HawkI: Homography & Mutual Information Guidance for 3D-free Single Image to Aerial View [2024 arXiv]
TMLR 저널에 Reject 되긴 했지만 ‘3D-FREE MEETS 3D PRIORS: NOVEL VIEW SYNTHESIS FROM A SINGLE IMAGE WITH PRETRAINED DIFFUSION GUIDANCE’ 논문의 기반이 되기 때문에 다뤄보도록 하겠습니다.

해당 모델은 입력 이미지와 text prompt가 들어가면, 해당 이미지를 항공 뷰의 시점으로 바꿔주는 모델입니다. 3D 데이터나, 3D 모델을 활용하지 않고 결과를 냈다는 점에서 주목해볼만 합니다.
Method
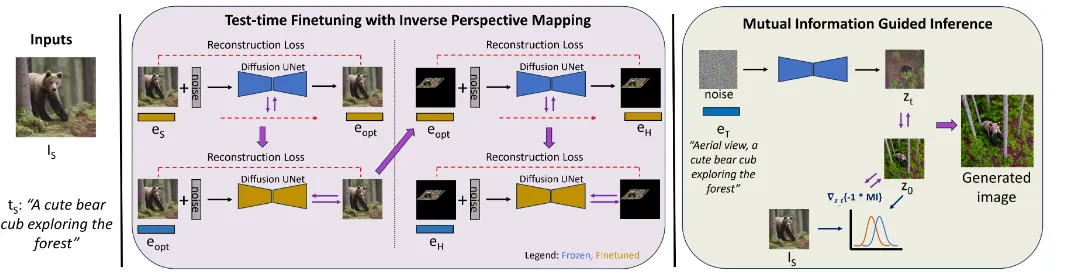
Test-time optimization
DreamBooth나 Imagic 같은 방식은 fine-tuning을 통해서 앉아있는 개를 서있게 하거나, 개를 애펠타워 앞에 있게 할 수 있습니다. 이러한 방식을 항공뷰(aerial view)에 적용할 경우 많은 변화를 줄 수 없습니다. 왜냐하면 이미지에 맞게 fine-tuning을 진행하면 overfitting이 심해진다고 합니다. 따라서 논문에서는 4개의 step을 통해서 충분한 변형을 가할 수 있도록 모델을 설계 했습니다.
Optimization using
첫번째 단계에서는 CLIP을 통해서 얻은 text embedding값 를 이미지를 잘 생성하는 라는 임베딩 값으로 변환하는 과정입니다. 이때 Diffusion model은 frozen 됩니다.
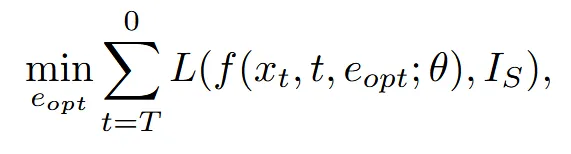
수식은 위와 같습니다. L은 DDPM의 loss function이므로 쉽게 말해서 원본 이미지 를 잘 설명하는 임베딩 를 생성하는 과정입니다.
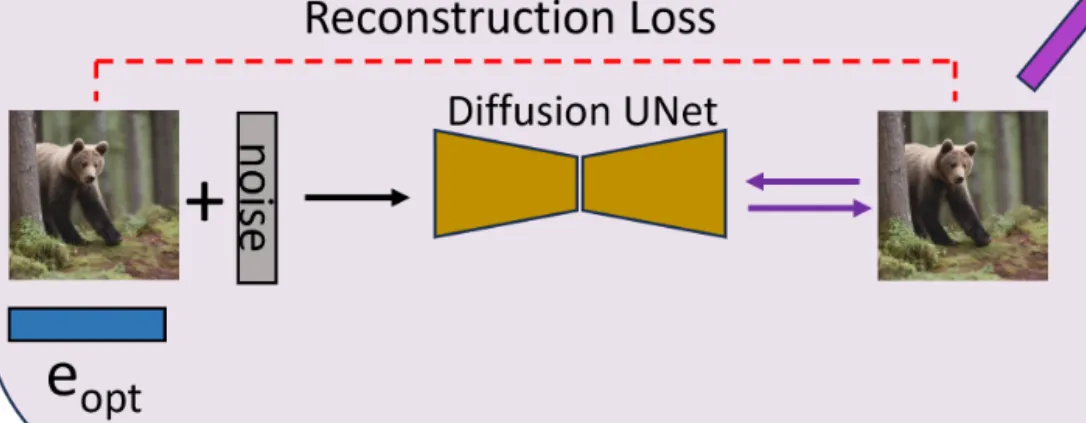
두번째 단계는 방금 생성한 를 이용해서 원본 이미지를 reconstruction을 잘하게 하는 과정입니다. 이때 사용하는 Diffusion UNet에 LoRA layer를 추가해서 파라미터만 학습하도록 합니다.
