Static Hashing
bucket은 entry를 포함하는 storage space
Hash function은 bucket을 결정하는 함수
search-key에 대한 bucket의 address를 결정
다른 search key도 같은 bucket에 mapping될 수 있음
전체 bucket은 sequential하게 search되어야 함
Hash index에서 bucket은 record에 대한 pointer를 entry로 저장
Hash file organization에서 bucket은 record 자체를 저장
bucket 개수는 고정
bucket은 순서대로 할당됨, 절대 할당이 풀리지 않음

Handling of Bucket Overflows
Bucket overflow는 다음과 같은 이유로 발생할 수 있음
- 불충분한 bucket
- record가 특정 bucket에 몰려있음(skew)
Skew는 다음과 같은 이유로 발생할 수 있음
- 다수의 record가 같은 key를 가짐 (해결 불가능)
- hash function이 key를 uniform하게 분배하지 않음(hash function 교체로 해결)
bucket overflow가 발생할 확률을 줄일 수는 있지만, 완전히 제거하지는 못함
overflow는 보통 overflow bucket을 통해 관리됨
Overflow chaining
- overflow bucket은 linked list로 연결되어 있음
- 이 방법은 closed addressing/hashing이라고도 불림
- overflow bucket을 사용하지 않는 open hashing도 있지만, DB에는 적합하지 않음
-- Linear probing: bucket overflow 발생 시 다음 bucket에 저장함
Hash file organization 예시
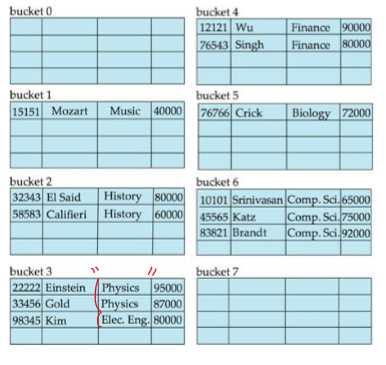
dept_name을 key로 사용
dept_name의 binary representation의 합 modulo 10을 hash function으로 사용
uniform distribution이 되지 않았음
Deficiencies of Static Hashing
static hasing에서, hash function은 key를 고정된 개수의 bucket address에 매핑함
database는 시간에 따라 커지거나 작아짐
- bucket 개수가 너무 적으면, overflow가 너무 많이 발생해 성능이 떨어짐
- bucket 개수가 너무 많으면, 비어있는 bucket이 많아지고, disk 공간이 낭비됨
해결책: Rehashing
- 주기적으로 새 hash function으로 file을 재구성함
- cost가 높다, disrupts normal operation
더 나은 해결책: bucket의 수를 유동적으로 설정 -> dynamic hashing
Dynamic Hashing
Linear Hashing
Extendible Hashing
- disk 기반 hashing에 적합, 다수의 hash value가 bucket을 공유
- 전체 bucket의 수를 2배로 증가시키지 않고(overflow 발생 bucket만 split됨), hash table의 entry를 두 배로 증가시킴
Basic idea behind Dynamic Hashing
