relative, absolute, fixed
웹페이지란 소비자 혹은 잠재고객을 끌어들이기 위한 수단이며, 그 자체로 수익을 창출하기란 여간 어려운일이다.
즉, 기능적으로 동작만 하는것은 반쪽짜리 웹페이지이며 사용자의 눈을 현혹하여 나의 페이지에 오랫동안 머물게 해야한다.
이를 위해서 세련되고 매혹적인 디자인은 필연적으로 그 중요성이 올라가게 된다.
그 중 웹페이지 디자인의 뼈대인 레이아웃을 짤 때 사용되는것이 바로 position 속성이다.
1. static
position 속성을 지정해주지 않은 경우 기본적으로 static 속성이 부여된다. 요소를 나열한 순서대로 배치한다. inline 요소라면 한줄에 나열될것이며, block 요소라면 입력한 순서에 맞게 줄별로 출력이 될 것이다.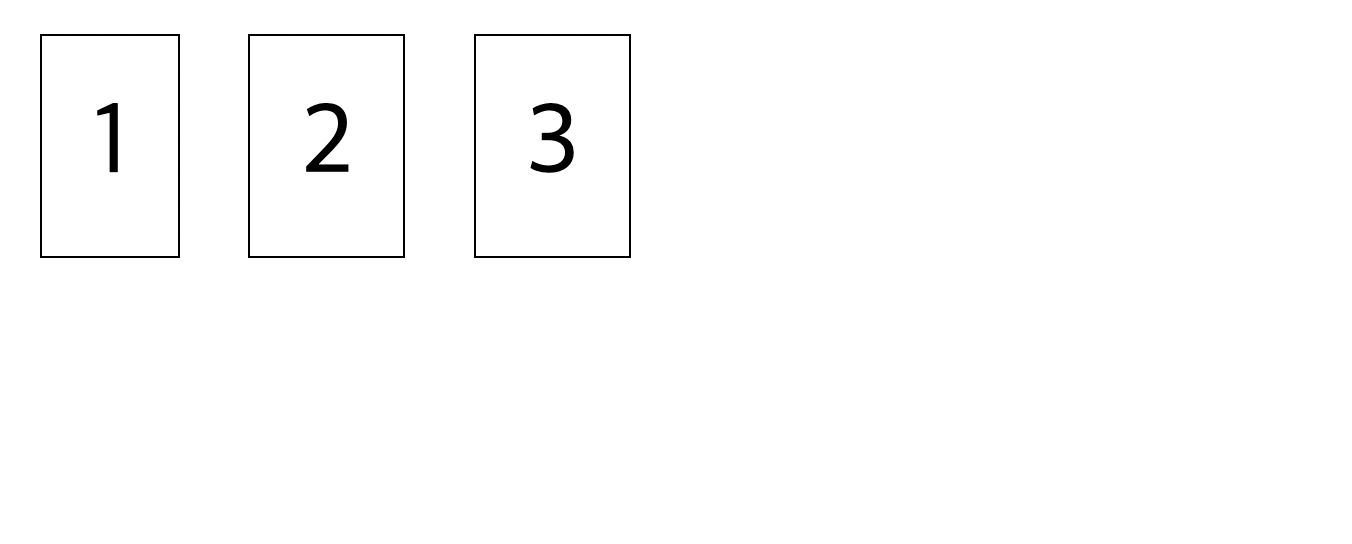
//index.html///////
<body>
<div class="container">
<span class="one">1</span>
<span class="two">2</span>
<span class="three">3</span>
</div>
</body>//styles.css//////
div {
margin-top: 55px;
}
span {
padding: 25px;
border: 1px solid black;
margin: 15px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 50px;
}2. relative
position 속성이 static일 때 를 기준으로의 위치에서 상대적으로 얼마나 더 움직일지를 지정할 수 있는 속성이다.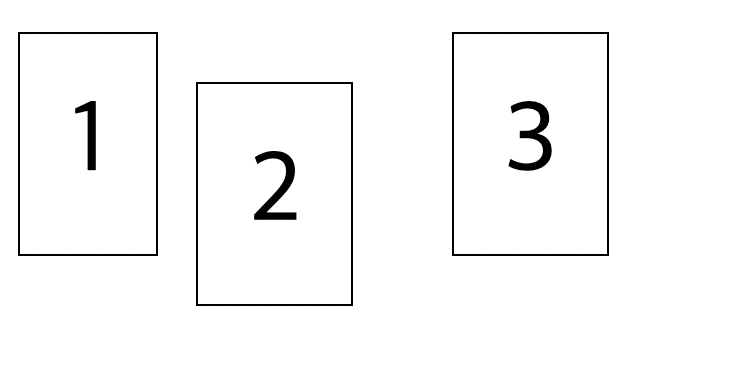
//index.html///////
<body>
<div class="container">
<span class="one">1</span>
<span class="two">2</span>
<span class="three">3</span>
</div>
</body>//styles.css//////
div {
margin-top: 55px;
}
span {
padding: 25px;
border: 1px solid black;
