[2021 ICML] [Simple review] High-Performance Large-Scale Image Recognition Without Normalization
Paper Info.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.06171

Abstract
(배경)
- BN은 image classification model에서 key componenet이지만,
the batch size and interactions between examples에 대한 dependence로부터 바람직하지 않은 특성이 있다.
(관련연구와 문제 1)
- 비록 training deep ResNets without normalization layers를 성공시킨 최근 연구들이 있지만,
the best batch-normalized networks의 test accuracies를 따라잡지 못하는 한계가 있다.
(문제 2)
- 그리고 large learning rates or strong data augmentations에 대해서 unstable하다.
(제안)
- 우리는 these instabilities를 극복하기 위한 an adaptive gradient clipping technique을 제안하고,
a significantly improved class of Normalizer-Free ResNets을 설계한다.
1. Introduction
- CV에서 최근 model들은 deep residual networks trained with BN의 variants이다.
이 두 architectural innovations의 조합은 deeper networks를 학습할 수 있게 도와준다.
BN은 또한 loss landsacpe을 smoothens시키고, 이로 인해 stable training with larger learning rates and at larger batch sizes를 가능하게 한다.
(BN의 세 가지 문제)
-
하지만 BN은 three significant practical disadvantages를 가진다
- BN은 예상보다 expensive computational primitive이므로, memory overhead를 유발하며,
일부 network에서는 gradient 계산 시간을 크게 증가시킨다. - training and at inference time에서 model의 behaviour의 discrepancy를 초래하여,
hidden hyper-parameters tuning을 필요로 한다. - 가장 중요한 문제로, BN은 minibatch 내 training examples 간의 independence를 깨뜨린다.
- BN은 예상보다 expensive computational primitive이므로, memory overhead를 유발하며,
-
세 번째 property는 다양한 netgative consequences를 초래한다.
예를 들어, practitioners들은 batch normalized networks가 서로 다른 HW 환경에서 정확히 동일하게 재현되기 어렵다는 점을 발견해 왔으며,
BN은 특히 distributed training 환경에서 subtle implementation errors의 원인이 되는 경우가 많다.
또한 BN은 일부 작업에서는 사용할 수 없는데, 이는 batch 내 training examples 간의 interaction이 특정 loss functions에 대해 network가 'cheat'할 수 있도록 만들기 때문이다.
예를 들어, contrastive learning algorithms에서는 information loss를 방지하기 위해 BN에 특별한 주의가 필요하다.
sequence modeling tasks에서도 주요한 우려 사항으로 적용하여...
...
BN의 challenges에 대한 문제점들은 Appendix B에서 더 자세히 논의한다.
(관련 연구)
-
따라서 BN은 수 년간 DL community에 상당한 발전을 가능하게 했음에도 불구하고, 장기적으로는 오히려 연구 진전을 저해할 가능성이 크다고 예상한다.
우리는 경쟁력 있는 test accuracies를 유지하면서도 다양한 tasks에 적용 가능한 alternative normalizers를 모색해야 한다고 본다. -
다행히 최근 몇 년 사이 two promising research themes가 등장했다.
첫 번째는 training 과정에서 BN이 제공하는 benefits의 근본 원인을 분석하는 연구들이며,
두 번째는 normalization layers 없이도 competitive accuracies로 deep ResNets을 학습시키려는 연구들이다. -
위 두 연구들의 key theme은 residual branch에서의 hidden activations의 scale을 suppressing함으로써
normalization 없이도 very deep ResNets을 학습할 수 있다는 점이다.
이를 달성하는 가장 간단한 방법은 each residual branch 끝에 a learnable scalar를 도입하고 이를 0으로 initialized하는 것이다.
그러나 이러한 trick만으로는 competitive test accuracies를 얻기에 충분하지 않다. -
또 다른 연구 흐름에서는 ReLU activations이 mean shift를 유발하여,
network depths가 증가함에 따라 서로 다른 training examples들의 hidden activations들이
점점 correlated되게 만든다는 점을 보였다.
최근 Brock et al.(2021)은 “Normalizer-Free” ResNet을 제안했는데,
이는 initialization에서 residual branch를 억제하고,
mean shift를 제거하기 위해 Scaled Weight Standardization을 적용한다.
