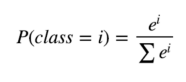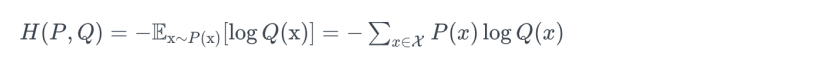📒 Softmax Classification
이거 먼저 읽기
📝 Softmax
- softmax는 하단 수식을 활용해서 모든 확률의 합을 1로 만들어준다.
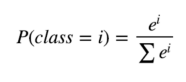
>>> z = torch.FloatTensor([1, 2, 3])
>>> hypothesis = F.softmax(z, dim=0)
>>> print(hypothesis)
tensor([0.0900, 0.2447, 0.6652])
>>> print(hypothesis.sum())
tensor(1.)
📝 Cross Entropy
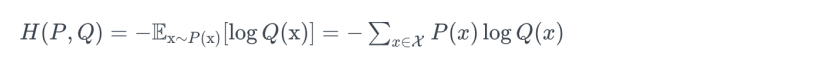
- P, Q 두개의 확률분포가 있다.
- P에서 x를 샘플링하고, Q에 넣은 후에 log를 취한 값의 평균을 구한다.
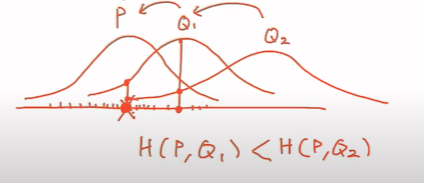
- Q가 점점 P에 가까워지게 만드는 작업이다.
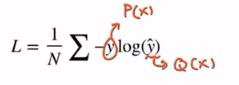
- Loss function은 다음과 같다.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
torch.manual_seed(1)
z = torch.rand(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
hypothesis = F.log_softmax(z, dim=1)
y = torch.randint(5, (3,)).long()
print(y)
y_one_hot = torch.zeros_like(hypothesis)
y_one_hot.scatter_(dim=1, y.unsqueeze(1), 1)
cost = y_one_hot * -F.log_softmax(z, dim=1))).sum(dim=1).mean()
cost = F.nll_loss(F.log_softmax(z, dim=1), y)
cost = F.cross_entropy(z, y)
print(cost)
📝 Training code
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
torch.manual_seed(1)
class SoftmaxClassifierModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(4, 3)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
x_train = [[1, 2, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 3, 2],
[3, 1, 3, 4],
[4, 1, 5, 5],
[1, 7, 5, 5],
[1, 2, 5, 6],
[1, 6, 6, 6],
[1, 7, 7, 7]]
y_train = [2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0]
x_train = torch.FloatTensor(x_train)
y_train = torch.LongTensor(y_train)
model = SoftmaxClassifierModel()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
nb_epochs = 1000
for epoch in range(nb_epochs + 1):
prediction = model(x_train)
cost = F.cross_entropy(prediction, y_train)
optimizer.zero_grad()
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
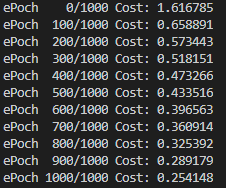
if epoch % 100 == 0:
print('ePoch {:4d}/{} Cost: {:.6f}'.format(epoch, nb_epochs, cost.item()))
- 점점 Cost가 낮아지는 것을 확인할 수 있다.