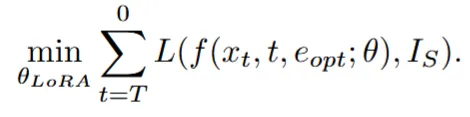
수식을 보면 이전 수식과 비슷한데 이전에는 업데이트 하는 값이 단순히 값 였다면 이번에는 Diffusion Unet에 추가한 LoRA layer의 가중치입니다.
Optimization using inverse perspective mapping.

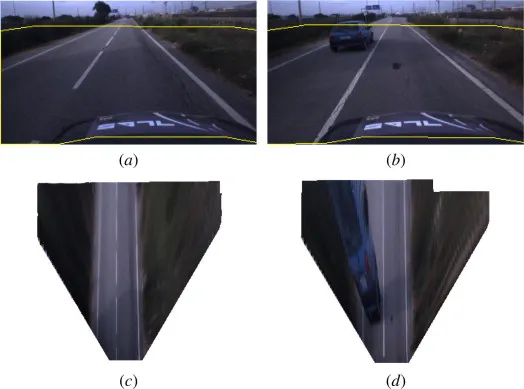
Inverse perspective mapping (IPM) 방식은 자율주행에서 많이 사용되는데 위와 같이 입력 이미지를 넣고 IPM 방식을 적용하면 위에서 보이는 것처럼 사진이 변합니다.
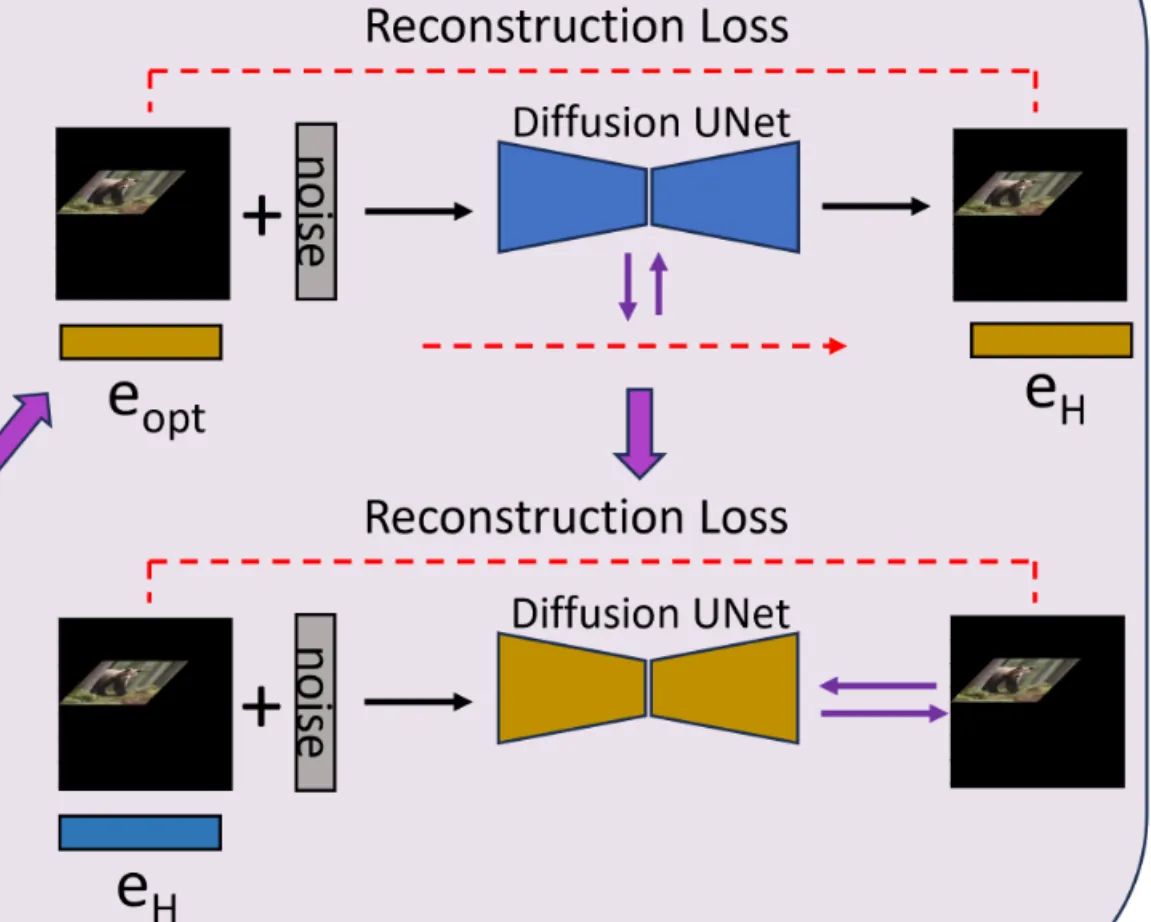
IPM을 적용한 이미지에 대해서 이전과 같이 적절한 임베딩 를 생성하고, 이를 이용해서 reconstrucion 과정을 진행하면서 LoRA를 업데이트 합니다.