여기에 additional regularization을 추가하여, these unnormalizeed networks는 batch-normalized ResNets과 유사한 성능을 달성할 수 있었다.
그러나 이 model들은 large batch sizes에서 not stable하며, 현재 SOTA인 EfficientNet과는 여전히 성능 격차가 존재한다.
본 논문은 이러한 연구 흐름을 기반으로 하여, 위에서 언급한 핵심적인 limitations을 해결하는 것을 목표로 한다. -
Our main contributions are as follow:
-
Adaptive Gradient Clipping (AGC)를 제안한다.
(AGC ,which clips gradients based on the unit-wise ratio of gradient norms to parameter norms)
AGC는 parameter norm 대비 gradient norm의 ratio를 unit-wise로 계산하여 gradient를 clipping하는 방법으로,
larger batch sizes and stronger data augmentations과 함께 Normalizer-Free Networks를 학습할 수 있게 함. -
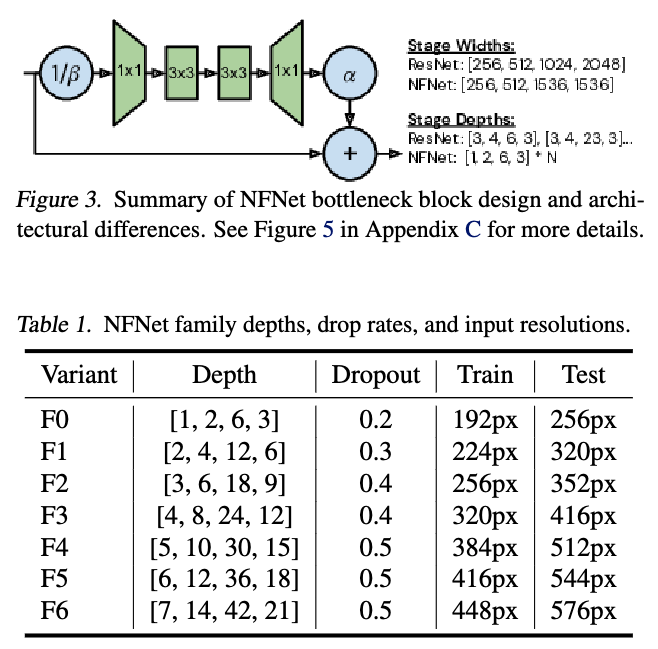
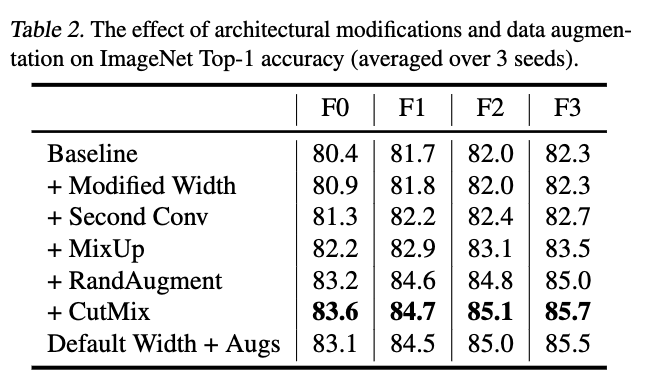
We design a family of Normalizer-Free ResNets, called NFNets, which set new state-of-the-art validation accuracies on ImageNet for a range of training latencies (See Figure 1).
Our NFNet-F1 model achieves similar accuracy to EfficientNet-B7 while being 8. faster to train, and our largest model sets a new overall state of the art without extra data of 86.5% top-1 accuracy.
