Chapter 9
Virtual Topology
1. Virtual Topology
개요
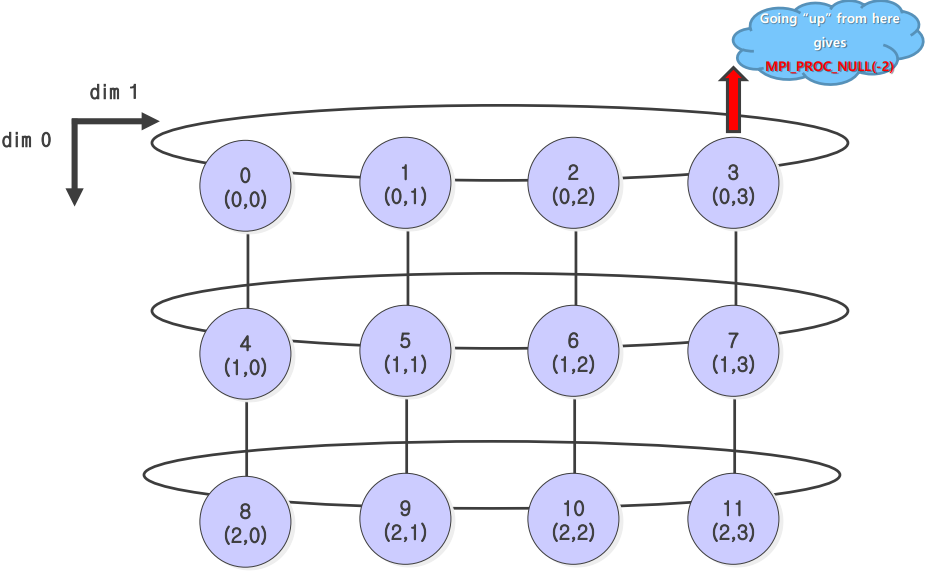
- rank를 2차원적으로 다루는 방법
- MPI에서 통신 최적화, 코드 작성 용이성, 프로세스 이름 작성 편리성 확보 가능
- 주기성을 줄 수 있음
ex. (0,0) -> (0,1) -> (0,2) -> (0,3) -> (0,0) - 주기성을 주지 않을 시,
MPI_PROC_NULL(-2)return
사용법
- Cartesian virtual topology 생성
MPI_Cart_create()로 MPI communicator 생성MPI_COMM_WORLD아닌 새로운 comm 생성
- Mapping 함수들을 이용한 접근
2. Cartesian Topology 생성
MPI_Dims_create()
int MPI_Dims_create( int nnodes, int ndims, int dims[] )- 전체 프로세스 개수
nnodes, 차원 수ndims지정 시 각 차원으로 배치할 프로세스의 개수 return - 사용자가 좌표 방향당 프로세스의 균형 있는 분포를 선택하는데 도움을 줌
MPI_Cart
1. MPI_Cart_create
MPI_Cart_create()
int MPI_Cart_create( MPI_Comm comm_old, int ndims, const int dims[],
const int periods[], int reorder, MPI_Comm *comm_cart ) - Cartesian topology 정보가 부착된 새로운 communicator를 생성하여 return
Arguments
| argument | 설명 |
|---|---|
| comm_old | 기존의 communicator (MPI_COMM_WORLD) |
| ndims | 좌표의 차원 수 |
| dims[] | 차원별 배치된 프로세스 수 |
| periods[] | 각 차원 별 주기성 여부 |
| reorder | False (보통 사용) (새로운 그룹에서 각 프로세스의 rank는 old group의 rank와 동일) / True (프로세스 랭크를 재할당). |
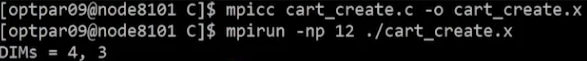
Example: C code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mpi.h>
#define NDIM (2)
int main(void)
{
int myrank, nprocs, dims[NDIM]={0},newprocs, newrank;
int reorder=0, periods[NDIM]={0,0};
MPI_Comm comm_cart;
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&myrank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&nprocs);
MPI_Dims_create(nprocs,NDIM,dims);
if(myrank==0) printf("DIMs = %d, %d\n",dims[0],dims[1]);
