Chapter 8
Scatter
1. MPI_Scatter
scatter
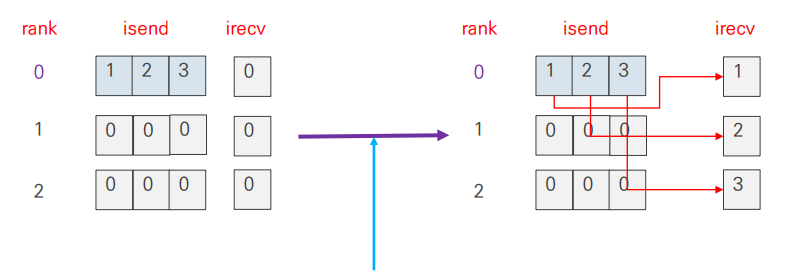
- root rank의 isend 버퍼 값을 각 rank로 전달
MPI_Gather()의 반대 연산
MPI_Scatter()
int MPI_Scatter( const void* sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void* recvbuf, int recvcount, MPI_Datatype recvtype, int root, MPI_Comm comm )2. Example: MPI_Scatter()
C code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mpi.h>
int main()
{
int i, myrank;
int isend[3]={0,}, irecv=0;
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&myrank);
if(myrank==0) for(i=0;i<3;i++) isend[i]=i+1;
MPI_Scatter(isend,1,MPI_INT,&irecv,1,MPI_INT,0,MPI_COMM_WORLD);
printf("myrank: %d irecv=%d\n",myrank,irecv);
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
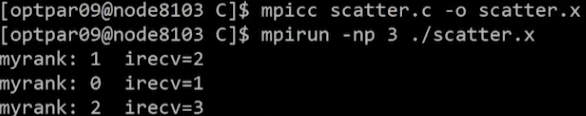
}Result
3. MPI_Scatterv
scatterv
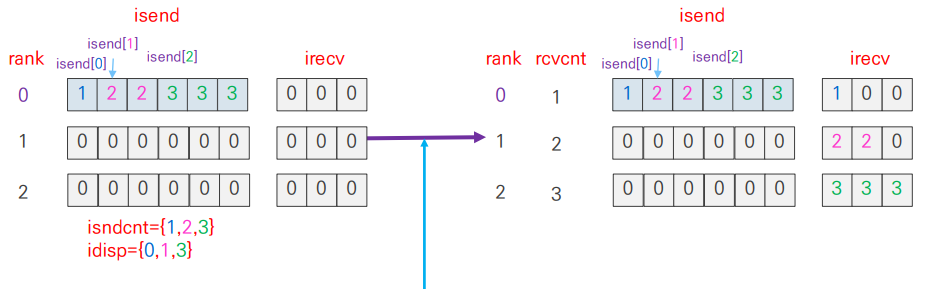
- 각 rank 별로 다른 크기의 data를 전달
MPI_Gather()의 반대 연산- 전체 input 값을 root에서 한번에 읽은 후 각 rank에 필요한 부분을 배분시킬 때 많이 사용
MPI_Scatterv()
int MPI_Scatterv( const void* sendbuf, const int sendcounts[], const int displs[],
MPI_Datatype sendtype, void* recvbuf, int recvcount, MPI_Datatype recvtype,
int root, MPI_Comm comm )Reduce
1. MPI_Reduce
reduce
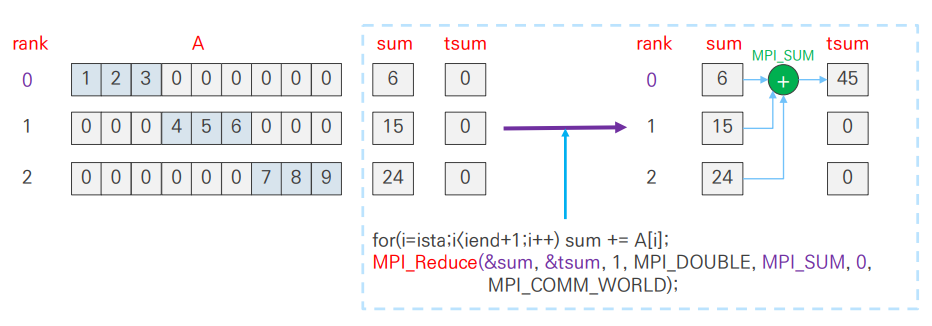
- 각 프로세스의 input buffer의 요소들을 op 연산을 수행한 후 root 랭크의 output buffer에 결과를 반환
- Input buffer와 output buffer의 type과 요소의 수(배열의 크기)는 일치해야 함
MPI_Reduce()
int MPI_Reduce( const void* sendbuf, void* recvbuf, int count,
MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Op op, int root, MPI_Comm comm )&sendbuf다음에 바로&recvbuf가 위치함
Operation & Data type
| Operation | Data type(C) |
|---|---|
| MPI_SUM(sum), MPI_PROD(product), MPI_MAX(maximum), MPI_MIN(minimum) | MPI_INT, MPI_LONG, MPI_SHORT, MPI_UNSIGNED_SHORT, MPI_UNSIGNED, MPI_UNSIGNED_LONG, MPI_FLOAT, MPI_DOUBLE, MPI_LONG_DOUBLE |
| MPI_MAXLOC(max value and location), MPI_MINLOC(min value and location) | MPI_FLOAT_INT, MPI_DOUBLE_INT, MPI_LONG_INT, MPI_2INT, MPI_SHORT_INT, MPI_LONG_DOUBLE_INT |