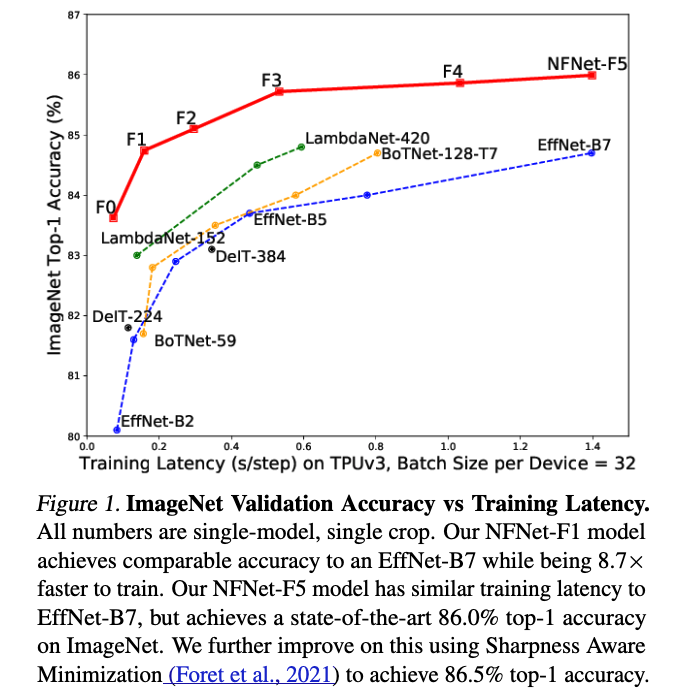
-
We show that NFNets achieve substantially higher validation accuracies than batch-normalized networks when fine-tuning on ImageNet after pre-training on a large private dataset of 300 million labelled images.
Our best model achieves 89.2% top-1 after fine-tuning.
-
2. Understanding Batch Normalization
-
networks without normalization을 train하기 위해,
먼저 BN의 benefits을 이해해야 하고,
이 benefits들을 recover하기 위한 alternative strategies를 확인해야 함. -
우리는 prior work에서 확인된 4가지 main benefits을 list한다.
BN downscales the residual branch
-
skip connection과 BN을 결합하면, significantly deeper networks를 학습할 수 있게 된다.
이러한 이점은 BN이 residual branch에 위치할 경우, 초기 단계에서 residual branch 내부의 hidden activation 값의 scale(크기)를 줄이기 때문에 발생한다. -
이로 인해 signal이 skip path쪽으로 치우치게 되며, 이는 training 초기에 gradient가 안정적으로 유지되도록 보장하여 efficient optimization을 가능하게 한다.
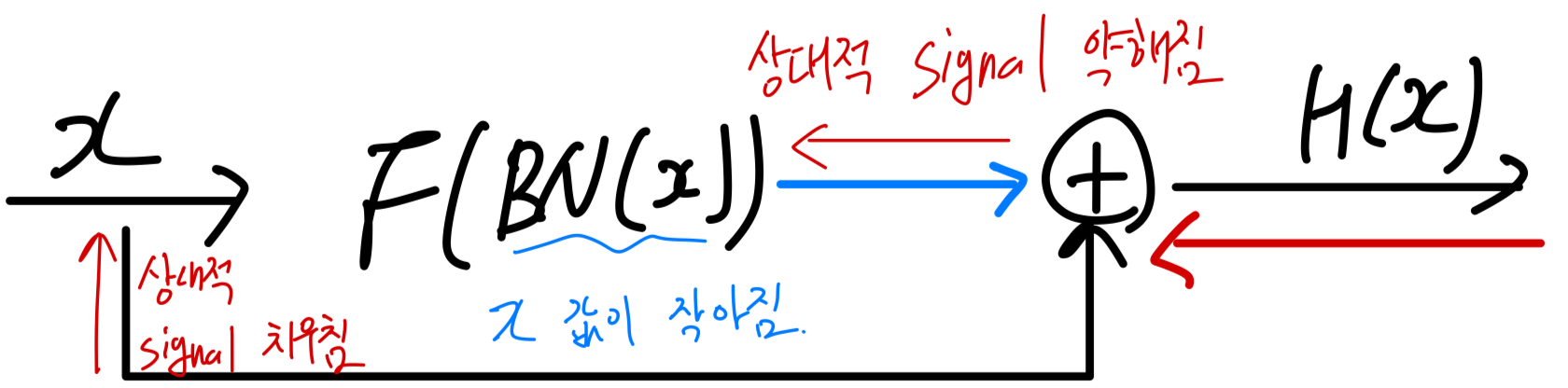
Batch normalization eliminates mean-shift
-
BN은 mean-shift 현상을 제거한다.
ReLU나 GELU와 같은 activation functions은 anti-symmetric이 아니기 때문에, non-zero activation을 갖는다.
그 결과, non-linearity 직후에 서로 독립적인 training examples 간 inner product는 일반적으로 large and positive 값이 된다. -
이 문제는 network depth가 증가할수록 누적되며,
각 channel에서 서로 다른 training sample의 activation 값에 대해 network depth에 비례하는 mean-shift를 유발한다.