MPI_Cart_create(MPI_COMM_WORLD,NDIM, dims, periods, reorder, &comm_cart);
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}Example: Result
2. Mapping Functions
MPI_Cart_rank()
int MPI_Cart_rank( MPI_Comm comm, const int cords[], int *rank )- Cartesian 좌표에 대한 rank를 반환
MPI_Cart_coords()
int MPI_Cart_coords( MPI_Comm comm, int rank, int maxdims, int coords[])- Rank에 해당하는 좌표를 반환
Example: C code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mpi.h>
int main(void){
MPI_Comm oldcomm, newcomm;
int ndims=2, dimsize[2];
int periods[2], reorder;
int myrank, nprocs, i,j, rank;
int coords[2]={0,};
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myrank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &nprocs);
oldcomm=MPI_COMM_WORLD;
dimsize[0]=3, dimsize[1]=2;
periods[0]=1, periods[1]=0;
reorder=0;
MPI_Cart_create(oldcomm, ndims,dimsize,periods,reorder,&newcomm);
if(myrank==0){
for(i=0;i<dimsize[0];i++){
for(j=0;j<dimsize[1];j++){
coords[0]=i, coords[1]=j;
MPI_Cart_rank(newcomm, coords, &rank);
printf("coords=%d, %d, rank=%d\n",coords[0], coords[1], rank);
}
}
}
if(myrank==0){
for(rank=0;rank<nprocs;rank++){
MPI_Cart_coords(newcomm, rank, ndims,coords);
printf("rank=%d, coord=%d, %d\n",rank, coords[0], coords[1]);
}
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}Example: Result
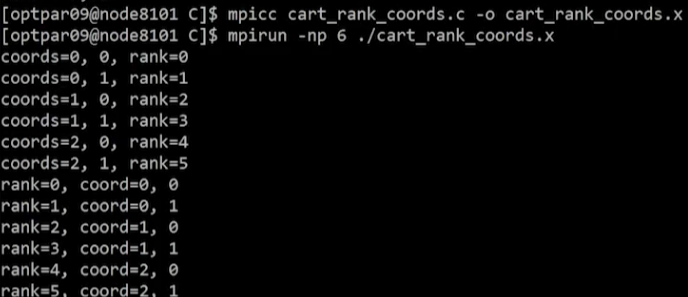
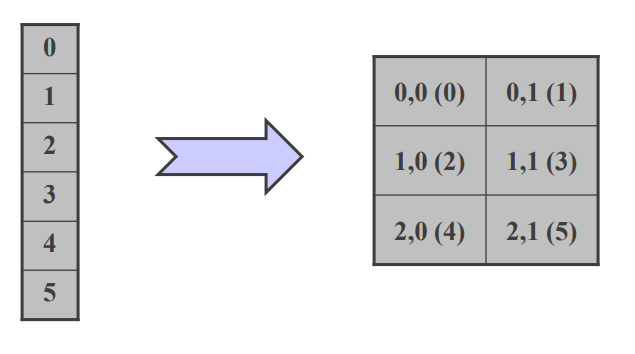
- input 좌표, output rank
- input rank, output 좌표
3. MPI_Cart_shift
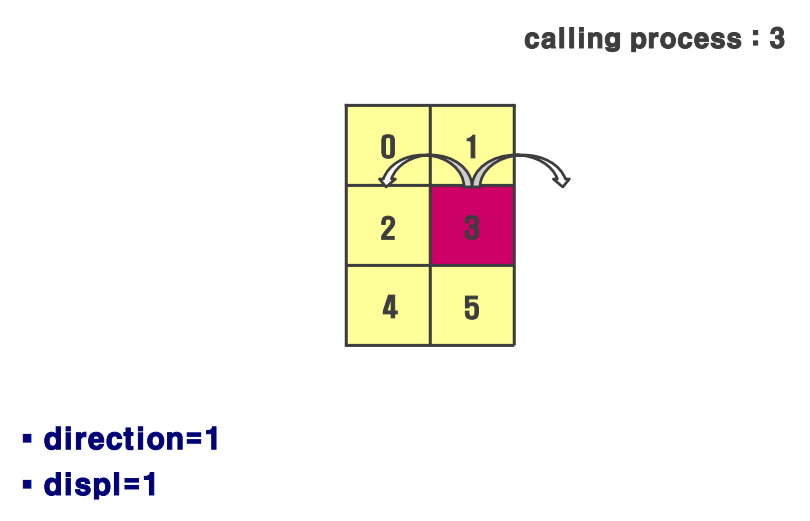
