Numpy
- 고성능 과학 계산용 패키지
- 반복문 없이 데이터 배열에 대한 처리를 지원
Ndarray
- np.array로 ndarray 객체를 생성
- 1가지 dtype으로만 저장할 수 있음
test_array = np.array(["1", "4", 5, 8], float) # 1가지 dtype으로만 생성 가능
test_array
# array([1., 4., 5., 8.])
type(test_array[3])
# numpy.float64- shape: dimension 반환. 나중에 추가되는 rank일수록 앞에 위치.
- dtype: data type 반환
- ndim: number of dimension(rank의 갯수)
- size: data의 갯수
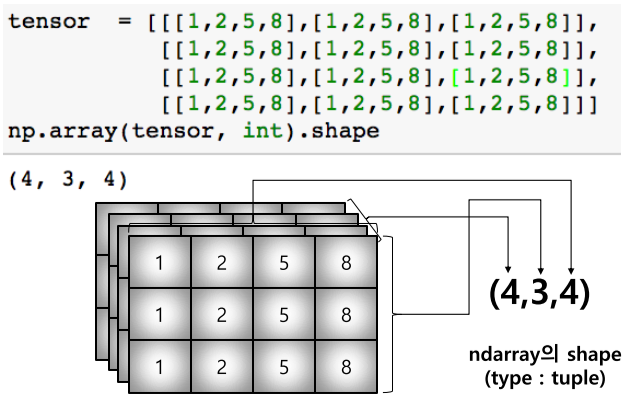
tensor = [[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]],
[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]],
[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]],
[[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8],[1,2,5,8]]]
np.array(tensor, int).shape
# (4, 3, 4)
np.array(tensor, int).ndim
# 3
np.array(tensor, int).size
# 48Handling Shape
reshape
- array의 크기를 변경, element의 갯수는 동일
- 원래 array는 변하지 않는다!
- -1을 넣으면 size를 기반으로 알아서 갯수를 알아서 변경해줌
test_matrix = [[1,2,3,4], [1,2,5,8]]
np.array(test_matrix).shape
# (2, 4)
np.array(test_matrix).reshape(2,2,2)
# array([[[1, 2],
# [3, 4]],
# [[1, 2],
# [5, 8]]])Flatten
- 1차원으로 펴줄 수 있음
test_matrix = [[[1,2,3,4], [1,2,5,8]], [[1,2,3,4], [1,2,5,8]]]
np.array(test_matrix).flatten()
# array([1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 5, 8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 5, 8])Creation Function
arange
- array의 범위를 지정해 list 생성
- step을 소수 단위로 줄 수 있다는 게 장점
np.arange(0, 5, 0.5) # 시작, 끝, step
# array([ 0. , 0.5, 1. , 1.5, 2. , 2.5, 3. , 3.5, 4. , 4.5])ones, zeros & empty
- empty: shape만 주어지고 빈 ndarray 생성
초기화를 안해서 이상한 값이 나옴 - ones_like, zeros_like, empty_like: 기존 ndarray의 shape만큼 1, 0, empty array를 반환
np.zeros(shape=(10,), dtype=np.int8) # 10 - zero vector 생성
# array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], dtype=int8)
np.ones(shape=(10,), dtype=np.int8)
# array([[ 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
# [ 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
np.empty(shape=(10,), dtype=np.int8)
