B+ Tree Index
B+tree는 아래 조건을 만족하는 rooted tree
각 node가 가질 수 있는 child의 최대 수 n : (차수/order)
- 모든 root to leaf path는 길이가 같아야 함(balanced tree)
- root나 leaf가 아닌 각 node는 최소 ⌈n/2⌉개, 최대 n개의 자식을 가짐
- leaf node는 최소 ⌈(n-1)/2⌉개, 최대 n-1개의 value를 가짐
- Special case
-- root가 leaf가 아니면 최소 2개의 자식을 가짐
-- root가 leaf면 최소 0 최대 n-1개의 value를 가짐
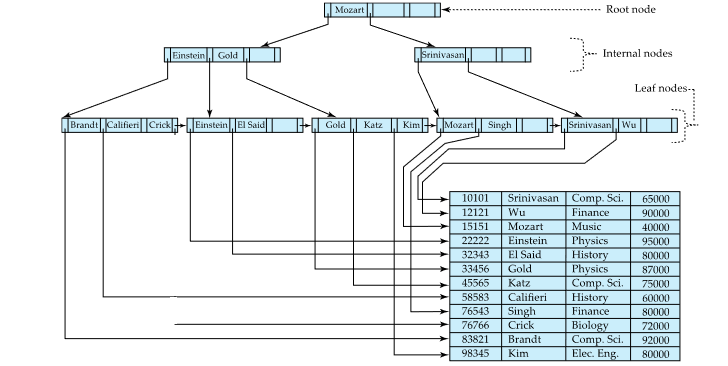
B+tree의 예시
B+ Tree Node Structure
Typical node
P1/K1/P2/.../Pn-1/Kn-1/Pn
Ki 는 search-key value
Pi는 자식 노드 pointer(internal node일 때) 혹은 record pointer(leaf node일 때)
search key는 정렬되어있음
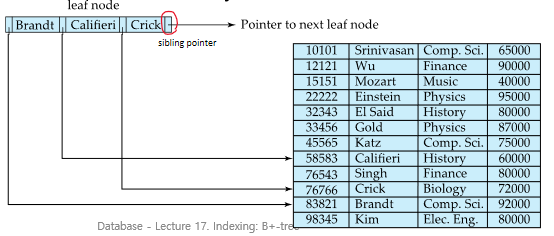
Leaf Nodes in B+ Trees
Pointer Pi 는 search key가 Ki인 record를 가리킴
leaf node Li, Lj (i<j) 가 있으면 Li의 모든 search key는 Lj의 것보다 작거나 같음
마지막 pointer Pn은 다음 leaf node를 가리킴
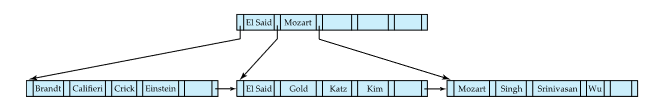
Non-Leaf Nodes in B+ Tree
non leaf node = internal node
non leaf node의 형태는 leaf node에 대한 multi-level sparse index
pointer P1은 K1보다 작은 key들의 subtree로 향하는 pointer
, Pi는 Ki-1보다 크거나 같고 Ki보다 작은 key들의 subtree로 향하는 pointer
Pn은 Kn-1보다 큰 key들의 subtree로 향하는 pointer
Example of B+tree
order = 6인 B+tree
leaf node는 3개 이상 5개 이하의 value를 가짐
internal node는 3개 이상 6개 이하의 child node를 가짐
root는 최소 2개의 child를 가짐 (child가 1개면 tree일 필요가 없음)
Observation about B+tree
node들은 포인터로 연결되었기 때문에 논리적으로 가까운 block일지라도 실제 메모리상에서는 가깝지 않을 수 있음
internal node는 multilevel sparse index의 형태
B+tree의 최대 height = (K = num of search key)
그러므로 search cost도 = tree height =
Queries on B+tree
find에 대한 pseudo code
find(V)
C = root
while(C is not leaf node){
V <= Ki를 만족하는 최소 i를 찾음
if (i == null) C = C.Pn //V보다 큰 key가 없는 경우
else if(V = C.Ki) C = C.Pi+1 // 일치하는 key를 찾은 경우
else C = C.Pi
if C에 V와 같은 key가 있다면 return 해당 key의 value
else return nullRange query는 주어진 range에 해당하는 모든 search key 의 value를 찾음
range의 최소값으로 find하고 거기부터는 순차적으로 최대값까지 탐색
보통 node는 disk block과 같은 크기 (보통 4kb)
보통 order는 약 100 (entry당 40byte)
1,000,000개의 search key, n=100에서 search를 한다고 하면
최대
같은 개수의 key를 가진 binary tree의 경우 20이 필요
Non-Unique Key
만약 search key가 unique하지 않다면, unique한 composite key의 index를 만들어서 운영
Insertion in B+Tree
넣을 search-key가 들어가야 할 leaf node를 찾음
해당 leaf node에 공간이 있으면 단순 삽입
