학원에서 학습한 내용을 개인정리한 글입니다.
오늘의 진도
수업
생성자 Constructor
- 객체가 처음 만들어질 때 자동으로 실행되어 초기화하는 역할
- 클래스 이름과 같아야 함
- 반환 타입 X
기본 생성자
접근제한자 클래스명() {} -> 기본 생성자public class D_ConstructorTest {
//생성자 선언하기
//접근제한자 클래스명() {} -> 기본 생성자
String data;
public D_ConstructorTest() {
System.out.println("기본 생성자 호출");
//필드 로직에 의한 기본값을 설정할 수 있음
if(C_InitialBlockTest.objCount == 0) {
data = "X";
} else {
data = "O";
}
}
}public class D_ConstructorMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
D_ConstructorTest ct = new D_ConstructorTest();
}
}QNA
Temi: 보통 클래스 안에 있는 생성자를 같은 이름으로 짓는지? 초기화용이라면 초기화용이라고 따로 빼는게 작업자가 알아보기 편할 것 같아서 물어봄
Teacher: 규칙임. 메소드랑은 다름. 문법이라 바꿀 수가 없음!
매개변수 생성자
접근제한자 클래스명(변수1(매개변수), 변수2...) {} -> 매개변수 있는 생성자 
//매개변수 있는 생성자
public D_ConstructorTest(String inputData) {
//매개변수에 전달된 값을 필드에 저장
this.data = inputData;
}
//타입을 보고 판단
//얘는 같은 String Type이라 불가!
//public D_ConstructorTest(String inputData) {
//
//}
public D_ConstructorTest(String inputData, int num) {
}public class D_ConstructorMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
D_ConstructorTest ct2 = new D_ConstructorTest("yap");
D_ConstructorTest ct3 = new D_ConstructorTest("새로운값");
System.out.println("data: " + ct2.data);
System.out.println("data: " + ct3.data);
}
}
QNA
Temi: 생성자와 메소드 차이는 알았는데, 그럼 초기화 블럭과 생성자의 차이는?
Teacher: 생성자는 매개변수의 타입 차이 같은 것으로 골라쓸 수 있고 초기화블록은 new로 생성됐을 때 무조건 실행되는 차이가 있다. 이후 얘기하겠지만, 오버로딩에 대해서 배울 때 자세히 알려줄 것.
💡QNA
Temi: 생성자에 생성된 곳에 데이터 대입해주는 것은 초기 세팅이기만 한거고 나중에 넘버 수정은 메소드나 퍼블릭 데이터 수정으로 하면 되는건지??
Teacher: 맞음. 처음 생성할 때만 사용
오버로딩
- 한 클래스 내에 동일한 이름의 메소드 여러개
- 매개변수의 개수와 타입만 달라짐
생성자 주의
- 만약 생성자를 따로 입력해주지 않았다면 자동 생성이 됨
- 생성자를 만들었을 때 오류가 났다면 기본 생성자를 입력했는지 확인!
