1.후기
서버... 클라이언트... 모르겠어요

2.새롭게 알게 된 것
Chapter1. CORS
-1. SOP & CORS
-2. CORS 동작 방식
-3. CORS 설정 방법
-4. 과제 - Mini Node Server
Chapter2. Refactor Express
-1. Express 시작하기
-2. Middleware
-4. 과제 - Mini Node Server Express로 변환

<Chapter1. CORS>

1.SOP
1) SOP(Same-Origin Policy, 동일 출처 정책)
같은 출처의 리소스만 공유가 가능
-동일 출처의 의미: 프로토콜, 호스트, 포트가 동일
ex.
http://codestates.com:81 vs http://codestates.com
-> 동일 출처❌, http 프로토콜의 기본 포트는 80
https://codestates.com:443 vs https://codestates.com
-> 동일 출처✅, https 프로토콜의 기본 포트는 443
-필요성
잠재적으로 해로울 수 있는 문서를 분리함으로써 공격받을 수 있는 경로를 줄여줌.
2) CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing, 교차 출처 리소스 공유)
-의미
추가 HTTP 헤더를 사용하여, 한 출처에서 실행 중인 웹 애플리케이션이 다른 출처의 선택한 자원에 접근할 수 있는 권한을 부여하도록 브라우저에 알려주는 체제. 즉, 브라우저는 SOP에 의해 기본적으로 다른 출처의 리소스 공유를 막지만, CORS를 사용하면 접근 권한을 얻을 수 있게 됨.
2.CORS 동작 방식
1) 프리플라이트 요청 (Preflight Request)
실제 요청을 보내기 전, OPTIONS 메서드로 사전 요청을 보내 해당 출처 리소스에 접근 권한이 있는지 확인
-권한 있는 경우
응답 헤더의 Access-Control-Allow-Origin으로 요청을 보낸 출처가 돌아오면 실제 요청을 보냄

