https://leetcode.com/problems/clone-graph/?envType=study-plan-v2&envId=top-interview-150
개요
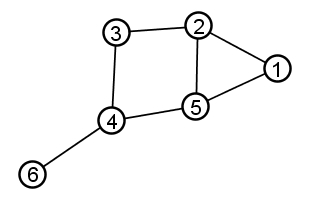
- 무방향 그래프의 노드가 주어진다.
- 모든 노드가 가진 val은 노드의 인덱스와 동일하다.
- 노드의 개수는 0개에서 100개
- 이 그래프를 Deep Copy 해라
- 모든 노드의 객체 자체를 새로 만들어야 한다.
문제 해결 아이디어
- 그래프의 노드에서 이웃 노드로 이동하며 전체 노드를 탐색할 수 있다.
- 생성된 모든 노드는 어떤 노드와 이웃일 수 있다.
➡️ 탐색 시 노드가 이미 접근한 노드인지 확인한다.
➡️ 모든 노드는 다른 노드를 생성할 때 참조해야할 수 있다.
🧐 인덱스를 통해 노드에 접근할 수 있도록 자료 구조를 활용하자
의사 코드
- 큐에 노드를 삽입한다.
- 큐에서 노드를 하나 가져온다.
- 이전에 방문한 노드이다. (분기)
3-1. (false) 노드 배열에 현재 노드의 인덱스로 참조되는 노드가 있다. (분기)
3-1-1. (false) 새 노드를 생성한 후 노드 배열에 저장한다. - (false) 노드 배열에 노드의 이웃 노드의 인덱스로 참조되는 노드가 있다. (분기)
4-1. (false) 새 노드를 생성한 후 노드 배열에 저장한다. - 현재 노드에
neighbors리스트에 노드 배열에서 참조한 값을 추가한다. - 큐에 이웃 노드를 추가한다.
- 현재 노드의
isVisited값을true로 한다.
while(큐가 비어있지 않음){
Node 현재노드 = 큐.poll();
if(노드가 이미 방문됨) continue;
else if(노드배열[현재노드.val] == null) 노드배열[현재노드.val] = new Node();
for(Node 이웃노드 : 현재 노드의 이웃들){
if(노드배열[이웃노드.val] == null) 노드배열[이웃노드.val] = new Node();
현재노드.이웃리스트.add(노드배열[이웃노드.val])
큐.offer(이웃노드);
}
현재노드.isVisted = true;
}
결과
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
if(node == null) return null;
Node visited[] = new Node[101]; // from the given constrain
Node copiedNode = new Node(node.val);
// Push the orinal node into the queue;
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(node);
// visited array of nodes to keep track of newly created nodes
visited[copiedNode.val] = copiedNode;
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Node popOrig = q.poll();
// go to the neighbors of original node
for(Node n:popOrig.neighbors){
//if neigbors are null create new node and mark them as visited;
// add them to the queue;
if(visited[n.val] == null){
visited[n.val] = new Node(n.val);
q.add(n);
}
// every time you mark there presence make sure to add them as the
// neighbours of the orinalNode;
visited[popOrig.val].neighbors.add(visited[n.val]);
}
}
return copiedNode;
}이 문제는 DFS와 BFS로 풀이할 수 있는데, 나는 BFS로 풀이했다.
위 풀이는 나랑 전체적인 접근 방식은 동일하다.
그런데 나는 큐에 있는 노드에 접근할 때와, 이웃 노드를 큐에 삽입할 때 모두 노드가 null인지 체크한다는 점이 다르다.
BFS이고 이웃에 접근하기 전에 해당 이웃 노드 무조건 먼저 생성하는 접근 방식이기 때문에, 굳이 이웃 노드가 null 인지 체크할 필요가 없다.
나는 그 부분을 간과해서 불필요한 코드가 더 있는데, 이 코드는 가시성도 좋고 메모리도 나보다 더 효율적이게 활용한 것 같다.
이렇게 접근 방식의 특성을 생각해서 코드를 짜는 부분도 꼭 염두에 두어야 겠다.
좋은 코드를 배워가는 것 같아 뿌듯하다.