개발일지 2일차
1. 학습내용
- z-index
- position 속성을 사용하면 요소를 겹치게 놓을 수 있다. 이 때 요소들의 수직 위치를 z-index 속성으로 정할 수 있다. 숫자가 높을 수록 앞쪽에 배치되고, 작을 수록 뒤로 배치된다. 이 때 position 속성중 3차원 속성에 해당하는 absolute, fixed, relative를 사용할 경우 요소가 겹치게 된다. static의 경우 2차원 속성이므로 요소가 겹치지 않는다.
index.html
<!-- z-index --> <div class="z-one"></div> <div class="z-two"></div>
style.css
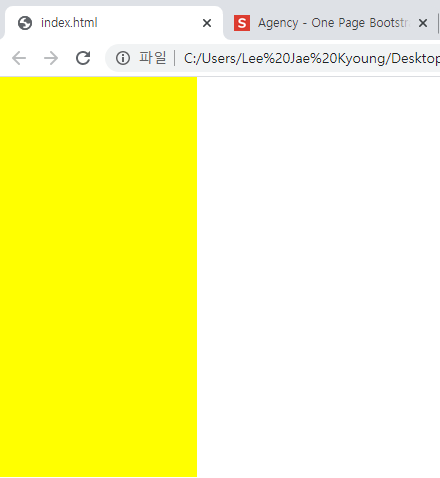
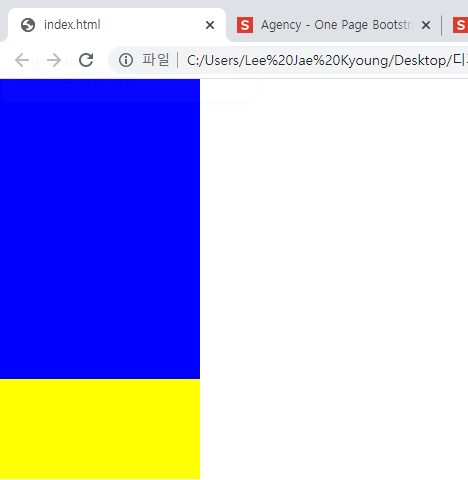
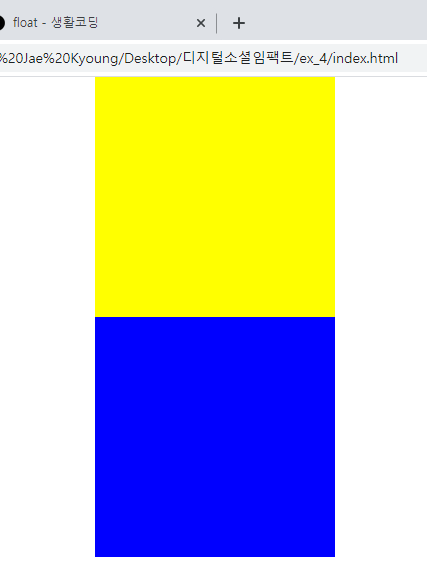
/*absolute, fixed를 사용하게 되면 레이어가 겹치는 현상이 발생함*/ .z-one { position: absolute; width: 200px; height: 400px; background-color: yellow; z-index: 20; } .z-two { position: absolute; width: 200px; height: 300px; background-color: blue; z-index: 10; }
- 결과
원래 position이 둘 다 absolute인 경우 뒤의 요소가 우선순위로 나와야하지만 z-index의 숫자가 더 높은 앞의 요소가 먼저 앞으로 배치되었다.- z-index가 없는 경우
- float
float는 레이아웃을 잡을 때 사용하는 기능이다. 레이어를 같은 선상에 놓을 수 있도록 한다.