MPI_Cart_shift()
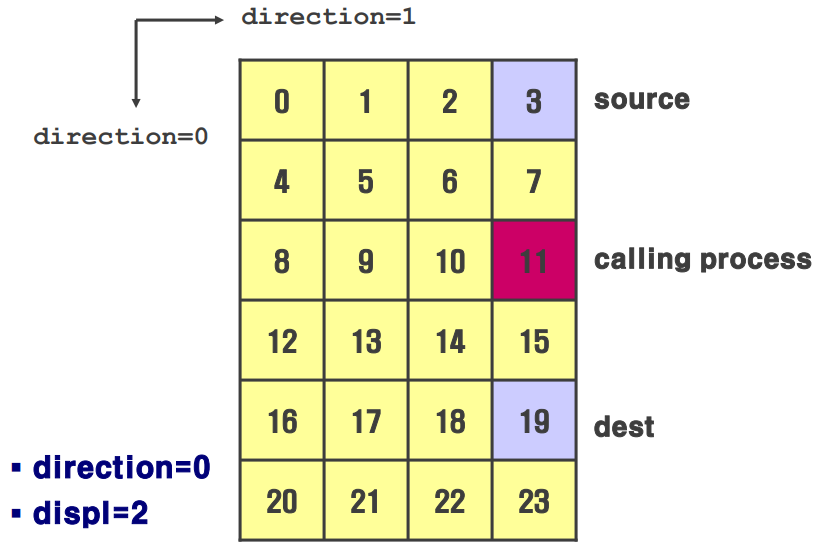
int MPI_Cart_shift( MPI_Comm comm, int direction, int disp, int* rank_source, int* rank_dest )- 직교 좌표 topology에서 특정 방향을 따라 프로세스의 이웃 프로세스를 찾는데 사용
- 검색된 두 프로세스를 각각 source rank(차원 진행방향 반대쪽)와 destination rank(차원 진행방향 쪽)이라 함
- input process와의 거리는 disp로 결정
- 즉, 어떤 프로세스에서 disp 만큼 떨어진 두 프로세스 source, dest를 찾는 과정이라 생각하면 됨
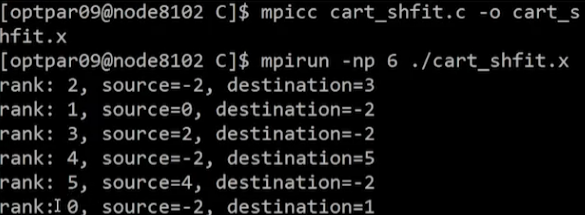
Example: C code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mpi.h>
int main(void)
{
MPI_Comm oldcomm,newcomm;
int ndims=2, dimsize[2];
int periods[2], reorder;
int myrank, nprocs, i,j, rank;
int coords[2];
int direction,disp, src, dest;
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&myrank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&nprocs);
oldcomm=MPI_COMM_WORLD;
dimsize[0]=3, dimsize[1]=2;
periods[0]=1, periods[1]=0;
reorder=0;
MPI_Cart_create(oldcomm, ndims,dimsize,periods,reorder,&newcomm);
direction=1;disp=1;
MPI_Cart_shift(newcomm, direction,disp, &src, &dest);
printf(“rank: %d, source=%d, destination=%d\n”,myrank, src, dest);
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}Example: Result
Neighborhood Collective Communication
1. Neighborhood Collective Communication
개요
- 프로세스 topology의 에지(edge)들을 따라서 통신을 수행하는 집합 통신
- Communicator에 있는 모든 프로세스들에 의해 호출되어야 함
- 이웃이 존재하지 않으면(주기성이 false 일 때), 그 이웃은
MPI_PROC_NULL(-2)로 정의됨
2. MPI_Neighbor_allgather
MPI_Neighbor_allgather()
int MPI_Neighbor_allgather( const void* sendbuf, int sendcount, MPIDatatype sendtype,
