Chapter 7
집합 통신
1. Collective Communications
개요
- communicator 내에 있는 모든 프로세스가 통신에 참여
- P2P(Point to Point) 통신 기반
- P2P 통신에 비해 코드 작성이 쉽고 효율적
Special feature
- communicator 내의 모든 프로세스들에 의해 호출
- message tag 없음
2. 종류
Broadcast
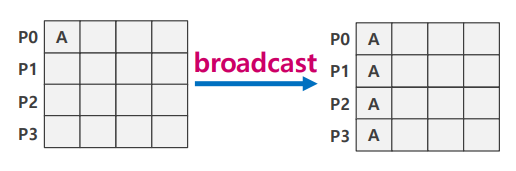
- P0의 data A를 전체 프로세스로 전달
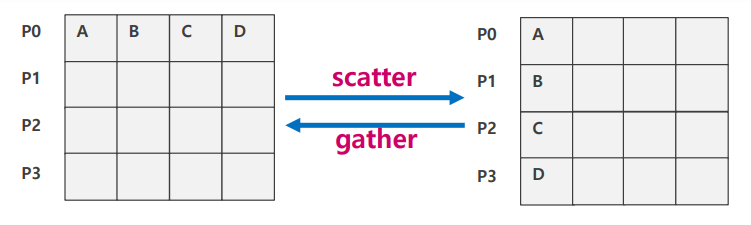
Scatter
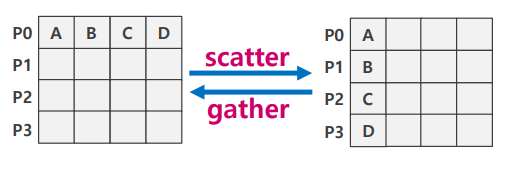
- P0의 A,B,C,D를 각 랭크로 분배
Gather
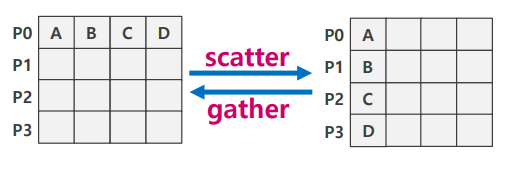
- 각 랭크에 흩어진 데이터를 한 랭크로 모아줌
- scatter, gather는 코드 작업에서 많이 사용 (ex. 계산)
Allgather
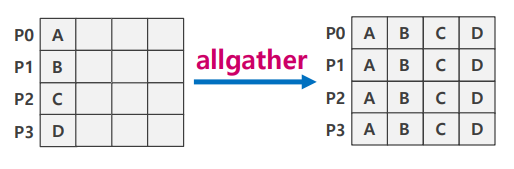
- 각 랭크에 흩어진 데이터를 모든 랭크에 다 모아줌
- gather + broadcast
Alltoall
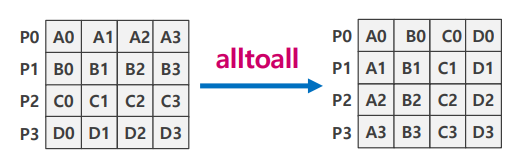
- 각 랭크의 data[i]를 rank[i]로 각각 모아줌
Reduce
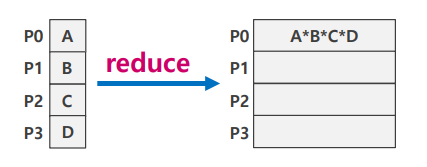
- 각 랭크에 흩어진 데이터를 한 랭크로 모으면서 연산을 함
Allreduce
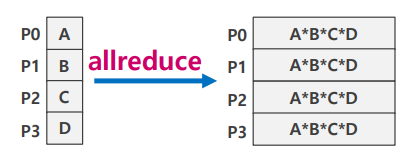
- reduce + broadcast
Broadcast, Gather
1. MPI_Bcast
broadcast
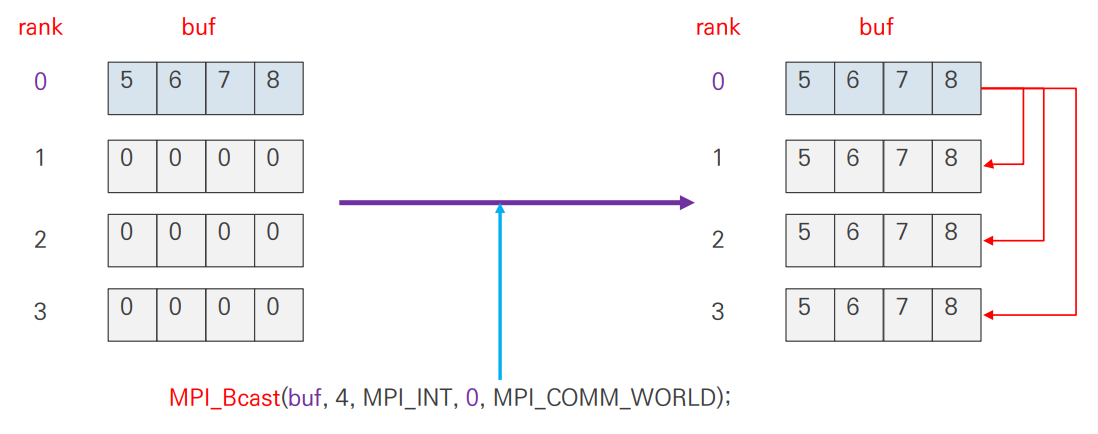
- 랭크 root는 자신을 포함한 모든 프로세스에 메세지를 전송
- MPI 3.0 이전까지는 blocking만 존재했으나, 이후에는 non-blocking도 지원
blocking broadcasting
int MPI_Bcast( void* buffer, int count,
MPI_Datatype datatype, int root, MPI_Comm comm )non-blocking broadcasting
int MPI_Ibcast( void* buffer, int count, MPI_Datatype datatype,
int root, MPI_Comm comm, MPI_Request *request )2. Example (MPI_Bcast)
C code
#include "stdio.h"
#include <mpi.h>
int main()
{
int i, nrank,nprocs, ROOT=0;
int buf[4]={0,}, buf2[4]={0,};
MPI_Request req;