index.html
<div class="left-1"></div> <div class="right-1"></div>style.css
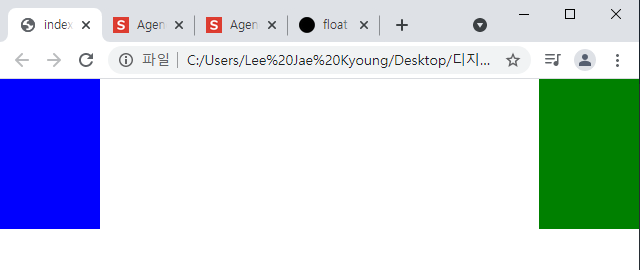
/* float */ .left-1 { float: left; width: 100px; height: 150px; background-color: blue; } .right-1 { float: right; width: 100px; height: 150px; background-color: green; }-결과
- float 사용시 주의할 점
- float를 사용할 경우 레이어가 틀어진다. 그래서 항상 고정값인 공간안에서 사용해야한다.
- float를 사용하고 더 이상 같은 선상에 레이어를 두지 않을 경우 float가 끝나는 태그 다음에 반드시 clear: both;를 통해 float를 닫아줘야한다.
- 순수 3차원에 속하는 position:absolute,fixed 사용시 float가 적용되지 않는다.
index.html
<header></header>
<section>
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="center"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</section>
<footer></footer>style.css
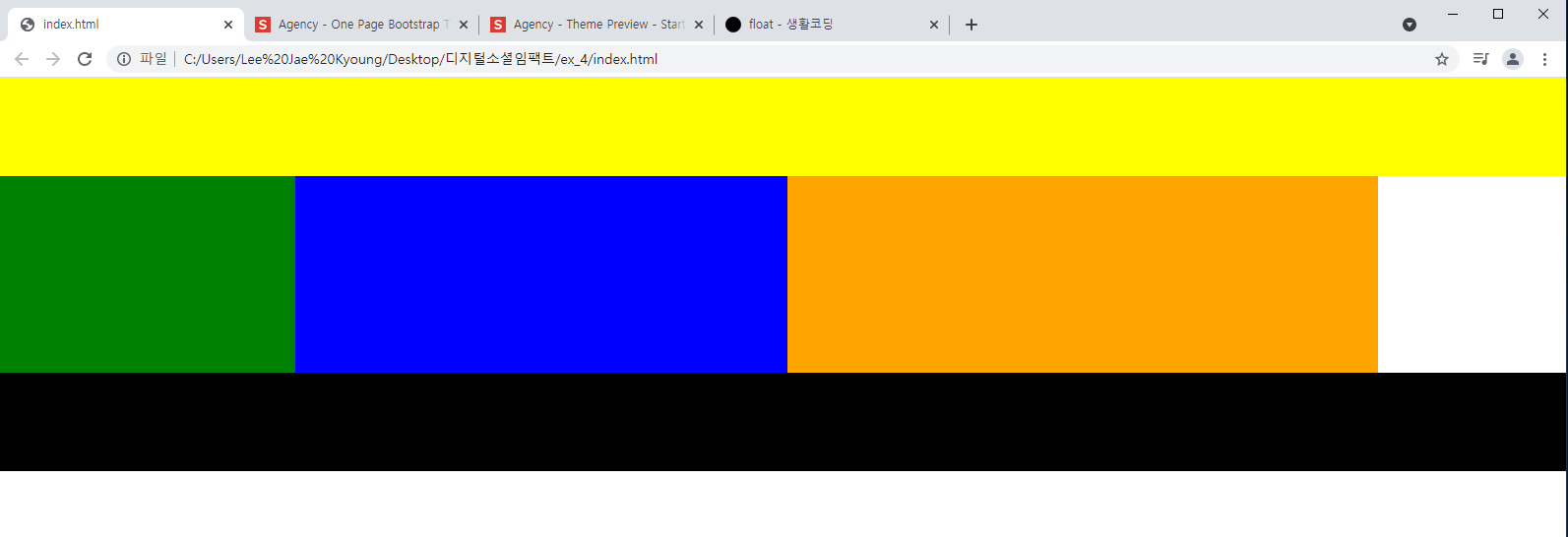
/* float */ header { width: 100%; height: 100px; background-color: yellow; } .left { float: left; width: 300px; height: 200px; background-color: pink; } .center { float: left; width: 500px; height: 200px; background-color: blue; } .right { position: absolute; float: right; width: 300px; height: 200px; background-color: green; } footer { clear: both; width: 100%; height: 100px; background-color: black; } section { width: 1400px; height: 200px; background-color: orange; }-결과
-overflow
박스안에 컨텐츠들이 너무 많아 컨텐츠들이 박스범위밖으로 초과될 때 그것을 어떻게 보여줄지를 지정한다.