margin: 15px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 50px;
}
.two {
position: relative;
top: 25px;
right: 15px;
}3. absolute
position 속성이 absolute인 경우는 relative 처럼 기존의 위치에 비교해서 top, bottom, right, left 값을 지정해 이동시키는것이 아닌 부모요소의 속성에 의존하여 그 결과를 달리한다.부모의 postion 속성이 static인 경우에는 화면의 (0, 0)을 기준으로 한다.
부모의 postion 속성이 static이 아닌 경우(예: absolute, relative, fixed)에는 부모의 시작점을 기준으로 한다.
스크롤시에는 그에 맞게 이동한다.
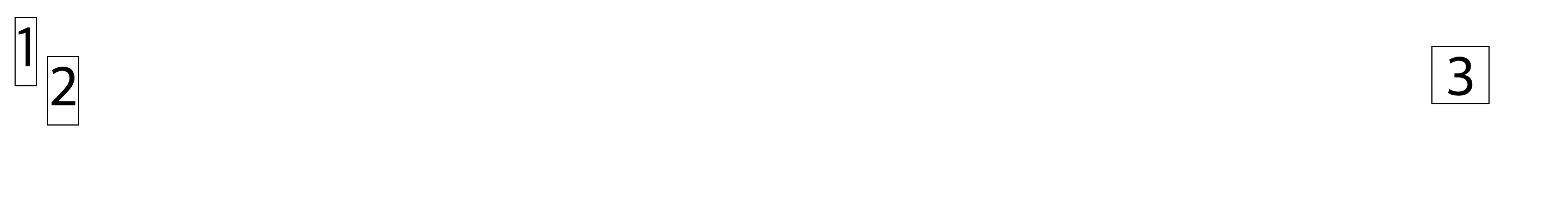
//index.html///////
<body>
<div class="container">
<span class="one">1</span>
<span class="two">2</span>
<span class="three">3</span>
</div>
</body>//styles.css//////
div {
margin-top: 25px;
}
span {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
border: 1px solid black;
margin: 15px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 50px;
}
.two {
position: relative;
top: 35px;
right: 25px;
}
.three {
position: absolute;
top: 35px;
right: 85px;
}4. fixed
position 속성이 fixed인 경우는 부모요소건 순서건 뭐건 그냥 아무 상관없이 브라우저창이 기준이 된다. 하여 스크롤을 움직이더라도 그 위치가 고정되어 브라우저상에 계속 표시되게 된다.예를 들어 상단의 메뉴바로서 흔히 사용된다.
허나 작금의 시대에는 flex와 grid의 등장으로 그 사용빈도가 줄어들었고 나 또한 편리한 flex와 grid에 손이 더 많이 가는것은 어쩔 수 없다.