-권한 없는 경우
브라우저에서 CORS 에러를 띄우게 되고, 실제 요청은 전달되지 않음

-필요성
- 리소스 측면에서 효율적
실제 요청을 통째로 보내기 전에 미리 권한 확인하기 때문 - CORS에 대비가 되어있지 않은 서버를 보호할 수 있음
CORS 이전에 만들어진 서버들은 SOP 요청만 들어오는 상황을 고려하고 만들어짐. 따라서 다른 출처에서 들어오는 요청에 대한 대비가 되어있지 않음. 이런 서버에 프리플라이트 과정 없이 바로 요청을 보내면, 응답을 보내기 전에 우선 요청을 처리하게 됨. 브라우저는 응답을 받은 후에야 CORS 권한이 없다는 것을 인지하지만, 브라우저가 에러를 띄운 후에는 이미 요청이 수행된 상태.
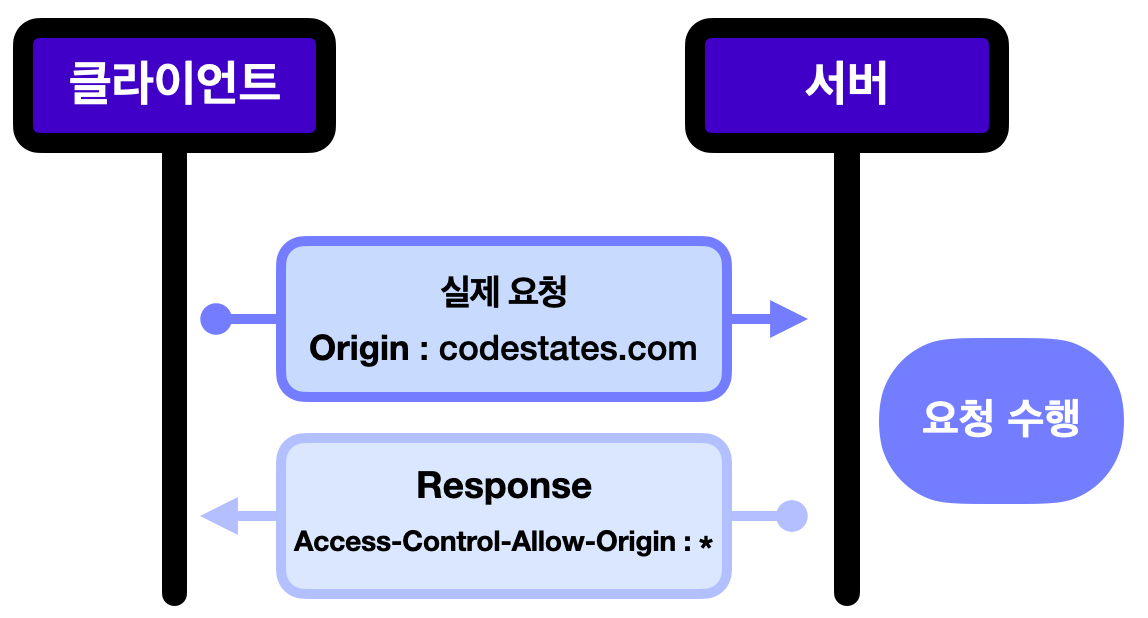
2) 단순 요청 (Simple Request)
특정 조건이 만족되면 프리플라이트 요청을 생략하고 요청을 보내는 것
-조건
- GET, HEAD, POST 요청 중 하나여야 함
- 자동으로 설정되는 헤더 외에, Accept, Accept-Language, Content-Language, Content-Type 헤더의 값만 수동으로 설정할 수 있음.(Content-Type 헤더에는 application/x-www-form-urlencoded, multipart/form-data, text/plain 값만 허용)
3) 인증정보를 포함한 요청 (Credentialed Request)
요청 헤더에 인증 정보를 담아 보내는 요청. 민감한 정보이므로 출처가 다를 경우에는 별도의 설정을 하지 않으면 쿠키를 보낼 수 없음. 이 경우에는 프론트, 서버 양측 모두 CORS 설정이 필요.
-주의점
- 프론트 측에서는 요청 헤더에 withCredentials : true 를 넣어줘야 함.
- 서버 측에서는 응답 헤더에 Access-Control-Allow-Credentials : true 를 넣어줘야 함.
- 서버 측에서 Access-Control-Allow-Origin 을 설정할 때, 모든 출처를 허용한다는 뜻의 와일드카드(*)로 설정하면 에러가 발생. 인증 정보를 다루는 만큼 출처를 정확하게 설정해주어야 함.
3.CORS 설정 방법
CORS는 Node.js 뿐만 아니라 Express, Fastify 등 다른 서버 환경에서도 CORS 설정 가능
1) Node.js 서버
Node.js로 간단한 HTTP 서버를 만들 경우, 다음과 같이 응답 헤더를 설정
const http = require('http');
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
// 모든 도메인
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*");
// 특정 도메인
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "https://codestates.com");
// 인증 정보를 포함한 요청을 받을 경우
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true");
})2) Express 서버
Express 프레임워크를 사용해서 서버를 만드는 경우, cors 미들웨어를 사용해서 보다 더 간단하게 CORS 설정 가능
const cors = require("cors");
const app = express();
//모든 도메인
app.use(cors());
//특정 도메인
const options = {
origin: "https://codestates.com", // 접근 권한을 부여하는 도메인
credentials: true, // 응답 헤더에 Access-Control-Allow-Credentials 추가
optionsSuccessStatus: 200, // 응답 상태 200으로 설정
};
app.use(cors(options));
//특정 요청
app.get("/example/:id", cors(), function (req, res, next) {
res.json({ msg: "example" });
});4.과제 - Mini Node Server

1) 코드
// <index.html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./style.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./variables.css" />
<link rel="icon" type="image/x-icon" href="./images/favicon.ico" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<h2>요청</h2>
<textarea
placeholder="여기에 작성한 데이터를 서버로 보내면 응답으로 받을 수 있어야 합니다."
class="input-text"
></textarea>
<div>
<button id="to-upper-case">toUpperCase</button>
<button id="to-lower-case">toLowerCase</button>
</div>
<h2>응답</h2>
<pre id="response-wrapper"></pre>
<img id="logo" src="./images/codestates-logo.png" />
</div>
<script src="./App.js"></script>
</body>
</html>// <App.js>
