📒 Perceptron
📝 인공 신경망
- 인공 신경망은 Neuron의 동작 방식을 본따서 만든 모델이다.
- 입력 신호가 들어왔을 때, 신호들의 총 합이 threshold를 넘으면 다음으로 전파되는 방식이다.
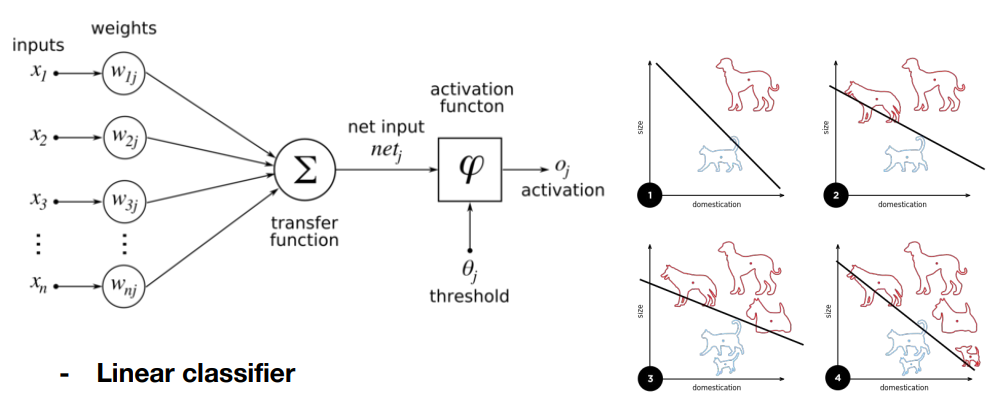
✏️ Perceptron
- 입력 x가 들어왔을 때 가중치를 각 곱하고, 합과 bias를 더해 output을 만든다.
- output은 activation function (sigmoid 등) 를 거쳐서 나오게 된다.
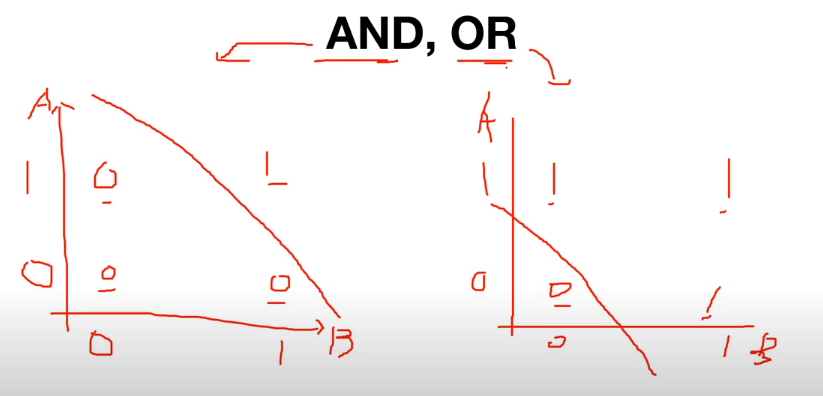
📝 AND, OR
- Perceptron으로 Linear하게 AND, OR 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
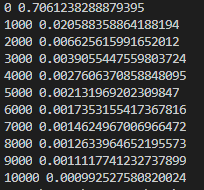
📝 XOR
X = torch.FloatTensor([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]])
Y = torch.FloatTensor([[0], [1], [1], [0]])
linear = torch.nn.Linear(2, 1, bias=True)
sigmoid = torch.nn.Sigmoid()
model = torch.nn.Sequential(linear, sigmoid)
criterion = torch.nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1)
for step in range(10001):
optimizer.zero_grad()
hypothesis = model(X)
cost = criterion(hypothesis, Y)
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
if step % 1000 == 0:
print(step, cost.item())
- cost function이 줄지 않는다.
📒 Multi Layer Perceptron
📝 XOR
- XOR은 하나의 구조를 갖는 Perceptron으로는 해결할 수가 없다.
- 여러개의 층을 갖는 Multi Layer Perceptron을 사용해야 된다.
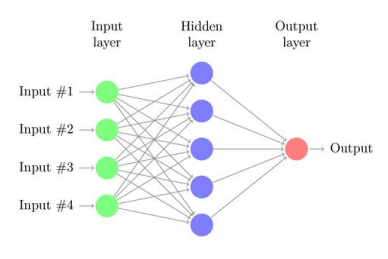
📝 Backpropagation
import torch
X = torch.FloatTensor([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]])
Y = torch.FloatTensor([[0], [1], [1], [0]])
linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(2, 2, bias=True)
linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(2, 1, bias=True)
sigmoid = torch.nn.Sigmoid()
model = torch.nn.Sequential(linear1, sigmoid, linear2, sigmoid)
criterion = torch.nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1)
for step in range(10001):
optimizer.zero_grad()
hypothesis = model(X)
cost = criterion(hypothesis, Y)
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
if step % 1000 == 0:
print(step, cost.item())
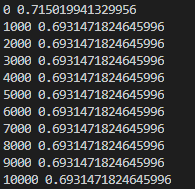
- Loss가 점점 줄어드는 것을 확인할 수 있다.