- 생성자 사용자 입력 → 자바에서 자동으로 만들어주는 기본 생성자 입력이 안됨
this
//생성된 객체 주소를 저장하는 변수 -> 나, 자기자신
this.data = inputData;생성자 재활용 -this() 생성자 이용
//생성된 생성자 재활용하기
//this() 생성자 이용
public D_ConstructorTest(String data, int num, char gender) {
this(data, num);
this.gender = gender;
}QNA
Temi:
Teacher
실습
생성자 이용해서 객체 생성 후 출력
- 기본생성자 선언
//minhyuk 12345 minhyuk@minhyuk.com 21 코딩,러닝,편식
public Member() {
}- 전체값을 설정하는 생성자 선언
//user03,3333 없음, 0, null
public Member(String id, String pw, String email, int age, String[] hobby) {
this.userId = id;
this.userPw = pw;
this.userEmail = email;
this.userAge = age;
this.userHobby = hobby;
System.out.printf(printFormatAll,
this.userId,
this.userPw,
this.userEmail,
this.userAge,
Arrays.toString(this.userHobby));
}- 아이디, 비밀번호만 설정하는 생성자 선언
public Member(String id, String pw) {
this.userId = id;
this.userPw = pw;
System.out.printf(printFormatAll,
this.userId,
this.userPw,
this.userEmail,
this.userAge,
Arrays.toString(this.userHobby));
}- 아이디, 비밀번호, 취미를 설정하는 생성자 선언
//user04,4444 없음, 0, 운동,코딩,산책
public Member(String id, String pw, String[] hobby) {
this.userId = id;
this.userPw = pw;
this.userHobby = hobby;
System.out.printf(printFormatAll,
this.userId,
this.userPw,
this.userEmail,
this.userAge,
Arrays.toString(this.userHobby));
}- 생성자 안에서 조건걸어서 필터
public Member(String id, String pw, String email, int age, String[] hobby) {
this.userId = id;
//프로그램 정지
if (pw.length() < 8) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("비밀번호를 8글자이상 입력하세요");
} else {
this.userPw = pw;
}
this.userEmail = email;
this.userAge = age;
this.userHobby = hobby;
System.out.printf(printFormatAll, this.userId, this.userPw, this.userEmail, this.userAge, Arrays.toString(this.userHobby));
}메소드
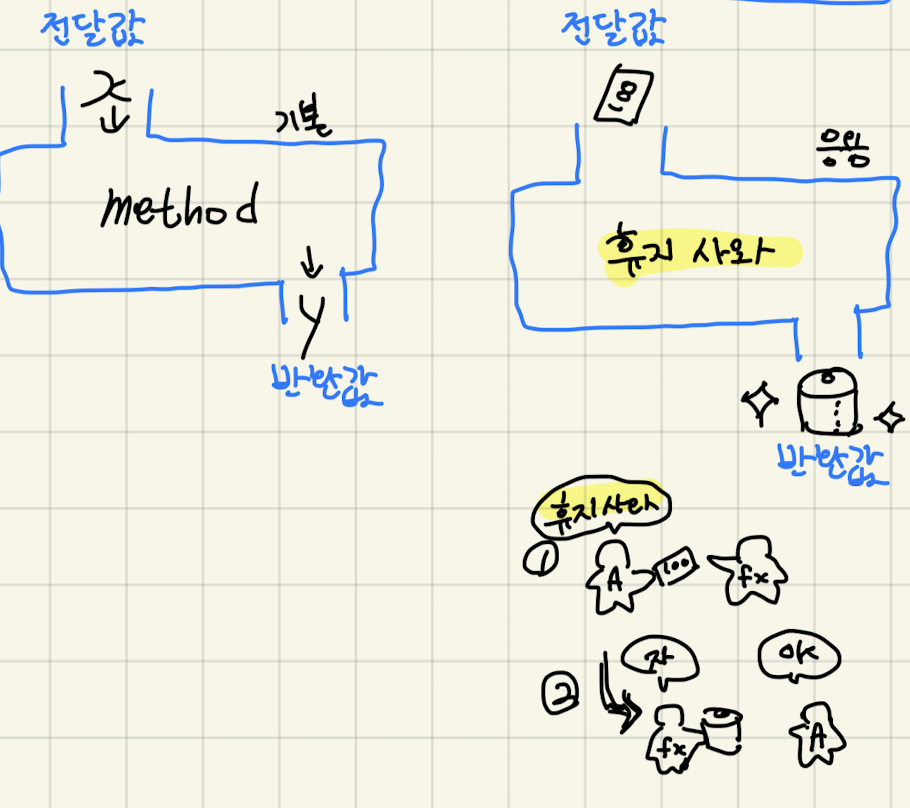
메소드 선언 및 사용
- 반환형이 없고 매개변수 없는 메소드
public class MyMethod {
//메소드 선언
//접근 제한자(public), 반환형(기본, 참조형, void), 메소드명([매개변수]) {로직}
//유형별 메소드 선언
//1 반환형이 없고 매개변수 없는 메소드
public void test1() {
System.out.println("반환형이 없고 매개변수 없는 메소드");
}
}public static void main(String[] args) {
//메소드 이용하기
MyMethod myMethod = new MyMethod();
myMethod.test1();
}- 반환형 없고 매개변수 있는 메소드
//2 반환형이 없고 매개변수 있는 메소드
public void test2(String msg) {
System.out.println("반환형이 없고 매개변수 있는 메소드: "+ msg);public class E_MethodMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//메소드 이용하기
MyMethod myMethod = new MyMethod();
myMethod.test2("흐어");
}
}- 반환형이 있고 매개변수 없는 메소드
- 돌아오는 결과값을 받을 수 있게 세팅한다
//메소드의 반환형을 설정하면 반드시 {}내부에
//return 예약어를 이용해서 반환형으로 선언한 타입의 값을 반환줘야함.
