KITTI 데이터셋의 LiDAR와 image 데이터를 사용하여 LiDAR data를 이미지에 projection 해보았다
1. data 형식
1-1. LiDAR data
- velodyne HDL-64E
- LiDAR data 파일 형식 :
*.bin - data format : x, y, z, intensity로 구성되어있다
- 수평 시야각 : 360도, 수직 시야각 26.8도
- 맨 위쪽부터 반시계 방향 순서로 데이터가 기록되어 있다
- LiDAR 좌표계
- LiDAR 센서 중심 (0,0,0)
- x축 : 전방
- y축 : 왼쪽
- z축 : 높이, 하늘 방향
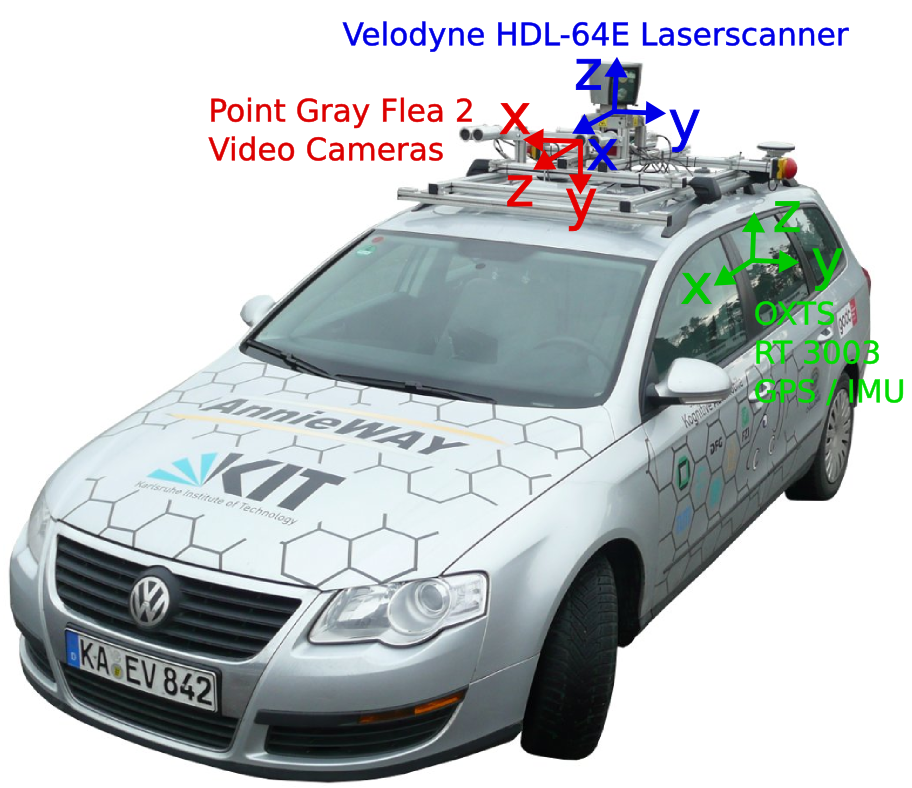

1-2. calibration data
- KITTI에서는 camera calibration과 관련된 데이터을 제공해준다 (camera calibration matrices of object data set)
calib 파일 (.txt) 내용
P0,P1,P2,P3: projection 행렬- world 좌표를 image 좌표로 projection 해주는 행렬
- 12개의 값 -> 3x4 행렬
- 아래와 같이 KITTI 데이터는 4대의 카메라(cam 0, cam1, cam2, cam3)을 사용한다
- 다운받은 데이터셋이 cam2이기 때문에
P2만 사용하면 된다 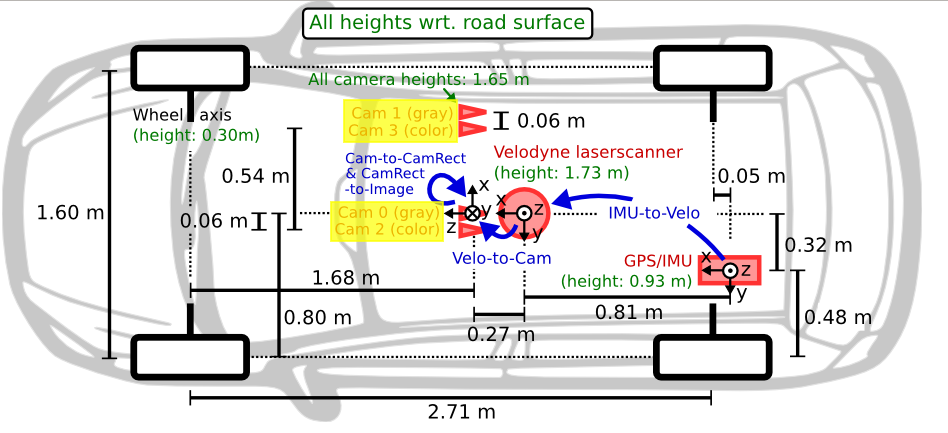
R0_rect: rectification- world 평면으로 회전시켜주는 회전 변환 행렬
- 9개의 값 -> 3x3 행렬
- KITTI는 사용하는 카메라가 4대이기 때문에 이들 간의 world 좌표를 맞춰주기 위해서 이 행렬을 사용한다
Tr_velo_to_cam: LiDAR 좌표 -> camera 좌표- LiDAR 좌표를 camera 좌표 (정확히는 cam0)으로 변환해주는 변환 행렬
- 9개의 값 -> 3x3 행렬
2. LiDAR와 camera mapping
- LiDAR 좌표 을 camera 기준 좌표계로 변환
- world 좌표로 변환
- cam0의 좌표를 최종적인 world 평면으로 회전시켜주는 과정
- KITTI의 카메라 4대가 스테레오 카메라처럼 일렬로 배치되어 있는데 스테레오 연산을 위해서는 이 카메라들이 동일한 world 평면에서 정렬되어 있어야하기 때문이다
- 카메라의 이미지 좌표로 변환
- 결과
- 결과 이미지 좌표로 (x, y, z)가 나오는데 이때 z는 1이기 때문에 계산을 수행한다
- 계산을 수행할 때 행렬의 크기를 고려해야한다. 3x4 행렬의 경우 (0,0,0,1)을 추가하여 4x4 행렬로 변환한 후 사용하여도 되고 아니면 3x1 좌표를 4x1로 변환하여 계산해도 된다