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&nrank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&nprocs);
if(nrank==ROOT) buf[0]=5, buf[1]=6, buf[2]=7, buf[3]=8;
if(nrank==nprocs-1) buf2[0]=50, buf2[1]=60, buf2[2]=70, buf2[3]=80;
printf("rank=%d, Before(buf): %d %d %d %d\n",nrank, buf[0],buf[1],buf[2],buf[3]);
MPI_Ibcast(buf2,4,MPI_INT,nprocs-1,MPI_COMM_WORLD,&req);
MPI_Bcast(buf,4,MPI_INT, ROOT,MPI_COMM_WORLD);
printf("rank=%d, After(buf): %d %d %d %d\n",nrank,buf[0],buf[1],buf[2],buf[3]);
MPI_Wait(&req,MPI_STATUS_IGNORE);
printf("rank=%d, AFTER(BUF2): %d %d %d %d\n",nrank, buf2[0],buf2[1],buf2[2],buf2[3]);
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}Result
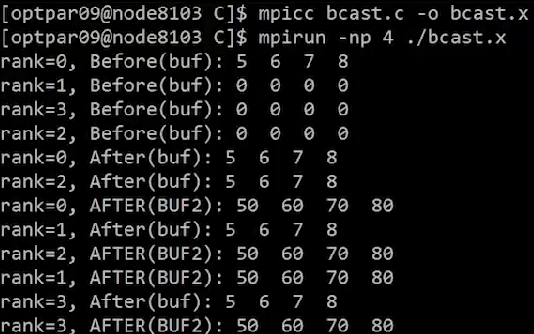
MPI_Ibcast()은 호출 후 즉시 return 되기 때문에MPI_Bcast()가 바로 시작됨MPI_Bcast()의 전송이 끝난 이후,MPI_Wait()에서MPI_Ibcast()의 broadcast가 끝날 때 까지 기다림- 출력 결과, buf, buf2의 broadcast 결과가 각각 잘 출력됨
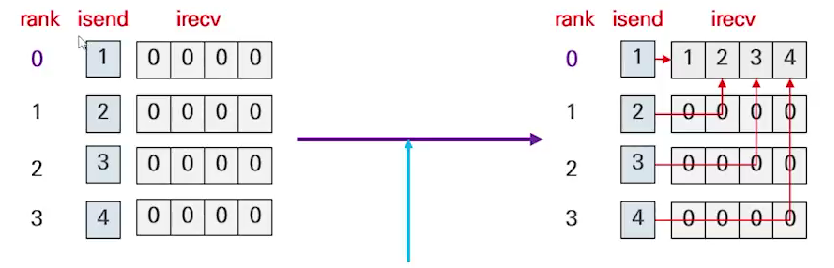
3. MPI_Gather
개요
- Root 프로세스도 포함하여 각 프로세스는 동일한 크기의 송신 버퍼의 내용을 root 프로세스로 전송
- Root 프로세스는 메세지를 받아서 각 랭크의 순서로 저장
gather
int MPI_Gather( const void* sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void* recvbuf, int recvcount, MPI_Datatype recvtype, int root, MPI_Comm comm )recvcount는 전체 data의 개수가 아니라 각 랭크에서root로 보내는 개별 data의 개수sendcount와recvcount는 보통 같은 수로 맞춤MPI_Igather()은 non-blocking gather 함수로, 마지막에 request argument만 추가
주의
- sendbuf, recvbuf는 같은 이름을 사용해선 안됨 (모든 collective communication에 해당)