public int test3() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int su = sc.nextInt();
if (su > 0) return su;
else return 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//메소드 이용하기
MyMethod myMethod = new MyMethod();
int result = myMethod.test3();
}- 반환형이 있고 매개변수 있는 메소드
- 돌아오는 결과값을 받을 수 있게 세팅한다
public long test4(int su1, int su2) {
su1 += 200;
su2 *= 10;
return su1 * su2;
} public static void main(String[] args) {
//메소드 이용하기
MyMethod myMethod = new MyMethod();
long result1 = myMethod.test4(4, 3);
}매개변수, 반환형에 참조형 타입 선언
- 리터럴값의 경우 값을 복사해서 사용하기 때문에 호출된 메소드에서 값을 반환받지 않으면 저장되지 않는다.
- 참조형의 경우(얕은 복사) 주소 값을 따라가서 수정해버리기 때문에 주의해야한다.
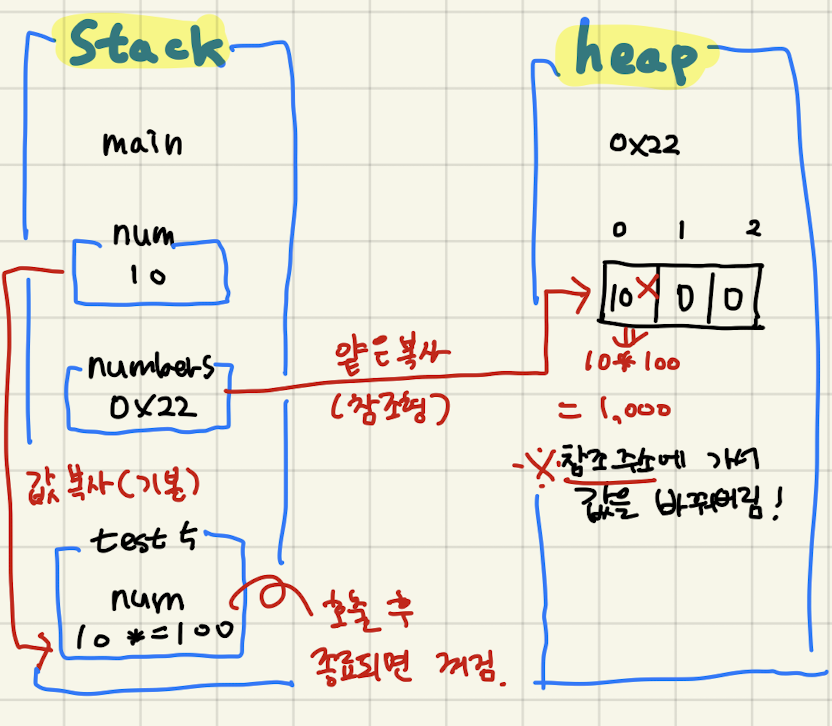
//매개변수, 반환형에 참조형 타입 선언하기
public void test5(int num) {
num *= 100;
}
public void test6(int[] num) {
num[0] *= 100;
}메소드 Static
- 객체를 생성(인스턴스화)하지 않고 만듬
- 필드에 접속이 불가능하다
//메소드의 에약어
//Static
public static void test8() {
System.out.println("static 메소드 실행 : ");
} public static void main(String[] args) {
MyMethod.test8();
}
필드를 사용하는 메소드
public class FieldUseMethod {
private int no;
private String name;
public FieldUseMethod(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
public String infoObject() {
return this.no + " " + this.name;
}
public void incrementNo() {
this.no++;
}
public void incrementByInputNum(int no) {
this.no += no;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//필드를 이용하는 메소드
FieldUseMethod fum = new FieldUseMethod(1, "ㅇㅇㅇ");
System.out.println(fum.infoObject());
fum.incrementNo();
System.out.println(fum.infoObject());
FieldUseMethod fum1 = new FieldUseMethod(55, "ㅁㅁ");
System.out.println(fum1.infoObject());
fum1.incrementByInputNum(10);
System.out.println(fum1.infoObject());
}QNA
Temi: 매개 변수에 int num || String a 같은 식으로 넣을 수 있는지?