// 전체 흐름: init -> toUpperCase/toLowerCase -> post -> render
class App {
// 'toUpperCase/toLowerCase' 버튼이 눌리면 toUpperCase/toLowerCase() 실행
init() {
document
.querySelector('#to-upper-case')
.addEventListener('click', this.toUpperCase.bind(this));
document
.querySelector('#to-lower-case')
.addEventListener('click', this.toLowerCase.bind(this));
}
// render() 실행
post(path, body) {
fetch(`http://localhost:4999/${path}`, {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(body),
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
})
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((res) => {
this.render(res);
});
}
// post() 실행
toLowerCase() {
const text = document.querySelector('.input-text').value;
this.post('lower', text);
}
toUpperCase() {
const text = document.querySelector('.input-text').value;
this.post('upper', text);
}
// post()의 res를 pre 태그 사이에 삽입, textarea 빈칸으로 변겅
render(response) {
const resultWrapper = document.querySelector('#response-wrapper');
document.querySelector('.input-text').value = '';
resultWrapper.innerHTML = response;
}
}
const app = new App();
app.init();// <basic-server.js>
const http = require('http');
const PORT = 4999;
const ip = 'localhost';
const server = http.createServer((request, response) => {
// 객체 구조 분해 할당
// {method, url} = {method: request.method, url: request.url}
// -> method = request.method, url = request.url
const { method, url } = request;
console.log(`http request method is ${method}, url is ${url}`);
// OPTIONS -> Preflight 요청
if (method === 'OPTIONS') {
response.writeHead(200, defaultCorsHeader);
response.end();
}
let body = [];
// POST -> 새로운 리소스 생성 요청
if (method === 'POST' && url === '/upper') {
request
// 데이터가 들어오면 실행
.on('data', (chunk) => {
body.push(chunk);
})
// 데이터 수집이 끝나면 실행
.on('end', () => {
body = Buffer.concat(body).toString().toUpperCase();
response.writeHead(201, defaultCorsHeader);
response.end(body);
});
} else if (method === 'POST' && url === '/lower') {
request
.on('data', (chunk) => {
body.push(chunk);
})
.on('end', () => {
body = Buffer.concat(body).toString().toLowerCase();
response.writeHead(201, defaultCorsHeader);
response.end(body);
});
} else {
response.writeHead(404, defaultCorsHeader);
response.end();
}
});
// 요청을 실제로 처리
server.listen(PORT, ip, () => {
console.log(`http server listen on ${ip}:${PORT}`);
});
const defaultCorsHeader = {
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*',
'Access-Control-Allow-Methods': 'GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS',
'Access-Control-Allow-Headers': 'Content-Type, Accept',
'Access-Control-Max-Age': 10,
};참고 사이트: https://nodejs.org/ko/docs/guides/anatomy-of-an-http-transaction/
2) HTTP Message(Post 시)
-Headers