3. LiDAR data 시각화하기
3-1. Open3D 라이브러리
def visualization_open3d(data):
pcd = open3d.geometry.PointCloud()
pcd.points = open3d.utility.Vector3dVector(data[:, :3])
open3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd])
file_name = '000000'
velo_file = f'./data_object_velodyne/training/velodyne/{file_name}.bin'
with open(velo_file, 'rb') as f:
data = np.fromfile(f, dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1,4)
visualization_open3d(data)
3-2. Mayavi 라이브러리
def visualization_mayavi(data):
x = data[:, 0]
y = data[:, 1]
z = data[:, 2]
mlab.figure(bgcolor=(0, 0, 0))
mlab.points3d(x, y, z, color=(0, 1, 0), mode='point')
# mlab.axes()
mlab.show()
file_name = '000000'
velo_file = f'./data_object_velodyne/training/velodyne/{file_name}.bin'
with open(velo_file, 'rb') as f:
data = np.fromfile(f, dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1,4)
visualization_mayavi(data)
4. projection 구현
4-1. calib 파일 불러오기
- projection 행렬들 중에서는 P2만 필요하기 때문에 4개의 projection 행렬 중에 P2만 가져온다
def read_calib_file(file_path):
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
P2 = np.array([float(i) for i in lines[2].split(' ')[1:]]).reshape(3,4)
R0_rect = np.array([float(i) for i in lines[4].split(' ')[1:]]).reshape(3,3)