Teacher: 안됨. 선언도 안됨. 정적타입이라 불가. 대신 타입이 처음부터 정해져있기 때문에 다른 언어보다 안정적.
Getter
- 기록된 값을 읽어서 요청한 쪽으로 읽은 값을 넘김
- get + “…” 카멜케이스 사용
Setter
- 변경할 값을 전달 받아서 필드 값을 변경
- set + “…” 카멜케이스 사용
public class Product {
private String productName;
private int productPrice;
private int productCategory;
public void setProductName(String name) {
this.productName = name;
}
public String getProductName() {
return this.productName;
}
}
//Main getter setter 이용
Product p = new Product();
p.setProductName("휴대폰");
System.out.println(p.getProductName());실습
상품클래스를 생성해보자
public class Product {
private int productPrice, productInventory;
private double productDiscountPercent;
private String productType, productName;
public static int productNum = 0;
public Product() {
}
// 타입, 이름, 가격만 설정가능
public Product(String productType, String productName, int productPrice){
this.productType = productType;
this.productName = productName;
this.productPrice = productPrice;
}
// 타입, 이름, 가격, 할인률 설정가능
public Product(String productType, String productName, int productPrice, double productDiscountPercent) {
this(productType, productName, productPrice);
this.productDiscountPercent = productDiscountPercent;
}
// 이름, 가격, 할인률, 재고 설정가능
public Product(String productName, int productPrice, double productDiscountPercent, int productInventory) {
this.productName = productName;
this.productPrice = productPrice;
this.productDiscountPercent = productDiscountPercent;
this.productInventory = productInventory;
}
private String printIntType(int num) {
String result = "";
result = (num != 0 ? (", " + num) : "");
return result;
}
private String printDoubleType(double num) {
String result = "";
result = (num != 0 ? (", " + num) : "");
return result;
}
//TODO: 여긴 하드코딩처럼 분기점 나누는거 말곤 지금 당장 생각이 X
private String printStringType(String productType, String productName, boolean isProductName) {
String result = "";
if ((productType != null) && (productName != null)) {
//productType 일 때
if (isProductName == false) {
result = productType;
//productName 일 때
} else {
result = ", " + productName;
}
} else if ((productType == null) && (productName != null)) {
//productType 일 때
if (isProductName == false) {
result = "";
//productName 일 때
} else {
result = productName;
}
//그 외
} else {
return "404";
}
return result;
}
public void printProductInfo() {
System.out.println(
printStringType(this.productType, this.productName, false) +
printStringType(this.productType, this.productName, true) +
printIntType(this.productPrice) +
printDoubleType(this.productDiscountPercent) +
printIntType(this.productInventory));
}
}
package com.myobj.run;
import com.myobj.vo.Product;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] Args) {
Product pdComputer = new Product("컴퓨터", "maxbook", 200);
Product.productNum++;
System.out.print(Product.productNum + " ");
pdComputer.printProductInfo();
Product pdPhone = new Product("핸드폰", "갤럭시노트", 120, 0.2);
Product.productNum++;
System.out.print(Product.productNum + " ");
pdPhone.printProductInfo();
Product pdMask = new Product("마스크", 10, 0.5, 100);
Product.productNum++;
System.out.print(Product.productNum + " ");
pdMask.printProductInfo();
}
}
미리 준비
- 실습 과제들 진행
느낀점
- 생각보다 lua랑 헷갈리는 것이 많아서 신경써야할 것 같다..
- 메소드로 어떻게든 빼서 기능을 만드려다가 복잡하게 꼬이는 일이 있는 것 같으니 조심해야겠다
- 순서도를 그려서 진행해봐야겠다는 생각이 들었다!