MPI_Gather()는 동일한 size의 data만 취합 가능- 다른 data size 취합을 위해서는
MPI_Gatherv()사용
4. Example (MPI_Gather)
#include <stdio.h>
#include "mpi.h" int main()
{
int isend,irecv[4]={0,},nprocs,nrank;
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&nrank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&nprocs);
isend=nrank+1;
printf("rank: %d, isend:%d\n",nrank,isend);
MPI_Gather(&isend,1,MPI_INT,irecv,1,MPI_INT,0,MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(nrank==0) printf("rank:%d irecv=%d %d %d %d\n",nrank,irecv[0],irecv[1],irecv[2],irecv[3]);
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}Result
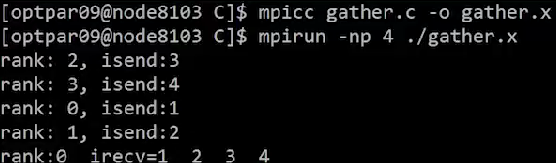
- 각 rank에서
isend=irank+1을 rank0(root)로MPI_Gather()을 이용하여 취합
Gatherv, Allgatherv
1. MPI_Gatherv
gatherv
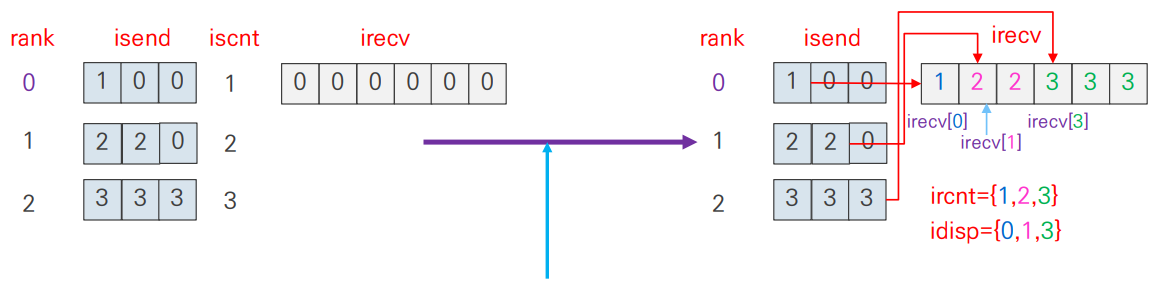
- 각 노드에서 다른 크기의 data를 gather할 때 사용
- 기능은 기본적으로
MPI_Gather()와 동일하나, 각 프로세스로부터의 데이터의 개수가 일정하지 않음
MPI_Gatherv()
int MPI_Gatherv( const void* sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void* recvbuf, const int recvcounts[], const int displs[], MPI_Datatype recvtype,
int root, MPI_Comm comm )- sendcount: sendbuf에서 보내는 data의 size
- recvcounts[]: recvbuf가 각 rank에서 받을 data의 size
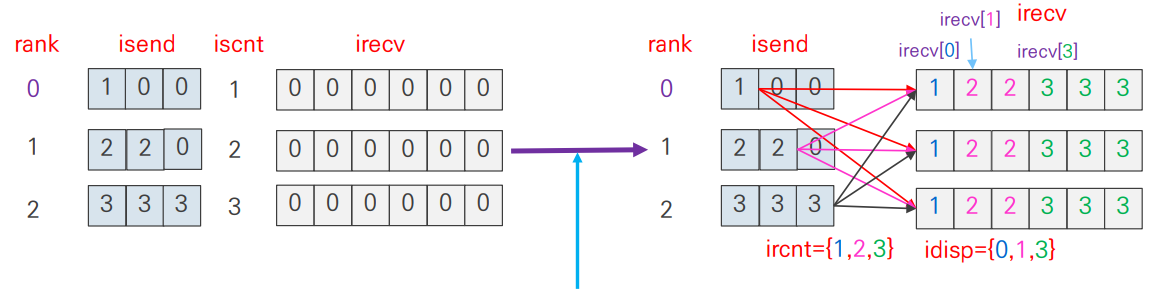
ex. rank0, rank1, rank2에서 1,2,3개의 data를 받을 경우 -> recvcounts=[1,2,3] - displs[]: 각 rank에서 gather한 data들이 위치할 배열의 index
ex. rank0, rank1, rank2에서 1,2,3개의 data를 받을 경우 -> displs=[0,1,3]
2. Example(MPI_Gatherv)