-visible : 기본값, 컨텐츠가 넘칠경우 박스 밖으로 벗어난다.
-hidden : 넘치는 부분은 잘려서 보여지지 않는다.
-scroll : 스크롤바가 추가되어 스크롤을 할 수 있다.
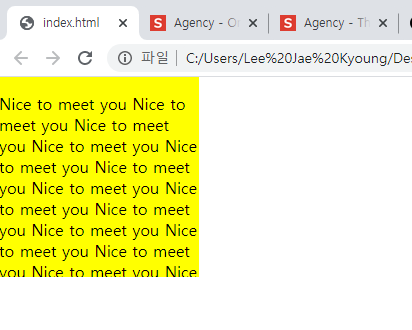
-auto : 컨텐츠양에 따라 스크롤바가 추가될 지 자동으로 선택된다.Hidden의 경우
index.html
<div class="over-box"> <p>Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you Nice to meet you</p> </div>style.css
.over-box { overflow: hidden; width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: yellow; }
-flex
flex 영역으로 지정된 부모의 자식들은 자동으로 x축으로 정렬된다.
display:flex는 부모의 자식들을 x축으로 정렬시킨다.
flex-wrap: nowrap은 부모 크기에 맞춰 자동으로 리사이즈시켜준다.
flex-direction: row(x축), column(y축),row-reverse(역순 x축), column-reverse(역순 y축)
justify-content(x축): flex-start(왼쪽부터 정렬),flex-end(오른쪽),center(중앙),space-between(3개의 영역의 균일한 간격),space-around(박스바깥쪽의 동일한 간격)
align-items(y축) : flex-start(가장 위쪽에 배치),flex-end(가장 아래쪽),center, baseline(박스가장 밑 부분 기준으로 정렬)index.html
<!-- flex --> <div class="container"> <div class="item one"></div> <div class="item two"></div> <div class="item three"></div> </div>style.css
.container { display: flex; /*flex-direction: row;*/ flex-wrap: nowrap; width: 1000px; border: solid 10px red; } .item { width: 200px; } .one { height: 100px; background-color: yellow; } .two { height: 200px; background-color: blue; } .three { width: 900px; height: 300px; background-color: orange; }참고자료) https://flexbox.help/
-중앙정렬
레이아웃 중앙정렬시키는 것
index.html
<div class="center-1"></div> <div class="center-2"></div>style.css
/*중앙정렬 1번째 방법*/ /*margin: 상하 좌우*/ /*margin: 0 auto*/ .center-1 { width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: yellow; margin: 0 auto; } /*중앙정렬 2번째 방법*/ /*left: 50% 왼쪽면 기준으로 50%*/ /*단점은 width 크기에 따라 margin-left의 크기도 바꿔줘야한다.*/ .center-2 { position: relative; width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: blue; left: 50%; margin-left: -150px; }-결과
2. 학습한 내용 중 어려웠던 점 또는 해결못한 것들
float 사용시 주의할 점들은 직접 코드 작성을 통한 결과를 확인해야만 이해하기가 쉬운 것 같다. 단순히 개념을 외운다고 학습이 되지않는 것 같다.
flex가 부모의 자식들을 x축으로 정렬한다는 것은 이해했지만 정렬하는 속성들을 아직 숙지하지 못하였다.
3. 해결방법 작성
float같은 경우 학습한 코드를 다시 작성해보고 결과를 확인해 해결 가능 할 것 같다.
flex같은 경우 flexbox.help를 통해 이해 중이다.
4. 학습 소감
공부에 도움이 되는 사이트를 참고 또는 사용하여 문제를 해결할 수 있어 학습에 도움이 된 것 같다.