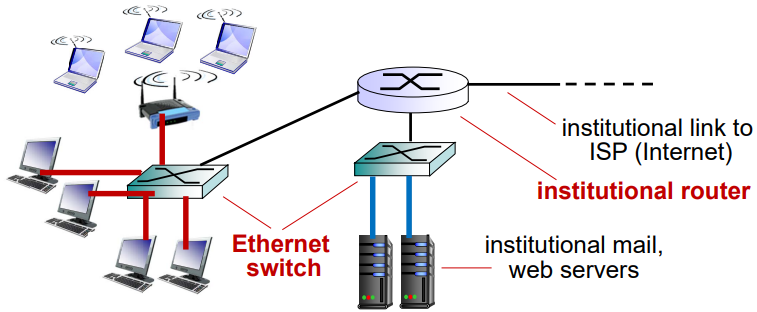
- L2 프로토콜
- L2 switch가 있음
- 주요 사용처 : 회사, 학교
- mix of wired, wireless link technologies, connecting a mix of switches and routers
- 속도
- Fast Ethernet (FE) 10/100 Mbps
- Gigabit Ethernet (GE) 1/10/100/1000 Gbps
2. Wi-Fi (wireless access point)
- shared wireless access network connects end system to router
- via base station aka “access point”
- Wireless local area networks (WLANs)
- typically within or around building (~100 ft)
Mobile network
3G,4G/LTE,5G
- wide-area wireless access
- provided by telco (cellular) operator, 10’s km
Network Edge
“Hosts : client & servers”
※ servers는 보편적으로 data centers에 위치
Host
- ≈ end system, end node, terminal, station
- 네트워크 트래픽을 생성/소비하는 장비
- Packet 단위로 데이터 전송
- Packet이란?
- Internet의 데이터 전송 단위
- Large Message(msg) = Multiple Small Packets(pkts)
- Transmission Delay (L-bit pkt, transmission rate R)
- (L-bit)/(R bps) = L/R sec
- Packet이란?
- 각기 다른 목적을 수행하기 위해 network apps 실행
Network Core
“Interconnected Routers”
Router
- router (layer1/2/3)
- L2-switch (layer 2/2)
- L3-switch(L2-switch + routing - WAN: VLAN을 지원하기위해 LAN 안에서 사용됨.)
- 두 개의 host 사이의 통신(데이터 교환)을 위해 "delivering (end) user data"를 목표로 하는 네트워크 장비들임
Core Networking 기술 : C.S vs. P.S
Circuit Switching
- End-to-end transmission delay for transmitting one message (=3 L-bit pkts) over four R bps link is NOT (3 x (L/R)) x 4 sec since multiple packets belonging to the same message are transmitted in parallel in core network.
Packet Switching
-
Basic operation of packing switching network : store and forward
- Store (L bits) in an input buffer
- checking the forwarding table to find the output link via which the packet will finally arrive at its destination computer.
- forwarding the L-bit packet to the output buffer of the output link
- may be waiting in the output buffer (this is queueing delay)
- transmitted ( L/R sec delay incurred for transmission )
-
Routing v.s. forwarding in the packet switching network
-
Routing is to determine the e2e path by exchanging control messages among routers.
from a source host to a destination host
-
Forwarding is to switch a packet at ONE router using the forward table (Forwarding Information Base, FIB).
from an input port to an output port
-
Transmission Delay
- Transmission delay for transmitting a L-bit packet over a R bps link = (L-bit)/(R bps) = L/R sec
- Transmission delay for transmitting one message (=3 L-bit pkts) over a R bps link = 3 x (L/R) sec
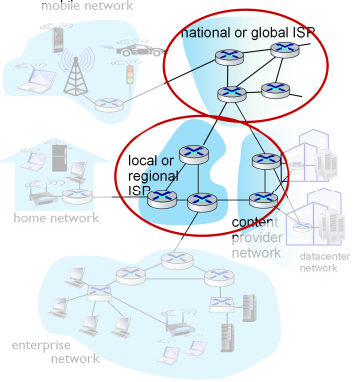
Internet Structure
- Internet structure: multi-tier hierarchy
- Two ways of connecting different networks (usually different ISPs): IXP and Peering
- What is Point of Presence (PoP)?
- What is the advantage of a multi-homed network?
- Content Provider Network (CPN) or Content Delivery/Distribution Network (CDN)
-
CPN and CDN are compatible, but CDN is more widely used.
-
The goal of CDN is which content users feel
to reduce latency
by wisely locating caches (usually closer to users)
-