Tr_velo_to_cam = np.array([float(i) for i in lines[5].split(' ')[1:]]).reshape(3,4)
return P2, R0_rect, Tr_velo_to_cam4-2. projection한 좌표 구하기
[z>0]을 하는 이유는 depth가 양수인 것만 투영하도록 하기 위해서이다. depth가 음수인 경우는 뒷쪽 lidar 데이터이기 때문이다
file_name = '000000'
calib_file = f'./calib/training/calib/{file_name}.txt'
image_file = f'./data_object_image_2/training/image_2/{file_name}.png'
velo_file = f'./data_object_velodyne/training/velodyne/{file_name}.bin' #lidar 파일
P2, R0_rect, Tr_velo_to_cam = read_calib_file(calib_file)
R0 = np.eye(4)
R0[:3, :3] = R0_rect #3x3 행렬인 R0_rect을 4x4 행렬로 변환
Tr = np.vstack([Tr_velo_to_cam, [0,0,0,1]]) #3x4 행렬인 Tr_velo_to_cam를 4x4 행렬로 변환
#lidar 데이터 불러오기
with open(velo_file, 'rb') as f:
data = np.fromfile(f, dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1,4)
XYZ1 = np.vstack([data[:,:3].T, np.ones((1, data.shape[0]))])
xyz = np.dot(P2,np.dot(R0,np.dot(Tr, XYZ1)))
z = xyz[2, :]
x = (xyz[0, :] / z).astype(np.int32)[z>0]
y = (xyz[1, :] / z).astype(np.int32)[z>0]4-3. 시각화하기
image, LiDAR
def visualization_plt(image_file, data, x, y):
img = cv2.imread(image_file)
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
aspect_ratio = float(img.shape[1]) / img.shape[0]
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(20, 25 ))
axs[0].imshow(img_rgb)
axs[0].axis('off')
x_values = data[:, 0]