# array([ 96, 48, -73, 116, 86, 85, 0, 0, 0, 0], dtype=int8)
test_matrix = np.arange(10).reshape(2, 5)
np.zeros_like(test_matrix)
# array([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
# [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])identity, eye, diag
- identity: 단위행렬 생성
- eye: 대각선이 1인 행렬, 시작점 설정가능
- diag: 대각행렬의 값을 추출
np.identity(n=3, dtype=np.int8)
# array([[1, 0, 0],
# [0, 1, 0],
# [0, 0, 1]], dtype=int8)
np.eye(N=3, M=5, k=2, dtype=np.int8)
# array([[ 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
# [ 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
# [ 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])
matrix = np.arange(9).reshape(3,3)
np.diag(matrix)
# array([0, 4, 8])
np.diag(matrix, k=1)
# array([1, 5])
random sampling
- 데이터 분포에 따른 sampling array 생성
np.random.uniform(0,1,10).reshape(2,5) # 균등분포
# array([[ 0.67406593, 0.71072857, 0.06963986, 0.09194939, 0.47293574],
# [ 0.13840676, 0.97410297, 0.60703044, 0.04002073, 0.08057727]])
np.random.normal(0,1,10).reshape(2,5) # 정규분포
# array([[ 1.02694847, 0.39354215, 0.63411928, -1.03639086, -1.76669162],
# [ 0.50628853, -1.42496802, 1.23288754, 1.26424168, 0.53718751]])Operation Functions
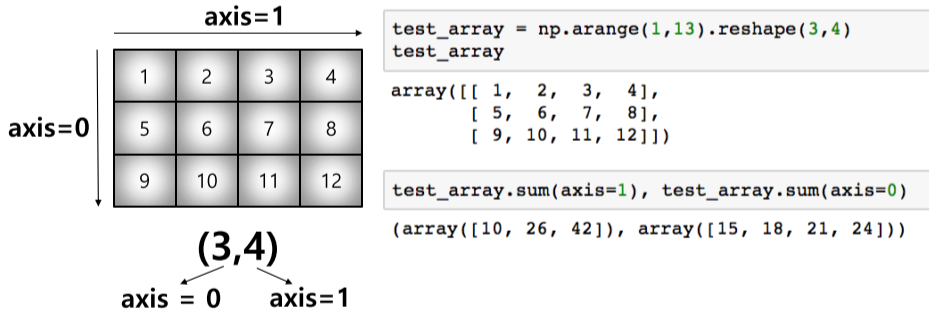
axis
- 모든 operation function을 실행할 때 기준이 되는 dimension 축
- opeation function은 np.something으로 확인 가능

concatenate
- numpy array를 붙이는 함수
- vstack(vertical) = (axis=0), hstack(horizontal) = (axis=1)
- axis의 갯수가 다를 경우 np.newaxis를 통해 축을 추가 가능
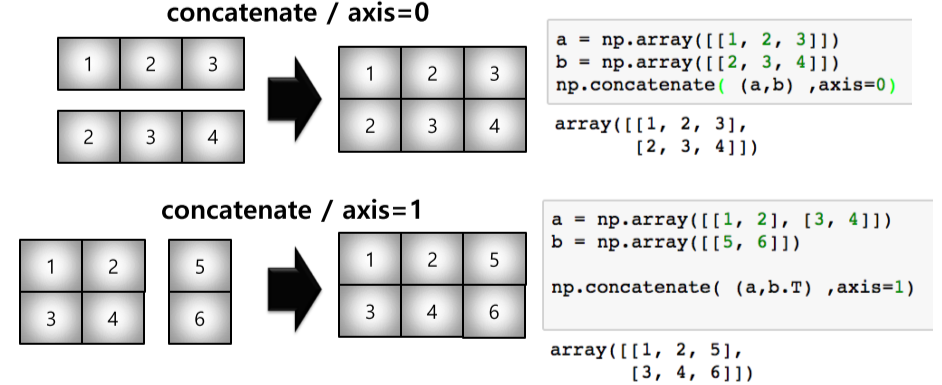
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
b = np.array([5, 6])
b = b[np.newaxis, :]
np.concatenate( (a,b.T) ,axis=1)
# array([[1, 2, 5],
# [3, 4, 6]])Array Operations
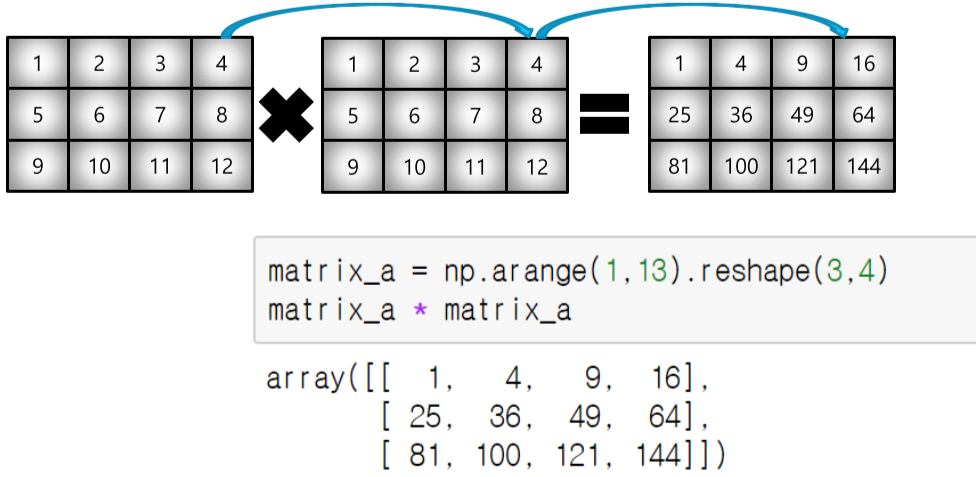
element-wise operations
- array의 각 element끼리 곱해줌
- array간 shape이 같을 경우에만 사용가능
broadcasting
- shape이 다른 array간 연산. 사칙연산, 제곱, 몫 연산 가능
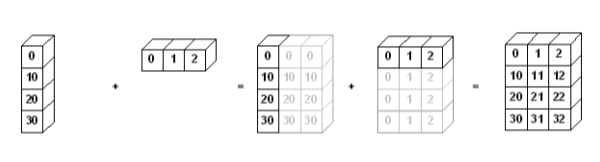
test_matrix = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]], float)