없으면 해당 node를 split
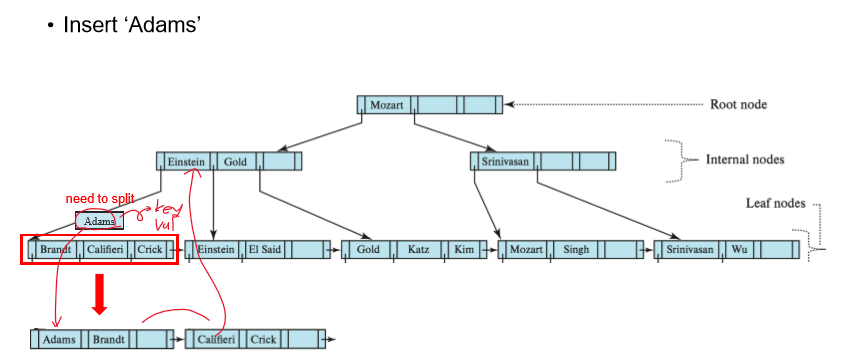
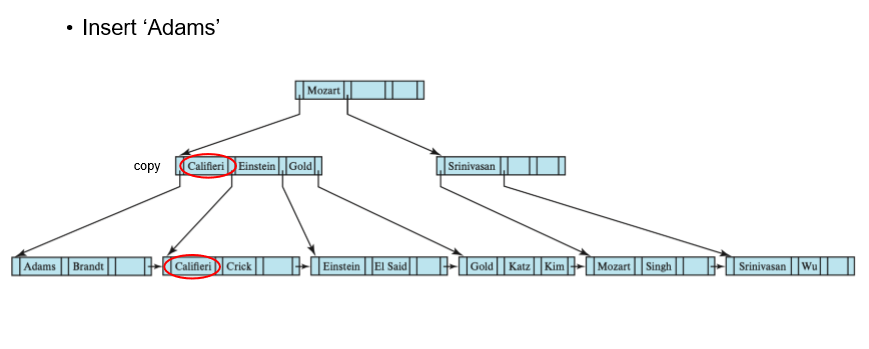
Splitting a leaf node
새로 들어온 key를 포함해 정렬
처음부터 ⌈n/2⌉번째까지를 원래 node에 나머지를 새 node에 넣음
parent node에 새로 생성된 node의 최소 key를 복사하여 삽입, 해당 node를 가리키는 pointer를 삽입
parent node도 가득 찼으면 split하여 계속 반복
split은 부모 노드에 빈 공간이 있을 때까지 반복됨 -> 최악의 경우 root가 split되고 tree height가 1 증가됨
Splitting a internal node
거의 leaf split과 같지만 ⌈n/2⌉번째 key를 parent node로 이동시킨다는 것이 차이 (split이 된 두 node에는 해당 key가 없음)
Insert 예시
Deletion in B+Tree
leaf node에서 해당 key, val을 삭제
만약 삭제가 일어난 node의 entry수가 적어서 sibling node와 합쳐도 n-1을 넘지 않는다면 합침
- 두 node의 모든 key, val을 하나의 node에 넣음 (논리상 좌측의 node에) 그리고 나머지 node를 삭제
- parent node에서 삭제된 node에 대한 entry를 삭제
만약 node entry가 삭제하기에 너무 수가 적지만, sibling과 합치기에는 많다면, redistribute함
- sibling과 해당 node 둘 다 최소 entry 수를 만족하도록 재분배
- 해당되는 key를 parent node에 update
삭제는 부모가 n/2 이상의 entry를 가질 때까지 계속 발생됨
삭제로 root가 하나의 entry만 가지게 되면, root를 삭제하고 그 child가 root가 됨
Complexity of Updates
single entry에 대한 insertion과 deletion의 cost(I/O 수)는 Tree height와 같음
실제로는 더 적음 (internal node는 buffer에 남으려는 경향이 있음/split과 merge는 잘 일어나지 않음)
B+Tree File Organization
leaf node의 entry는 pointer가 아닌 record를 저장
insert/delete/update가 일어나도 data record가 cluster를 유지하도록 함

pointer보다 공간을 더 차지하는 record를 가지기 때문에 공간 최적화가 중요
공간 최적화를 향상하기 위해 split/merge시 더 많은 sibling node를 포함하여 수행
- 좌, 우 sibling과 redistribution 수행
- 각 node는 최소 ⌊2n/3⌋개의 entry를 가짐
Other Issues in Indexing
Record relocation and secondary indices
record가 이동하면 모든 secondary indices는 update 되어야 함(record pointer를 가지기 때문)
B+tree file organization의 split은 매우 cost가 커짐
solution: secondary index에서 record pointer 대신 B+tree의 search key를 저장
Indexing Strings
Variable length string 을 key로 사용
- key의 분기율이 일정하지 않음
- pointer의 수가 아닌 실제 공간 활용도를 기준으로 split함
Prefix compression
- internal node의 key값은 전체 키의 일부만으로도 충분할 수 있음 (예: Silas와 Silberschatz는 Silb만으로도 구분 가능)
- 공간절약, 검색속도 향상
Bulk Loading and Bottom-up Build
entry를 하나씩 insert하면 entry당 IO가 1번 이상씩 필요
많은 entry를 insert하는데 매우 비효율적(bulk loading)
대안 1:
- insert할 entry를 미리 정렬시킴
- 그리고 순서대로 insert함
대안 2: Bottom-up B+tree construction
- entry를 정렬하기 전에 leaf부터 반대로 tree를 구성