C code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "mpi.h"
int main()
{
int i,myrank;
int isend[3], *irecv;
// ircnt, idisp hard coding
int iscnt, ircnt[3]={1,2,3}, idisp[3]={0,1,3};
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD,&myrank);
// recvbuf에 memory 할당
if(myrank==0) irecv=(int*)malloc(6*sizeof(int));
// 한번에 모든 renk의 값을 초기화
for(i=0;i<myrank+1;i++) isend[i]=myrank+1;
// rank+1 개의 data를 각각 전송
iscnt=myrank+1;
MPI_Gatherv(isend, iscnt,MPI_INT, irecv, ircnt,idisp,MPI_INT,0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myrank==0){
printf("irecv="); for(i=0;i<6;i++) printf(" %d", irecv[i]);
printf("\n");
}
if(myrank==0) free(irecv);
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}Result
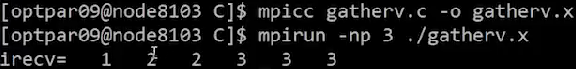
3. allgather/ allgatherv
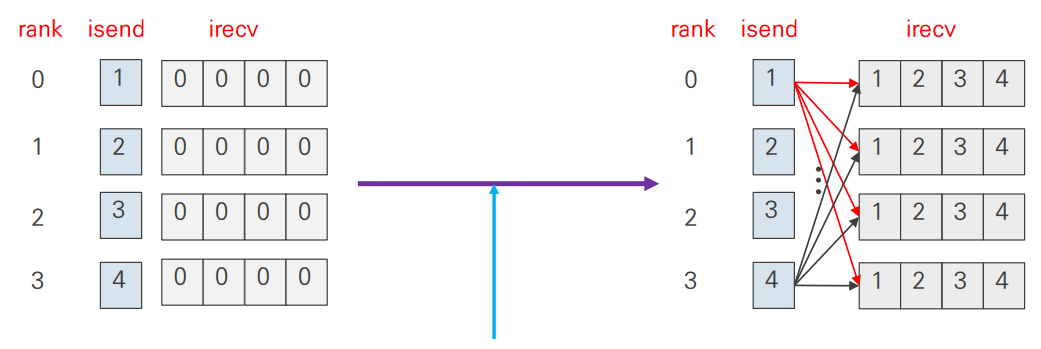
allgather
int MPI_Allgather( const void* sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void* recvbuf, int recvcount, MPI_Datatype recvtype, MPI_Comm comm )- 전체 프로세스가 결과를 수신 받는 것을 제외하면
MPI_Gather()와 동일 MPI_Gather()의 argument 중 root만 빠진 형태MPI_Gather()+MPI_Bcast()
allgatherv
int MPI_Allgatherv(const void* sendbuf, int sendcount, MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void* recvbuf, const int recvcounts[], const int displs[], MPI_Datatype recvtype, MPI_Comm comm )- 전체 프로세스가 결과를 수신 받는 것을 제외하면
MPI_Gatherv()와 동일 MPI_Allgather()의 argument 중 root만 빠진 형태MPI_Gatherv()+MPI_Bcast()