- Bucket의 수를 두 배 증가시킴(directories)
- indirection의 level을 추가
- directory를 doubling하여 bucket을 doubling
- overflow 발생한 bucket만 split
Extendible Hashing
postfix or prefix hash key 사용
postfix의 길이가 i bit, 라고 하자
- directory(bucket address table) size =
- initially
- i의 크기는 database가 커지고 작아짐에 따라 커지고 작아짐
다수의 directory entry가 같은 bucket을 point할 수 있음
그러므로 실제 bucket의 수는 보다 적음
General extendible hash structure
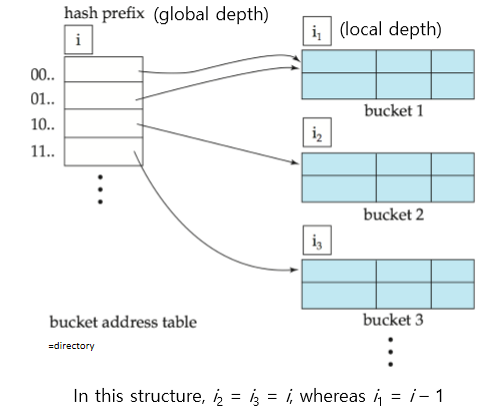
Extendible Hashing의 동작
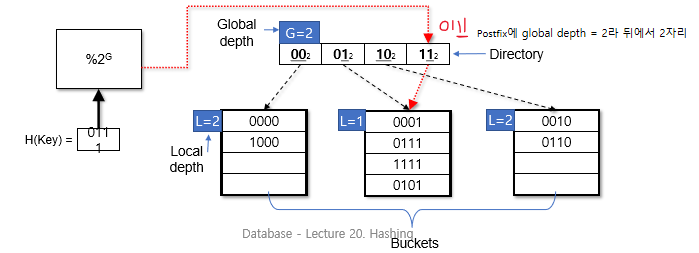
Directory size가 4이면, 각 entry는 2bit가 필요
key K에 대한 bucket을 찾으려면, global depth 사용
global depth = least significant bits of h(K)
if h(K) = 5 = 0101, global depth = 2이면, bucket은 01로 point됨
if h(K) = 7 = 0111, bucket은 11로 point됨
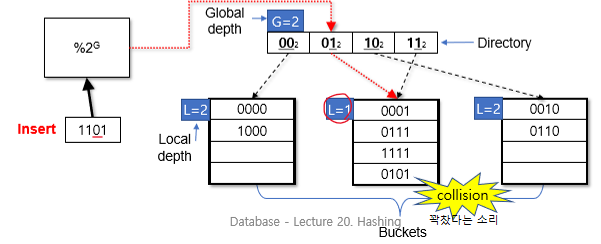
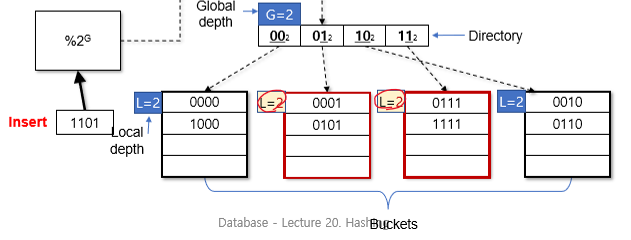
Bucket Split
Global depth가 local depth보다 큰 경우 (G > L)
새 bucket을 할당하고 L = L + 1
directory에 새 bucket update
overflow된 bucket에서 새 bucket으로 record들 옮김
여전히 bucket이 가득 차 있으면 더 split함
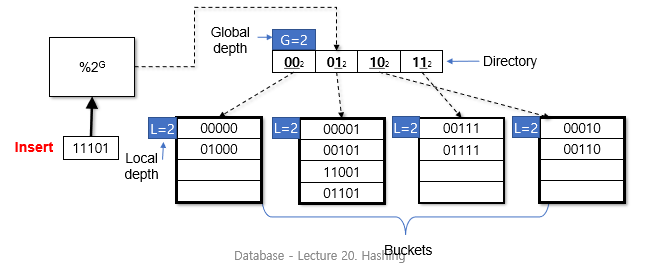
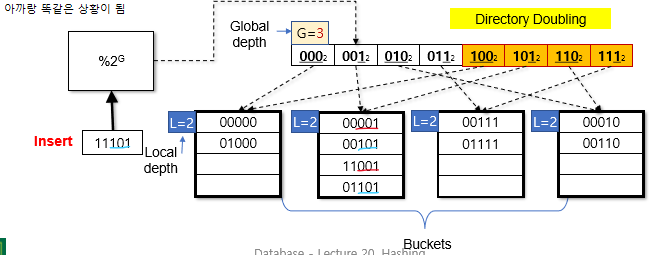
Bucket split -> Directory Doubling
G == L인경우
G를 증가시켜 directory의 크기를 2배로 키움
각 entry를 같은 bucket을 가르키는 두 entry로 만듦
이제 G > L이 됐으므로 이전 상황과 똑같아짐
Extendible hashing의 장점
- file이 커짐에 따라 hash perfomance가 떨어지지 않음
- space overhead가 최소화됨
Extendible hashing의 단점
- extra level of indirection to find desired record
- Bucket address table이 매우 커질 수 있음
-- 매우 큰 연속된 공간을 할당할 수 없음
-- bucket address table을 B+tree 구조로 함으로 해결 가능 - bucket address table의 크기를 변경하는것은 비용이 큰 operation
Linear hashing은 대체 mechanism
- directory의 점진적인 증가를 허용
- At the cost of more bucket overflows
Linear Hashing