이때 최적화 과정은 이전 와 이전에 학습한 LoRA를 기반으로 진행됩니다. 가 아닌 를 기반으로 진행했기 때문에 저자는 embedding space를 유지하면서 이미지의 결과가 왜곡돼지 않는다고 했습니다.
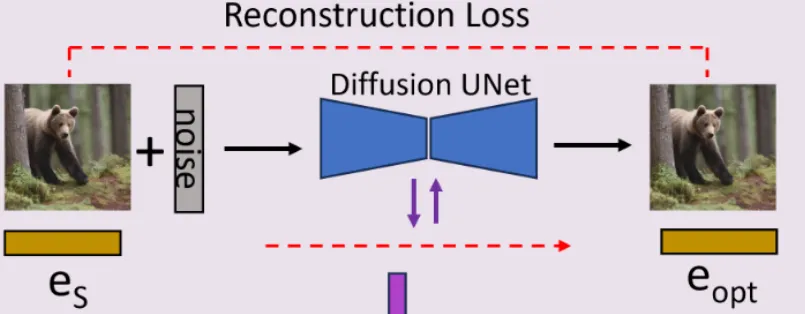
Mutual Information Guided Inference
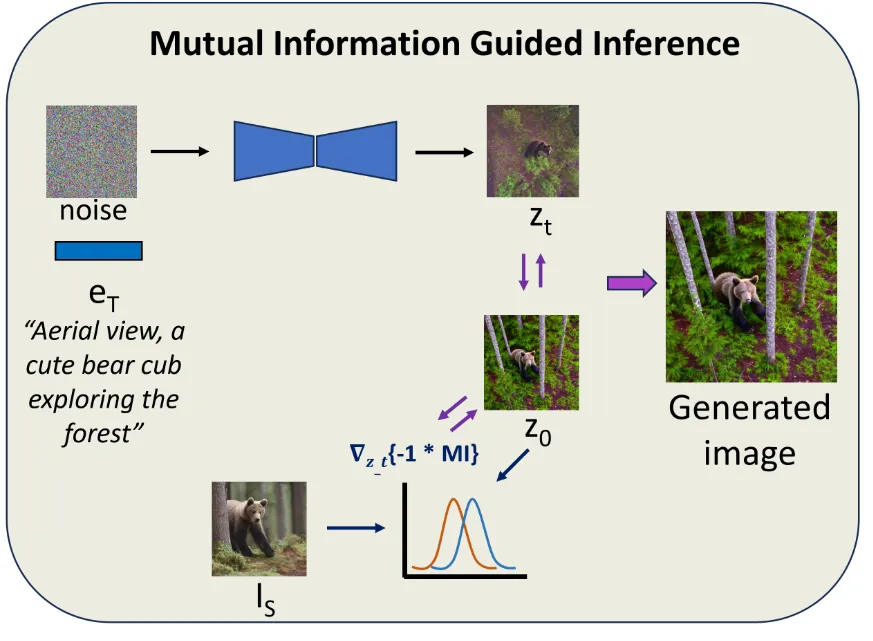
이렇게 우리는 항공뷰를 생성하는데 최적화된 임베딩과 Diffusion Unet 모델을 얻었습니다. 이를 기반으로 이미지를 생성할 경우 항공뷰의 이미지가 나오긴 하지만 원본 이미지와는 다른 결과가 나올 수 있습니다. 따라서 원본 이미지와 유사하게 학습하도록 Mutual information을 사용했습니다.