void* recvbuf, int recvcount, MPI_Datatype recvtype, MPI_Comm comm)- argument들은
MPI_Allgather()와 동일 - 통신 순서: dim 0 source -> dim 0 dest -> dim 1 source -> dim 1 dest
- MPI_PROC_NULL인 경우 통신이 발생하지 않음
Example: C code
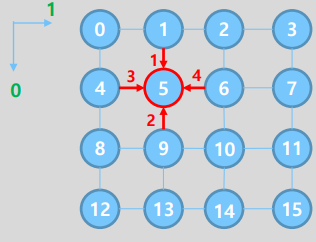
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mpi.h>
int main(void)
{
int myrank,procs;
MPI_Comm comm_cart;
int ndim=2,dims[2], recvbuf[4]={-10,};
int periods[2]={0,0}, reorder=0;
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&myrank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&procs);
dims[0]=4, dims[1]=4;
MPI_Cart_create(MPI_COMM_WORLD,ndim,dims,periods,reorder,&comm_cart);
MPI_Neighbor_allgather(&myrank,1,MPI_INT,recvbuf,1,MPI_INT,comm_cart);
printf("myrank : %d, recvbuf: %d, %d, %d, %d\n",myrank, recvbuf[0],recvbuf[1],recvbuf[2],recvbuf[3]);
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}Example: Result

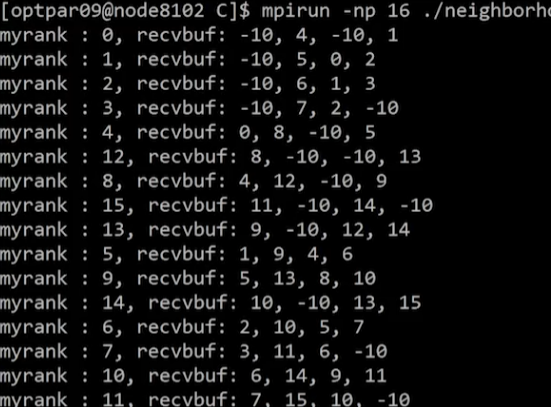
- 주기성이 dim 0, dim 1 모두 없기 때문에 neighbor가 없는 노드의 경우
recvbuf의 초기값인 -10 출력
3. MPI_Neighbor_alltoallv
MPI_Neighbor_alltoallv()
int MPI_Neighbor_alltoallv( const void *sendbuf, const int sendcounts[],
const int sdispls[], MPI_Datatype sendtype, void *recvbuf, const int recvcounts[],
const int rdispls[], MPI_Datatype recvtype, MPI_Comm comm)MPI_Alltoallv()와 argument는 모두 같음- 통신 순서: dim 0 source -> dim 0 dest -> dim 1 source -> dim 1 dest
- MPI_PROC_NULL인 경우 통신이 발생하지 않음
사용
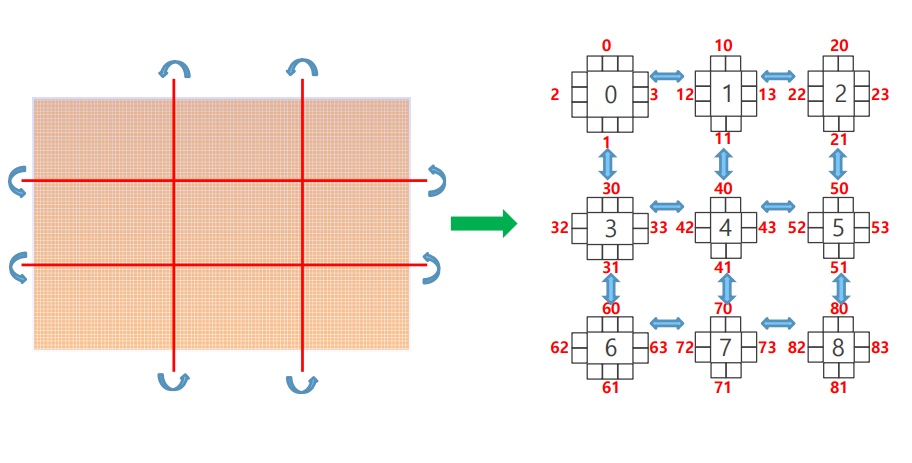
- 연산을 위해서 인접한 노드의 값들이 필요한 경우
- Send, Recv 함수로도 할 수 있지만,
MPI_Neighbor_alltoallv()를 사용하면 한꺼번에 처리할 수 있음