데이터 분석(SQL) 3일차 - mysql 사용
1. Subquery 활용
💡 Subquery를 활용하여 복잡한 연산을 수행할 수 있다.
☝ Subquery가 필요한 경우
- 여러번의 연산을 수행해야 할때
- 조건문에 연산 결과를 사용해야 할때
- 조건에 Query결과를 사용하고 싶을때
1) Subquery문의 기본 구조
select column1, special_column
from
( # subquery #
select column1, column2 special_column
from table1
) a
- [연습문제1] 음식 주문시간이 25분보다 초과한 시간을 가져오기
select order_id, restaurant_name, if(over_time>=0, over_time, 0) over_time
from
(
select order_id, restaurant_name, food_preparation_time-25 over_time
from food_orders
) a
- [연습문제2] 음식점의 평균 단가별 segmentation 을 진행하고, 그룹에 따라 수수료 연산하기
select restaurant_name,
price_per_plate*ratio_of_add "수수료"
from
(
select restaurant_name,
case when price_per_plate<5000 then 0.005
when price_per_plate between 5000 and 19999 then 0.01
when price_per_plate between 20000 and 29999 then 0.02
else 0.03 end ratio_of_add,
price_per_plate
from
(
select restaurant_name, avg(price/quantity) price_per_plate
from food_orders
group by 1
) a
) b
2. Join 활용
💡 필요한 데이터가 서로 다른 테이블에 있을때 join 사용
1) Join의 기본 원리와 종류
-
공통 컬럼을 기준으로 두 테이블을 합쳐서, 각각 테이블에서 필요한 데이터를 조회할 수 있도록 만들어 주는 것
-
Join의 종류
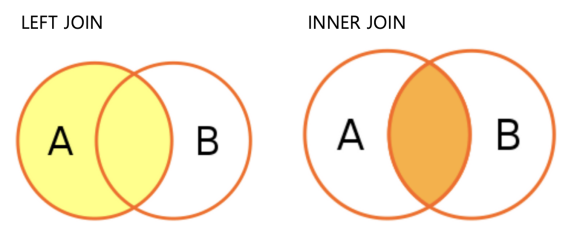
✔️ LEFT JOIN : 공통 컬럼 (키값) 을 기준으로, 하나의 테이블에 값이 없더라도 모두 조회되는 경우를 의미합니다.
✔️ INNER JOIN : 공통 컬럼 (키값) 을 기준으로, 두 테이블 모두에 있는 값만 조회합니다.
- Join의 기본 구조
-- LEFT JOIN
select 조회 할 컬럼
from 테이블1 a left join 테이블2 b on a.공통컬럼명=b.공통컬럼명
-- INNER JOIN
select 조회 할 컬럼
from 테이블1 a inner join 테이블2 b on a.공통컬럼명=b.공통컬럼명
❗팁 - 공통컬럼은 묶어주기 위한 ‘공통 값’ 이기 때문에 두 테이블의 컬럼명은 달라도 괜찮습니다.
예를 들어 주문정보에는 ‘고객ID’, 고객정보에는 ‘고객아이디’ 라고 컬럼명이 되어있다면,
테이블1.고객ID=테이블2.고객아이디 와 같이 묶어줄 수 있습니다.