L1 loss나 코사인 유사도를 사용해서도 두 사진을 유사하게 학습시킬 수 있지만, 이는 픽셀값이 비슷해지도록 학습할 뿐 두 이미지의 특성 자체를 비슷해지게 학습할 수 없습니다.
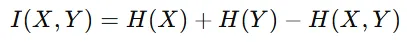
따라서 Mutual intromation을 통해서 항공뷰 이미지가 원본 이미지의 특성과 유사하게 변하면서 항공뷰라는 특징은 변하지 않게 합니다. Mutual information은 위의 수식과 같은데 두 이미지의 엔트로피에서 공통된 엔트로피를 뺀 결과입니다.
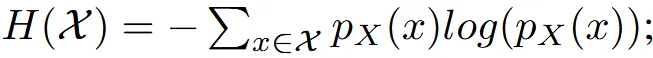
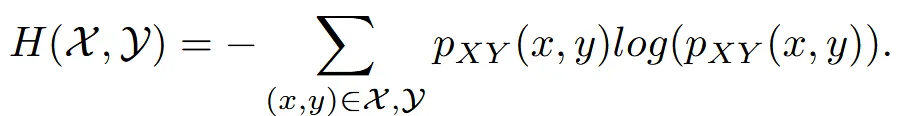
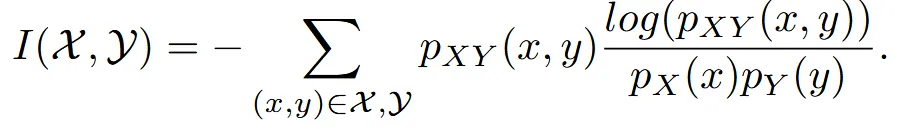
수식은 위와 같은데 그냥 쉽게 말해서 2개의 데이터의 분포를 비슷하게 학습시키는 과정입니다.
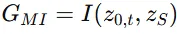
Mutual infomation 값이 커질수록 두 이미지의 분포가 비슷해지기때문에 위의 guidance function을 이용해서 값을 최대화 합니다. 그리고 의 gradient를 이용해서 매 timestep마다 latent를 수정합니다.
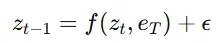
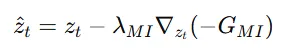
결론적으로 샘플링 과정이 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 Mutual information을 사용한 수식으로 변경됩니다.
Experiments
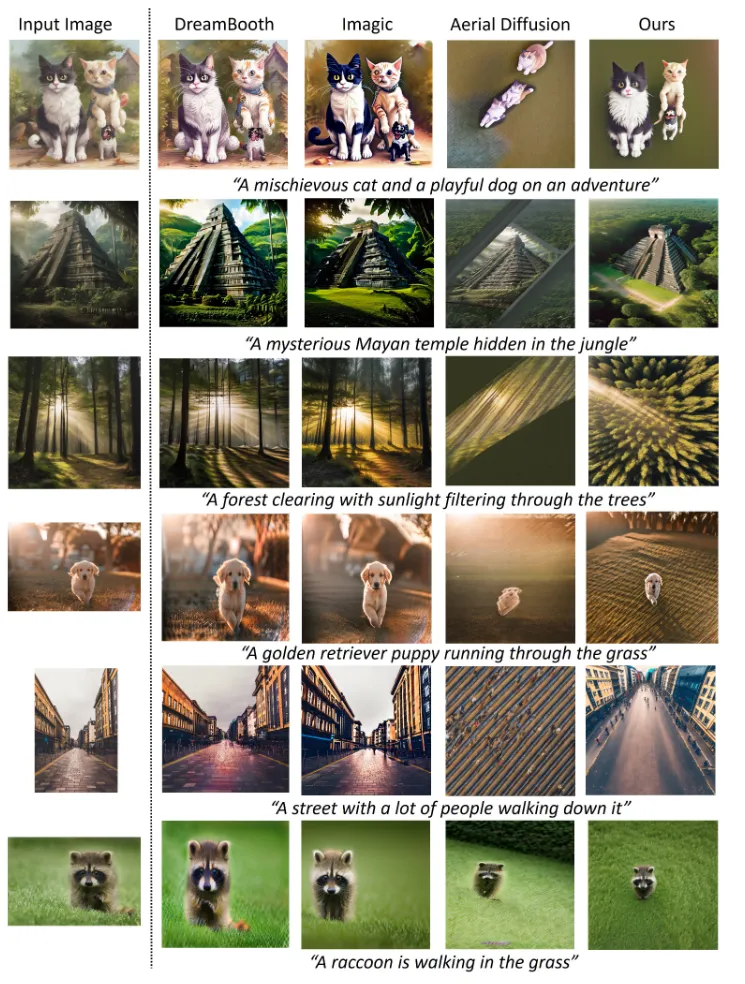
입력 이미지를 넣었을 때 항공뷰의 결과입니다. 확실히 Ours의 결과가 더 좋게 나타난 것을 알 수 있습니다.