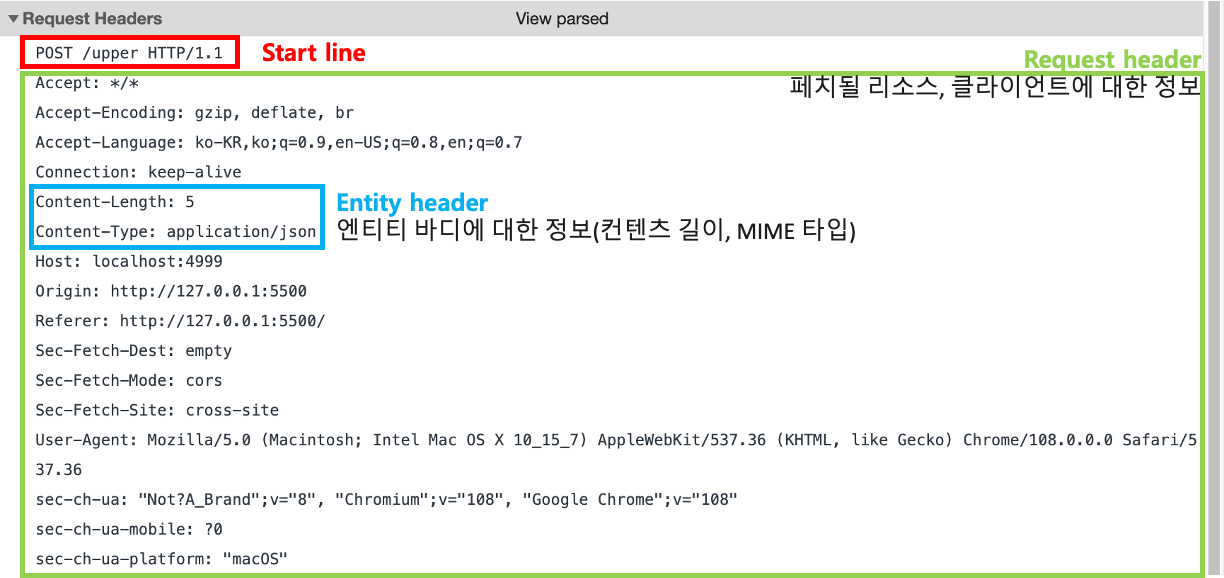
-Body

<기타>
1.클라이언트 port와 서버 port는 반드시 달라야 함
ex.Mini Node Server 과제
5500 -> 클라이언트
4999 -> 서버
2.writeHead
response.writeHead(statusCode[, statusMessage][, headers])1) 작성 위치
❌전체 한번에 쓰기
✅if문 마다 적기
전체 한번에 써도 작동하지만 if문 마다 넣어주는 것이 좋음
2) setHeader와의 차이
writeHead -> 여러 줄
setHeader -> 한 줄
// writeHead
var json = JSON.stringify(result.rows);
response.writeHead(200, {'content-type':'application/json', 'content-length':Buffer.byteLength(json)});
response.end(json);
//setHeader
var json = JSON.stringify(result.rows);
response.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json');
response.end(json);3.chunk, buffer, stream
chunk: 데이터 조각
buffer: chunk를 받아주는 용기, 다 차면 buffer을 통째로 전송하고 아직 옮기지 못한 데이터는 새로운 buffer에 저장
stream: buffer가 다 차면 이를 전송하고 다시 buffer를 채우는 버퍼링 작업을 연속하는 것
4.find/findIndex
1) find()
주어진 판별 함수를 만족하는 첫 번째 요소의 값을 반환
2) findIndex()
주어진 판별 함수를 만족하는 배열의 첫 번째 요소에 대한 인덱스를 반환
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
const isLargeNumber = (element) => element > 13;
array1.find(isLargeNumber); // 130
array1.findIndex(isLargeNumber); // 35.end 이벤트 안에 response.end() 위치시킴
6.GET/POST/PUT,PATCH
GET: 리소스의 데이터 요청
POST: 리소스 새로 생성
PUT,PATCH: 리소스 업데이트
<Chapter2. Refactor Express>
-MERN stack
: MongoDB, Express, React, Node.js
Express: Node.js 환경에서 웹 서버, 또는 API 서버를 제작하기 위해 사용되는 인기 있는 프레임워크
-Express로 구현한 서버가 Node.js HTTP 모듈로 작성한 서버와 다른 점
-> 미들웨어 추가 가능, 라우터 제공
1.Express 시작하기
1) Express 설치
참고 사이트: https://expressjs.com/ko/starter/installing.html
2) 간단한 웹 서버 만들기
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const port = 3000
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello World!')
})
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Example app listening on port ${port}`)
})3) 라우팅
메서드와 url(/lower, /upper 등)로 분기점을 만드는 것(클라이언트의 요청에 해당하는 Endpoint에 따라 서버가 응답하는 방법을 결정하는 것)
// <Node.js>
const requestHandler = (req, res) => {
if(req.url === '/lower') {
if (req.method === 'GET') {
res.end(data)
} else if (req.method === 'POST') {
req.on('data', (req, res) => {
// do something ...
})
}
}
}
// <Express>
const router = express.Router()
router.get('/lower', (req, res) => {
res.send(data);
})
router.post('/lower', (req, res) => {
// do something
})2.Express Middleware
Middleware: 서로 다른 애플리케이션이 서로 통신하는 데 사용되는 소프트웨어
1) POST 요청 등에 포함된 body(payload)를 구조화할 때 -> jsonParser
npm install body-parser// <Node.js>
// 네트워크 상의 chunk를 합치고, buffer를 문자열로 변환하는 작업이 필요
let body = [];
request.on('data', (chunk) => {
body.push(chunk);
}).on('end', () => {
body = Buffer.concat(body).toString();
// body 변수에는 문자열 형태로 payload가 담겨져 있습니다.
});
// <Express>
// Express v4.16.0이전
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const jsonParser = bodyParser.json();
...
app.post('/users', jsonParser, function (req, res) {
})
// Express v4.16.0부터
const jsonParser = express.json();
...
app.post('/api/users', jsonParser, function (req, res) {
})2) 모든 요청/응답에 CORS 헤더를 붙일 때 -> app.use(cors())
npm install cors// <Node.js>
const defaultCorsHeader = {
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*',
'Access-Control-Allow-Methods': 'GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, OPTIONS',
'Access-Control-Allow-Headers': 'Content-Type, Accept',
'Access-Control-Max-Age': 10
};
// 생략
if (req.method === 'OPTIONS') {
res.writeHead(201, defaultCorsHeader);
res.end()
}
// <Express>
// Express(모든 요청에 대해 CORS 허용)
const cors = require('cors');
// 생략
app.use(cors());
// Express(특정 요청에 대해 CORS 허용)
const cors = require('cors')
// 생략
app.get('/products/:id', cors(), function (req, res, next) {
res.json({msg: 'This is CORS-enabled for a Single Route'})
})3) 모든 요청에 대해 url이나 메서드를 확인할 때 -> app.use()
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const myLogger = function (req, res, next) {
console.log('LOGGED');
next();
};
// 모든 요청에 대해 LOGGED가 출력
app.use(myLogger);
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello World!');
});
app.listen(3000);4) 요청 헤더에 사용자 인증 정보가 담겨있는지 확인할 때 -> app.use, token
// Express
app.use((req, res, next) => {
// 토큰이 있는지 확인, 없으면 받아줄 수 없음.
if(req.headers.token){
req.isLoggedIn = true;
next();
} else {
res.status(400).send('invalid user')
}
})3.과제 - Mini Node Server Express로 변환
// Express - router 사용 안함
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 4999;
const cors = require('cors');
const jsonParser = express.json({ strict: false });
app.use(cors());
app.post('/upper', jsonParser, (req, res) => {
let data = req.body.toUpperCase();
res.status(200).json(data);
});
app.post('/lower', jsonParser, (req, res) => {
let data = req.body.toLowerCase();
res.status(200).json(data);
});
app.listen(port);