directory를 사용하지 않고 long overflow chain을 해결하기 위한 dynamic hashing 기법
- 일시적으로 overflow page가 사용됨
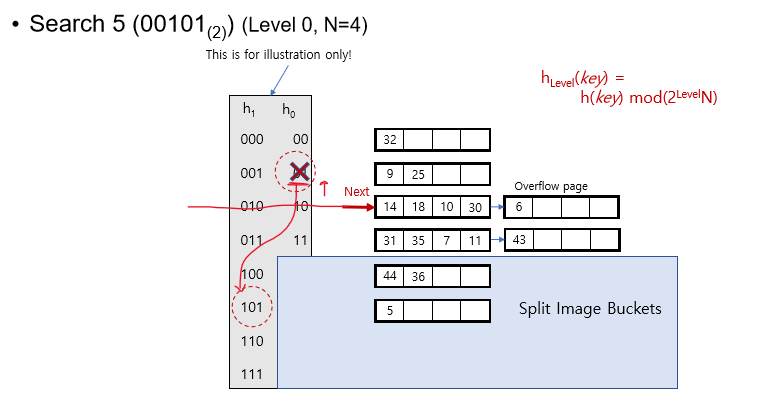
- split 될 bucket은 round-robin 방식으로 선택됨
bucket이 overflow되면 next pointer의 bucket을 split함 그리고 next pointer는 다음 bucket으로 이동 (next pointer는 insert하는 bucket과 상관없이 bucket을 순서대로 쭉 순회)
Algorithm proceeds in rounds (next pointer가 몇바퀴 돌았냐)
current round number is level
처음 상태의 bucket 수 = N
bucket의 수는
0부터 Next-1까지의 bucket들은 split된 상태
모든 bucket이 분할되면 next pointer는 분할된 새 bucket으로 넘어가지 않고 0으로 돌아와서 다시 순회 시작
Insert
들어갈 bucket을 찾음, 자리 있으면 그냥 넣음
없으면
- 해당 bucket의 overflow page를 붙이고 거기다가 넣음
- next pointer가 가리키는 bucket을 split하고 next pointer를 한 칸 뒤로 이동시킴
-- 이 과정은 overflow 일어난 bucket이 어디건 상관 없이 무조건 next pointer가 가리키고 있던 bucket을 split함
-- split하고 난 뒤 level이 +1된 hash에 맞춰 re-distribute
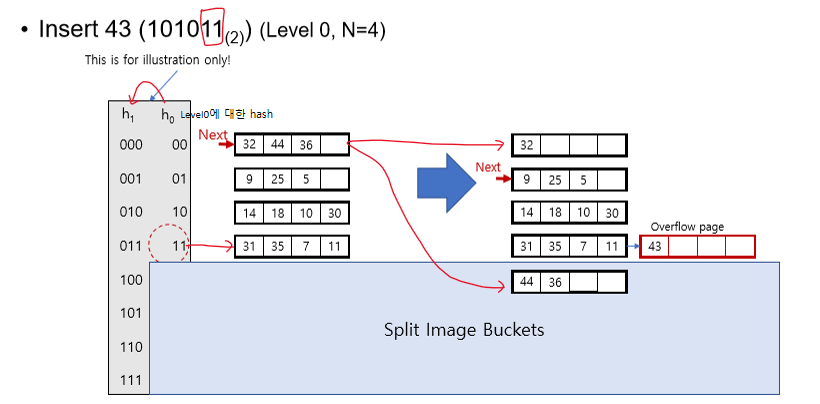
Search
entry r의 bucket을 찾기 위해서는
bucket이 아직 이번 round에 split되지 않음
=> 인 경우 단순히 bucket에 가서 찾으면 됨
bucket이 이미 split 됨
=> 이나 두 곳을 찾아야 함
아니면 을 찾으면 됨
Comparison of Ordered indexing and Hashing
Cost of periodic re-organization: ordered > hashing
빈번한 삽입/삭제가 일어나는 경우 re-organization cost를 고려해야 함
Hashing은 average access time이 작지만 worst case access time이 큼
Ordering index는 차이가 적음
query에 따른 적합성
- hashing은 point query에 적합
- ordered index는 range query에 적합
Multi-key access and Bitmap Index
query에 여러 index를 사용하는 경우
예시)
select ID
from instructor
where dept_name = "Finance" and salary = 80000Bitmap index는 여러 key를 참조하는 query에 효율적임
Bitmap은 단순 bit의 나열
Bitmap index는 attribute의 각 value에 대한 bitmap을 가짐
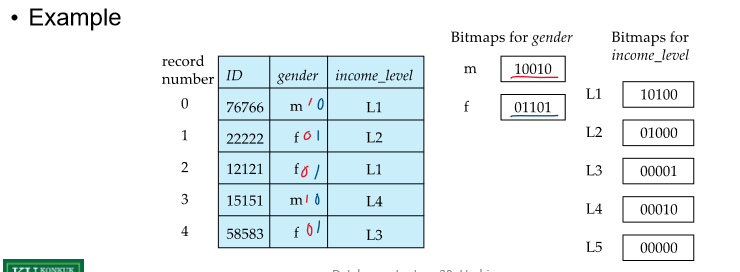
AND, OR 연산으로 query 처리
예시) income level이 L1인 male => 10100 AND 10010 = 10000 즉 0번 record만 해당됨