Comparisons against 3D based novel view synthesis (NVS) methods

개인적으로 Zero-1-to-3에 관련된 논문을 많이 읽었어서 해당 논문과의 비교를 진행해보는 부분이 흥미로웠습니다. 사진으로도 해당 논문의 결과가 더 좋았고 CLIP Score나 DINO Score를 비교해봐도 수치적으로도 더 좋게 나왔었습니다.
Ablation Study

Mutual intromation과 Inverse perspective mapping (IPM) 적용 유무에 따른 결과입니다. 아무것도 안하면 항공뷰의 이미지를 생성하는게 아니라 거의 원본을 복원하는 step1,2만 진행했기 때문에 원본 이미지와 유사합니다. MI를 진행하지 않은 경우 원본의 형태와 다르게 나오고, Inverse perspective mapping (IPM)를 진행하지 않았을 경우 항공뷰의 느낌이 부족합니다.
Limitation
- 항공뷰만 가능하고 특정 시점의 이미지를 생성할 수 없다.
- Mutual intromation를 적용했지만 원본이미지와 다른 hallucination 현상 존재
리뷰어 코멘트 정리
Comment:
The reviewers expressed many concerns in their initial reviewer, encompassing the following aspects:
- Experiments (qualitative results, comparisons to other methods)
- Presentation (clarity, quality)
- Motivation of the work
- Some methodological choices
Weaknesses
- Motivation for this work is unconvincing. The manuscript repeatedly highlights that a key advantage of the proposed method is its ability to function without any multi-view or 3D information. However, the rationale for excluding multi-view or 3D information is insufficiently discussed. For example, what is the essential bottleneck of the aerial-view synthesis task? If the issue lies in the lack of multi-view or 3D datasets, this claim does not hold, as numerous large-scale multi-view/3D datasets have emerged, such as Objaverse(-XL) [1, 2], MVImageNet (V1 and V2) [3, 4], DL3DV [5], etc., and numerous video datasets that could serve as potential data sources. Furthermore, as discussed in Sec. 4.8, many multi-view or 3D pretrained models incorporating 3D priors could be beneficial for this task. This lack of justification could represent a fundamental flaw of the proposed approach.
- Proposed techniques do not seem to make sense. The manuscript asserts that utilizing mutual information guidance during sampling preserves semantic consistency between generated and reference images. However, the used mutual information appears to be computed at the RGB pixel statistical level rather than the image or semantic distribution level. This is evident as the authors construct 2D histograms to calculate marginal and joint PDFs, whereas the scores provided by diffusion models should ideally be employed for mutual information computation, like Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD) [6, 7]. Consequently, the so-called "mutual information guidance" seems to primarily focus on aligning color distributions between generated and reference images. Furthermore, the use of inverse perspective-mapped images as pseudo-supervision also seems to be strange, as these images significantly deviate from the expected aerial views and are heavily distorted compared to natural image distributions.
- Generation quality of the proposed method is poor and some comparisons are unfair. As previously mentioned, due to some design flaws, the generated images are over-saturated and deviate significantly from the reference images, although the authors compared their method to some baseline techniques, which are considered to be out of date. Meanwhile, methods proposed for object novel view synthesis (Zero123 and Zero123++) are compared with the proposed method, while scene novel view synthesis methods, such as GeNVS [8] and ZeroNVS [9], are not discussed.
- Presentation of this work requires improvement. For instance, the citation format is incorrectly applied as
\citeinstead of\citep. Additionally, the term "CLIP text-image embedding" is unclear and likely intended to mean "CLIP text embedding", as "CLIP text-image embedding" typically refers to a pair of embeddings that include both text and image components. Some expressions also lack clarity, such as "bias-variance trade-off", which is commonly used in the context of deterministic models. However, in the context of generative models, "bias" and "variance" are not well-defined, though I could understand these terms might correspond to "fidelity" and "diversity" respectively.