| MPI_LAND(logical AND), MPI_LOR(logical OR), MPI_LXOR(logical XOR) | MPI_INT, MPI_LONG, MPI_SHORT, MPI_UNSIGNED_SHORT, MPI_UNSIGNED, MPI_UNSIGNED_LONG |
| MPI_BAND(bitwise AND), MPI_BOR(bitwise OR), MPI_BXOR(bitwise XOR) | MPI_INT, MPI_LONG, MPI_SHORT, MPI_UNSIGNED_SHORT, MPI_UNSIGNED, MPI_UNSIGNED_LONG, MPI_BYTE |
- MPI_2INT = { MPI_INT, MPI_INT }
2. Example
C code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mpi.h>
int main()
{
int nrank,ista,iend,i;
double A[9]={0.0,}, sum=0.0, tsum=0.0;
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&nrank);
ista=nrank*3; iend=ista+2;
for(i=ista;i<iend+1;i++) A[i]=i+1;
sum=0.0;
for(i=ista;i<iend+1;i++) sum += A[i];
MPI_Reduce(&sum,&tsum,1,MPI_DOUBLE,MPI_SUM, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(nrank==0) printf("rank(%d):sum=%.2f\n",nrank,tsum);
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}- rank 0: sum = 1+2+3 = 6
- rank 1: sum = 4+5+6 = 15
- rank 2: sum = 7+8+9 = 24
Result

3. MPI_Allreduce
allreduce
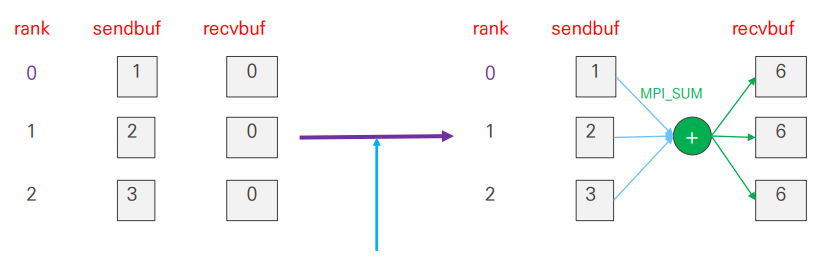
- 각 프로세스의 input buffer의 요소들을 op 연산을 수행한 후 전체 프로세스에 그 결과값을 전달
MPI_Allreduce()
int MPI_Allreduce(const void* sendbuf, void* recvbuf, int count,
MPI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Op op, MPI_Comm comm )MPI_Reduce()연산에서 root argument가 빠진 형태
AlltoAll
1. MPI_Alltoall
alltoall
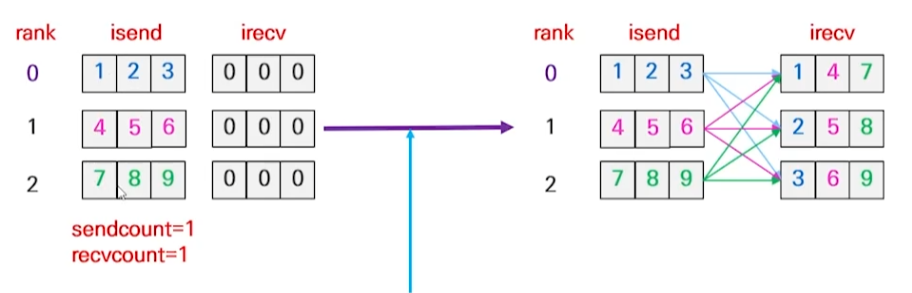
- 각 rank 순서대로 scatter 연산을 수행하는 형태
- 각 rank의 i번째 data들을 rank i로 전송
MPI_Alltoall()
int MPI_Alltoall(const void* sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void* recvbuf, int recvcount, MPI_Datatype recvtype, MPI_Comm comm )2. Example: MPI_Alltoall
C code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mpi.h>
int main()
{
int isend[3],irecv[3];
int i,nprocs,myrank;
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&nprocs);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&myrank);
for(i=0;i<nprocs;i++) isend[i]=1+i+nprocs*myrank;
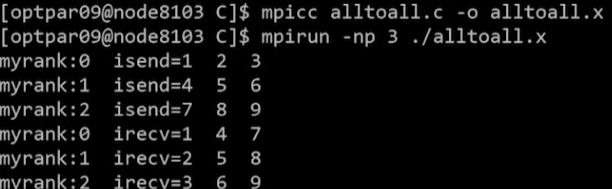
printf("myrank:%d isend=%d %d %d\n",myrank,isend[0],isend[1],isend[2]);