scalar = 3
test_matrix + scalar
# array([[ 4., 5., 6.],
# [ 7., 8., 9.]])
test_matrix = np.arange(1,13).reshape(4,3)
test_vector = np.arange(10,40,10)
test_matrix+ test_vector
# array([[11, 22, 33],
# [14, 25, 36],
# [17, 28, 39],
# [20, 31, 42]])Comparisons
all, any
- array의 전부(and) 혹은 일부(or)가 조건에 만족 여부 반환
a = np.arange(10)
a
# array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
a>5
# array([False, False, False, False, False, False, True, True, True, True])
np.any(a>5), np.any(a<0) # 하나라도 만족하면
# (True, False)
np.all(a>5) , np.all(a < 10) # 모두 만족할 경우
# (False, True)comparison operation
- numpy는 array의 shape이 같을때 element-wise 비교를 한다
test_a = np.array([1, 3, 0], float)
test_b = np.array([5, 2, 1], float)
test_a > test_b
# array([False, True, False])
test_a == test_b
# array([False, False, False])- logic 적용 가능
a = np.array([1, 3, 0], float)
np.logical_and(a > 0, a < 3) # and 조건의 condition
# array([ True, False, False])
b = np.array([True, False, True], bool)
np.logical_not(b) # NOT 조건의 condition
# array([False, True, False])np.where
- 삼항연산자처럼 사용 가능
where(조건, true일때의 value, false일때의 value) - 조건에 해당하는 index값 반환
a = np.array([1, 3, 0], float)
np.where(a > 0, 3, 2) # true, true, false
# array([3, 3, 2])
a = np.arange(5, 15)
np.where(a>10)
# (array([6, 7, 8, 9]),)argmax & argmin
- array내 최대값 혹은 최소값의 index를 반환함
a = np.array([1,2,4,5,8,78,23,3])
np.argmax(a) , np.argmin(a)
# (5, 0)
a=np.array([[1,2,4,7],[9,88,6,45],[9,76,3,4]])
np.argmax(a, axis=1) , np.argmin(a, axis=0) # 축을 기준으로 최대, 최소의 index
# (array([3, 1, 1]), array([0, 0, 2, 2]))boolean & fancy index
boolean index
- 특정 조건에 해당하는 값을 array로 추출
test_array = np.array([1, 4, 0, 2, 3, 8, 9, 7], float)
condition = test_array < 3
test_array[condition]
# array([1., 0., 2.])fancy index
- array를 index value로 사용해서 값 추출
- index value로 쓸 array는 반드시 int로 선언
- matrix 형태도 사용 가능
a = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8], float)
b = np.array([0,0,1,3,2,1], int) # 반드시 integer로 선언
a[b] # bracket index, b 배열의 값을 index로 하여 a의 값을 추출
# array([2., 2., 4., 8., 6., 4.])
a.take(b) #take 함수: bracket index와 같은 효과
# array([2., 2., 4., 8., 6., 4.])
a = np.array([[1, 4], [9, 16]], float)
b = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1, 0], int)
c = np.array([0, 1, 1, 1, 1], int)
a[b,c] # b를 row index, c를 column index로 변환하여 표시함
# array([ 1., 4., 16., 16., 4.])