이로 인해 초기에 all training examples에 대해 same label을 predict하는 현상이 발생할 수 있다. -
BN은 current batch에 대해 각 channel의 mean activation을 0으로 강제함으로써, 이러한 mean shift를 제거한다.
Batch normalization has a regularizing effect
- BN은 a subset of the training data에서 계산되는 batch statistics의 noise 덕분에
test set accuracy를 향상시키는 regularizer로서 역할을 한다고 널리 알려져 있다.
Batch normalization allows efficient large-batch training
-
BN은 loss landscape를 smoothens한다고 알려져 있다.
이 속성은 the batch size is small일 때 practical benefits을 가지지는 않다. -
비록 Large-batch training이 a fixed epoch budget에서 higher test accuracies를 달성하지는 않지만,
multiple devices에서 parallelized될 때 training speed를 굉장히 향상시킬 수 있다.
3. Towards Removing Batch Normalization
-
ResNets w/o normalization을 학습시키기 위해 많은 연구들이 있었다.
(1) 대부분의 이 연구들은 small constants or leanable scalars를 곱해줌으로써
residual branch에 the scale of the activations을 suppress하는 접근이다.
(2) 추가적으로, 어떤 연구는 additional regularization으로 unnormalized ResNets의 성능을 향상시킬 수 있음을 관찰했다. -
하지만 위 두 BN의 장점으로는 competitive test accuracies를 달성하기에 충분하지 않다.
-
이 논문에서, 우리는 "Normalizer-Free ResNets" (NF-ResNets) (Brock et al., 2021)을 기반으로 연구했다.