- [실습1] 한국 음식의 주문별 결제 수단과 수수료율을 조회하기
select a.order_id,
a.restaurant_name,
a.price,
b.pay_type,
b.vat
from food_orders a left join payments b on a.order_id=b.order_id
where cuisine_type='Korean'
3. Subquery와 Join 함께 쓴 실습문제
- [실습] 50세 이상 고객의 연령에 따라 경로 할인율을 적용하고, 음식 타입별로 원래 가격과 할인 적용 가격 합을 구하기
(조회 컬럼 : 음식 타입, 원래 가격, 할인 적용 가격, 할인 가격)
*할인 : 나이-50*0.005
* 고객 정보가 없는 경우도 포함하여 조회, 할인 금액이 큰 순서대로 정렬
select cuisine_type,
sum(price) "원래 가격",
sum(price)-sum(discount_price) "할인 적용 가격",
sum(discount_price) "할인 가격"
from
(
select a.cuisine_type,
price,
price((b.age-50)0.005) discount_price
from food_orders a inner join customers b on a.customer_id=b.customer_id
where b.age>=50
) t
group by 1
order by 4 desc
4. 문제 풀이중 배운것
- programmers 오랜 기간 보호한 동물(1) : left join 과 is null 함께 사용하는 SQL 쿼리
1) 쉬운 예시 설명
예) ✅ LEFT JOIN + IS NULL 예제
📌 Customers 테이블 (고객 정보)
| CustomerID | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Alice |
| 2 | Bob |
| 3 | Charlie |
| 4 | David |
📌 Orders 테이블 (주문 정보)
| OrderID | CustomerID | Product |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | 1 | Laptop |
| 102 | 3 | Phone |
✅ LEFT JOIN 실행 결과
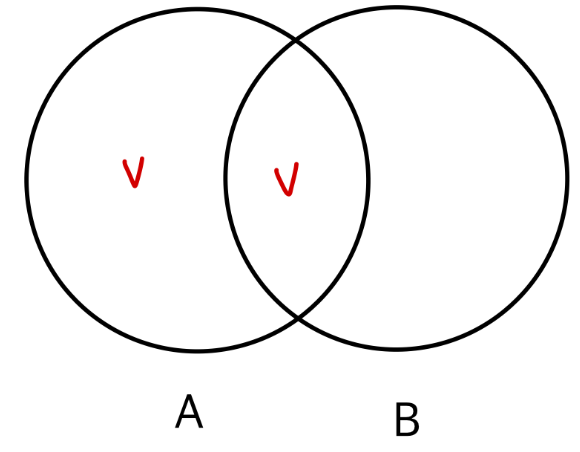
SELECT C.CustomerID, C.Name, O.OrderID, O.Product
FROM Customers C
LEFT JOIN Orders O ON C.CustomerID = O.CustomerID| CustomerID | Name | OrderID | Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alice | 101 | Laptop |
| 2 | Bob | NULL | NULL |
| 3 | Charlie | 102 | Phone |
| 4 | David | NULL | NULL |
✅ LEFT JOIN + IS NULL (주문하지 않은 고객 찾기)
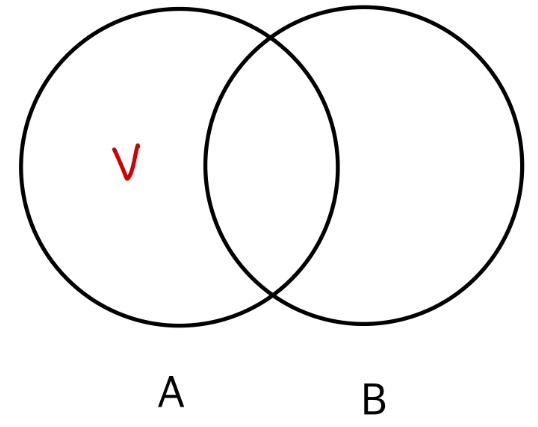
SELECT C.CustomerID, C.Name
FROM Customers C
LEFT JOIN Orders O ON C.CustomerID = O.CustomerID
WHERE O.OrderID IS NULL;| CustomerID | Name |
|---|---|
| 2 | Bob |
| 4 | David |
2) programmers 오랜 기간 보호한 동물(1) 풀이
SELECT i.name, i.datetime
from animal_ins i left join animal_outs o on i.animal_id = o.animal_id
where o.animal_id is null
order by 2
limit 3✅ LEFT JOIN 실행 결과 (WHERE 조건 없이 실행)
| i.animal_id | i.name | i.datetime | o.animal_id |
|---|---|---|---|
| A001 | Bella | 2022-01-01 | A001 |
| A002 | Max | 2022-01-02 | NULL |
| A003 | Coco | 2022-01-03 | A003 |
| A004 | Daisy | 2022-01-04 | NULL |
| A005 | Rocky | 2022-01-05 | NULL |
❗이래서 where 절에서 o.animal_id is null 이라고 사용한것!!