x_min, x_max = np.percentile(x_values, 1), np.percentile(x_values, 99)
scatter = axs[1].scatter(x, img.shape[0] - y, c=x_values, cmap='jet', marker='.', s=15, vmin=x_min, vmax=x_max)
axs[1].set_xlim([0, img.shape[1]])
axs[1].set_ylim([0, img.shape[0]])
axs[1].axis('off')
for ax in axs:
ax.set_aspect(aspect_ratio)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()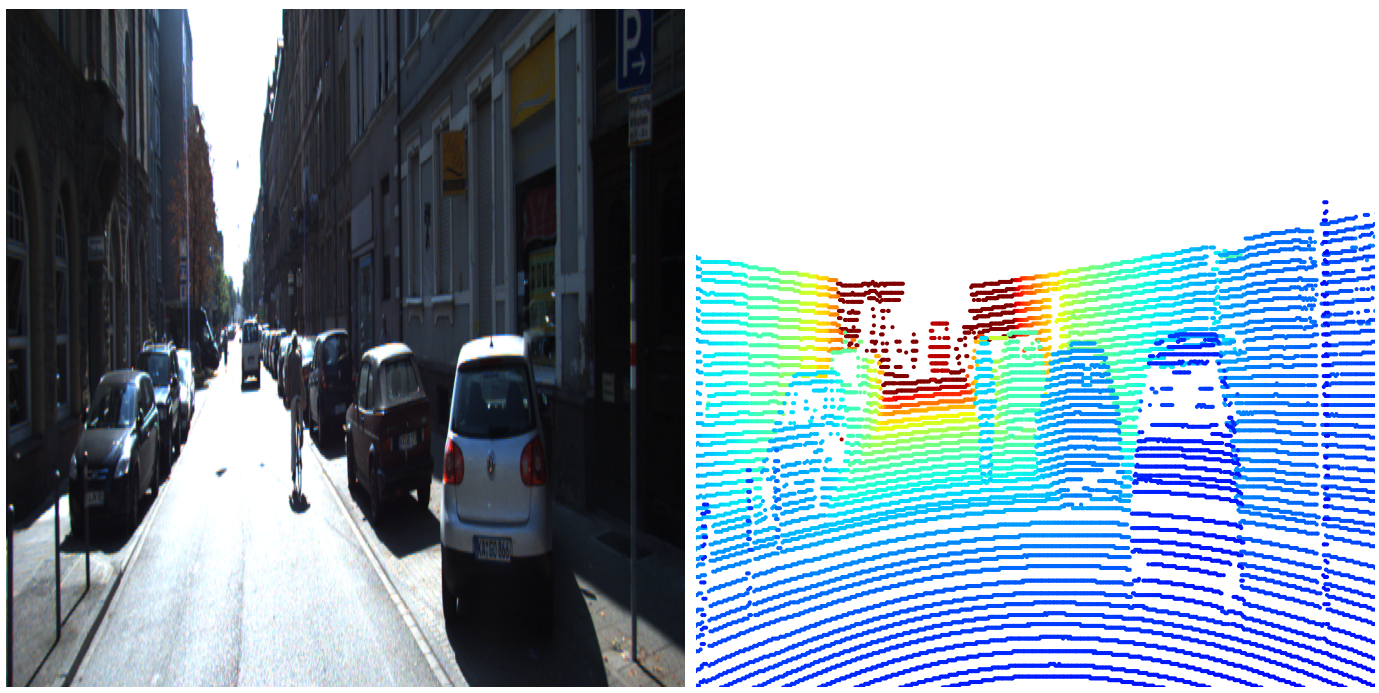
LiDAR 데이터를 이미지 위로 시각화하였다
def visualization_projection(image_file, data, x, y):
img = cv2.imread(image_file)
img_mapped = img.copy()
img_h, img_w = img.shape[:2]
# 거리에 따라 color값을 다르게 주기 위한 부분
x_normalized = (data[:, 0] - np.min(data[:, 0])) / (np.max(data[:, 0]) - np.min(data[:, 0]))
colors = plt.cm.magma(x_normalized)
for i, (ix, iy) in enumerate(zip(x, y)):
if 0 <= ix < img_w and 0 <= iy < img_h:
color = (colors[i] * 255).astype(np.uint8)[:3]
color = (int(color[2]), int(color[1]), int(color[0]))
cv2.circle(img_mapped, (ix, iy), radius=1, color=color, thickness=2)
img_mapped_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img_mapped, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.imshow(img_mapped_rgb)
plt.show()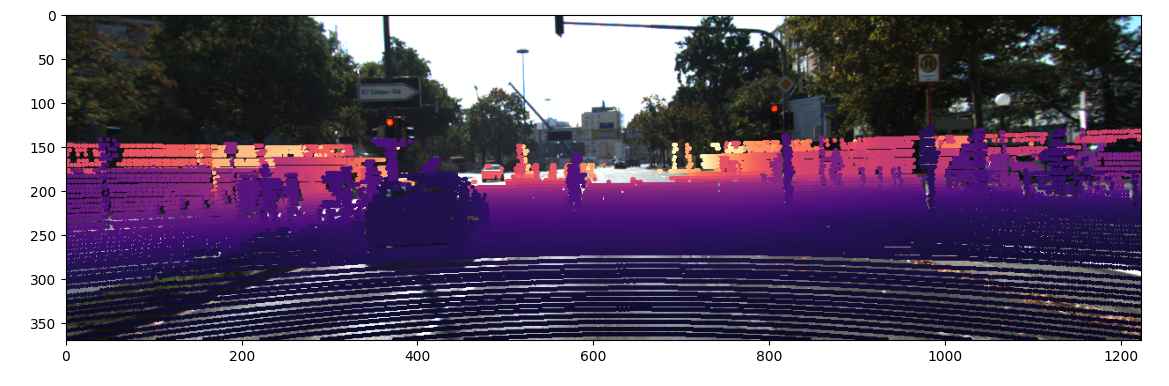
reference
https://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/setup.php
https://darkpgmr.tistory.com/190