NF-ResNets은 아래와 같은 Form의 a residual block을 사용한다.
(아래는 NF-ResNets 관련 연구에 대한 설명임. 이 논문에서 제안하는 것은 아직 안 나옴)

(아래 문단 내용이 쉽게 이해되지 않았어서 정리해봄)
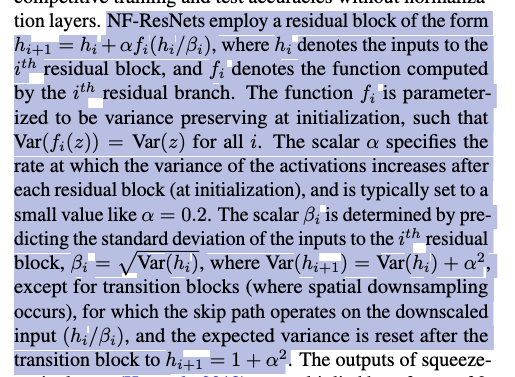
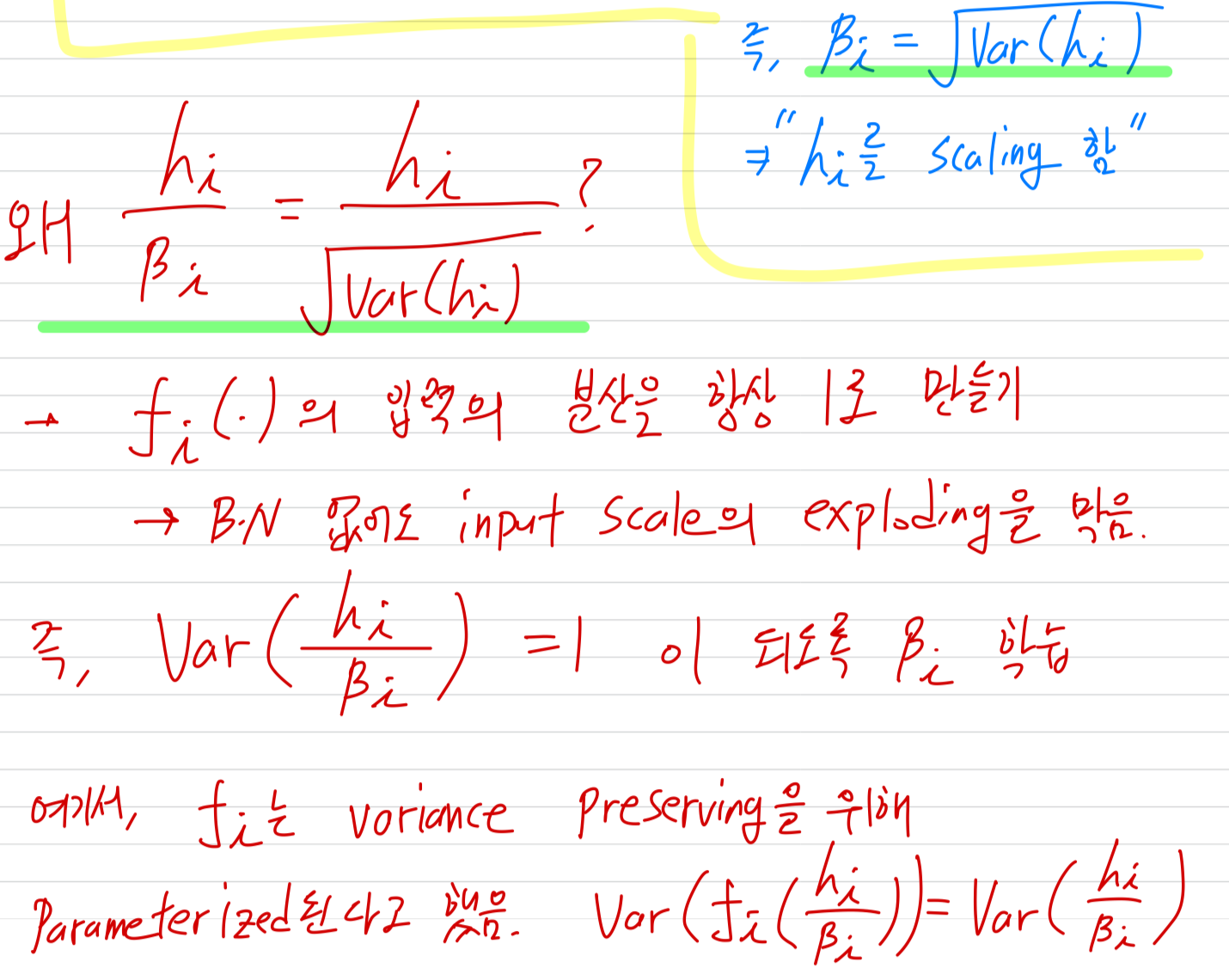

-
추가로, (Brock et al., 2021)에서는 Scaled Weight Standardization을 도입함으로써
the mergence of a mean-shift in the hidden activations을 예방함.
Scaled Weight Standardization은 convolutional layers를 다음과 같이 reparameterize함: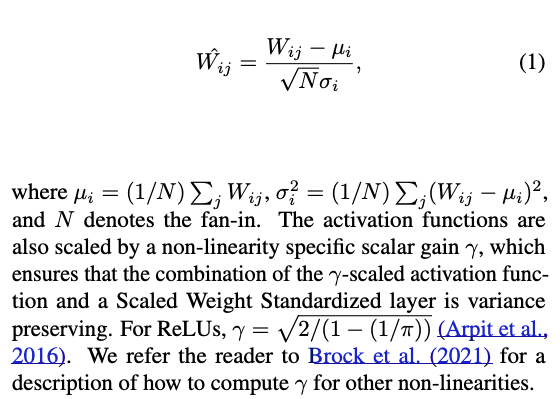
4. Adaptive Gradient Clipping for Efficient Large-Batch Training
-
NF-ResNets을 larger batch sizes로 확장하기 위해, 우리는 다양한 gradient clipping strategies를 탐구한다.
Gradient clipping은 language modeling에서 training stabilizing을 위해 자주 사용되어 왔으며,
최근 연구에 따르면 Gradient descent 대비 더 큰 learning rates를 사용할 수 있게 해 convergence를 accelerating하는 효과가 있음이 보고되었다.
이는 특히 loss lanscapes의 poorly conditioned 상황이거나 large batch sizes로 학습할 때 중요한데,
이러한 상황에서는 optimal learning rate가 maximum stable learning rate(Smith et al. 2020)에 의해 제한되기 때문이다.(?)
이에 우리는 gradient clipping이 NF-ResNet을 large-batch setting으로 효율적으로 확장하는 데 도움이 될 것이라 가정한다. -
일반적으로 gradient clipping은 gradient의 norm을 제한하는 방식으로 수행된다.