MPI_Alltoall(isend,1,MPI_INT, irecv,1,MPI_INT,MPI_COMM_WORLD);
printf("myrank:%d irecv=%d %d %d\n",myrank,irecv[0],irecv[1],irecv[2]);
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}Result
3. MPI_Alltoallv
alltoallv
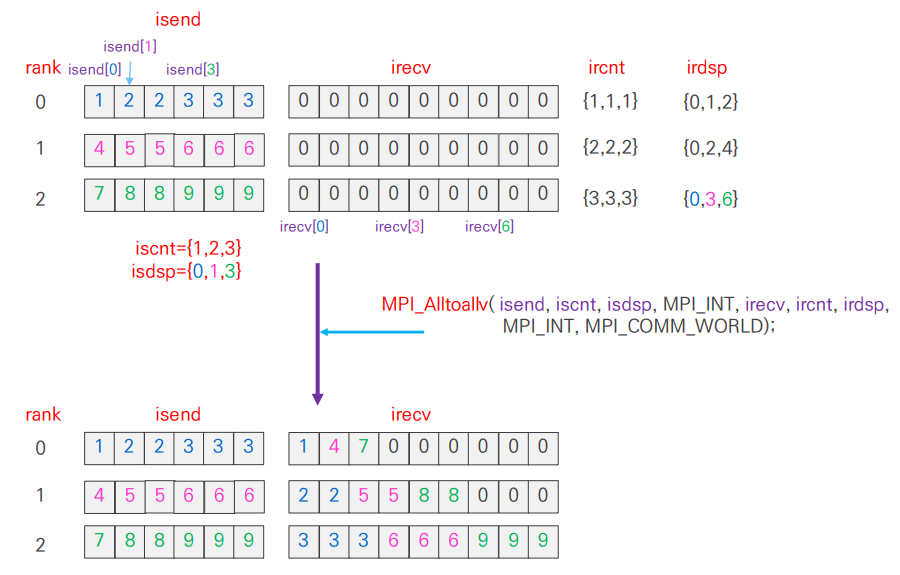
MPI_Alltoall()에 유연성을 추가- 송신 데이터의 위치는
sdispls에 지정 - 수신 측의 수신 데이터의 위치는
rdispls에 추가됨
MPI_Alltoallv()
int MPI_Alltoallv(const void* sendbuf, const int sendcounts[], const int sdispls[],
MPI_Datatype sendtype, void* recvbuf,const int recvcounts[], const int rdispls[],
MPI_Datatype recvtype, MPI_Comm comm )4. Example: MPI_Alltoallv
C code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <mpi.h>
int main()
{
// Hard Coding
int isend[6]={1,2,2,3,3,3}, irecv[9]={0,};
int iscnt[3]={1,2,3}, isdsp[3]={0,1,3}, ircnt[3], irdsp[3];
int myrank,nprocs,i;
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&nprocs);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&myrank);
for(i=0;i<6;i++) isend[i]=nprocs*myrank+isend[i];
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
if(myrank==0) ircnt[i]=1,irdsp[i]=i;
else if(myrank==1) ircnt[i]=2, irdsp[i]=2*i;
else if(myrank==2) ircnt[i]=3, irdsp[i]=3*i;
}
MPI_Alltoallv(isend,iscnt,isdsp,MPI_INT,irecv,ircnt,irdsp,MPI_INT,MPI_COMM_WORLD);
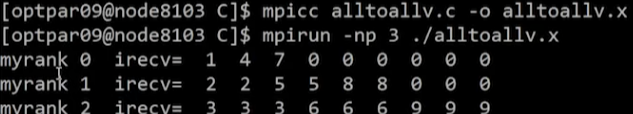
printf("myrank %d irecv=",myrank);
for(i=0;i<9;i++) printf(" %d",irecv[i]);
printf("\n");
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}Result
Barrier, Wtime
Barrier
int MPI_Barrier(MPI_Comm comm)int MPI_Ibarrier(MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Request *request)- communicator내의 모든 프로세스가 호출한 지점에 도달할 때까지 진행을 멈춤
Wtime
double MPI_Wtime(void)- Wall clock time을 return
Example
…
Double s_time, e_time, t_time;
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
s_time=MPI_Wtime(); // 여기까지 걸린 시간
// 계산
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
e_time=MPI_Wtime(); // 여기까지 걸린 시간
t_time = e_time – s_time;t_time = e_time – s_time은 실제 계산하는 데에 걸린 시간