4-1강) Object Oriented Programming
- Naming Rule
snake_case: 함수, 변수명에 사용
CamelCase: Class명에 사용
Inheritance: 상속
- 부모 클래스로부터 속성과 method를 물려받은 자식 클래스를 생성
# 부모 클래스
class Person2(object):
def __init__(self, name, age, gender):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.gender = gender
def about_me(self):
print("제 이름은", self.name, "이고, 제 나이는", str(self.age), "입니다")
class Employee(Person2): #부모 클래스 Person2로부터 상속
def __init__(self, name, age, gender, salary, hire_date):
super().__init__(name, age, gender) # 부모객체 사용
self.salary = salary
self.hire_date = hire_date
# 새로운 메서드 추가
def do_work(self):
print("Work Well")
# 부모 클래스 함수 재정의
def about_me(self):
super().about_me() # 부모 클래스 함수 사용
print("제 급여는", self.salary, "원이고, 제 입사일은", self.hire_date, "입니다")
myPerson = Person2("John", 45, "Male")
myPerson.about_me()
# 제 이름은 John 이고, 제 나이는 45 입니다
myEmployee = Employee("Daeho", 68, "Male", 3000000, "2014/23/55")
# 제 이름은 Daeho 이고, 제 나이는 68 입니다
myEmployee.about_me()
# 제 급여는 3000000 원이고, 제 입사일은 2014/23/55 입니다Polymorphism
- 다른 클래스에서 함수 이름을 같게 해서 사용
class Animal:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def talk(self):
raise NotImplementedError("subclass must implement abstract method")
class Cat(Animal):
def talk(self):
return "Meow"
class Dog(Animal):
def talk(self):
return "Woof!!"
animals = [Cat('Missy'), Cat('MSSSS'), Dog("LAssie")]
for animal in animals:
print(animal.name + ': ' + animal.talk())
# Missy: Meow
# MSSSS: Meow
# LAssie: Woof!!Visibility
접근제어자
python은 다른 언어와 달리 naming으로 접근제어함
하지만 실질적 접근을 제어하는 것은 아니고 외부에서 쉽게 접근할 수 없게 변수명만 바꾸는 것
- public:
public - protected:
_protected - private:
__private
class Example():
def __init__(self):
pass
def public(self):
print('public')
def _protected(self):
print('protected')
def _private(self):
print('private')Get, Set
다른 언어에서는 private 속성값을 가져올 때 get, set 메소드를 사용
파이썬에서는 다음과 같이 쓸 수 있다
class Person():
def __init__(self):
self.__name = 'Me'
def get_name(self):
return self.__name
def set_name(self, name):
self.__name = name@property
파이썬에서는 @property와 @메소드이름.setter로 데코레이터를 이용해 직관적 표현이 가능
class Person():
def __init__(self):
self.__name = 'Me'
@property
def name(self):
return self.__name
@name.setter
def name(self, name):
self.__name = name
person = Person()
print(person.name)
# Me
person.name = you
print(person.name)
# you- get, set을 name이라는 한 메소드로 합칠 수 있다
- property는 setter보다 앞에 와야함
Decorator
- 대상 함수를 wrap하고, wrap된 함수 앞뒤에 추가적으로 꾸며질 구문들을 정의해 손쉽게 사용을 가능하게 함(wrap된 함수 중간에는 간섭 불가!)
def star(func):
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
print(args[1] * 30)
func(*args, **kwargs)
print(args[1] * 30)
return inner
@star
def printer(msg, mark):
print(msg)
printer("Hello", "&")
# &&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&
# Hello
# &&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&사용방법
1. 먼저 decorator 역할을 하는 함수를 정의하고, 이 함수에서 decorator가 적용될 함수를 인자로 받는다
2. decorator 역할을 하는 함수 내부에 또 한번 함수를 선언(nested function)하여 여기에 추가적인 작업을 선언
3. nested 함수를 return (closure function)
5-1강) Exception / File / Log Handling
Exception Handling
-
Exception의 종류
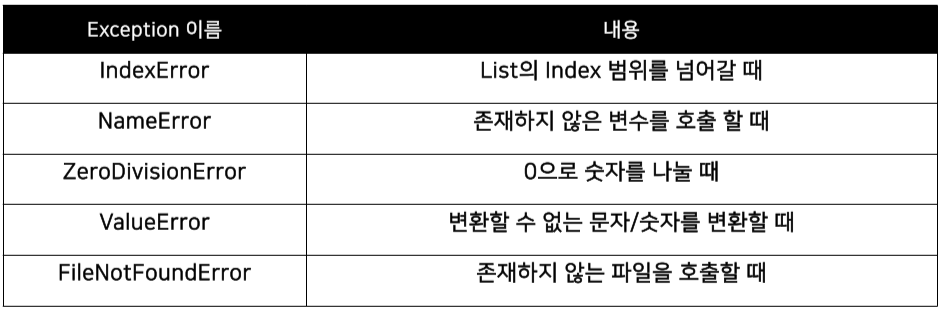
-
예외처리 방법
- try~except~else
try:
예외 발생 가능한 코드
except <Exception Type>:
예외 발생시 동작하는 코드
else:
예외가 발생하지 않을시 동작하는 코드- try~except~finally
try:
예외 발생 가능한 코드
except <Exception Type>:
예외 발생시 동작하는 코드
finally:
예외 발생 여부에 상관없이 동작하는 코드- raise <Exception Type>(예외정보)
- 강제로 예외를 발생시킴
value = "DDDD"
for digit in value:
if digit not in "0123456789":
raise ValueError("숫자 아님!") # 강제로 예외 발생시킴
# ValueError: 숫자 아님!- assert 예외조건
- 특정 조건에 만족하지 않을 경우 예외 발생
def get_binary_number(decimal_number):
assert isinstance(decimal_number, int) # 특정 조건을 만족하지 않을 경우 예외 발생
return bin(decimal_number)
print(get_binary_number("ABC"))
# AssertionError!File Handling
pickle
list, class 같은 텍스트가 아닌 자료형은 일반적인 파일 입출력으로 저장하지 못하기 때문에pickle이라는 모듈을 이용해 저장
import pickle
f = open("list.pickle", "wb")
test = [1,2,3,4,5]
pickle.dump(test, f)
f.close()
f = open("list.pickle", "rb")
test_pickle = pickle.load(f)
print(test_pickle)
f.close()