구체적으로, loss를 , model 전체 parameter vector를 라고 할 때,
gradient vector 에 대해
standard clipping algorithm은 를 updating하기 전에 다음과 같이 gradient를 계산한다:
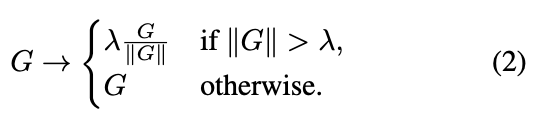 여기서 clipping threshold 는 hyper-parameter이다.
여기서 clipping threshold 는 hyper-parameter이다. -
standard clipping algorithm은 이전보다 큰 batch size에서 학습을 가능하게 했지만,
training stability가 매우 sensitive해서 the clipping threshold 를 tuning하는 것이 매우 힘들었다.
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해, 우리는 “Adaptive Gradient Clipping” (AGC)를 제안한다.
Let denote the weight matrix of the layer,
denote the gradient with respect to ,
and denote the Frobenius norm, i.e., .
AGC는 layer 에서 gradient norm과 weight norm의 ratio 는
a single gradient descent step이 the original weights 을 얼만큼 크게 변화시키는지를 간단히 나타내는 metric이라는 observation에서 motivated된다.
예를 들어, momentum 없이 gradient descent를 사용하여 train하는 경우,
,
여기서 , 는 learning rate이다.
직관적으로, 이 ratio 가 크면 training이 unstable해질 가능성이 높다. -
이에 우리는 gradient norm과 parameter norm의 ratio에 기반한 clipping 전략을 제안한다.
실제로, layer-wise norm ratios 보다는 unit-wise ratios를 사용하는 것이 경험적으로 더 효과적임을 발견했다.
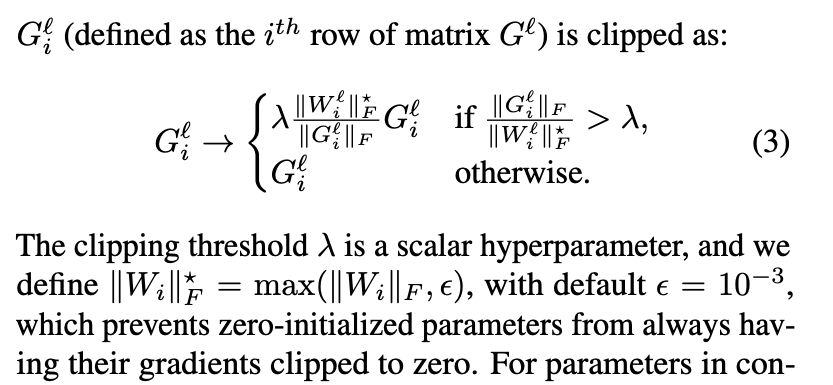
따라서 AGC에서는 (-th layer의 gradient 의 각 unit ) = (defined as the row of matrix )는 다음과 같이 clipped된다:
4.1. Ablations for Adaptive Gradient Clipping (AGC)
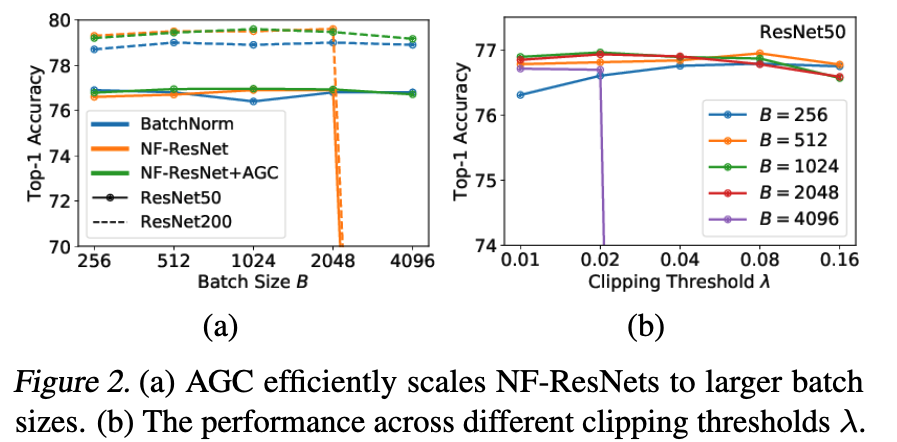
5. Normalizer-Free Architectures with Improved Accuracy and Training Speed